Abstract
Background: Diabetes is referred to a group of diseases characterized by high glucose levels in blood. It is caused by a deficiency in the production or function of insulin or both, which can occur because of different reasons, resulting in protein and lipid metabolic disorders. The aim of this study was to systematically review the prevalence and incidence of type 1 diabetes in the world.
Methods: A systematic search of resources was conducted to investigate the prevalence and incidence of type 1 diabetes in the world. The databases of Medline (via PubMed and Ovid),ProQuest, Scopus, and Web of Science from January 1980 to September 2019 were searched to locate English articles. The located articles were screened in multiple levels of title, abstract,and full-text and final studies that met the inclusion criteria were retrieved and included in the study.
Results: From 1202 located articles, 193 studies were included in this systematic review. The results of meta-analysis showed that the incidence of type 1 diabetes was 15 per 100,000 people and the prevalence was 9.5% (95% CI: 0.07 to 0.12) in the world, which was statistically significant.
Conclusion: According to the results, the incidence and prevalence of type 1 diabetes are increasing in the world. As a result, insulin will be difficult to access and afford, especially in underdeveloped and developing countries.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus, Incidence, Prevalence, Systematic review, Type 1, World
Introduction
Diabetes is referred to a group of diseases characterized by high glucose levels in blood. It is caused by a deficiency in the production or function of insulin or both, which can occur because of different reasons, resulting in protein and lipid metabolic disorders.1 The long-term effects of hypoglycemia are tissue and organ damage.2
Symptoms of diabetes include polyuria, thirst, vision disorders, and weight loss. In some cases there are more severe forms of diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar that may lead to stupor and coma. But most symptoms are not severe, which may cause damage or even failure of different organs in the long run and lead to irreparable injuries such as blindness, amputation, stroke and eventually death. Previously, type 1 diabetes was called insulin-dependent diabetes and it could happen at any age but is most common in children and young people.3
People with type 1 diabetes are not able to produce enough insulin. This type constitutes about 5%–10% of all cases of diabetes. In this type, the cellular destruction of beta cells occurs in the pancreas. In type 1 diabetes, the pancreas does not release any insulin. Since there is no epidemiologically accurate information on the prevalence and incidence of type 1 diabetes in the world and in the region, therefore, the present study was designed and implemented as a systematic review and meta-analysis, because of geopolitical map of the policy on the prevention and treatment of this disease can be done better.
Materials and Methods
In this systematic review and meta-analysis, a systematic search of resources was conducted by a librarian (N.V.) to investigate the prevalence and incidence of type 1 diabetes (condition) in the people (population) of the world (context). The PICO of study based on the JBI protocol as CoCoPop for prevalence and incidence studies.
Data sources and search strategy
The databases of Medline via (PubMed, Ovid), Embase, Scopus, Web of Science from January 1980 to September 2019 were searched to locate English articles. Also, SID, Magiran, and Barakat databases were searched for Persian studies. The grey literature and ongoing studies were searched using the following: OpenGrey, Google Scholar and for thesis and dissertations ProQuest and studies presented at conferences were also searched. Also, experts and professionals on this subject were reached and their opinions were gathered for information on published and unpublished studies. The search was performed using MESH and free keywords. The keywords selected for the search were: “type 1 diabetes”, “prevalence”, and “incidence” with this search strategy: (((“Diabetes Mellitus, Type 1”[Mesh]) OR ((((((((((((((((((((IDDM[Title/Abstract]) OR T1DM[Title/Abstract]) OR “Type 1 Diabetes”[Title/Abstract]) OR “Autoimmune Diabetes”[Title/Abstract]) OR “Juvenile Onset Diabetes”[Title/Abstract]) OR “Juvenile-Onset Diabetes”[Title/Abstract]) OR “Brittle Diabetes Mellitus”[Title/Abstract]) OR “brittle diabetes”[Title/Abstract]) OR “diabetes mellitus type 1”[Title/Abstract]) OR “diabetes mellitus type I”[Title/Abstract]) OR “diabetes type 1”[Title/Abstract]) OR “diabetes type I”[Title/Abstract]) OR “early onset diabetes mellitus”[Title/Abstract]) OR “insulin dependent diabetes”[Title/Abstract]) OR “juvenile diabetes”[Title/Abstract]) OR “juvenile diabetes mellitus”[Title/Abstract]) OR “type I diabetes”[Title/Abstract]) OR “type I diabetes mellitus”[Title/Abstract]) OR “Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus”[Title/Abstract]) OR “Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus”[Title/Abstract]))) AND ((((“Prevalence”[Mesh]) OR ((Prevalence[Title/Abstract]) OR Prevalences[Title/Abstract]))) OR ((“Incidence”[Mesh]) OR ((Incidence[Title/Abstract]) OR Incidences[Title/Abstract]))). The complete search strategy of Medline and Embase is in Supplementary file 1.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusioncriteria for selecting studies include: 1. Articles published between 1980 and 2019; 2. Articles published in English and Persian. The exclusion criteria were: 1. Studies with no reported sample size; 2. Studies that had low quality; 3. Studies that were published before 1990.
Study selection
The located articles were screened in multiple levels of title, abstract, and full-text and final studies that met the inclusion criteria were retrieved and included in the study. The studies were critically appraised by 2 subject specialists and low-quality studies were excluded. In cases of disagreements between two experts (M.M. and M.S.) at each stage of selection and appraisal, third person opinion was used.
Quality appraisal
Articles were evaluated using the STROBE checklist. In this checklist, the minimum score was 2 and the maximum was 4. Finally, articles that received a score of 4 on checklist questions were included in the research, 128 articles earned 4 score, 46 articles earned 3 score and 19 articles earned 2 score and finally their data were extracted to perform the meta-analysis.
Data extraction and quality assessment
The information extracted from the articles were entered in the extraction form. Extracted data included: first author, year of publication, country of study, sample size, and incidence of diabetes in the studies.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using CMA v.2.0 software and P value less than 0.05 was considered as significant. The binomial distribution was used to calculate the variance. Weighted mean was used to combine the prevalence rate of different studies. Meta-analysis was used to obtain the incidence of type 1 diabetes. The heterogeneity between studies was assessed by Cochran (Q) and I2 statistics, which expressed the percentage of variation between studies. Random effects model was used to calculate the overall and pooled effect size.
Results
Search results and study characteristics
In a systematic search of sources, 65 765 articles were identified. A total of 58 239 articles were duplicates, and 7107 were excluded after reviewing the title and abstract of the articles. After reviewing the full-text articles, 49 articles were excluded. Finally, 193 studies were included in the systematic review and meta-analysis. Figure 1 shows the identified and retrieved articles in the study. Tables 1, 2 and 3 show the specifications of the articles that were studied.
Figure 1.
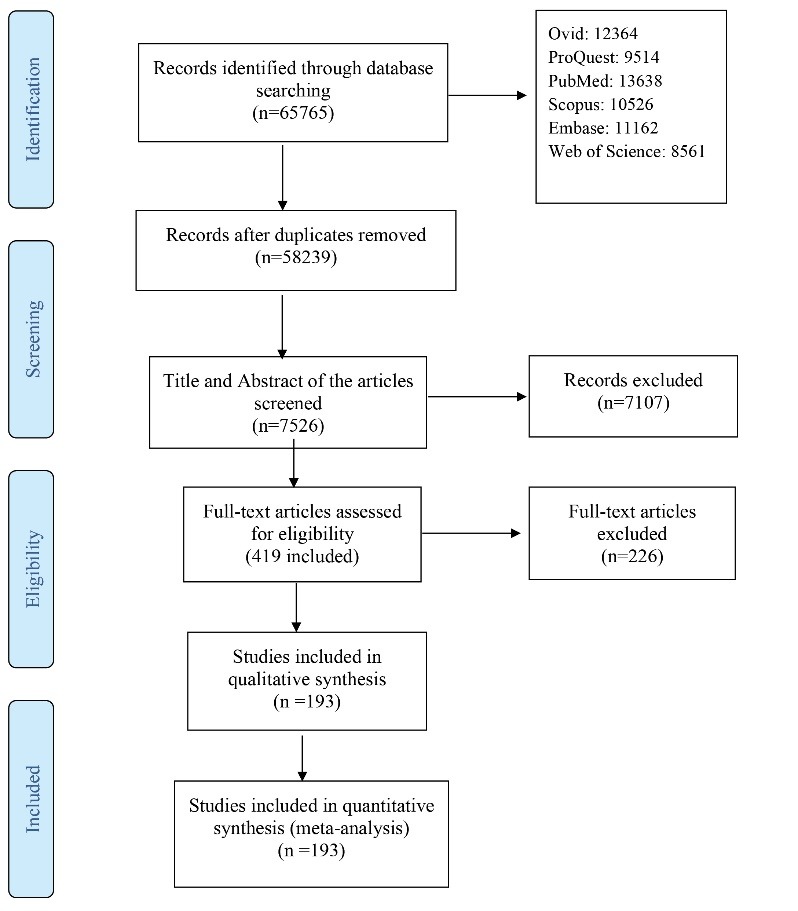
Flow chart of systematic review.
Table 1. Characteristics of studies incidence of type 1 diabetes .
| Study | Year | Country | Continent | Sample size | Incidence per 10000 |
| Abduljabbar et al4 | 2010 | Saudi Arabia | Asia | 1028 | 0.02752 |
| Abdul-Rasoul et al5 | 2002 | Kuwait | Asia | 760 | 0.02018 |
| Abellana et al6 | 2009 | Spain | Europe | 448 | 0.0118 |
| Ajlouni et al7 | 1999 | Jordan | Asia | 123 | 0.0032 |
| 107 | 0.0028 | ||||
| 138 | 0.0036 | ||||
| Alaghehbandan et al8 | 2006 | Canada | USA | 716 | 0.019 |
| Alemu et al9 | 2009 | Ethiopia | Africa | 81 | 0.0021 |
| Algert CS et al10 | 2009 | Australia | Asia | 605 | 0.016 |
| Altobelli et al11 | 1998 | Italy | Europe | 355 | 0.00934 |
| Arpi et al12 | 2002 | Catania | Europe | 470 | 0.01238 |
| Aschner et al13 | 2014 | America | USA | 279 | 0.00731 |
| Bahíllo et al14 | 2007 | Spain | Europe | 835 | 0.02222 |
| Barat et al15 | 2008 | French | Europe | 510 | 0.01347 |
| Battelino and Kržišnik16 | 1998 | Slovenia | Europe | 305 | 0.008 |
| Berhan et al17 | 2011 | Sweden | Europe | 1612 | 0.0439 |
| Bessaoud et al18 | 1990 | Algeria | Africa | 168 | 0.0044 |
| Bizzarri et al19 | 2010 | Italy | Europe | 593 | 0.01568 |
| Blanchard et al20 | 1997 | Canada | USA | 768 | 0.0204 |
| Blumenfeld et al21 | 2014 | Asia | Asia | 433 | 0.0114 |
| Bratina et al22 | 2001 | Bosnia and Herzegovina | Europe | 325 | 0.00854 |
| Bruno et al23 | 1990 | Italy | Europe | 259 | 0.00678 |
| Bruno et al24 | 1993 | Italy | Europe | 256 | 0.0067 |
| Bruno et al25 | 1997 | Italy | Europe | 282 | 0.00739 |
| Bruno et al26 | 2001 | Italy | Europe | 297 | 0.00778 |
| Bruno et al27 | 2009 | Italy | Europe | 354 | 0.0093 |
| Bruno et al28 | 2010 | Italy | Europe | 465 | 0.01226 |
| Bruno et al29 | 2013 | Italy | Europe | 1644 | 0.0448 |
| Calle-Pascual et al30 | 1993 | Spain | Europe | 565 | 0.01493 |
| Calori et al31 | 1990 | Italy | Europe | 253 | 0.00663 |
| Campbell-Stokes and Taylor32 | 2005 | New Zealand | Europe | 675 | 0.0179 |
| Cardwell et al33 | 2006 | Ireland | Europe | 925 | 0.0247 |
