Abstract
The strength of light-matter interaction is of central importance in photonics and optoelectronics. For many widely studied two-dimensional semiconductors, such as MoS2, the optical absorption due to exciton resonances increases with thickness. However, here we will show, few-layer black phosphorus exhibits an opposite trend. We determine the optical conductivity of few-layer black phosphorus with thickness down to bilayer by infrared spectroscopy. On the contrary to our expectations, the frequency-integrated exciton absorption is found to be enhanced in thinner samples. Moreover, the continuum absorption near the band edge is almost a constant, independent of the thickness. We will show such scenario is related to the quanta of the universal optical conductivity of graphene (σ0 = e2/4ħ), with a prefactor originating from the band anisotropy.
Subject terms: Two-dimensional materials, Infrared spectroscopy, Electronic properties and materials
For many two-dimensional semiconductors, such as MoS2, the exciton absorption increases with thickness. Here, the authors show that, in black phosphorus, less material absorbs more light due to exciton resonances.
Introduction
In recent years, two-dimensional (2D) materials including graphene, transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDCs) and black phosphorus (BP), are at the forefront of scientific research. Strong light-matter interactions have been demonstrated in these atomically thin materials1–12, holding great promise for photonic and optoelectronic applications. Optical absorption in 2D materials is a fundamental light-matter interaction process, basically governed by the optical sheet conductivity σ(ħω). Graphene is a well-known 2D example, which exhibits a universal conductivity σ0 = e2/4ħ in a broad frequency range, where e is the electron charge and ħ is the reduced Plank constant1,2. Moreover, N-layer graphene exhibits an optical conductivity of Nσ0, showing quantized optical transparency1,13. In semiconducting TMDCs, such as MoS2, the optical conductivity due to K-point exciton increases with layer number14. However, in this paper, we will show that excitons in thinner samples absorb more light in few-layer BP. Meanwhile, the absorption due to the electron-hole continuum near its own edge is almost the same for each thickness, with a value close to that in monolayer graphene.
Few-layer BP is an elemental 2D semiconductor beyond graphene, with a strongly layer-dependent direct bandgap15–18, offering an ideal platform to probe the layer-dependent properties and dimensional crossover from 3D to 2D. Moreover, the intrinsic in-plane band anisotropy definitely distinguishes few-layer BP from other widely studied 2D materials, such as graphene, TMDCs and InSe. Along with the moderate bandgap and large tunability, few-layer BP is unique and promising in polarized IR detectors and emitters. From this point of view, a quantitative determination and thorough understanding of the optical absorption in few-layer BP is in great demand. The optical absorption of few-layer BP is found to be dominated by robust excitons10–12. In previous optical studies10,15,16, the absorption intensity is not well quantified. In other words, quantitative insight of the absolute absorption is yet to be gained, though it is highly desirable for future optoelectronic applications, such as evaluating the quantum efficiency of photoluminescence (PL) and photocurrent generation. Our study resolves this issue and provides new insights into light-matter interaction in anisotropic 2D gapped materials.
Results
Sample preparation and IR characterization
A Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectrometer was used to obtain the extinction spectra (1 − T/T0) of few-layer BP on polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) or quartz substrates (see Methods for sample preparation and IR characterization), where T and T0 denote the light transmittance of the substrate with and without BP samples, respectively, as illustrated in Fig. 1d. For atomically thin materials on a thick transparent substrate, like in our case, when the optical conductivity is not large, the extinction (1 − T/T0) is approximately proportional to (the real part of) the optical conductivity2,4: σ(ħω) = (1 − T/T0) · (ns + 1) · c/8π, where ns is the refractive index of the substrate (ns = 1.39 for PDMS in the measured IR range19) and c is the speed of light.
