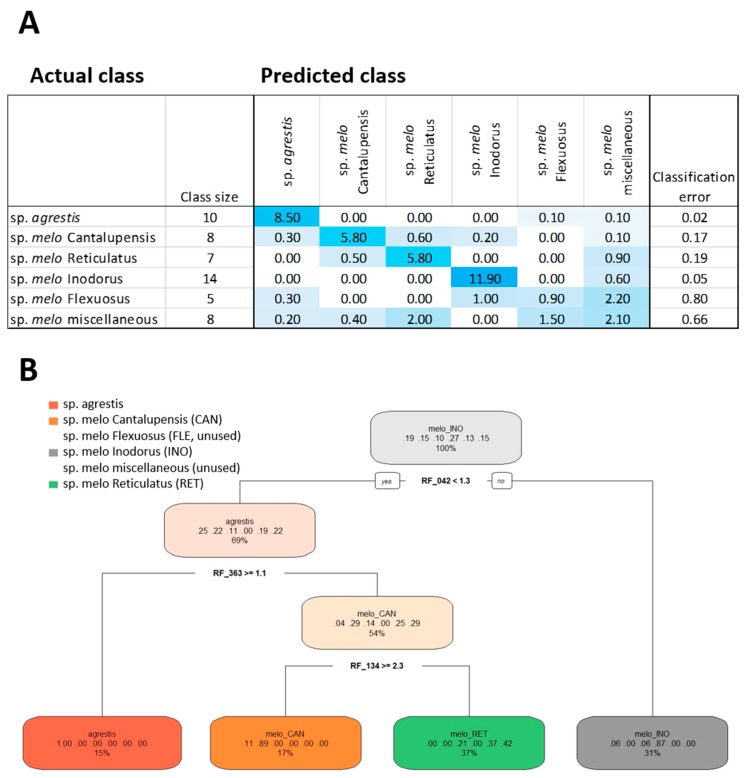
Figure 4.
Random forest (RF) analysis (A) and decision tree classification (B) of six C. melo accession classes using a subset of 605 provisionally annotated molecular features. Classification of six pre-defined melon accession classes was performed. The classification table (A) lists classes, class size, the actual and predicted class membership, and the classification error (means of 10 iterations using hyperparameter-tuned RF settings). The decision tree uses the top 20 most informative molecular features ranked by the mean decrease in accuracy. The node information of the decision tree reports the used molecular feature code (Table S4) and threshold value. The branch information (colored ovals) lists the main class, the fraction of classified samples, left to right, subsp. agrestis, Cantalupensis, Flexuosus, Inodorus, miscellaneous, and Reticulatus accessions of subsp. melo. The percentage value indicates the fraction of the 52 accession samples that fall into each of the diagnostic categories.