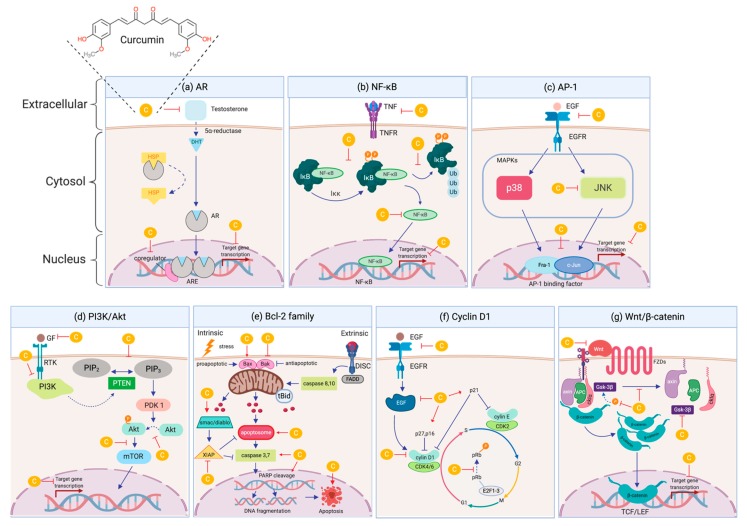
Figure 4.
Mode of actions of curcumin as anti-cancer agent on the key molecular targets in aberrant signalling pathways of PCa. Curcumin exhibits anti-cancer properties by inhibiting signalling pathways and molecular targets; (a) Androgen receptor (AR) signalling; (b) Nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB); (c) Activating protein-1 (AP-1); (d) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases/the serine/threonine kinase (PI3K/Akt); (e) B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2); (f) Cyclin D1 and (g) Wingless (Wnt)/ß-catenin signalling. Molecular targets and signalling pathways that are induced by curcumin are noted by using →, while the inhibition represented by ⊣ symbol.