Figure 6.
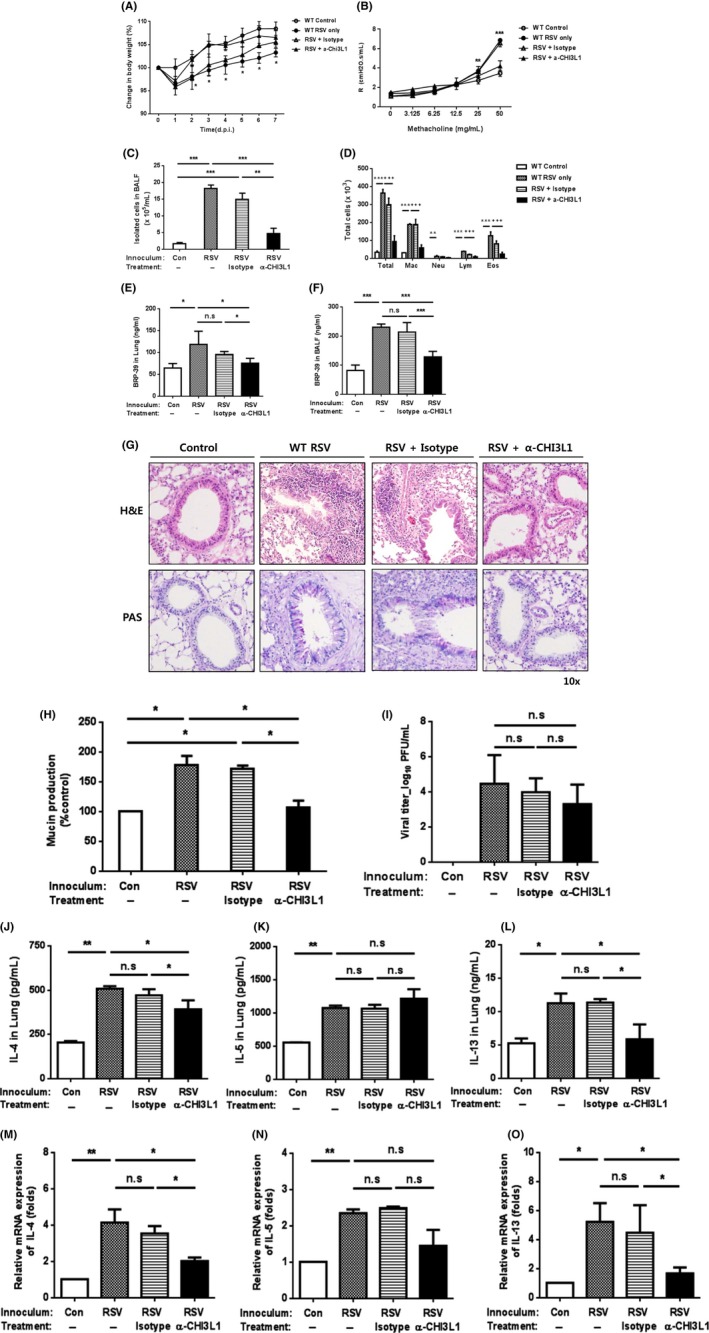
Neutralizing chitinase 3‐like 1 protein (CHI3L1) antibody suppresses respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)‐induced airway inflammation. Anti‐CHI3L1 antibody treatment in RSV‐infected mice decreased inflammation caused by RSV infection. A, wild‐type (WT) mice treated with anti‐CHI3L1 antibody 24 h after RSV infection showed less body weight loss than RSV‐infected mice without any treatment. B‐F, At 7 dpi, AHR (B), total and differentiated bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) cells (C,D), and breast regression protein‐39 levels (E,F) were evaluated. G, Airway inflammation and mucus production were assessed by H&E and periodic acid‐Schiff staining, respectively. H, Mucus production was also measured by ELISA. I, There was no difference in viral load among groups. J‐L, IL‐13 was the most prominent Th2 cytokine in BALF induced by RSV infection and decreased by anti‐CHI3L1 antibody treatment. M‐O, Th2 cytokine mRNA levels in lungs were also decreased by treatment with anti‐CHI3L1 antibody in RSV‐infected mice, with IL‐13 levels showing the greatest change. Data from three mice per group are plotted as mean ± SD. n.s., not significant. In panels B and C, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 for WT PBS vs WT RSV and isotype control [Colour figure can be viewed at http://wileyonlinelibrary.com]