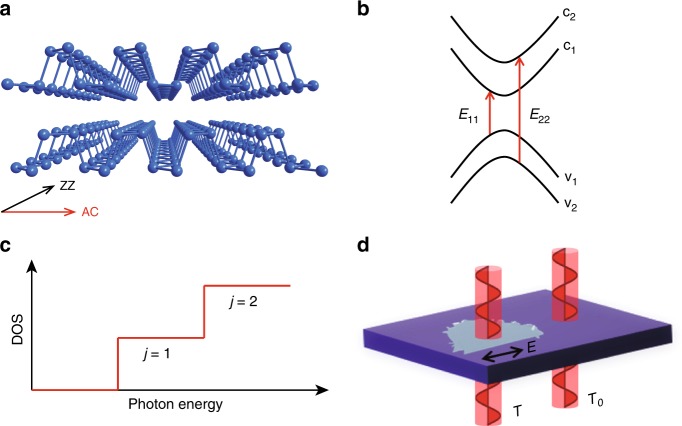
Fig. 1. Crystal structure and IR characterization of few-layer BP.
a Puckered structure of 2 L BP, with two characteristic crystal orientations: AC and ZZ. b Schematic illustration of optical transitions between quantized subbands, with the symbols E11 and E22 denoting transitions v1 → c1 and v2 → c2, respectively. c Illustration of joint DOS in 2D systems, showing step-like features. d FTIR measurement configuration with T and T0 denoting the light transmittance of the substrate with and without BP samples, respectively. The arrow indicates the polarization of the incident IR beam, along the AC direction of the BP sample.
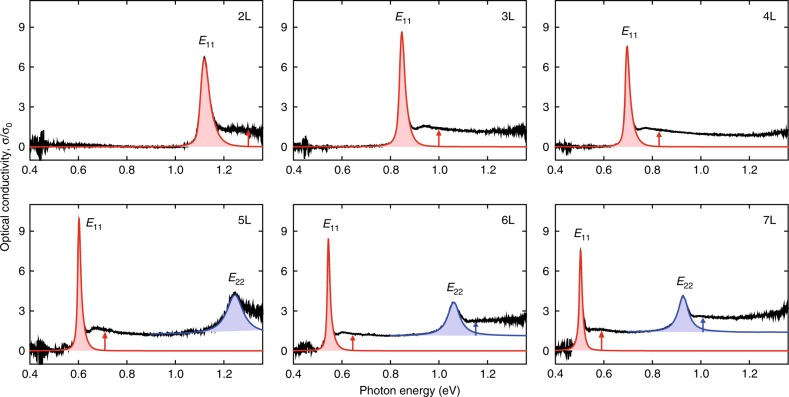
We systematically measured IR conductivity σ(ħω) spectra (in the unit of σ0) for 2–7 L BP in a broad range of 0.4–1.36 eV at room temperature, as shown in Fig. 2. The incident light is normal to the layer plane and polarized along the armchair (AC) direction. The spectra for zigzag (ZZ) polarization are featureless15, hence not discussed here. Previous studies have revealed quantized subband structures of few-layer BP15,16, due to the quantum confinement in the out-of-plane direction and considerable interlayer interactions, in analogy to traditional quantum wells (QWs). In symmetric QWs with normal light incidence, optical transitions obey the ∆j = 0 selection rule (j is the subband index)20,21. Ejj denotes the exciton resonance associated with the optical transition between the jth pair of subbands (vj → cj) at Γ point of the 2D Brillouin zone, as illustrated in Fig. 1b. As seen from Fig. 2, the E11 resonance exhibits a very narrow linewidth even at room temperature, especially for thicker BP. In addition, the Stokes shift of few-layer BP is almost negligible (see Supplementary Fig. 1 as an example of 3 L), indicating good sample quality. The IR conductivity σ(ħω) at the E11 resonance reaches 6.6σ0 in 2 L BP, directly translated to a light absorption of 15% in free-standing case. This suggests very strong light-matter interactions in this atomically thin material. Moreover, we can observe a spectrally flat and broad response above the exciton energy, attributed to the continuum of band-to-band transitions. Step-like features of continuum absorption underline the step-like 2D joint density of states (DOS) in QW-like structures, as sketched in Fig. 1c, this still holds in anisotropic few-layer BP22.
Fig. 2. Room-temperature IR measurements.
Optical conductivity σ(ħω) spectra of few-layer BP with layer number N = 2–7, with incident light polarized along the AC direction, in the unit of σ0 = e2/4ħ. E11 (E22) denotes the 1 s excitonic transition associated with the first (second) pair of subbands, as illustrated in Fig. 1b. The slightly asymmetric E11 peaks are fitted using Eq. (3) in Methods (red curves), while E22 peaks are fitted to symmetric Lorentzian lineshapes (blue curves). The exciton absorption (or conductivity σI) is proportional to the integrated areas of the exciton peaks, as indicated by the shaded areas. The vertical arrows indicate the height of the continuum absorption for each subband transition.
