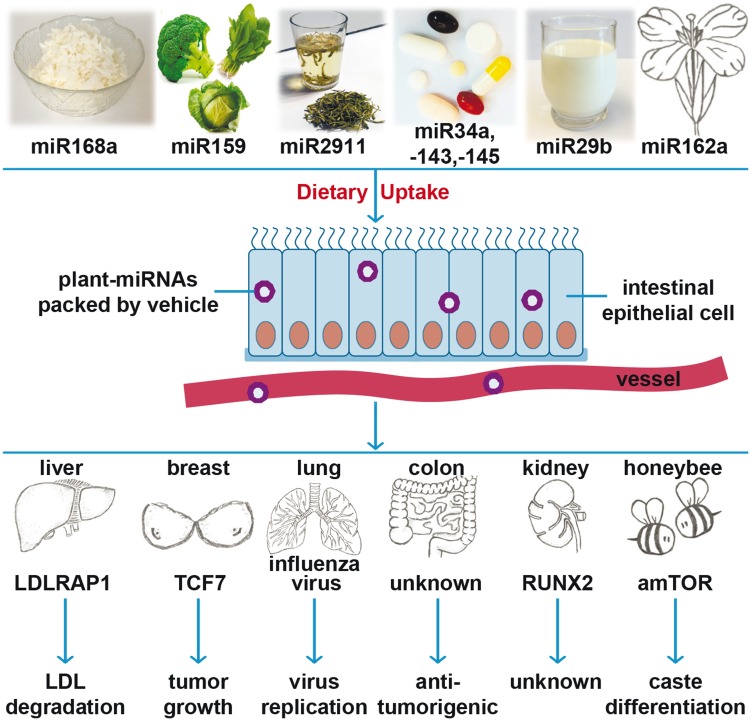
Figure 1. Cartoon of recent findings of plant miRNA actions.
Recent studies suggest that the dietary uptake of miR-168a from rice, miR-159 from broccoli, miR-2911 from honeysuckle, a cocktail of plant-miRs (-34a, -143 and -145), miR-29b from cow milk, and miR-162a from Brassica campestris safely pass the gastrointestinal tract and can be found in the blood stream or tissue of consumers. Cross-kingdom regulatory effects of plant-derived miRs in other species have described: miR-168 effects low-density lipoprotein removal by targeting low-density lipoprotein receptor adapter protein (LDLRAP1); miR-159 inhibits breast cancer growth by targeting transcription factor 7 (TCF7); miR2911 suppresses viral infection by inhibiting virus replication; a cocktail of plant-miRs (-34a, -143 and -145) reduces colon tumour burden through an unrevealed mechanism; miR-29 targets runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2); and miR-162a regulates honeybee caste development by targeting mTOR.