Abstract
The pathogenesis of Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) centers around Th17/Treg dysfunction illustrated by lesional elevation of IL-17A, IL-6, and other inflammatory mediators resulting in a chronic feed-forward inflammatory cascade. Similar inflammatory mechanisms have been identified in psoriasis and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in which traditional immunosuppressants (including methotrexate) are routinely used with reasonable levels of disease control. Methotrexate’s mechanism of action in these instances include downregulation of the Th17 axis via alterations in dendritic cell and T-cell activity and maturation. Published data suggests methotrexate in an ineffective therapy in HS, which does not pair with our current understanding of the mechanisms of disease. The reasons behind this, including are discussed. Some HS patients may benefit from drugs such as methotrexate, and acknowledgement of the potential of disease heterogeneity will allow exploration of which factors may enable identification of such individuals.
Keywords: Hidradenitis Suppurativa, Acne Inversa, Methotrexate, Th17, Efficacy, Pathogenesis
The pathogenesis of Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) centers around Th17/Treg dysfunction illustrated by lesional elevation of IL-17A, IL-6, and other inflammatory mediators resulting in a chronic feed-forward inflammatory cascade in the setting of follicular occlusion1. Similar inflammatory mechanisms have been identified in psoriasis and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in which traditional immunosuppressants (including methotrexate) are routinely used with reasonable levels of disease control2,3. Methotrexate’s mechanism of action in these instances include downregulation of the Th17 axis via alterations in dendritic cell and T-cell activity and maturation4.
Since the FDA approval of Adalimumab for Hidradenitis Suppurativa in 2015, interest in the use of traditional immunosuppressant in HS has significantly decreased. Methotrexate, cyclosporine and dapsone are reported in HS with varying degrees of efficacy (Figure 1)5. Taking into account the significant rates of placebo effects in HS clinical trials (up to 30% patients achieving HiSCR on placebo alone6) further question the true efficacy of these drugs. When traditional immunosuppressive agents are utilized, publication bias results in only isolated case reports of successful treatment, suggesting that broadly speaking, traditional immunosuppressants have poor efficacy in HS (Figure 1). This lack of efficacy does not pair with our current understanding of the mechanisms of disease1.
Figure 1:
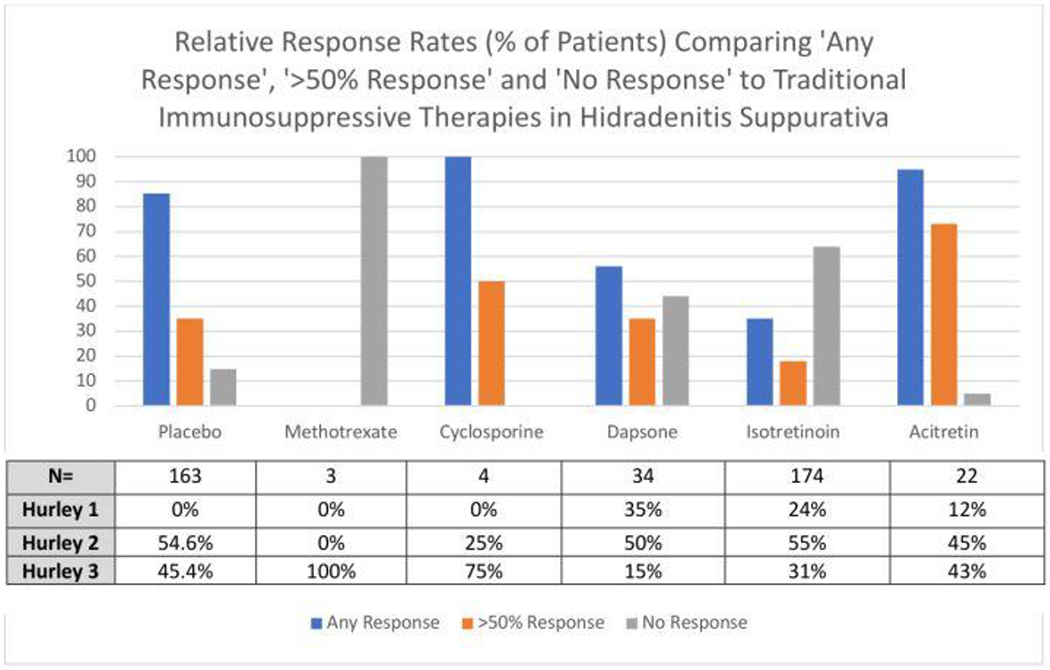
Relative Efficacy of Systemic Immunosuppressants in Hidradenitis Suppurativa. Data adapted from Kimball et al6 and Blok et al5. The corresponding table presents the number of patients exposed to each intervention, along with the subgrouping by Hurley stage. The external validity of the response data for each intervention is dependent upon the clinical presentation of the cohort (including severity of disease), known level of placebo effect and dosages administered.
