Abstract
Sentiment lexicon plays a vital role in lexicon-based sentiment analysis. The lexicon-based method is often preferred because it leads to more explainable answers in comparison with many machine learning-based methods. But, semantic orientation of a word depends on its domain. Hence, a general-purpose sentiment lexicon may gives sub-optimal performance compare with a domain-specific lexicon. However, it is challenging to manually generate a domain-specific sentiment lexicon for each domain. Still, it is impractical to generate complete sentiment lexicon for a domain from a single corpus. To this end, we propose an approach to automatically generate a domain-specific sentiment lexicon using a vector model enriched by weights. Importantly, we propose an incremental approach for updating an existing lexicon to either the same domain or different domain (domain-adaptation). Finally, we discuss how to incorporate sentiment lexicons information in neural models (word embedding) for better performance.
Keywords: Domain-specific, Sentiment analysis, Sentiment lexicon, Word embedding, Machine learning
Motivation
Sentiment lexicon is a dictionary of a lexical item with the corresponding semantic orientation. Recently, with the issue of growing concern about interpretable and explainable artificial intelligence, domains that require high explainability in sentiment analysis task (eg., health domain and financial domain), lexicon-based sentiment analysis approaches are often preferred over machine-learning-based approaches [12, 13]. However, sentiment lexicons are domain-dependent, a word may convey two different connotations in a different domain. For example, the word high may have a positive connotation in economics (e.g., he has a high salary), and negative connotation in medicine (e.g., he has a high blood pressure). Therefore, general-purpose sentiment lexicon may not give the expected predictive accuracy across different domains. Thus, a lexicon-based approach with domain-specific lexicons are used to achieve better performance [1, 4].
Although research has been carried out on corpus-based approaches for automatic generation of a domain-specific lexicon [1, 4, 5, 7, 9, 10, 14], existing approaches focused on creation of a lexicon from a single corpus [4]. Afterwards, one cannot automatically update the lexicon with a new corpus. There are many reasons one would want to update an existing lexicon: (i) the existing lexicon may not contain sufficient number of sentiment-bearing words (i.e., it is limited) and it needs to be extended with a corpus from the same domain with a source corpus; (ii) the language may have evolved (new words and meaning changes) and it is necessary to update the existing lexicon with a new corpus. The new corpus may not be large to enable generation of a new lexicon from scratch. Thus, it is better to update the existing lexicon with the new corpus; and (iii) we need to update an existing lexicon to another domain (domain-adaptation) with a corpus from different domain with the source corpus. To this end, this work proposes an incremental approach for the automatic generation of a domain-specific sentiment lexicon.
Research Questions and Methodology
We aim to investigate an incremental technique for automatically generating domain-specific sentiment lexicon from a corpus. Specifically, we aim to answer the following three research questions:
RQ1: Can we automatically generate a sentiment lexicon from a corpus and improves the existing approaches?
RQ2: Can we automatically update an existing sentiment lexicon given a new corpus from the same domain (i.e., to extend an existing lexicon to have more entries) or from a different domain (i.e., to adapt the existing lexicon to a new domain - domain adaptation)?
RQ3: How can we enrich the existing sentiment lexicons using information obtained from neural models (word embedding)?
To the best of our knowledge, no one attempted to design an approach for automatic construction of a sentiment lexicon in an incremental fashion. But, incremental approaches are common in the area of data streaming [15]; thus, our work could fill this gap and represent a novel contribution. The research plan is structured as follows: Sect. 2.1 attempts to answer RQ1, Sect. 2.2 attempts to answer RQ2, and Sect. 2.3 attempts to answer RQ3.
Sentiment Lexicon Generation Using Weight Vector Model (non-Incremental)
Sattam et al. [4] introduced a novel domain agnostic sentiment lexicon-generation approach from a review corpus annotated with star-ratings. We propose an extended approach that includes the use of weight vector. Also, our approach includes verbs and nouns in the lexicon as studies show they contain sentiment [7, 11]. The process includes the following four steps: (i) gathering data annotated with star-ratings; (ii) pre-processing the data; (iii) obtaining word-tag rating distribution, as shown in Fig. 1 from the corpus introduced in [16]; and (iv) generation of sentiment value for each word-tag pair using the equation: 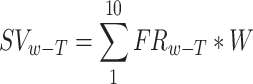 . Where
. Where 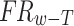 represents the frequency of word-tag pair and
represents the frequency of word-tag pair and 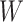 is a weight vector. If the result is positive, the word is categorize as positive, otherwise it is negative. This basic approach of sentiment lexicon generation forms the basis of the incremental approach proposes in Sect. 2.2.
is a weight vector. If the result is positive, the word is categorize as positive, otherwise it is negative. This basic approach of sentiment lexicon generation forms the basis of the incremental approach proposes in Sect. 2.2.
Fig. 1.
