Abstract
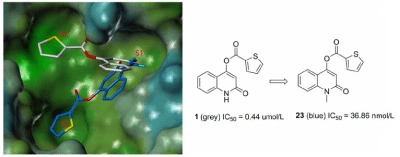
SARS CoV 3CLpro is known to be a promising target for development of therapeutic agents against the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS). A quinolinone compound 1 was selected via virtual screening, and it was synthetized and tested for enzymatic inhibition in vitro. Compound 1 showed potent inhibitory activity (IC50=0.44 µmol/L) toward SARS CoV 3CLpro. Further work on a series of quinolinone derivatives resulted in the discovery of the most potent compound 23, inhibiting SARS CoV 3CLpro with an IC50 of 36.86 nmol/L. The structure‐activity relationships were also discussed.
Keywords: SARS, SARS CoV 3CLpro, inhibitors, quinolinone
Quinolinone derivatives were selected via virtual screening, and they were synthesised and tested for SARS CoV 3CLpro enzymatic inhibition in vitro. Compound 23 showed the most potent inhibitory activity (IC50=36.86 nmol/L). The binding model was also discussed using docking studies.
Supporting information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re‐organized for online delivery, but are not copy‐edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
suppl
REFERENCES
- 1. Konno, S. ; Pillaiyar, T. ; Takehito, Y. . Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2013, 21, 412. 23245752 [Google Scholar]
- 2. Shao, Y. M. ; Yang, W. B. ; Kuo, T. H. . Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2008, 16, 4652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Ramajayam, P. ; Tan, K. P. ; Liu, H. G. . Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2010, 18, 7849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Mukherjee, P. . J. Chem. Inf. Model., 2011, 51, 1376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Ahn, T. Y. ; Kuo, C. J. ; Liu, H. G. . Bull. Korean Chem. Soc., 2010, 31, 87. [Google Scholar]
- 6. Yang, S. ; Chen, S. J. ; Hsu, M. F. . J. Med. Chem., 2006, 49, 4971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Shao, Y. M. ; Yang, W. B. ; Peng, H. P. . ChemBioChem, 2007, 8, 1654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Yin, J. ; Niu, C. Y. ; Cherney, M. M. . J. Mol. Biol., 2007, 371, 1060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Sydnes, M. O. ; Yoshio, H. ; Sharma, V. K. . Tetrahedron, 2006, 62, 8601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Yang, H. T. ; Yang, M. J. ; Ding, Y. . PNAS, 2003, 100, 13190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Zhou, L. ; Liu, Y. ; Zhang, W. L. . J. Med. Chem., 2006, 49, 3440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Regnier, T. ; Sarma, D. ; Hidaka, K. . Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2009, 19, 2722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re‐organized for online delivery, but are not copy‐edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
suppl


