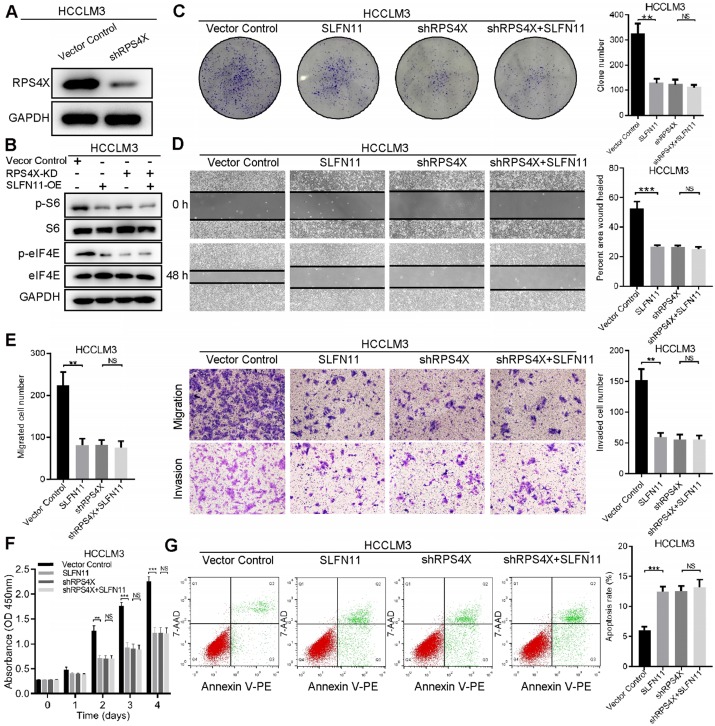
Figure 5.
RPS4X is an essential factor in SLFN11-mediated inhibition of the mTOR signaling pathway. (A) Western blot of the knockdown efficiency of RPS4X in HCCLM3 cells. (B) Western blot indicates that once RPS4X was knocked down in HCCLM3 cells, regardless of whether SLFN11 was overexpressed, the phosphorylation of S6 and eIF4E were inhibited at almost the same level. (C) Colony formation assays were conducted to study cell proliferation of HCCLM3-VectorControl cells and HCCLM3-SLFN11 cells with or without RPS4X knockdown. (D) Wound healing assays were performed to detect cell migratory abilities of HCCLM3-VectorControl cells and HCCLM3-SLFN11 cells with or without RPS4X knockdown. (E) Transwell assays were used to investigate the cell migratory and invasive capacities of HCCLM3-VectorControl cells and HCCLM3-SLFN11 cells with or without RPS4X knockdown. (F) CCK-8 assays were conducted to determine the cell proliferation of HCCLM3-VectorControl cells and HCCLM3-SLFN11 cells with or without RPS4X knockdown. (G) Cell apoptosis was assessed by flow cytometry in HCCLM3-VectorControl cells and HCCLM3-SLFN11 cells with or without RPS4X knockdown. ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, NS, not significant.