| Carrasco et al34 | 1996 | Chile | USA | 90 | 0.00236 |
| Carrasco et al35 | 2006 | Chile | USA | 251 | 0.00658 |
| Carrasco et al36 | 2006 | Chile | USA | 154 | 0.00402 |
| Casu et al37 | 2004 | Sardinia | Europe | 1433 | 0.0388 |
| Cherubini et al38 | 1994 | Italy | Europe | 309 | 0.0081 |
| Chong et al39 | 2007 | Australia | Asia | 731 | 0.0194 |
| Cinek et al40 | 2000 | Czech Republic | Europe | 384 | 0.0101 |
| Cinek et al41 | 2003 | Czech Republic | Europe | 444 | 0.0117 |
| Compés et al42 | 2013 | Spain | Europe | 723 | 0.0192 |
| Cotellessa et al43 | 2003 | Italy | Europe | 476 | 0.01256 |
| Crow et al44 | 1991 | England | Europe | 560 | 0.0148 |
| 508 | 0.0134 | ||||
| Dabelea et al45 | 2009 | Navajo nation | USA | 86 | 0.00224 |
| 841 | 0.0224 | ||||
| 1452 | 0.03934 | ||||
| Dacou-Voutetakis et al46 | 1995 | Greece | Europe | 239 | 0.00625 |
| Demirbilek et al47 | 2013 | Turkey | Asia | 275 | 0.0072 |
| Derraik et al48 | 2012 | New Zealand | Europe | 845 | 0.0225 |
| Dziatkowiak et al49 | 2002 | Poland | Europe | 316 | 0.0083 |
| 244 | 0.0064 | ||||
| 301 | 0.0079 | ||||
| Ehehalt et al50 | 2012 | Europe | Europe | 579 | 0.0153 |
| Ehehalt et al51 | 2009 | Italy | Europe | 560 | 0.0148 |
| Ehehalt et al52 | 2012 | Europe | Europe | 579 | 0.0153 |
| El-Ziny et al53 | 2014 | Egypt | Africa | 119 | 0.0031 |
| Feltbower et al54 | 2002 | UK | Europe | 493 | 0.013 |
| Ferreira et al55 | 1993 | Brazil | USA | 290 | 0.0076 |
| Forga et al56 | 2013 | Spain | Europe | 331 | 0.0087 |
| Formosa et al57 | 2012 | Malta | Africa | 821 | 0.02186 |
| Frazer De Llado et al58 | 1998 | Puerto Rico | USA | 679 | 0.018 |
| Frongia et al59 | 1997 | Italy | Europe | 1411 | 0.0382 |
| Gardner et al60 | 1997 | USA | USA | 701 | 0.0186 |
| Charkaluk et al61 | 2002 | France | Europe | 364 | 0.00958 |
| Giralt et al62 | 2001 | Spain | Europe | 973 | 0.026 |
| Goday et al63 | 1992 | Spain | Europe | 407 | 0.0107 |
| Gong et al64 | 2013 | China | Asia | 56 | 0.00145 |
| Gopinath et al65 | 2008 | Sweden | Europe | 914 | 0.02438 |
| Gorham et al66 | 1993 | USA | USA | 801 | 0.0213 |
| Grabauskas et al67 | 1991 | Lithuania | Europe | 256 | 0.0067 |
| Green and Patterson68 | 2001 | Hungary | Europe | 686 | 0.0182 |
| Harjutsalo et al69 | 2008 | Finland | Europe | 1577 | 0.0429 |
| Harjutsalo et al70 | 2013 | Finland | Europe | 2264 | 0.0629 |
| Huen et al71 | 2000 | Hong Kong | Asia | 54 | 0.0014 |
| Jarosz-Chobot et al72 | 2010 | Poland | Europe | 375 | 0.00987 |
| Jarosz-Chobot et al73 | 2011 | Poland | Europe | 388 | 0.0102 |
| Ji et al74 | 2010 | Sweden | Europe | 27 | 0.00071 |
| Kadiki and Moawad75 | 1994 | Libya | Africa | 335 | 0.0088 |
| Kadiki et al76 | 1996 | Libya | Africa | 343 | 0.009 |
| Karvonen et al77 | 1996 | Finland | Europe | 1319 | 0.0356 |
| Karvonen et al78 | 2000 | China & Venezuela | Asia | 4 | 0.0001 |
| Karvonen et al79 | 1997 | Finland | Europe | 1507 | 0.0409 |
| Kida et al80 | 1999 | Japan | Asia | 58 | 0.0015 |
| Koton81 | 2007 | Asia | Asia | 305 | 0.008 |
| Kulaylat and Narchi82 | 2000 | Saudi Arabia | Asia | 437 | 0.0115 |
| Lammi et al83 | 2007 | Finland | Europe | 601 | 0.0159 |
| Larenas et al84 | 1996 | Chile | USA | 49 | 0.00127 |
| Lawrence et al85 | 2014 | USA | USA | 914 | 0.0244 |
| Legault and Polychronakos86 | 2006 | Canada | USA | 568 | 0.015 |
| Libman et al87 | 1998 | USA | USA | 631 | 0.0167 |
| Lin et al88 | 2014 | Taiwan | Asia | 128 | 0.00334 |
| Lipman89 | 1993 | USA | USA | 494 | 0.01302 |
| Lipman et al90 | 2002 | USA | USA | 504 | 0.0133 |
| Lipman et al91 | 2006 | USA | USA | 560 | 0.0148 |
| Lipman et al92 | 2013 | USA | USA | 642 | 0.017 |
| Lipton et al93 | 2002 | USA | USA | 575 | 0.0152 |
| Lisbôa et al94 | 1998 | Brazil | USA | 455 | 0.012 |
| Li et al95 | 2000 | China | Asia | 22 | 0.00056 |
| Lora-Gómez et al96 | 2005 | Spain | Europe | 635 | 0.0168 |
| Mamoulakis et al97 | 2003 | Crete | Europe | 233 | 0.0061 |
| Martinucci et al98 | 2002 | Belarus | Europe | 176 | 0.0046 |
| Mauny et al99 | 2005 | France | Europe | 230 | 0.00603 |
| Mayer-Davis et al100 | 2009 | USA | USA | 594 | 0.0157 |
| Mazzella et al101 | 1994 | Italy | Europe | 445 | 0.01172 |
| Metcalfe and Baum102 | 1991 | Britain | Europe | 512 | 0.0135 |
| Michalková et al103 | 2004 | Slovakia | Europe | 529 | 0.01396 |
| Morales-Pérez et al104 | 2000 | Spain | Europe | 485 | 0.0128 |
| Muiña et al105 | 2012 | Spain | Europe | 1031 | 0.0276 |
| Muntoni et al106 | 1992 | Sardinia | Europe | 911 | 0.0243 |
| Muntoni et al107 | 1997 | Italy | Europe | 1255 | 0.0338 |
| Neu et al108 | 1997 | German | Europe | 440 | 0.0116 |
| Neu et al109 | 2001 | Europe | Europe | 474 | 0.0125 |
| Newhook et al110 | 2004 | Canada | USA | 1331 | 0.03593 |
| Newhook et al111 | 2008 | Canada | USA | 1300 | 0.03508 |
| Newhook et al112 | 2012 | Canada | USA | 1394 | 0.0377 |
| Ostrauskas et al113 | 2011 | Lithuania | Europe | 316 | 0.0083 |
| Patterson et al114 | 2000 | Macedonia | Europe | 123 | 0.0032 |
| Patterson et al115 | 2001 | Finland | Europe | 1482 | 0.0402 |
| Peter116 | 2007 | Bahamas | USA | 384 | 0.0101 |
| Pinelli et al117 | 1998 | Italy | Europe | 407 | 0.0107 |
| Pishdad118 | 2005 | Iran | Asia | 120 | 0.00314 |
| Podar et al119 | 1992 | Estonia | Europe | 448 | 0.0118 |
| Polanska et al120 | 2014 | Poland | Europe | 452 | 0.01192 |
| Prisco et al121 | 1996 | Italy | Europe | 232 | 0.00607 |
| Pronina et al122 | 2008 | Moscow | Europe | 489 | 0.0129 |
| Pundziute-Lyckå et al123 | 2003 | Lithuania | Europe | 361 | 0.0095 |
| 263 | 0.0069 | ||||
| Radosevic et al124 | 2013 | Bosnia and Herzegovina | Europe | 286 | 0.0075 |
| Slovenia | 474 | 0.0125 | |||
| Ramachandran et al125 | 1996 | India | Asia | 399 | 0.0105 |
| Rami et al126 | 2001 | Austria | Asia | 342 | 0.00899 |
| Rangasami et al127 | 1997 | Scotland | Europe | 896 | 0.0239 |
| Serrano Río et al128 | 1990 | Spain | Europe | 429 | 0.0113 |
| Roche et al129 | 2002 | Ireland | Europe | 627 | 0.0166 |
| Rosenbauer et al130 | 1999 | Europe | Europe | 309 | 0.0081 |
| Aude Rueda et al131 | 1998 | Mexico | USA | 44 | 0.00115 |
| Rytkönen et al132 | 2003 | Finland | Europe | 1383 | 0.0374 |
| Samardzic et al133 | 2010 | Montenegro | Europe | 508 | 0.0134 |
| Samuelsson et al134 | 1994 | Sweden | Europe | 944 | 0.0252 |
| Santos et al135 | 2001 | Chile | USA | 157 | 0.00411 |
| Sasaki and Okamoto136 | 1992 | Japan | Asia | 64 | 0.00168 |
| 77 | 0.002 | ||||
| Schober et al137 | 1995 | Australia | Asia | 301 | 0.0079 |
| Schober et al138 | 2009 | Austria | Asia | 694 | 0.0184 |
| Schoenle et al139 | 2001 | Switzerland | Europe | 399 | 0.0105 |
| Scott et al140 | 1992 | New Zealand | Europe | 482 | 0.0127 |
| Sebastiani et al141 | 1996 | Italy | Europe | 301 | 0.0079 |
| Sella et al142 | 2010 | Asia | Asia | 481 | 0.01269 |
| Sereday et al143 | 1994 | Argentina | USA | 2694 | 0.0759 |
| Shaltout et al144 | 2002 | Kuwait | Asia | 757 | 0.0201 |
| Shamis et al145 | 1997 | Asia | Asia | 278 | 0.0073 |
| López Siguero et al146 | 1997 | Malaga | Europe | 541 | 0.0143 |
| Sipetic et al147 | 2013 | Serbia | Europe | 395 | 0.0104 |
| Skordis and Hadjiloizou148 | 1997 | Greece | Europe | 399 | 0.0105 |
| Skordis et al149 | 2002 | Greece | Europe | 430 | 0.01132 |
| Skordis et al150 | 2012 | Cyprus | Asia | 473 | 0.01246 |
| Skrivarhaug et al151 | 2014 | Norway | Europe | 1215 | 0.0327 |
| Smith et al152 | 2007 | USA | USA | 683 | 0.0181 |
| Staines et al153 | 1993 | UK | Europe | 519 | 0.0137 |
| Staines et al154 | 1997 | Pakistan | Asia | 39 | 0.00102 |
| Stipancic et al155 | 2008 | Croatia | Europe | 338 | 0.00887 |
| Svensson et al156 | 2002 | Denmark | Europe | 731 | 0.0194 |
| Svensson et al157 | 2008 | Denmark | Europe | 827 | 0.022 |
| Swai et al158 | 1993 | Tanzania | Africa | 58 | 0.0015 |
| Tahirovic et al159 | 2007 | Bosnia and Herzegovina | Europe | 271 | 0.0071 |
| Taplin et al160 | 2005 | New South Wales | Asia | 786 | 0.0209 |
| Teeäär et al161 | 2009 | Estonia | Europe | 649 | 0.0172 |
| Thunander et al162 | 2008 | Sweden | Europe | 1397 | 0.0378 |
| Torffvit et al163 | 2007 | Sweden | Europe | 482 | 0.0127 |
| Toth et al164 | 1997 | Canada | USA | 962 | 0.0257 |
| Toumba et al165 | 2007 | Cyprus | Asia | 452 | 0.0119 |
| Tran et al166 | 2014 | Australia | Asia | 827 | 0.022 |
| Tuchinda et al167 | 2002 | Thailand | Asia | 63 | 0.00165 |
| Tull et al168 | 1991 | Virgin Islands | USA | 286 | 0.0075 |
| Tuomilehto et al169 | 1991 | Finland | Europe | 1219 | 0.0328 |
| Tuomilehto-Wolf et al170 | 1991 | Estonia | Europe | 407 | 0.0107 |
| Tuomilehto et al171 | 1992 | Finland | Europe | 1305 | 0.0352 |
| Tuomilehto et al172 | 1992 | Finland | Europe | 1031 | 0.0276 |
| Tuomilehto et al173 | 1993 | Mauritius | Africa | 81 | 0.0021 |
| Tuomilehto et al174 | 199 | Finland | Europe | 1369 | 0.037 |
| Tzaneva et al175 | 1998 | Bulgaria | Europe | 241 | 0.00632 |
| Vandewalle et al176 | 1997 | Belgium | Europe | 448 | 0.0118 |
| Vehik177 | 2007 | Colorado | USA | 560 | 0.0148 |
| Verge et al178 | 1994 | Australia | Asia | 549 | 0.0145 |
| Vichi et al179 | 2014 | Italy | Europe | 508 | 0.0134 |
| Vlajinac et al180 | 1995 | Serbia | Europe | 294 | 0.0077 |
| Vos et al181 | 1996 | Netherland | Europe | 753 | 0.02 |
| Wadsworth et al182 | 1995 | England | Europe | 354 | 0.0093 |
| Washington et al183 | 2012 | USAVirgin Islands | USA | 579 | 0.0153 |
| Willis et al184 | 2002 | New Zealand | Europe | 757 | 0.02012 |
| Wong185 | 1994 | China | Asia | 65 | 0.0017 |
| Wong et al186 | 1993 | Hong Kong | Asia | 77 | 0.002 |
| Yang et al187 | 1998 | China | Asia | 18 | 0.00048 |
| Yang et al188 | 2005 | China | Asia | 18 | 0.00047 |
| Zalutskaya et al189 | 2004 | Gomel area | Europe | 300 | 0.00786 |
| Minsk area | 127 | 0.00332 | |||
| Zhao et al190 | 1999 | England | Europe | 564 | 0.0149 |
| Zhao et al191 | 2014 | China | China | 119 | 0.0031 |
| Zubkiewicz-Kucharska and Noczyńska192 | 2010 | Poland | Europe | 471 | 0.01241 |
Table 2. Prevalence and incidence of type 1 diabetes in the world .