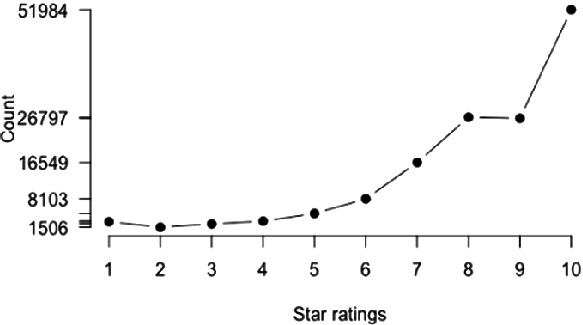
Distribution of the word-tag pair(excellent, a)
Incremental Approach for Sentiment Lexicon Generation Using Sufficient Statistics
We propose an incremental approach for sentiment lexicon expansion to either the same domain or different domain (domain-adaptation). To illustrate the approaches, assume we have a sentiment lexicon 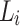 generated from a corpus
generated from a corpus 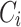 (using the approach described in Sect. 2.1). Then, we receive a new batch of corpus
(using the approach described in Sect. 2.1). Then, we receive a new batch of corpus 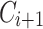 (of the same or different domain with
(of the same or different domain with 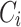 ). The incremental approach aims to generate an updated sentiment lexicon
). The incremental approach aims to generate an updated sentiment lexicon 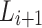 that would improve the accuracy of the lexicon
that would improve the accuracy of the lexicon 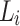 .
.
Updating Lexicon Using a Corpus in the Same Domain: Assume we receive 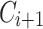 and we want to update
and we want to update 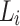 . Assume we have the distributions of all the words in the previous corpus (
. Assume we have the distributions of all the words in the previous corpus (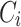 ) saved. A naive approach would involve generating distributions of all the words in the new batch (
) saved. A naive approach would involve generating distributions of all the words in the new batch (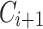 ) without creating a new lexicon from it. Such a distribution represents the so-called “sufficient statistics” [15] and we can construct lexicon from each set of the distributions. To update
) without creating a new lexicon from it. Such a distribution represents the so-called “sufficient statistics” [15] and we can construct lexicon from each set of the distributions. To update 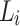 , the two sets of distributions (from
, the two sets of distributions (from 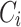 and
and 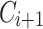 ) are first merged and updated lexicon (
) are first merged and updated lexicon (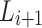 ) is generated using the approach described in Sect. 2.1. However, this approach may be inefficient since we update all the words in the existing lexicon.
) is generated using the approach described in Sect. 2.1. However, this approach may be inefficient since we update all the words in the existing lexicon.
An enhanced and more efficient approach aims to update only subset of the words in 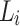 whose orientation may have changed. This approach use
whose orientation may have changed. This approach use 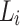 to predict the user’s sentiment rating scores on the new labelled corpus
to predict the user’s sentiment rating scores on the new labelled corpus 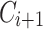 sentences. If the predicted rating scores are the same with the user’s sentiment ratings, we can skip those sentences and only consider those sentences where the predicted rating is significantly different from the user’s sentiment rating scores. We extract the words from these sentences (reviews), elaborate the corresponding distribution of sentiment values, merge the distribution with the corresponding subset in the
sentences. If the predicted rating scores are the same with the user’s sentiment ratings, we can skip those sentences and only consider those sentences where the predicted rating is significantly different from the user’s sentiment rating scores. We extract the words from these sentences (reviews), elaborate the corresponding distribution of sentiment values, merge the distribution with the corresponding subset in the 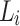 and generate a new sentiment lexicon
and generate a new sentiment lexicon 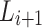 .
.
Updating Lexicon Using a Corpus from Different Domain: Assume we receive 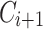 and we want to update
and we want to update 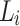 to a new domain. Firstly, we propose to detect if
to a new domain. Firstly, we propose to detect if 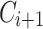 and
and 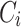 are from different domain. To do this, we generate the distribution of
are from different domain. To do this, we generate the distribution of 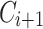 and compare it with the distribution of
and compare it with the distribution of 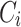 . If the distributions of the two corpora differ significantly, it indicates a domain shift. Alternatively, we can use
. If the distributions of the two corpora differ significantly, it indicates a domain shift. Alternatively, we can use 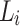 to predict the user’s sentiment rating scores on the new labelled corpus
to predict the user’s sentiment rating scores on the new labelled corpus 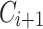 sentences. If the prediction accuracy is below some predefined threshold, we can conclude there is a domain shift. After detecting the domain shift, we merge the distribution using a similar approach discussed (in updating using the same corpus) and generate the lexicon. However, in this case, we give different weight to the two distributions by taking into consideration not only their size, but also recency. More recent batches will be given more weight than the previous ones.
sentences. If the prediction accuracy is below some predefined threshold, we can conclude there is a domain shift. After detecting the domain shift, we merge the distribution using a similar approach discussed (in updating using the same corpus) and generate the lexicon. However, in this case, we give different weight to the two distributions by taking into consideration not only their size, but also recency. More recent batches will be given more weight than the previous ones.
Word Embedding
The idea of word embedding have been widely used for generation of sentiment lexicon because of their advantage for giving semantic representation of words [9]. If two words appear in similar contexts, they will have similar embedding. We propose to use word embedding in the following way. Suppose we have seed words with their sentiment values, and we encounter some word, say Wx, for which we do not have a sentiment value (SVal) yet. But if we have its embedding, we can look for the most similar embedding in the embedding space and retrieve the corresponding word, Wy, retrieve its SVal and use it as a SVal of Wx. As reported in [11], neural models performance can increase by including lexicon information. We aim to further study litreture and find how to exploit combination of an existing sentiment lexicon (more explainable) and neural models performance.
