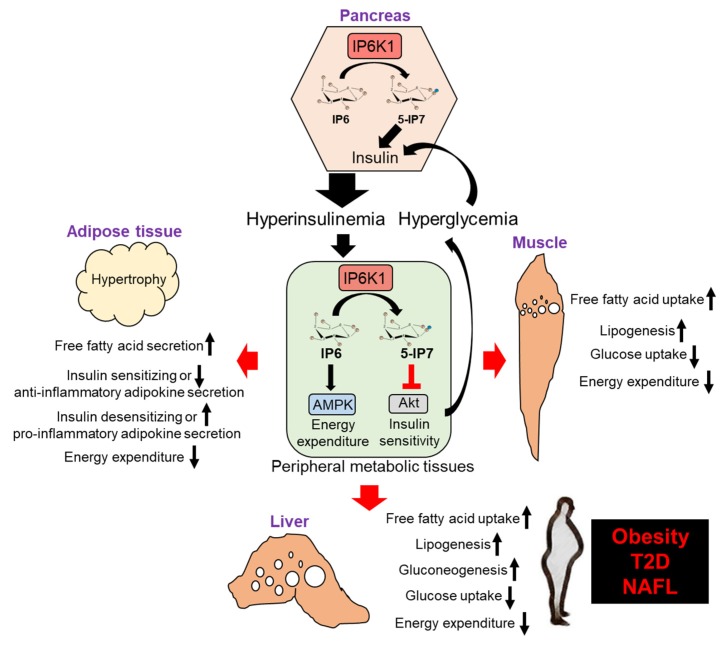
Figure 2.
In obesity, 5-IP7 mediated inhibition of Akt causes insulin resistance in metabolic tissues (green box) causes hyperglycemia, which induces 5-IP7 mediated insulin secretion from pancreatic β cells (hexagon), resulting in hyperinsulinemia. Moreover, IP6K1 mediated conversion of IP6 to 5-IP7 reduces IP6′s stimulatory effects on AMPK mediated energy expenditure in the adipose tissue, leading to adipocyte dysfunction. Dysfunctional adipocytes secrete free fatty acids and insulin desensitizing and pro-inflammatory adipokines. Circulating free fatty acids are taken up by the liver from the serum. Although the rate of glucose uptake is lower in this condition, hyperinsulinemia causes a portion of glucose to enter the liver. Gluconeogenesis is also increased. Consequently, the liver accumulates fat (white droplets) by conversion of free fatty acids to triglycerides and de novo lipogenesis. The skeletal muscle also accumulates fat and becomes insulin resistant in a similar fashion. Therefore, increased IP6K1’s actions cause obesity, T2D and NAFL.