| Prevalence Per 10 000 | Incidence Per 100 000 | |
| World | 5.9 | 15 |
| Asia | 9.6 | 15 |
| Africa | 5.3 | 8 |
| Europe | 2.12 | |
| America | 3.9 | 20 |
Table 3. Characteristics of studies prevalence of type 1 diabetes .
| Study | Country | Sample Size | Prevalence Per 100 000 |
| Akazawa193 | Japan | 40 | 10 |
| Akesen et al194 | Turkey | 26 | 67 |
| Al-Herbish et al195 | Saudi Arabia | 42 | 109.5 |
| Aschner et al13 | America | 2827 | 8000 |
| Bessaoud et al18 | Algeria | 10 | 27 |
| Dabelea et al45 | Navajo nation | 40 | 11 |
| 31 | 81 | ||
| 106 | 278 | ||
| Dabelea et al196 | USA | 57 | 148 |
| Ehehalt et al51 | Italy | 3761 | 11000 |
| Elamin et al197 | Sudan | 17 | 42.98 |
| El-Ziny et al53 | Egypt | 10 | 26.8 |
| Eriksson et al198 | Finland | 1009 | 2700 |
| Evans et al199 | Scotland | 6592 | 22000 |
| Frongia et al59 | Italy | 176 | 459 |
| Garancini et al200 | Italy | 31 | 80 |
| Gujral et al201 | UK | 29 | 75 |
| Jorge et al202 | Portugal | 49 | 128 |
| Kemper et al203 | USA | 70 | 183 |
| Mayer-Davis et al100 | USA | 218 | 570 |
| Moussa et al204 | Kuwait | 103 | 269.9 |
| Ostrauskas205 | Lithuania | 31 | 80.64 |
| Ostrauskas and Žalinkevičius206 | Lithuania | 27 | 70.23 |
| Peter et al116 | Bahamas | 12 | 31 |
| Pettitt et al207 | USA | 74 | 193 |
| Ramachandran et al208 | India | 10 | 26 |
| Rangasami et al127 | Scotland | 58 | 150 |
| Scott et al140 | New Zealand | 44 | 115 |
| López Siguero et al146 | Malaga | 297 | 780 |
| Soliman et al209 | Oman | 50 | 13.25 |
| Songini et al210 | Sardinia | 46 | 119 |
| Wong185 | China | 30 | 8.3 |
| Wu et al211 | New Zealand | 87 | 227 |
Prevalence and incidence of type 1 diabetes in Asia
Prevalence and incidence of type 1 diabetes were extracted from meta-analysis studies. In type 1 diabetes incidence, the heterogeneity between studies in the meta-analysis was significant (Q = 50.51; df = 16; P < 0.001; I2 = 68.33), but in the prevalence of diabetes 1, the heterogeneity was not significant (Q = 5220; df = 6; P < 0.001; I2 = 99.88). The incidence of type 1 diabetes in Asia was 15 per 100 000 population, which was statistically significant (Incidence = 0.015, 95% CI = 0.010 to 0.021, P < 0.001), and the prevalence of type 1 diabetes was 6.9 per 10 000 people, which was statistically significant (Prevalence = 0.069, 95% CI = 0.020 to 0.214, P < 0.001). Figures 2A and 2B show the forest plot of prevalence and incidence of type 1 diabetes in Asia.
Figure 2.
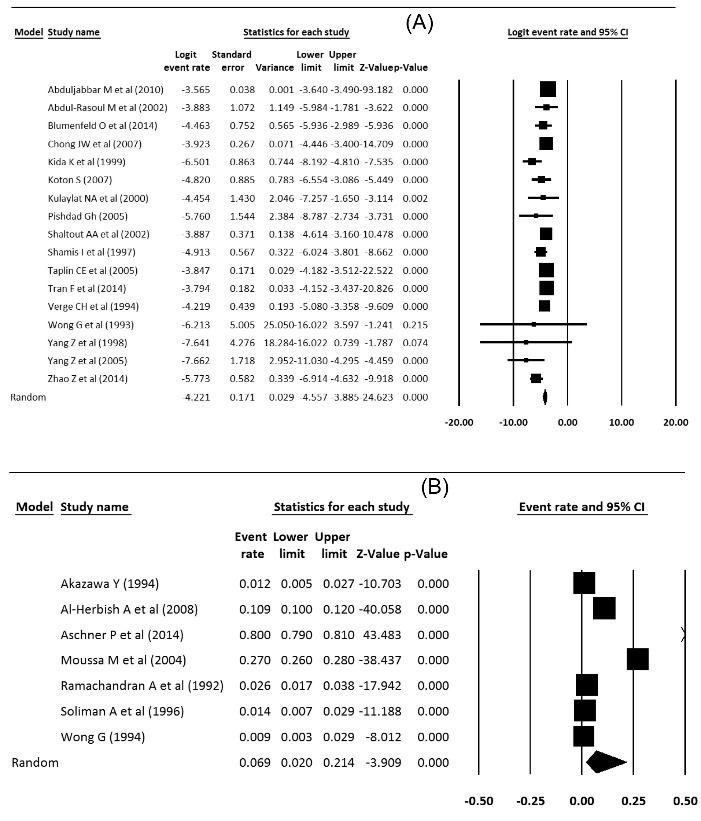
(A) Incidence and (B) prevalence of type 1 diabetes in Asia.
Prevalence and incidence of type 1 diabetes in Africa
Prevalence and incidence of type 1 diabetes were extracted from meta-analysis studies. In type 1 diabetes incidence, the heterogeneity between studies in the meta-analysis was not significant (Q = 23.79; df = 6; P < 0.001; I2 = 74.78) and in the prevalence of diabetes 1, the heterogeneity was not significant too, (Q = 4.4; df = 1; P < 0.001; I2 = 77.27). The incidence of type 1 diabetes in Africa was 8 per 100 000 population, which was statistically significant (Incidence = 0.008, 95% CI = 0.003 to 0.021 P < 0.001), and the prevalence of type 1 diabetes was 3.5 per 10 000 people, which was not statistically significant (prevalence = 0.035, 95% CI: 0.022 to 0.055, P < 0.001). Figures 3A and 3B show the forest plot of prevalence and incidence of type 1 diabetes in Africa.
Figure 3.
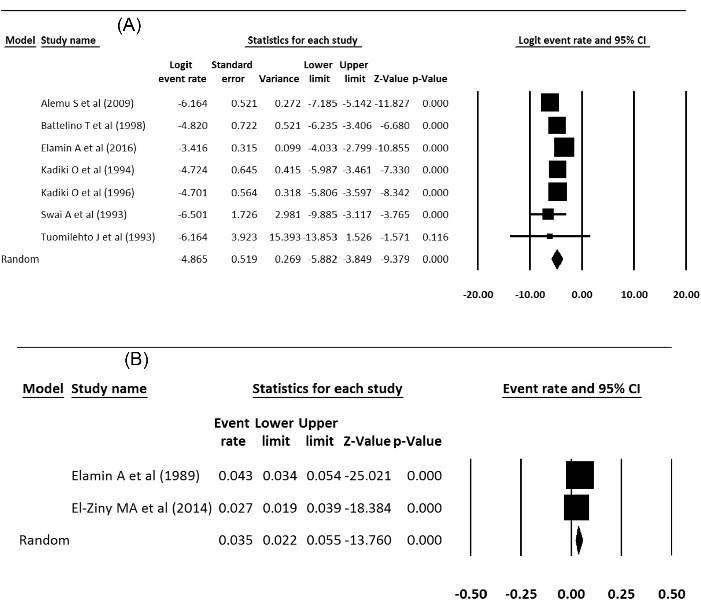
(A) Incidence and (B) prevalence of type 1 diabetes in Africa.
Prevalence and incidence of type 1 diabetes in Europe
Prevalence and incidence of type 1 diabetes were extracted from meta-analysis studies. In type 1 diabetes incidence, the heterogeneity between studies in the meta-analysis was significant (Q = 895.56, df = 96, P < 0.001, I2 = 89.28) but in the prevalence of diabetes 1, the heterogeneity was not significant, (Q = 5792.85, df = 15, P < 0.001, I2 = 99.74). The incidence of type 1 diabetes in Europe was 15 per 100 000 population, which was statistically significant (Incidence = 0.015, 95% CI = 0.013 to 0.018, P < 0.001), and the prevalence of type 1 diabetes was 12.2 per 10 000 people, which was statistically significant (Prevalence = 0.122, 95% CI = 0.085 to 0.171, P < 0.001). Figures 4 and 5 show the forest plot of prevalence and incidence of type 1 diabetes in Europe.
Figure 4.
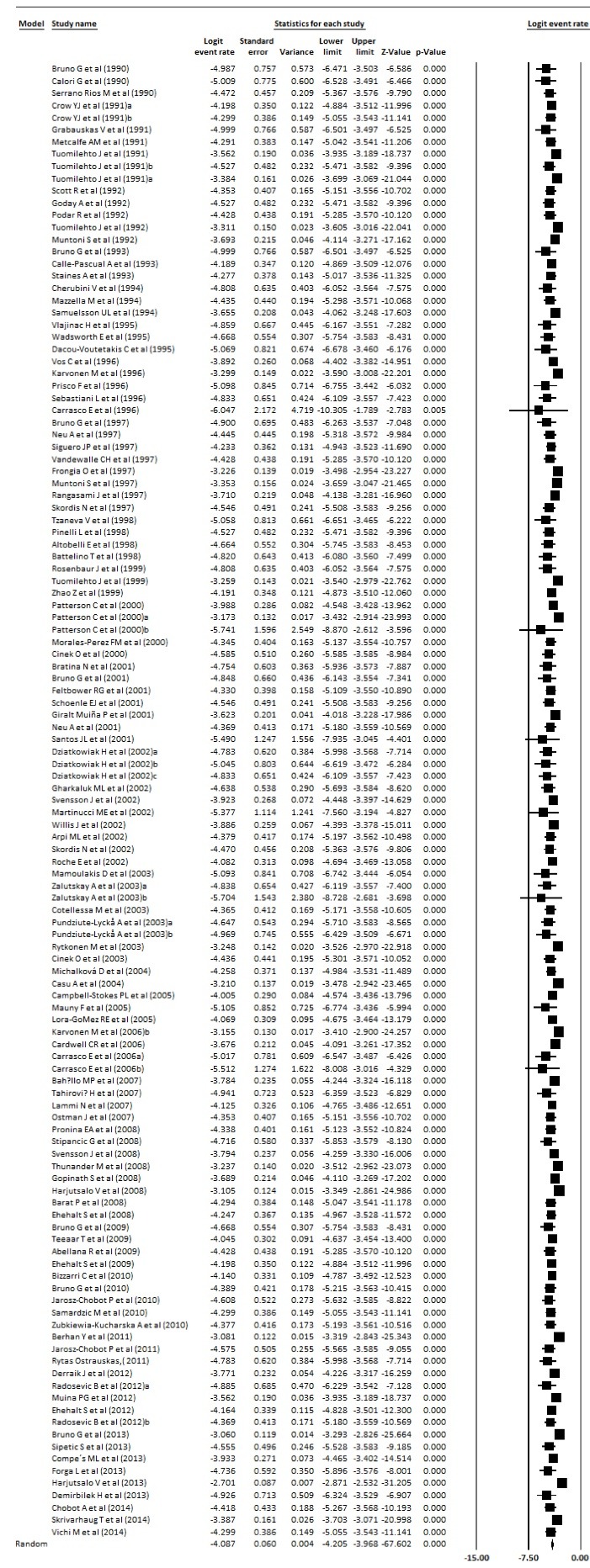
Incidence of type 1 diabetes in Europe.
Figure 5.
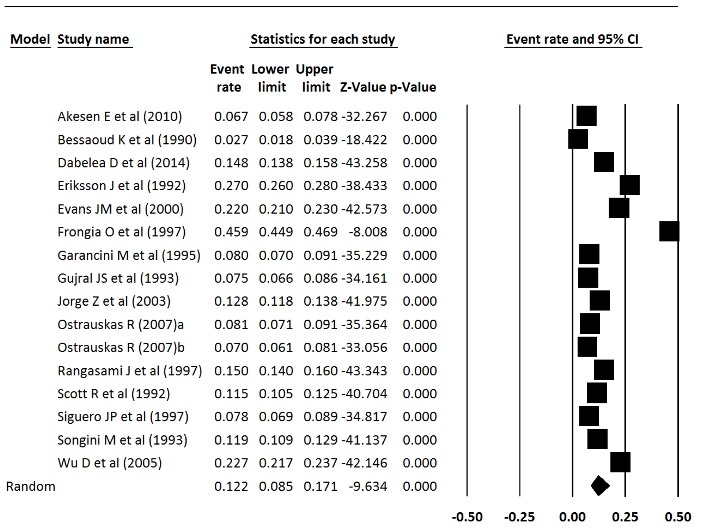
Prevalence of type 1 diabetes in Europe.