Evaluation
We plan to evaluate our system and compare it with other five existing lexicons: SentiWords, SPLM, SO-CAL, Bing Liu’s Opinion Lexicon, and SentiWordNet [14]. The evaluation task will be on three sentiment analysis tasks (movie review, polarity of tweets and hotel review). In these comparisons we will compare (1) the precision of the predictions of sentiment values and (2) runtime to carry out updates of the lexicon.
Research Issues for Discussion
We seek suggestions on how our proposal can be improved. More importantly, discussion on how to exploit combination of word embedding with sentiment lexicon. We also welcome comments.
Acknowledgement
This project was partially financed by the Portuguese funding agency, FCT - Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, through national funds, and co-funded by the FEDER.
Contributor Information
Joemon M. Jose, Email: joemon.jose@glasgow.ac.uk
Emine Yilmaz, Email: emine.yilmaz@ucl.ac.uk.
João Magalhães, Email: jm.magalhaes@fct.unl.pt.
Pablo Castells, Email: pablo.castells@uam.es.
Nicola Ferro, Email: ferro@dei.unipd.it.
Mário J. Silva, Email: mjs@inesc-id.pt
Flávio Martins, Email: flaviomartins@acm.org.
Shamsuddeen Hassan Muhammad, Email: shamsuddeen.muhammad@inesctec.pt.
Pavel Brazdil, Email: pbrazdil@inesctec.pt.
Alípio Jorge, Email: alipio.jorge@inesctec.pt.
References
- 1.Xing FZ, Pallucchini F, Cambria E. Cognitive-inspired domain adaptation of sentiment lexicons. Inf. Process. Manag. 2019 doi: 10.1016/j.ipm.2018.11.002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Liu, B.: Sentiment Lexicon Generation. In: Sentiment Analysis: Mining Opinions, Sentiments, and Emotions, pp. 189–201. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2015). 10.1017/CBO9781139084789.008
- 3.Alqasemi F, Abdelwahab A, Abdelkader H. Constructing automatic domain-specific sentiment lexicon using KNN search via terms discrimination vectors. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2019 doi: 10.1080/1206212X.2017.1409477. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Almatarneh, S., Gamallo, P.: Automatic construction of domain-specific sentiment lexicons for polarity classification. In: Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing. pp. 175–182 (2017). 10.1007/978-3-319-61578-3_17
- 5.Hamilton, W.L., Clark, K., Leskovec, J., Jurafsky, D.: Inducing domain-specific sentiment lexicons from unlabeled corpora. In: Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (2016). 10.18653/v1/D16-1057 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 6.Forte, A.C., Brazdil, P.B.: Determining the level of clients’ dissatisfaction from their commentaries. In: Proceedings of PROPOR-2015, vol. 9727, pp. 74–85 (2016). 10.1007/978-3-319-41552-9_7
- 7.Taboada M, Brooke J, Tofiloski M, Voll K, Stede M. Lexicon-based methods for sentiment analysis. Comput. Linguist. 2011;37:267–307. doi: 10.1162/COLI\_a_00049. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sedinkina, M., Breitkopf, N., Schütze, H.: Automatic domain adaptation outperforms manual domain adaptation for predicting financial outcomes (2019). 10.18653/v1/p19-1034
- 9.Ano, E.C., Morisio, M.: Word embeddings for sentiment analysis: a comprehensive empirical survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:1902.00753 (2019)
- 10.Wang, L., Xia, R.: Sentiment lexicon construction with representation learning based on hierarchical sentiment supervision. In: Proceedings of EMNLP 2017 - Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (2017). 10.18653/v1/d17-1052
- 11.Barnes, J., Touileb, S., Øvrelid, L., Velldal, E.: Lexicon information in neural sentiment analysis: a multi-task learning approach. In: Proceedings of the 22nd Nordic Conference on Computational Linguistics, pp. 175–186 (2019)
- 12.Zucco, C., Liang, H., Fatta, G.D., Cannataro, M.: Explainable sentiment analysis with applications in medicine. In: Proceedings - 2018 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine, BIBM 2018 (2019). 10.1109/BIBM.2018.8621359
- 13.Dosilovic, F.K., Brcic, M., Hlupic, N.: Explainable artificial intelligence: a survey. In: 2018 41st International Convention on Information and Communication Technology, Electronics and Microelectronics, MIPRO 2018 - Proceedings (2018). 10.23919/MIPRO.2018.8400040
- 14.Muhammad, S.H.: An overview of sentiment analysis approaches. In: MAP-i Seminar Proceedings, pp. 65–70 (2019)
- 15.Gama J. Knowledge Discovery From Data Streams. New York: Chapman & Hall/CRC; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Potts C. On the negativity of negation. Semant. Linguist. Theory. 2015;20:636. doi: 10.3765/salt.v0i20.2565. [DOI] [Google Scholar]