Despite the decreased interest in the routine treatment of HS with such immunosuppressants, their utility should not be completely discarded. The fact that methotrexate has no evidence for clinical efficacy in HS leads to two possible conclusions: either that our pathogenic model of HS requires revision, or the existing data is prone to selection bias. In RA, methotrexate resistant disease is associated with longer disease duration, female gender, and increased levels of monocytes and neutrophils3. Anecdotally, these factors may be present in patients with ‘typical’ (axillary-mammary or LC1) HS. This also correlates with reports of ‘syndromic’ HS (associated with SAPHO or PASH syndrome) benefiting from methotrexate administration7, and the fact that the studies of methotrexate in HS patients involved severe, Hurley stage 3 ‘treatment resistant’ patients8.
Currently, investigations into HS (clinical, serological, microbiological, transcriptomic and genetic) consider HS as a homogenous disease. Such underlying assumptions may preclude identification of low-concentration or low-frequency markers important in pathogenesis, predictive of disease activity and/or treatment in specific subsets of HS patients. Preliminary data demonstrates differences in inflammatory cytokines in inflamed versus fibrotic HS lesional tissue9; and in other inflammatory skin diseases such as scleroderma, hierarchal clustering of transcriptomic data by clinical phenotype has provided valuable insights into differential activity of various mechanistic pathways in this disease. A similar approach would provide valuable insights in HS. Sufficient evidence exists to support the role of Th17/Treg axis in the inflammatory mechanisms of HS1,9, but not necessarily in all presentations and in all stages of disease, and certainly not the sole pathogenic pathway. It follows, therefore, that the role of traditional immunosuppressants in HS has not yet been satisfactorily settled. Some HS patients may benefit from drugs such as methotrexate, and acknowledgement of the potential of disease heterogeneity will allow exploration of which factors may enable identification of such individuals.
Acknowledgments
Funding Sources: Supported in part by grant # UL1 TR001866 from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS), National Institutes of Health (NIH) Clinical and Translational Science Award (CTSA) program.
Footnotes
Conflict of Interest Disclosures: The author has no conflict of interest to declare
References:
- 1).Melnik BC, John SM, Chen W, Plewig G.T helper 17 cell/regulatory T-cell imbalance in hidradenitis suppurativa/acne inversa: the link to hair follicle dissection, obesity, smoking and autoimmune comorbidities. Br J Dermatol. 2018;179(2):260–272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2).West J, Ogston S, Foerster J (2016) Safety and Efficacy of Methotrexate in Psoriasis: A Meta-Analysis of Published Trials. PLoS ONE 11(5): e0153740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3).Yu MB, Firek A, Langridge WHR Predicting methotrexate resistance in rheumatoid arthritis patients Inflammopharmacology 2018;26:699–708 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4).Yu X, Wang C, Luo J, Zhao X, Wang L, Li X (2013) Combination with methotrexate and cyclophosphamide attenuated maturation of dendritic cells: inducing Treg skewing and Th17 suppression in vivo. Clin Dev Immunol 2013:238035 10.1155/2013/23803 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5).Blok JL, van Hattem S, Jonkman MF, Horvath B Systemic therapy with immunosuppressive agents and retinoids in hidradenitis suppurativa: a systematic review Br J Dermatol. 2013. Feb;168(2):243–52 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6).Kimball AB, Okun MM, Williams DA, Gottlieb AB Papp KA Zouboulis CC et al. Two Phase 3 Trials of Adalimumab for Hidradenitis Suppurativa. N Engl J Med 2016;375:422–434 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7).Vekic DA, Woods J, Lin P, Cains GD SAPHO syndrome associated with Hidradenitis Suppurativa and pyoderma gangrenosum successfully treated with adalimumab and methotrexate: a case report and review of the literature” Int J Dermatol 2018;57:10–18 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8).Jemec GBE Methotrexate is of limited value in the treatment of Hidradenitis Suppurativa Clin Exp Dermatol 2002;27:523–529 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9).Frew JW, Hawkes JE and Krueger JG. A systematic review and critical evaluation of inflammatory cytokine associations in hidradenitis suppurativa [version 1; referees: awaiting peer review]. F1000Research 2018, 7:1930 ( 10.12688/f1000research.17267.1) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10).Milano A, Pendergrass SA, Sargent JL, George LK, McCalmont TH 2008. Molecular subsets in the Gene Expression Signatures of Scleroderma Skin PLoS One 3(7):e2696 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002696 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