Prevalence and incidence of type 1 diabetes in America
Prevalence and incidence of type 1 diabetes were extracted from meta-analysis studies. In type 1 diabetes incidence, the heterogeneity between studies in the meta-analysis was significant (Q = 18.88, df = 16, P = 0.27, I2 = 15.28) and in the prevalence of diabetes 1, the heterogeneity was significant too, (Q = 1120.79, df = 7, P < 0.001, I2 = 99.38). The incidence of type 1 diabetes in America was 20 per 100 000 population, which was statistically significant (Incidence = 0.020, 95% CI = 0.010 to 0.021, P < 0.001), and the prevalence of type 1 diabetes was 12.2 per 10 000 people, which was statistically significant (Prevalence = 0.093, 95% CI = 0.063 to 0.137, P < 0.001). Figures 6A and 6B show the forest plot of prevalence and incidence of type 1 diabetes in America. A sensitivity analysis was done for Incidence of type 1 diabetes in America based on excluding studies with too wide CIs. Sensitivity analysis’s results show that the incidence of type 1 diabetes in America is 19 per 100 000 population, which is statistically significant (Incidence = 0.019, 95% CI = 0.016 to 0.022, P < 0.001).
Figure 6.
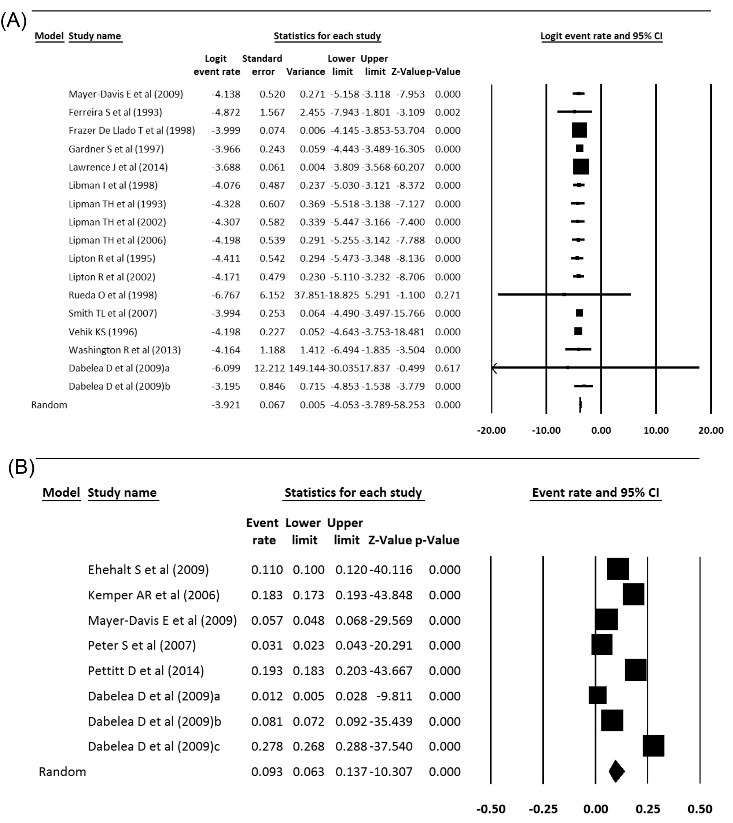
(A) Incidence and (B) prevalence of type 1 diabetes in America.
Prevalence and incidence of type 1 diabetes in the world
Prevalence and incidence of type 1 diabetes were extracted from meta-analysis studies. In type 1 diabetes incidence, the heterogeneity between studies in the meta-analysis was significant (Q = 1020.30, df = 137, P < 0.001, I2 = 86.57) and in the prevalence of diabetes 1, the heterogeneity was significant too, (Q = 14760.32, df = 32, P < 0.001, I2 = 99.78). The incidence of type 1 diabetes in world was 15 per 100 000 population, which was statistically significant (Incidence = 0.015, 95% CI = 0.013 to 0.017, P < 0.001), and the prevalence of type 1 diabetes was 9.5 per 10 000 people, which was statistically significant (prevalence = 0.095, 95% CI = 0.070 to 0.128, P < 0.001). Figure 7 shows the forest plot of prevalence and incidence of type 1 diabetes in the world.
Figure 7.
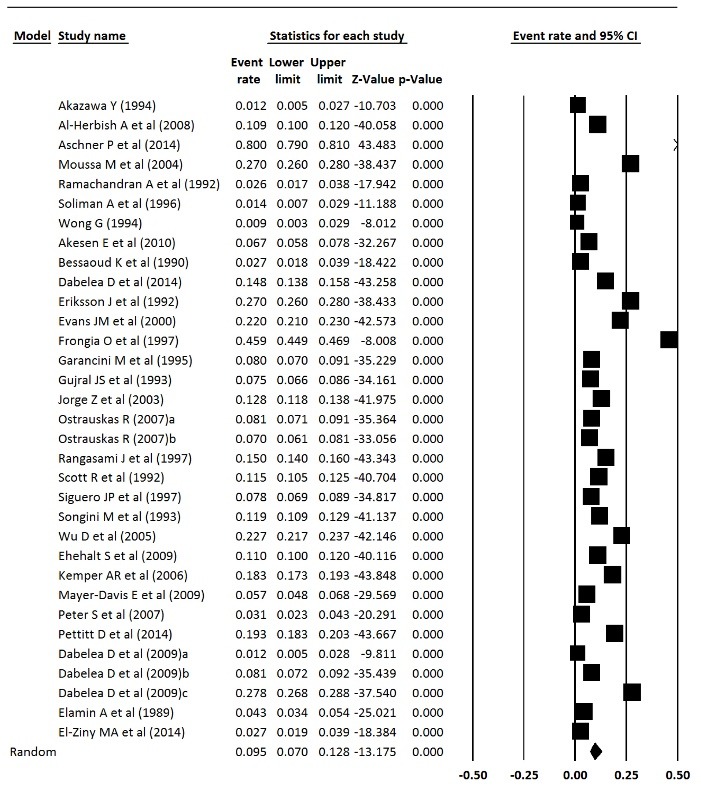
Prevalence of type 1 diabetes in the world.
Publication bias
In order to assess the publication bias, Eggers Regression test was used. Based on the results, the population bias between studies was not significant (t-value = 1.26, df 93, P = 0.21).
Meta-Regression
Meta-regression was used to determine the effect of time on type 1 diabetes incidence. The results showed that the incidence of type 1 diabetes has increased over time. The meta-regression plot is shown in Figure 8.
Figure 8.
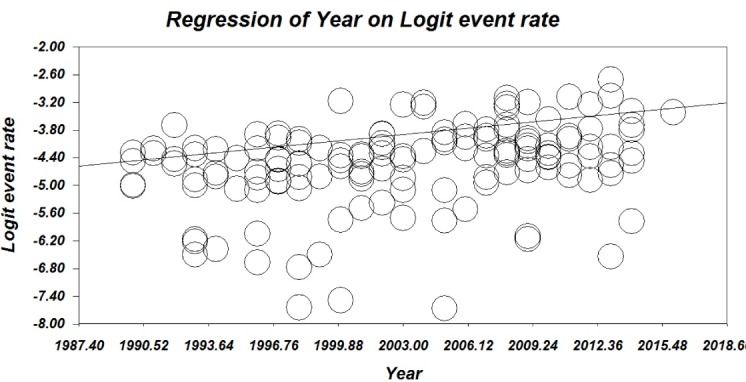
The meta-regression plot.
Discussion
The global trend of increasing prevalence of type 1 diabetes, with multiple etiologies, operates through multiple mechanisms. In the present study, data were extracted from 193 articles between 1990 and 2019. The results showed that the incidence of type 1 diabetes in continental subgroups (Asia, Africa, Europe, and America) was 15 per 100 000, 8 per 100 000, 15 per 100 000 and 20 per 100, respectively. Also, the global prevalence of continental subtypes of type 1 diabetes in the above regions was, 6.9 per 10 000, 3.5 per 10 000, and 12.2 per 10 000, respectively.
Relative differences between obtained results and previous statistics may be due to different research time periods and new global population status. Especially in recent years (social, political and economic migration), the changing global climate coupled with new policies and sanctions that have led to poorer middle-income and low-income countries.212
The pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes is known, which is associated with different genes and the involvement of multiple factors. Type 2 diabetes can be prevented and treated by removing or reducing these factors. Most of the warnings of national and international health bodies and diabetes associations are based on lifestyle changes and stress reduction that can prevent diabetes.213
But in type 1 diabetes, that make up 5 to 15 percent of diabetics and often involve children, Prevention ways have not yet been defined. However, screening of type 1 diabetes in prone families in relation to autoantibodies has recently been proposed. Also, clinical studies on the prevention of type 1 diabetes have been conducted.214
If one foot was amputated every 30 seconds, today it’s every 15 seconds. Need for dialysis equipment will increase. The CCU and ICU beds will be full of stroke and myocardial infarction patients. The population of the blind increases and unfortunately, new, effective, and less complicated treatments become more expensive.215
The disease shows a significant increase in glucose and possibly DKA. These patients definitely need insulin due to the pathogenesis of insulin deficiency. Manufacturing and production of insulin (traditional insulins and analog insulins) and insulin pumps, despite being inexpensive in producing countries, is shipped to low- and middle-income countries for high prices which is a major problem for the managing of type 1 diabetes patients. Certainly, uncontrolled hyperglycemia in type 1 diabetic patients will make all the problems more severe.216
Limitations
One of the limitations of the study was the poor quality of some articles and, despite a careful search, the lack of access to some of the full text of the published articles.
Conclusion
According to the results, the incidence and prevalence of type 1 diabetes are increasing in the world. As a result, insulin will be difficult to access and afford, especially in underdeveloped and developing countries. Thus, warnings about this can help international organizations and countries to plan for preventive measures.
Ethical approval
This research was approved by the Local Ethics Committee with No. 61701.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Funding
This article was supported by the Research Center for Evidence-Based Medicine, and the Research Vice-Chancellor of Tabriz University of Medical Sciences.
Authors’ contributions
Concept: MM. Study design: MSH and TA. Systematic search: NV. Critical reviews: MM and TA. Data extraction: MSH and MGH. Data analysis: MGH and HHF. Writing: NV, TA and MM. All authors had primary responsibility for the final content of the manuscript and read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgments
Special thanks to the Research Vice-Chancellor of Tabriz University of Medical Sciences for financial support for this study.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary file 1 contains search strategy.
