Figure 4.
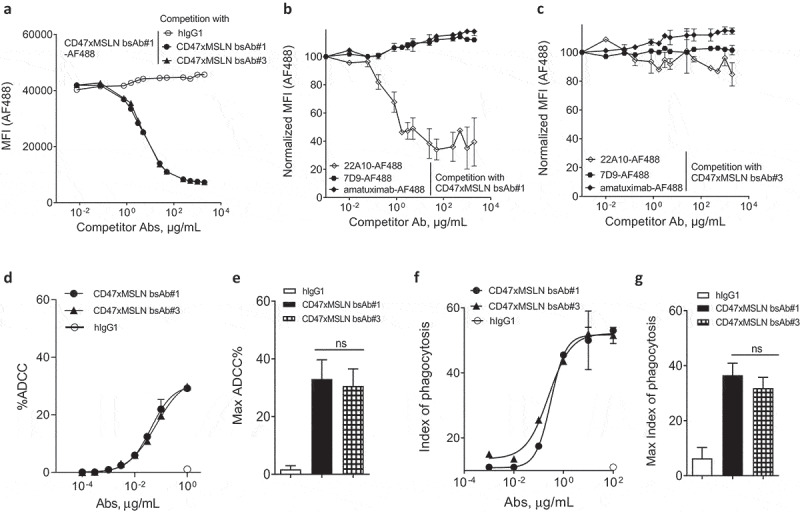
Targeting different membrane-proximal epitopes within MSLN affords CD47-targeting bsAbs similar tumoricidal activity. Binding domain characterization of CD47xMSLN bsAb#1 and bsAb#3 (a–c) using a cell-based fluorescence assay format and NCI-N87 cells as a target. AF488-labeled CD47xMSLN bsAb#1 tested at 10 μg/mL was incubated with a dose–response (7.5 ng/mL – 2 mg/mL) of naked CD47xMSLN bsAb#1, bsAb#3, or an irrelevant isotype control used as competitor antibodies (a). AF488-labeled anti-MSLN mAbs (22A10, 7D9, or amatuximab) tested at 10 μg/mL were incubated with a dose–response of naked CD47xMSLN bsAb#1 (b) or bsAb#3 (c) used as competitors. The mixtures were incubated on NCI-N87 cells for 10 min at 4°C. Resulting fluorescence was analyzed by flow cytometry. Data represent the mean values ± SEM of a minimum of two independent experiments. Comparative in vitro tumoricidal activities by ADCC (d, e) and ADCP (f, g). A representative dose-–response is shown for ADCC (d) and ADCP (f). Maximum killing ADCC (e) and ADCP (g) efficacy mediated by CD47xMSLN bsAb#1 and bsAb#3 are presented, all tested at 1 μg/mL or 100 μg/mL, respectively. Data are means ± SEM of a minimum of five independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed using the unpaired T-test: ns = not significant.