References
- 1. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2010;33 Suppl 1:S62-9. doi: 10.2337/dc10-S062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 2.Davis IC, Ahmadizadeh I, Randell J, Younk L, Davis SN. Understanding the impact of hypoglycemia on the cardiovascular system. Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab. 2017;12(1):21–33. doi: 10.1080/17446651.2017.1275960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Gale EA. The rise of childhood type 1 diabetes in the 20th century. Diabetes. 2002;51(12):3353–61. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.51.12.3353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Abduljabbar MA, Aljubeh JM, Amalraj A, Cherian MP. Incidence trends of childhood type 1 diabetes in eastern Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med J. 2010;31(4):413–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Abdul-Rasoul M, Al-Qattan H, Al-Haj A, Habib H, Ismael A. Incidence and seasonal variation of type 1 diabetes in children in Farwania area, Kuwait (1995-1999) Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2002;56(2):153–7. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8227(01)00371-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Abellana R, Ascaso C, Carrasco JL, Castell C, Tresserras R. Geographical variability of the incidence of type 1 diabetes in subjects younger than 30 years in Catalonia, Spain. Med Clin (Barc) 2009;132(12):454–8. doi: 10.1016/j.medcli.2008.10.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ajlouni K, Qusous Y, Khawaldeh AK, Jaddou H, Batiehah A, Ammari F. et al. Incidence of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in Jordanian children aged 0-14 y during 1992-1996. Acta Paediatr Suppl. 1999;88(427):11–3. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1999.tb14334.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Alaghehbandan R, Collins KD, Newhook LA, MacDonald D. Childhood type 1 diabetes mellitus in Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2006;74(1):82–9. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2006.03.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Alemu S, Dessie A, Seid E, Bard E, Lee PT, Trimble ER. et al. Insulin-requiring diabetes in rural Ethiopia: should we reopen the case for malnutrition-related diabetes? Diabetologia. 2009;52(9):1842–5. doi: 10.1007/s00125-009-1433-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Algert CS, McElduff A, Morris JM, Roberts CL. Perinatal risk factors for early onset of type 1 diabetes in a 2000-2005 birth cohort. Diabet Med. 2009;26(12):1193–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2009.02878.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Altobelli E, Chiarelli F, Valenti M, Verrotti A, Tumini S, Di Orio F. Incidence of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (0-14 years) in the Abruzzo Region, Italy, 1990-1995: results from a population-based register. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 1998;11(4):555–62. doi: 10.1515/jpem.1998.11.4.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Arpi ML, Fichera G, Mancuso M, Lucenti C, Italia S, Tomaselli L. et al. A ten-year (1989-1998) perspective study of the incidence of type 1 diabetes in the district of Catania (Sicily) in a 0-14 year age group. J Endocrinol Invest. 2002;25(5):414–9. doi: 10.1007/bf03344030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Aschner P, Aguilar-Salinas C, Aguirre L, Franco L, Gagliardino JJ, de Lapertosa SG. et al. Diabetes in South and Central America: an update. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2014;103(2):238–43. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2013.11.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bahíllo MP, Hermoso F, Ochoa C, García-Fernández JA, Rodrigo J, Marugán JM. et al. Incidence and prevalence of type 1 diabetes in children aged <15 yr in Castilla-Leon (Spain) Pediatr Diabetes. 2007;8(6):369–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-5448.2007.00255.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Barat P, Valade A, Brosselin P, Alberti C, Maurice-Tison S, Lévy-Marchal C. The growing incidence of type 1 diabetes in children: the 17-year French experience in Aquitaine. Diabetes Metab. 2008;34(6 Pt 1):601–5. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2008.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Battelino T, Kržišnik C. Incidence of type 1 diabetes mellitus in children in Slovenia during the years 1988-1995. Acta Diabetol. 1998;35(2):112–4. doi: 10.1007/s005920050115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Berhan Y, Waernbaum I, Lind T, Möllsten A, Dahlquist G. Thirty years of prospective nationwide incidence of childhood type 1 diabetes: the accelerating increase by time tends to level off in Sweden. Diabetes. 2011;60(2):577–81. doi: 10.2337/db10-0813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bessaoud K, Boudraa G, Deschamps I, Hors J, Benbouabdallah M, Touhami M. Epidemiology of juvenile insulin-dependent diabetes in Algeria (Wilaya of Oran) Rev Epidemiol Sante Publique. 1990;38(2):91–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Bizzarri C, Patera PI, Arnaldi C, Petrucci S, Bitti ML, Scrocca R. et al. Incidence of type 1 diabetes has doubled in Rome and the Lazio region in the 0- to 14-year age-group: a 6-year prospective study (2004-2009) Diabetes Care. 2010;33(11):e140. doi: 10.2337/dc10-1168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Blanchard JF, Dean H, Anderson K, Wajda A, Ludwig S, Depew N. Incidence and prevalence of diabetes in children aged 0-14 years in Manitoba, Canada, 1985-1993. Diabetes Care. 1997;20(4):512–5. doi: 10.2337/diacare.20.4.512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Blumenfeld O, Dichtiar R, Shohat T. Trends in the incidence of type 1 diabetes among Jews and Arabs in Israel. Pediatr Diabetes. 2014;15(6):422–7. doi: 10.1111/pedi.12101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Bratina NU, Tahirović H, Battelino T, Krzisnik C. Incidence of childhood-onset type I diabetes in Slovenia and the Tuzia region (Bosnia and Herzegovina) in the period 1990-1998. Diabetologia. 2001;44 Suppl 3:B27–31. doi: 10.1007/pl00002949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bruno G, Merletti F, Pisu E, Pastore G, Marengo C, Pagano G. Incidence of IDDM during 1984-1986 in population aged less than 30 yr. Residents of Turin, Italy. Diabetes Care. 1990;13(10):1051–6. doi: 10.2337/diacare.13.10.1051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bruno G, Merletti F, Vuolo A, Pisu E, Giorio M, Pagano G. Sex differences in incidence of IDDM in age-group 15-29 yr. Higher risk in males in province of Turin, Italy. Diabetes Care. 1993;16(1):133–6. doi: 10.2337/diacare.16.1.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bruno G, Merletti F, De Salvia A, Lezo A, Arcari R, Pagano G. Comparison of incidence of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in children and young adults in the province of Turin, Italy, 1984-91. Piedmont Study Group for Diabetes Epidemiology. Diabet Med. 1997;14(11):964–9. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-9136(199711)14:11<964::aiddia493>3.0.co;2-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bruno G, Merletti F, Biggeri A, Cerutti F, Grosso N, De Salvia A. et al. Increasing trend of type I diabetes in children and young adults in the province of Turin (Italy). Analysis of age, period and birth cohort effects from 1984 to 1996. Diabetologia. 2001;44(1):22–5. doi: 10.1007/s001250051575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bruno G, Novelli G, Panero F, Perotto M, Monasterolo F, Bona G. et al. The incidence of type 1 diabetes is increasing in both children and young adults in Northern Italy: 1984-2004 temporal trends. Diabetologia. 2009;52(12):2531–5. doi: 10.1007/s00125-009-1538-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Bruno G, Maule M, Merletti F, Novelli G, Falorni A, Iannilli A. et al. Age-period-cohort analysis of 1990-2003 incidence time trends of childhood diabetes in Italy: the RIDI study. Diabetes. 2010;59(9):2281–7. doi: 10.2337/db10-0151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Bruno G, Maule M, Biggeri A, Ledda A, Mannu C, Merletti F. et al. More than 20 years of registration of type 1 diabetes in Sardinian children: temporal variations of incidence with age, period of diagnosis, and year of birth. Diabetes. 2013;62(10):3542–6. doi: 10.2337/db12-1771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Calle-Pascual AL, Vicente A, Martin-Alvarez PJ, Yuste E, de Matias J, Calle JR. et al. Estimation of the prevalence of diabetes mellitus diagnosed, and incidence of type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus in the Avila Health Care region of Spain. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1993;19(1):75–81. doi: 10.1016/0168-8227(93)90147-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Calori G, Gallus G, Garancini P, Repetto F, Micossi P. Identification of the cohort of type 1 diabetes presenting in Lombardy in 1983-84: a validated assessment. Diabet Med. 1990;7(7):595–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1990.tb01455.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Campbell-Stokes PL, Taylor BJ. Prospective incidence study of diabetes mellitus in New Zealand children aged 0 to 14 years. Diabetologia. 2005;48(4):643–8. doi: 10.1007/s00125-005-1697-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Cardwell CR, Carson DJ, Patterson CC. Higher incidence of childhood-onset type 1 diabetes mellitus in remote areas: a UK regional small-area analysis. Diabetologia. 2006;49(9):2074–7. doi: 10.1007/s00125-006-0342-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Carrasco E, Pérez-Bravo F, Santos JL, López G, Calvillán M, Wolff C. et al. One of the lowest validated incidence rates of insulin dependent diabetes mellitus in the Americas: Santiago, Chile. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1996;34 Suppl:S153–7. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8227(96)90023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Carrasco E, Pérez-Bravo F, Dorman J, Mondragón A, Santos JL. Increasing incidence of type 1 diabetes in population from Santiago of Chile: trends in a period of 18 years (1986-2003) Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2006;22(1):34–7. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Carrasco E, Angel B, Codner E, García D, Ugarte F, Bruzzone ME. et al. Type 1 diabetes mellitus incidence in Santiago, Chile. Analysis by counties in the period 2000-2004. Rev Med Chil. 2006;134(10):1258–64. doi: 10.4067/s0034-98872006001000007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Casu A, Pascutto C, Bernardinelli L, Songini M. Type 1 diabetes among Sardinian children is increasing: the Sardinian diabetes register for children aged 0-14 years (1989-1999) Diabetes Care. 2004;27(7):1623–9. doi: 10.2337/diacare.27.7.1623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Cherubini V, Cantarini M, Ravaglia E, Bartolotta E. Incidence of IDDM in the Marche region, Italy. Diabetes Care. 1994;17(5):432–5. doi: 10.2337/diacare.17.5.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Chong JW, Craig ME, Cameron FJ, Clarke CF, Rodda CP, Donath SM. et al. Marked increase in type 1 diabetes mellitus incidence in children aged 0-14 yr in Victoria, Australia, from 1999 to 2002. Pediatr Diabetes. 2007;8(2):67–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-5448.2007.00229.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Cinek O, Lánská V, Kolousková S, Sumník Z, Snajderová M, Rønningen KS. et al. ype 1 diabetes mellitus in Czech children diagnosed in 1990-1997: a significant increase in incidence and male predominance in the age group 0-4 years. Collaborators of the Czech Childhood Diabetes Registry. Diabet Med. 2000;17(1):64–9. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-5491.2000.00202.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Cinek O, Sumnik Z, Vavrinec J. Continuing increase in incidence of childhood-onset type 1 diabetes in the Czech Republic 1990-2001. Eur J Pediatr. 2003;162(6):428–9. doi: 10.1007/s00431-003-1211-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Compés ML, Feja C, Niño De Guzman E, Aguilar I, Conde S, Alonso JP. et al. Bayesian analysis of the geographical variation of type 1 diabetes mellitus in under 15 yr olds in northeast Spain, 1991-2009. Pediatr Diabetes. 2013;14(1):66–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-5448.2012.00892.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Cotellessa M, Barbieri P, Mazzella M, Bonassi S, Minicucci L, Lorini R. High incidence of childhood type 1 diabetes in Liguria, Italy, from 1989 to 1998. Diabetes Care. 2003;26(6):1786–9. doi: 10.2337/diacare.26.6.1786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Crow YJ, Alberti KG, Parkin JM. Insulin dependent diabetes in childhood and material deprivation in northern England, 1977-86. BMJ. 1991;303(6795):158–60. doi: 10.1136/bmj.303.6795.158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Dabelea D, DeGroat J, Sorrelman C, Glass M, Percy CA, Avery C. et al. Diabetes in Navajo youth: prevalence, incidence, and clinical characteristics: the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study. Diabetes Care. 2009;32 (Suppl 2):S141–7. doi: 10.2337/dc09-S206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Dacou-Voutetakis C, Karavanaki K, Tsoka-Gennatas H. National data on the epidemiology of IDDM in Greece. Cases diagnosed in 1992. Hellenic Epidemiology Study Group. Diabetes Care. 1995;18(4):552–4. doi: 10.2337/diacare.18.4.552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Demirbilek H, Özbek MN, Baran RT. Incidence of type 1 diabetes mellitus in Turkish children from the southeastern region of the country: a regional report. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2013;5(2):98–103. doi: 10.4274/Jcrpe.954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Derraik JG, Reed PW, Jefferies C, Cutfield SW, Hofman PL, Cutfield WS. Increasing incidence and age at diagnosis among children with type 1 diabetes mellitus over a 20-year period in Auckland (New Zealand) PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e32640. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Dziatkowiak H, Ciechanowska M, Wasikowa R, Symonides-ławecka A, Bieniasz J, Trippenbach-Dulska H. et al. Increase in the incidence of type 1 diabetes mellitus in children in three cities in Poland, 1987-1999. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2002;15(8):1153–60. doi: 10.1515/jpem.2002.15.8.1153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Ehehalt S, Blumenstock G, Willasch AM, Hub R, Ranke MB, Neu A. Continuous rise in incidence of childhood type 1 diabetes in Germany. Diabet Med. 2008;25(6):755–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2008.02450.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Ehehalt S, Popovic P, Muntoni S, Muntoni S, Willasch A, Hub R. et al. Incidence of diabetes mellitus among children of Italian migrants substantiates the role of genetic factors in the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes. Eur J Pediatr. 2009;168(5):613–7. doi: 10.1007/s00431-008-0808-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Ehehalt S, Dietz K, Willasch AM, Neu A. Prediction model for the incidence and prevalence of type 1 diabetes in childhood and adolescence: evidence for a cohort-dependent increase within the next two decades in Germany. Pediatr Diabetes. 2012;13(1):15–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-5448.2011.00799.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.El-Ziny MA, Salem NA, El-Hawary AK, Chalaby NM, Elsharkawy AA. Epidemiology of childhood type 1 diabetes mellitus in Nile Delta, northern Egypt - a retrospective study. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2014;6(1):9–15. doi: 10.4274/Jcrpe.1171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Feltbower RG, Bodansky HJ, McKinney PA, Houghton J, Stephenson CR, Haigh D. Trends in the incidence of childhood diabetes in south Asians and other children in Bradford, UK. Diabet Med. 2002;19(2):162–6. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-5491.2002.00691.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Ferreira SR, Franco LJ, Vivolo MA, Negrato CA, Simoes AC, Ventureli CR. Population-based incidence of IDDM in the state of São Paulo, Brazil. Diabetes Care. 1993;16(5):701–4. doi: 10.2337/diacare.16.5.701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Forga L, Goñi MJ, Cambra K, Ibáñez B, Mozas D, Chueca M. [Differences by age and gender in the incidence of type 1 diabetes in Navarre, Spain (2009-2011)] Gac Sanit. 2013;27(6):537–40. doi: 10.1016/j.gaceta.2012.12.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Formosa N, Calleja N, Torpiano J. Incidence and modes of presentation of childhood type 1 diabetes mellitus in Malta between 2006 and 2010. Pediatr Diabetes. 2012;13(6):484–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-5448.2011.00839.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Frazer de Llado TE, Gonzalez de Pijem L, Hawk B. Incidence of IDDM in children living in Puerto Rico. Puerto Rican IDDM Coalition. Diabetes Care. 1998;21(5):744–6. doi: 10.2337/diacare.21.5.744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Frongia O, Mastinu F, Sechi GM. Prevalence and 4-year incidence of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in the province of Oristano (Sardinia, Italy) Acta Diabetol. 1997;34(3):199–205. doi: 10.1007/s005920050074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Gardner SG, Bingley PJ, Sawtell PA, Weeks S, Gale EA. Rising incidence of insulin dependent diabetes in children aged under 5 years in the Oxford region: time trend analysis. The Bart’s-Oxford Study Group. BMJ. 1997;315(7110):713–7. doi: 10.1136/bmj.315.7110.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Charkaluk ML, Czernichow P, Lévy-Marchal C. Incidence data of childhood-onset type I diabetes in France during 1988-1997: the case for a shift toward younger age at onset. Pediatr Res. 2002;52(6):859–62. doi: 10.1203/00006450-200212000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Giralt Muiña P, Santillana Ferrer L, Madrigal Barchino D, Merlo Garrido A, Toledo De La Torre B, Anaya Barea F. Incidence of diabetes mellitus and prevalence of type 1A diabetes mellitus in children younger than 16 years old from the province of Ciudad Real. An Esp Pediatr. 2001;55(3):213–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Goday A, Castell C, Tresserras R, Canela J, Taberner JL, Lloveras G. Incidence of type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus in Catalonia, Spain. The Catalan Epidemiology Diabetes Study Group. Diabetologia. 1992;35(3):267–71. doi: 10.1007/bf00400928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Gong C, Meng X, Saenger P, Wu D, Cao B, Wu D. et al. Trends in the incidence of childhood type 1 diabetes mellitus in Beijing based on hospitalization data from 1995 to 2010. Horm Res Paediatr. 2013;80(5):328–34. doi: 10.1159/000355388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Gopinath S, Örtqvist E, Norgren S, Green A, Sanjeevi CB. Variations in incidence of type 1 diabetes in different municipalities of Stockholm. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008;1150:200–7. doi: 10.1196/annals.1447.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Gorham ED, Garland FC, Barrett-Connor E, Garland CF, Wingard DL, Pugh WM. Incidence of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in young adults: experience of 1,587,630 US Navy enlisted personnel. Am J Epidemiol. 1993;138(11):984–7. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a116818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Grabauskas V, Urbonaite B, Padaiga Z. Incidence of childhood insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in Lithuania 1983-1988. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1991;80(6-7):718–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1991.tb11934.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Green A, Patterson CC. Trends in the incidence of childhood-onset diabetes in Europe 1989-1998. Diabetologia. 2001;44 Suppl 3:B3–8. doi: 10.1007/pl00002950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Harjutsalo V, Sjöberg L, Tuomilehto J. Time trends in the incidence of type 1 diabetes in Finnish children: a cohort study. Lancet. 2008;371(9626):1777–82. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(08)60765-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Harjutsalo V, Sund R, Knip M, Groop PH. Incidence of type 1 diabetes in Finland. JAMA. 2013;310(4):427–8. doi: 10.1001/jama.2013.8399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Huen KF, Low LC, Wong GW, Tse WW, Yu AC, Lam YY. et al. Epidemiology of diabetes mellitus in children in Hong Kong: the Hong Kong childhood diabetes register. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2000;13(3):297–302. doi: 10.1515/jpem.2000.13.3.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Jarosz-Chobot P, Deja G, Polanska J. Epidemiology of type 1 diabetes among Silesian children aged 0-14 years, 1989-2005. Acta Diabetol. 2010;47(1):29–33. doi: 10.1007/s00592-009-0094-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Jarosz-Chobot P, Polanska J, Szadkowska A, Kretowski A, Bandurska-Stankiewicz E, Ciechanowska M. et al. Rapid increase in the incidence of type 1 diabetes in Polish children from 1989 to 2004, and predictions for 2010 to 2025. Diabetologia. 2011;54(3):508–15. doi: 10.1007/s00125-010-1993-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Ji J, Hemminki K, Sundquist J, Sundquist K. Ethnic differences in incidence of type 1 diabetes among second-generation immigrants and adoptees from abroad. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95(2):847–50. doi: 10.1210/jc.2009-1818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Kadiki OA, Moawad SE. Ten-year incidence (1981-90) of insulin-dependent diabetes in the 0-29-year-old age group in Benghazi, Libya. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1994;26(3):223–8. doi: 10.1016/0168-8227(94)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Kadiki OA, Reddy MR, Marzouk AA. Incidence of insulin-dependent diabetes (IDDM) and non-insulin-dependent diabetes (NIDDM) (0-34 years at onset) in Benghazi, Libya. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1996;32(3):165–73. doi: 10.1016/0168-8227(96)01262-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Karvonen M, Tuomilehto J, Virtala E, Pitkäniemi J, Reunanen A, Tuomilehto-Wolf E. et al. Seasonality in the clinical onset of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in Finnish children. Childhood Diabetes in Finland (DiMe) Study Group. Am J Epidemiol. 1996;143(2):167–76. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a008726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Karvonen M, Viik-Kajander M, Moltchanova E, Libman I, LaPorte R, Tuomilehto J. Incidence of childhood type 1 diabetes worldwide. Diabetes Mondiale (DiaMond) Project Group. Diabetes Care. 2000;23(10):1516–26. doi: 10.2337/diacare.23.10.1516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Karvonen M, Rusanen J, Sundberg M, Virtala E, Colpaert A, Naukkarinen A. et al. Regional differences in the incidence of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus among children in Finland from 1987 to 1991. Childhood Diabetes in Finland (DiMe) Study Group. Ann Med. 1997;29(4):297–304. doi: 10.3109/07853899708999351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Kida K, Kaino Y, Ito T, Hirai H, Nakamura K. Immunogenetics of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Acta Paediatr. 1999;88(s427):3–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1999.tb14332.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Koton S. Incidence of type 1 diabetes mellitus in the 0- to 17-yr-old Israel population, 1997-2003. Pediatr Diabetes. 2007;8(2):60–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-5448.2007.00230.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Kulaylat NA, Narchi H. A twelve year study of the incidence of childhood type 1 diabetes mellitus in the Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2000;13(2):135–40. doi: 10.1515/jpem.2000.13.2.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Lammi N, Taskinen O, Moltchanova E, Notkola IL, Eriksson JG, Tuomilehto J. et al. A high incidence of type 1 diabetes and an alarming increase in the incidence of type 2 diabetes among young adults in Finland between 1992 and 1996. Diabetologia. 2007;50(7):1393–400. doi: 10.1007/s00125-007-0690-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Larenas G, Montecinos A, Manosalva M, Barthou M, Vidal T. Incidence of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in the IX region of Chile: ethnic differences. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1996;34 Suppl:S147–51. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8227(96)90022-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Lawrence JM, Imperatore G, Dabelea D, Mayer-Davis EJ, Linder B, Saydah S. et al. Trends in incidence of type 1 diabetes among non-Hispanic white youth in the U.S., 2002-2009. Diabetes. 2014;63(11):3938–45. doi: 10.2337/db13-1891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Legault L, Polychronakos C. Annual incidence of type 1 diabetes in Quebec between 1989-2000 in children. Clin Invest Med. 2006;29(1):10–3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Libman IM, LaPorte RE, Becker D, Dorman JS, Drash AL, Kuller L. Was there an epidemic of diabetes in nonwhite adolescents in Allegheny County, Pennsylvania? Diabetes Care. 1998;21(8):1278–81. doi: 10.2337/diacare.21.8.1278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Lin WH, Wang MC, Wang WM, Yang DC, Lam CF, Roan JN. et al. Incidence of and mortality from type I diabetes in Taiwan from 1999 through 2010: a nationwide cohort study. PLoS One. 2014;9(1):e86172. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Lipman TH. The epidemiology of type I diabetes in children 0-14 yr of age in Philadelphia. Diabetes Care. 1993;16(6):922–5. doi: 10.2337/diacare.16.6.922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Lipman TH, Chang Y, Murphy KM. The epidemiology of type 1 diabetes in children in Philadelphia 1990-1994: evidence of an epidemic. Diabetes Care. 2002;25(11):1969–75. doi: 10.2337/diacare.25.11.1969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Lipman TH, Jawad AF, Murphy KM, Tuttle A, Thompson RL, Ratcliffe SJ. et al. Incidence of type 1 diabetes in Philadelphia is higher in black than white children from 1995 to 1999: epidemic or misclassification? Diabetes Care. 2006;29(11):2391–5. doi: 10.2337/dc06-0517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Lipman TH, Levitt Katz LE, Ratcliffe SJ, Murphy KM, Aguilar A, Rezvani I. et al. Increasing incidence of type 1 diabetes in youth: twenty years of the Philadelphia Pediatric Diabetes Registry. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(6):1597–603. doi: 10.2337/dc12-0767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Lipton R, Keenan H, Onyemere KU, Freels S. Incidence and onset features of diabetes in African-American and Latino children in Chicago, 1985-1994. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2002;18(2):135–42. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Lisbôa HR, Graebin R, Butzke L, Rodrigues CS. Incidence of type 1 diabetes mellitus in Passo Fundo, RS, Brazil. Braz J Med Biol Res. 1998;31(12):1553–6. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x1998001200007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Li XH, Li TL, Yang Z, Liu ZY, Wei YD, Jin SX. et al. A nine-year prospective study on the incidence of childhood type 1 diabetes mellitus in China. Biomed Environ Sci. 2000;13(4):263–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Lora-Gómez RE, Morales-Pérez FM, Arroyo-Díez FJ, Barquero-Romero J. Incidence of Type 1 diabetes in children in Cáceres, Spain, during 1988-1999. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2005;69(2):169–74. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2004.11.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Mamoulakis D, Galanakis E, Bicouvarakis S, Paraskakis E, Sbyrakis S. Epidemiology of childhood type I diabetes in Crete, 1990-2001. Acta Paediatr. 2003;92(6):737–9. doi: 10.1080/08035250310002588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Martinucci ME, Curradi G, Fasulo A, Medici A, Toni S, Osovik G. et al. Incidence of childhood type 1 diabetes mellitus in Gomel, Belarus. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2002;15(1):53–7. doi: 10.1515/jpem.2002.15.1.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Mauny F, Grandmottet M, Lestradet C, Guitard J, Crenn D, Floret N. et al. Increasing trend of childhood type 1 diabetes in Franche-Comté (France): analysis of age and period effects from 1980 to 1998. Eur J Epidemiol. 2005;20(4):325–9. doi: 10.1007/s10654-005-0329-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Mayer-Davis EJ, Beyer J, Bell RA, Dabelea D, D’Agostino R Jr, Imperatore G. et al. Diabetes in African American youth: prevalence, incidence, and clinical characteristics: the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study. Diabetes Care. 2009;32 Suppl 2:S112–22. doi: 10.2337/dc09-S203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Mazzella M, Cotellessa M, Bonassi S, Mulas R, Caratozzolo A, Gaber S. et al. Incidence of type I diabetes in the Liguria Region, Italy. Results of a prospective study in a 0- to 14-year age-group. Diabetes Care. 1994;17(10):1193–6. doi: 10.2337/diacare.17.10.1193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Metcalfe MA, Baum JD. Incidence of insulin dependent diabetes in children aged under 15 years in the British Isles during 1988. BMJ. 1991;302(6774):443–7. doi: 10.1136/bmj.302.6774.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Michalková D, Minárik P, Hlava P, Camajová J, Nazarov V. Trends in the incidence of childhood-onset type 1 diabetes in Slovakia 1985 - 2000. Cent Eur J Public Health. 2004;12(2):75–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Morales-Pérez FM, Barquero-Romero J, Pérez-Miranda M. Incidence of type I diabetes among children and young adults (0-29 years) in the province of Badajoz, Spain during 1992 to 1996. Acta Paediatr. 2000;89(1):101–4. doi: 10.1080/080352500750029158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Muiña PG, Herrera MJ, Atance EP, Donado JJ, Sánchez G, Ferrer LS. Epidemiological study of type 1 diabetes in children under 15 years-old in Castilla-La Mancha (Spain) An Pediatr (Barc) 2012;76(2):83–91. doi: 10.1016/j.anpedi.2011.02.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Muntoni S, Songini M. High incidence rate of IDDM in Sardinia. Sardinian Collaborative Group for Epidemiology of IDDM. Diabetes Care. 1992;15(10):1317–22. doi: 10.2337/diacare.15.10.1317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Muntoni S, Fonte MT, Stoduto S, Marietti G, Bizzarri C, Crinò A. et al. Incidence of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus among Sardinian-heritage children born in Lazio region, Italy. Lancet. 1997;349(9046):160–2. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(96)04241-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Neu A, Kehrer M, Hub R, Ranke MB. Incidence of IDDM in German children aged 0-14 years. A 6-year population-based study (1987-1993) Diabetes Care. 1997;20(4):530–3. doi: 10.2337/diacare.20.4.530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Neu A, Willasch A, Ehehalt S, Kehrer M, Hub R, Ranke MB. Diabetes incidence in children of different nationalities: an epidemiological approach to the pathogenesis of diabetes. Diabetologia. 2001;44 Suppl 3:B21–6. doi: 10.1007/pl00002948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Newhook LA, Curtis J, Hagerty D, Grant M, Paterson AD, Crummel C. et al. High incidence of childhood type 1 diabetes in the Avalon Peninsula, Newfoundland, Canada. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(4):885–8. doi: 10.2337/diacare.27.4.885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Newhook LA, Grant M, Sloka S, Hoque M, Paterson AD, Hagerty D. et al. Very high and increasing incidence of type 1 diabetes mellitus in Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. Pediatr Diabetes. 2008;9(3 Pt 2):62–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-5448.2007.00315.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Newhook LA, Penney S, Fiander J, Dowden J. Recent incidence of type 1 diabetes mellitus in children 0-14 years in Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada climbs to over 45/100 000: a retrospective time trend study. BMC Res Notes. 2012;5:628. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-5-628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Ostrauskas R, Žalinkevičius R, Jurgevičienė N, Radzevičienė L, Lašaitė L. The incidence of type 1 diabetes mellitus among 15-34 years aged Lithuanian population: 18-year incidence study based on prospective databases. BMC Public Health. 2011;11:813. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-11-813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Patterson CC, Dahlquist G, Soltesz G, Green A. Variation and trends in incidence of childhood diabetes in Europe. Lancet. 2000;355(9207):873–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Patterson CC, Dahlquist G, Soltész G, Green A. Is childhood-onset type I diabetes a wealth-related disease? An ecological analysis of European incidence rates. Diabetologia. 2001;44 (Suppl 3):B9–16. doi: 10.1007/pl00002961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Peter S. Trends in the incidence of type I diabetes mellitus worldwide. West Indian Med J. 2007;56(3):264–9. doi: 10.1590/s0043-31442007000300015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Pinelli L, Beretta F, Dalla Bernardina P, Gonfiantini E, Groff P. Incidence of insulin dependent diabetes mellitus in children 0-14 years old in the Veneto Region, Italy. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 1998;11(3):447–50. doi: 10.1515/jpem.1998.11.3.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Pishdad GR. Low incidence of type 1 diabetes in Iran. Diabetes Care. 2005;28(4):927–8. doi: 10.2337/diacare.28.4.927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Podar T, Tuomilehto-Wolf E, Tuomilehto J, LaPorte RE, Adojaan B. Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in native Estonians and immigrants to Estonia. Am J Epidemiol. 1992;135(11):1231–6. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a116229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Polanska J, Deja G, Chobot A, Jarosz-Chobot P. The increase of incidence rate of diabetes mellitus type 1(T1DM) among Silesian children (Poland) still maintains the high tempo, in years 1989-2012. Pediatr Diabetes. 2014;15:49–137. doi: 10.1111/pedi.12194_2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Prisco F, Vicedomini D, Iafusco D, De Felice E, Amodeo BM, Palumbo F. Incidence of IDDM in the Campania region, Italy. Diabetes Care. 1996;19(12):1454–5. doi: 10.2337/diacare.19.12.1454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Pronina EA, Petraikina EE, Antsiferov MB, Duchareva OV, Petrone A, Buzzetti R. et al. A 10-year (1996-2005) prospective study of the incidence of type 1 diabetes in Moscow in the age group 0-14 years. Diabet Med. 2008;25(8):956–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2008.02508.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Pundziute-Lyckå A, Urbonaite B, Ostrauskas R, Zalinkevicius R, Dahlquist GG. Incidence of type 1 diabetes in Lithuanians aged 0-39 years varies by the urban-rural setting, and the time change differs for men and women during 1991-2000. Diabetes Care. 2003;26(3):671–6. doi: 10.2337/diacare.26.3.671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Radosevic B, Bukara-Radujkovic G, Miljkovic V, Pejicic S, Bratina N, Battelino T. The incidence of type 1 diabetes in Republic of Srpska (Bosnia and Herzegovina) and Slovenia in the period 1998-2010. Pediatr Diabetes. 2013;14(4):273–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-5448.2012.00898.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Ramachandran A, Snehalatha C, Krishnaswamy CV. Incidence of IDDM in children in urban population in southern India. Madras IDDM Registry Group Madras, South India. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1996;34(2):79–82. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8227(96)01338-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Rami B, Waldhör T, Schober E. Incidence of type I diabetes mellitus in children and young adults in the province of Upper Austria, 1994-1996. Diabetologia. 2001;44 (Suppl 3):B45–7. doi: 10.1007/pl00002953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Rangasami JJ, Greenwood DC, McSporran B, Smail PJ, Patterson CC, Waugh NR. Rising incidence of type 1 diabetes in Scottish children, 1984-93. The Scottish Study Group for the Care of Young Diabetics. Arch Dis Child. 1997;77(3):210–3. doi: 10.1136/adc.77.3.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Serrano Ríos M, Moy CS, Martín Serrano R, Minuesa Asensio A, de Tomás Labat ME, Zarandieta Romero G. et al. Incidence of type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus in subjects 0-14 years of age in the Comunidad of Madrid, Spain. Diabetologia. 1990;33(7):422–4. doi: 10.1007/bf00404093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Roche E, Menon A, Gill D, Hoey HM. National incidence of type 1 diabetes in childhood and adolescence. Ir Med J. 2002;95(4):115–6, 8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Rosenbauer J, Herzig P, von Kries R, Neu A, Giani G. Temporal, seasonal, and geographical incidence patterns of type I diabetes mellitus in children under 5 years of age in Germany. Diabetologia. 1999;42(9):1055–9. doi: 10.1007/s001250051270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Aude Rueda O, Libman IM, Altamirano Bustamante N, Robles Valdes C, LaPorte RE. Low incidence of IDDM in children of Veracruz-Boca del Rio, Veracruz. Results of the first validated IDDM registry in Mexico. Diabetes Care. 1998;21(8):1372–3. doi: 10.2337/diacare.21.8.1372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Rytkönen M, Moltchanova E, Ranta J, Taskinen O, Tuomilehto J, Karvonen M. The incidence of type 1 diabetes among children in Finland--rural-urban difference. Health Place. 2003;9(4):315–25. doi: 10.1016/s1353-8292(02)00064-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Samardzic M, Marinkovic J, Kocev N, Curovic N, Terzic N. Increasing incidence of childhood type 1 diabetes in Montenegro from 1997 to 2006. Pediatr Diabetes. 2010;11(6):412–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-5448.2009.00617.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Samuelsson U, Johansson C, Carstensen J, Ludvigsson J. Space-time clustering in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) in south-east Sweden. Int J Epidemiol. 1994;23(1):138–42. doi: 10.1093/ije/23.1.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Santos J, Carrasco E, Moore A, Pérez-Bravo F, Albala C. Incidence rate and spatio-temporal clustering of type 1 diabetes in Santiago, Chile, from 1997 to 1998. Rev Saude Publica. 2001;35(1):96–100. doi: 10.1590/s0034-89102001000100014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Sasaki A, Okamoto N. Epidemiology of childhood diabetes in Osaka District, Japan, using the documents from the medical benefits system specific for childhood diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1992;18(3):191–6. doi: 10.1016/0168-8227(92)90145-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Schober E, Schneider U, Waldhör T, Tuomilehto J. Increasing incidence of IDDM in Austrian children. A nationwide study 1979-1993. Austrian Diabetes Incidence Study Group. Diabetes Care. 1995;18(9):1280–3. doi: 10.2337/diacare.18.9.1280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138. Schober E, Waldhoer T, Rami B, Hofer S. Incidence and time trend of type 1 and type 2 diabetes in Austrian children 1999-2007. J Pediatr 2009;155(2):190-3.e1. 10.1016/j.jpeds.2009.03.010 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 139.Schoenle EJ, Lang-Muritano M, Gschwend S, Laimbacher J, Mullis PE, Torresani T. et al. Epidemiology of type I diabetes mellitus in Switzerland: steep rise in incidence in under 5 year old children in the past decade. Diabetologia. 2001;44(3):286–9. doi: 10.1007/s001250051615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Scott RS, Brown LJ, Darlow BA, Forbes LV, Moore MP. Temporal variation in incidence of IDDM in Canterbury, New Zealand. Diabetes Care. 1992;15(7):895–9. doi: 10.2337/diacare.15.7.895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Sebastiani L, Visalli N, Adorisio E, Suppa MA, Buzzetti R, De Cicco AL. et al. A 5-year (1989-1993) prospective study of the incidence of IDDM in Rome and the Lazio region in the age-group 0-14 years. Diabetes Care. 1996;19(1):70–3. doi: 10.2337/diacare.19.1.70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Sella T, Shoshan A, Goren I, Shalev V, Blumenfeld O, Laron Z. et al. A retrospective study of the incidence of diagnosed Type 1 diabetes among children and adolescents in a large health organization in Israel, 2000-2008. Diabet Med. 2011;28(1):48–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2010.03174.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Sereday MS, Martí ML, Damiano MM, Moser ME. Establishment of a registry and incidence of IDDM in Avellaneda, Argentina. Diabetes Care. 1994;17(9):1022–5. doi: 10.2337/diacare.17.9.1022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Shaltout AA, Moussa MA, Qabazard M, Abdella N, Karvonen M, Al-Khawari M. et al. Further evidence for the rising incidence of childhood Type 1 diabetes in Kuwait. Diabet Med. 2002;19(6):522–5. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-5491.2002.00703.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Shamis I, Gordon O, Albag Y, Goldsand G, Laron Z. Ethnic differences in the incidence of childhood IDDM in Israel (1965-1993). Marked increase since 1985, especially in Yemenite Jews. Diabetes Care. 1997;20(4):504–8. doi: 10.2337/diacare.20.4.504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146. López Siguero JP, Martínez Aedo Ollero MJ, Molina JA, Lora Espinosa A, Valverde AM. Evolución de la incidencia de la diabetes mellitus tipo I en niños de 0 a 14 años en Málaga (1982-1993). An Esp Pediatr 1997;47(1):17-22. [Spanish]. [PubMed]
- 147.Sipetic S, Maksimovic J, Vlajinac H, Ratkov I, Sajic S, Zdravkovic D. et al. Rising incidence of type 1 diabetes in Belgrade children aged 0-14 years in the period from 1982 to 2005. J Endocrinol Invest. 2013;36(5):307–12. doi: 10.3275/8619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Skordis N, Hadjiloizou S. Incidence of insulin dependent diabetes mellitus in Greek Cypriot children and adolescents, 1990-1994. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 1997;10(2):203–7. doi: 10.1515/jpem.1997.10.2.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Skordis N, Theodorou S, Apsiotou T, Stavrou S, Herakleous E, Savva SC. The incidence of type 1 diabetes mellitus in Greek-Cypriot children and adolescents in 1990-2000. Pediatr Diabetes. 2002;3(4):200–4. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-5448.2002.30406.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Skordis N, Efstathiou E, Kyriakides TC, Savvidou A, Savva SC, Phylactou LA. et al. Epidemiology of type 1 diabetes mellitus in Cyprus: rising incidence at the dawn of the 21st century. Hormones (Athens) 2012;11(1):86–93. doi: 10.1007/bf03401541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Skrivarhaug T, Stene LC, Drivvoll AK, Strom H, Joner G. Incidence of type 1 diabetes in Norway among children aged 0-14 years between 1989 and 2012: has the incidence stopped rising? results from the Norwegian Childhood Diabetes Registry. Diabetologia. 2014;57(1):57–62. doi: 10.1007/s00125-013-3090-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Smith TL, Drum ML, Lipton RB. Incidence of childhood type I and non-type 1 diabetes mellitus in a diverse population: the Chicago Childhood Diabetes Registry, 1994 to 2003. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2007;20(10):1093–107. doi: 10.1515/jpem.2007.20.10.1093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Staines A, Bodansky HJ, Lilley HE, Stephenson C, McNally RJ, Cartwright RA. The epidemiology of diabetes mellitus in the United Kingdom: the Yorkshire regional childhood diabetes register. Diabetologia. 1993;36(12):1282–7. doi: 10.1007/bf00400806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Staines A, Bodansky HJ, McKinney PA, Alexander FE, McNally RJ, Law GR. et al. Small area variation in the incidence of childhood insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in Yorkshire, UK: links with overcrowding and population density. Int J Epidemiol. 1997;26(6):1307–13. doi: 10.1093/ije/26.6.1307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Stipancic G, La Grasta Sabolic L, Malenica M, Radica A, Skrabic V, Tiljak MK. Incidence and trends of childhood type 1 diabetes in Croatia from 1995 to 2003. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2008;80(1):122–7. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2007.10.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Svensson J, Carstensen B, Molbak A, Christau B, Mortensen HB, Nerup J. et al. Increased risk of childhood type 1 diabetes in children born after 1985. Diabetes Care. 2002;25(12):2197–201. doi: 10.2337/diacare.25.12.2197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Svensson J, Ramelius A, Eising S, Mortensen H, Lernmark Å, Pociot F. et al. Decreasing humoral activity in siblings of type 1 diabetes children over a ten year period with increasing incidence of the disease. Diabetologia. 2008;51(S1):232–3. [Google Scholar]
- 158.Swai AB, Lutale JL, McLarty DG. Prospective study of incidence of juvenile diabetes mellitus over 10 years in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. BMJ. 1993;306(6892):1570–2. doi: 10.1136/bmj.306.6892.1570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Tahirovic H, Toromanovic A, Bacaj D, Hasanovic E. Ketoacidosis at onset of type 1 diabetes mellitus in children in Bosnia and Herzegovina: frequency and clinical presentation. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2007;20(10):1137–40. doi: 10.1515/jpem.2007.20.10.1137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Taplin CE, Craig ME, Lloyd M, Taylor C, Crock P, Silink M. et al. The rising incidence of childhood type 1 diabetes in New South Wales, 1990-2002. Med J Aust. 2005;183(5):243–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Teeäär T, Liivak N, Heilman K, Kool P, Sor R, Paal M. et al. Increasing incidence of childhood-onset type 1 diabetes mellitus among Estonian children in 1999-2006. Time trend analysis 1983-2006. Pediatr Diabetes. 2010;11(2):107–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-5448.2009.00535.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Thunander M, Petersson C, Jonzon K, Fornander J, Ossiansson B, Torn C. et al. Incidence of type 1 and type 2 diabetes in adults and children in Kronoberg, Sweden. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2008;82(2):247–55. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2008.07.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Torffvit O, Eriksson JW, Henricsson M, Sundkvist G, Arnqvist HJ, Blohmé G. et al. Early changes in glomerular size selectivity in young adults with type 1 diabetes and retinopathy. Results from the Diabetes Incidence Study in Sweden. J Diabetes Complications. 2007;21(4):246–51. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2006.01.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Toth EL, Lee KC, Couch RM, Martin LF. High incidence of IDDM over 6 years in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. Diabetes Care. 1997;20(3):311–3. doi: 10.2337/diacare.20.3.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Toumba M, Savva SC, Bacopoulou I, Apsiotou T, Georgiou T, Stavrou S. et al. Rising incidence of type 1 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents in Cyprus in 2000-2004. Pediatr Diabetes. 2007;8(6):374–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-5448.2007.00262.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Tran F, Stone M, Huang CY, Lloyd M, Woodhead HJ, Elliott KD. et al. Population-based incidence of diabetes in Australian youth aged 10-18 yr: increase in type 1 diabetes but not type 2 diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes. 2014;15(8):585–90. doi: 10.1111/pedi.12131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Tuchinda C, Likitmaskul S, Unachak K, Panamonta O, Patarakijavanich N, Chetthakul T. The epidemiology of type 1 diabetes in Thai children. J Med Assoc Thai. 2002;85(6):648–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Tull ES, Roseman JM, Christian CL. Epidemiology of childhood IDDM in U.S. Virgin Islands from 1979 to 1988. Evidence of an epidemic in early 1980s and variation by degree of racial admixture. Diabetes Care. 1991;14(7):558–64. doi: 10.2337/diacare.14.7.558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Tuomilehto J, Podar T, Reunanen A, Kalits I, Lounamaa R, Tuomilehto-Wolf E. et al. Comparison of incidence of IDDM in childhood between Estonia and Finland, 1980-1988. Diabetes Care. 1991;14(11):982–8. doi: 10.2337/diacare.14.11.982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Tuomilehto-Wolf E, Podar T, Adojaan B, Kalits I, Tuomilehto J. Can the difference in incidence of type 1 diabetes between Estonia and Finland be partly explained by genetic reasons. Diabetologia. 1991;34(Suppl 2):A65. [Google Scholar]
- 171.Tuomilehto J, Lounamaa R, Tuomilehto-Wolf E, Reunanen A, Virtala E, Kaprio EA. et al. Epidemiology of childhood diabetes mellitus in Finland--background of a nationwide study of type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. The Childhood Diabetes in Finland (DiMe) Study Group. Diabetologia. 1992;35(1):70–6. doi: 10.1007/bf00400854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Tuomilehto J, Podar T, Brigis G, Urbonaite B, Rewers M, Adojaan B. et al. Comparison of the incidence of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in childhood among five Baltic populations during 1983-1988. Int J Epidemiol. 1992;21(3):518–27. doi: 10.1093/ije/21.3.518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Tuomilehto J, Dabee J, Karvonen M, Dowse GK, Gareeboo H, Virtala E. et al. Incidence of IDDM in Mauritian children and adolescents from 1986 to 1990. Diabetes Care. 1993;16(12):1588–91. doi: 10.2337/diacare.16.12.1588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Tuomilehto J, Karvonen M, Pitkaniemi J, Virtala E, Kohtamaki K, Toivanen L. et al. Record-high incidence of type I (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus in Finnish children. The Finnish Childhood Type I Diabetes Registry Group. Diabetologia. 1999;42(6):655–60. doi: 10.1007/s001250051212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Tzaneva V, Iotova V, Bruining GJ. Increase in IDDM incidence in Bulgarian children (1974-1995) J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 1998;11(6):725–32. doi: 10.1515/jpem.1998.11.6.725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Vandewalle CL, Coeckelberghs MI, De Leeuw IH, Du Caju MV, Schuit FC, Pipeleers DG. et al. Epidemiology, clinical aspects, and biology of IDDM patients under age 40 years. Comparison of data from Antwerp with complete ascertainment with data from Belgium with 40% ascertainment. The Belgian Diabetes Registry. Diabetes Care. 1997;20(10):1556–61. doi: 10.2337/diacare.20.10.1556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Vehik K, Hamman RF, Lezotte D, Norris JM, Klingensmith G, Bloch C. et al. Increasing incidence of type 1 diabetes in 0-to 17-year-old Colorado youth. Diabetes Care. 2007;30(3):503–9. doi: 10.2337/dc06-1837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Verge CF, Silink M, Howard NJ. The incidence of childhood IDDM in New South Wales, Australia. Diabetes Care. 1994;17(7):693–6. doi: 10.2337/diacare.17.7.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Vichi M, Iafusco D, Galderisi A, Stazi MA, Nisticò L. An easy, fast, effective tool to monitor the incidence of type 1 diabetes among children aged 0-4 years in Italy: the Italian Hospital Discharge Registry (IHDR) Acta Diabetol. 2014;51(2):287–94. doi: 10.1007/s00592-014-0556-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Vlajinac HD, Bojović BM, Sipetić SB, Adanja BJ, Jarebinski MS, Radmanović SZ. et al. Insulin dependent diabetes mellitus: incidence in childhood in Belgrade 1982-92. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1995;49(1):107–8. doi: 10.1136/jech.49.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Vos C, Reeser HM, Hirasing RA, Bruining GJ. Confirmation of high incidence of type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus in Moroccan children in The Netherlands. Diabet Med. 1997;14(5):397–400. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-9136(199705)14:5<397::aid-dia358>3.0.co;2-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Wadsworth E, Shield J, Hunt L, Baum D. Insulin dependent diabetes in children under 5: incidence and ascertainment validation for 1992. BMJ. 1995;310(6981):700–3. doi: 10.1136/bmj.310.6981.700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Washington RE, Orchard TJ, Arena VC, LaPorte RE, Tull ES. Incidence of type 1 and type 2 diabetes in youth in the US Virgin Islands, 2001–2010. Pediatr Diabetes. 2012;14(4):280–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-5448.2012.00912.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Willis JA, Scott RS, Darlow BA, Nesbit JW, Anderson P, Moore MP. et al. Incidence of type 1 diabetes mellitus diagnosed before age 20 years in Canterbury, New Zealand over the last 30 years. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2002;15(5):637–43. doi: 10.1515/jpem.2002.15.5.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Wong GW. Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in southern Chinese children: an overview. J Paediatr Child Health. 1994;30(6):490–1. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1754.1994.tb00718.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Wong GW, Leung SS, Oppenheimer SJ. Epidemiology of IDDM in southern Chinese children in Hong Kong. Diabetes Care. 1993;16(6):926–8. doi: 10.2337/diacare.16.6.926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Yang Z, Wang K, Li T, Sun W, Li Y, Chang YF. et al. Childhood diabetes in China. Enormous variation by place and ethnic group. Diabetes Care. 1998;21(4):525–9. doi: 10.2337/diacare.21.4.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Yang Z, Long X, Shen J, Liu D, Dorman JS, Laporte RE. et al. Epidemics of type 1 diabetes in China. Pediatr Diabetes. 2005;6(3):122–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-543X.2005.00116.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Zalutskaya A, Bornstein SR, Mokhort T, Garmaev D. Did the Chernobyl incident cause an increase in type 1 diabetes mellitus incidence in children and adolescents? Diabetologia. 2004;47(1):147–8. doi: 10.1007/s00125-003-1271-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Zhao HX, Stenhouse E, Soper C, Hughes P, Sanderson E, Baumer JH. et al. Incidence of childhood-onset type 1 diabetes mellitus in Devon and Cornwall, England, 1975-1996. Diabet Med. 1999;16(12):1030–5. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-5491.1999.00175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Zhao Z, Sun C, Wang C, Li P, Wang W, Ye J. et al. Rapidly rising incidence of childhood type 1 diabetes in Chinese population: epidemiology in Shanghai during 1997-2011. Acta Diabetol. 2014;51(6):947–53. doi: 10.1007/s00592-014-0590-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Zubkiewicz-Kucharska A, Noczyńska A. Epidemiology of type 1 diabetes in Lower Silesia in the years 2000-2005. Pediatr Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2010;16(1):45–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Akazawa Y. Prevalence and incidence of diabetes mellitus by WHO criteria. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1994;24 Suppl:S23–7. doi: 10.1016/0168-8227(94)90223-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Akesen E, Turan S, Güran T, Atay Z, Save D, Bereket A. Prevalence of type 1 diabetes mellitus in 6-18-yr-old school children living in Istanbul, Turkey. Pediatr Diabetes. 2011;12(6):567–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-5448.2010.00744.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Al-Herbish AS, El-Mouzan MI, Al-Salloum AA, Al-Qurachi MM, Al-Omar AA. Prevalence of type 1 diabetes mellitus in Saudi Arabian children and adolescents. Saudi Med J. 2008;29(9):1285–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Dabelea D, Mayer-Davis EJ, Saydah S, Imperatore G, Linder B, Divers J. et al. Prevalence of type 1 and type 2 diabetes among children and adolescents from 2001 to 2009. JAMA. 2014;311(17):1778–86. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.3201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Elamin A, Omer MI, Hofvander Y, Tuvemo T. Prevalence of IDDM in schoolchildren in Khartoum, Sudan. Diabetes Care. 1989;12(6):430–2. doi: 10.2337/diacare.12.6.430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Eriksson J, Forsen B, Haggblom M, Teppo AM, Groop L. Clinical and metabolic characteristics of type 1 and type 2 diabetes: an epidemiological study from the Närpes community in western Finland. Diabet Med. 1992;9(7):654–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1992.tb01862.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Evans JM, Newton RW, Ruta DA, MacDonald TM, Morris AD. Socio-economic status, obesity and prevalence of type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med. 2000;17(6):478–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Garancini MP, Calori G, Ruotolo G, Manara E, Izzo A, Ebbli E. et al. Prevalence of NIDDM and impaired glucose tolerance in Italy: an OGTT-based population study. Diabetologia. 1995;38(3):306–13. doi: 10.1007/bf00400635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201.Gujral JS, McNally PG, Botha JL, Burden AC. Childhood-onset diabetes in the white and South Asian population in Leicestershire, UK. Diabet Med. 1994;11(6):570–2. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1994.tb02037.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 202.Jorge Z, Lacerda Nobre E, Macedo A, Jácome De Castro J. Prevalence of type 1 diabetes mellitus in Portugal, 1995-1999: cohort of young men. Acta Med Port. 2003;16(4):251–3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203.Kemper AR, Dombkowski KJ, Menon RK, Davis MM. Trends in diabetes mellitus among privately insured children, 1998-2002. Ambul Pediatr. 2006;6(3):178–81. doi: 10.1016/j.ambp.2006.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 204.Moussa MA, Alsaeid M, Abdella N, Refai TM, Al-Sheikh N, Gomez JE. Prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus among Kuwaiti children and adolescents. Med Princ Pract. 2008;17(4):270–5. doi: 10.1159/000129604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205.Ostrauskas R. The prevalence of type 1 diabetes mellitus among adolescents and adults in Lithuania during 1991-2004. Medicina (Kaunas) 2007;43(3):242–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 206.Ostrauskas R, Žalinkevičius R. The prevalence of type 1 diabetes mellitus over twelve consecutive years among adults in Lithuania. Baltic Endocrinology. 2006;2(1):1–7. [Google Scholar]
- 207.Pettitt DJ, Talton J, Dabelea D, Divers J, Imperatore G, Lawrence JM. et al. Prevalence of diabetes in U.S. youth in 2009: the SEARCH for diabetes in youth study. Diabetes Care. 2014;37(2):402–8. doi: 10.2337/dc13-1838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 208.Ramachandran A, Snehalatha C, Abdul Khader OM, Joseph TA, Viswanathan M. Prevalence of childhood diabetes in an urban population in south India. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1992;17(3):227–31. doi: 10.1016/0168-8227(92)90098-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 209.Soliman AT, al-Salmi IS, Asfour MG. Epidemiology of childhood insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in the Sultanate of Oman. Diabet Med. 1996;13(6):582–6. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-9136(199606)13:6<582::aiddia114>3.0.co;2-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 210.Songini M, Loche M, Muntoni S, Stabilini M, Coppola A, Dessi G. et al. Increasing prevalence of juvenile onset type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus in Sardinia: the military service approach. Diabetologia. 1993;36(6):547–52. doi: 10.1007/bf02743272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 211.Wu D, Kendall D, Lunt H, Willis J, Darlow B, Frampton C. Prevalence of type 1 diabetes in New Zealanders aged 0-24 years. N Z Med J. 2005;118(1218):U1557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 212.Mehta S, Yu EA, Ahamed SF, Bonam W, Kenneth J. Rifampin resistance and diabetes mellitus in a cross-sectional study of adult patients in rural South India. BMC Infect Dis. 2015;15:451. doi: 10.1186/s12879-015-1204-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 213.Lin YH, Chen CP, Chen PY, Huang JC, Ho C, Weng HH. et al. Screening for pulmonary tuberculosis in type 2 diabetes elderly: a cross-sectional study in a community hospital. BMC Public Health. 2015;15:3. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-15-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 214.Jawad F, Shera AS, Memon R, Ansari G. Glucose intolerance in pulmonary tuberculosis. J Pak Med Assoc. 1995;45(9):237–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 215.Kumpatla S, Sekar A, Achanta S, Sharath BN, Kumar AM, Harries AD. et al. Characteristics of patients with diabetes screened for tuberculosis in a tertiary care hospital in South India. Public Health Action. 2013;3(Suppl 1):S23–8. doi: 10.5588/pha.13.0035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 216.Jali MV, Mahishale VK, Hiremath MB. Bidirectional screening of tuberculosis patients for diabetes mellitus and diabetes patients for tuberculosis. Diabetes Metab J. 2013;37(4):291–5. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2013.37.4.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary file 1 contains search strategy.