Layer-dependent exciton absorption
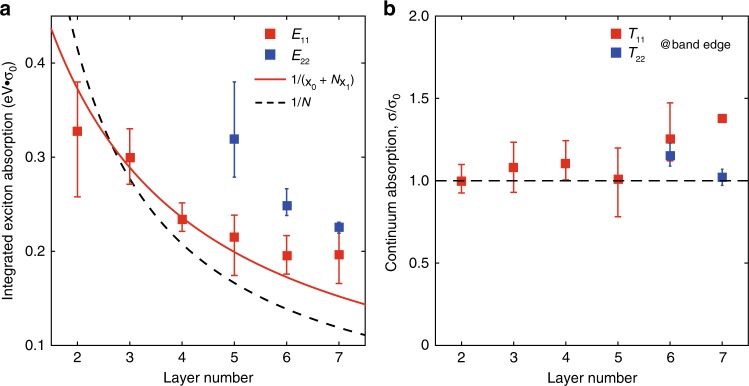
The σ(ħω) spectra can provide a wealth of information on the exciton oscillator strength, which is directly related to the frequency-integrated conductivity (or absorption) of excitons23,24, as indicated by the shaded areas in Fig. 2. The peak height of the exciton feature is not as informative, since it is sensitive to the sample quality. Figure 3a shows the integrated conductivity σI of the ground state (1 s) exciton of few-layer BP as a function of layer number N. The details for spectral fitting and extraction of σI are presented in Methods. For each layer thickness, at least three samples were measured, with the error bar defined as the spread of the data. From Fig. 3a, one can find that thinner BP has larger absorption. In other words, it manifests a fact that less material absorbs more light at exciton resonances. This remarkable result is in sharp contrast to widely studied 2D semiconducting TMDCs, in which the exciton absorption increases with layer number (see Supplementary Fig. 2 for the absorption of 1–4 L MoS2 and also ref. 14). To be more quantitative, the integrated absorption due to excitons is directly proportional to , where Lz is the thickness of the sample, |φex(0)|2 is the modular square of the exciton wavefunction at origin, describing the probability to find the electron and the hole at the same location23–25. Certainly, the smaller the thickness is, the larger the confinement in the z direction is and hence the larger |φex(0)|2 is. Theory has predicted that |φex(0)|2 ~ 1/Lz2 for QWs26, if the penetration of the electron and hole wavefunctions into the barriers is negligible27,28. This gives the integrated absorption ~1/Lz (Lz ~ N for BP), which means stronger absorption for thinner samples. This argument correctly predicts the trend but the fitting with such a relation does not work well. The prediction shows a much steeper decrease than what we observed, as shown in Fig. 3a (black dashed curve), which calls for a more refined model.
Fig. 3. Exciton and continuum absorption in few-layer BP.
a The frequency-integrated conductivity σI of the 1 s exciton as a function of layer number, in the unit of eV·σ0. For each layer number, at least three samples were measured, the squares denote the average values. The solid curve is the fitting to the E11 data using the relation σI = h/(χ0 + Nχ1), with χ0 and χ1 describing the screening effect from the PDMS substrate and single-layer BP, respectively. h is the only fitting parameter, extracted to be 5.78 eV·σ0·Å. The dashed curve shows the 1/N relation for guideline. b The continuum height of each subband transition near the corresponding band edge (ħω ≈ Eg) is plotted as a function of layer number. The continuum absorption nearly shows a constant value, independent of the material thickness. The black dashed line indicates the well-known universal conductivity σ0 = e2/4ħ for guideline. Data are extracted from Fig. 2 with error bars indicating sample-to-sample variation.
We can tackle this problem from another perspective. In the 2D hydrogen model for excitons, we find that the integrated absorption for the 1 s exciton is proportional to the exciton binding energy (Eb) (see Supplementary Note 1 for details). This is a very reasonable conclusion, since the larger the binding energy is, the closer the electron is to the hole, which favors light absorption at exciton resonances. We adopt this result for our analysis, even though excitons are not ideally 2D in few-layer BP. Olsen et al. proposed a simple screened hydrogen model for 2D excitons29, in which Eb can be analytically expressed as a function of the reduced effective mass μ and the 2D sheet polarizability χ. Under the condition of 32πμχ/3 >> 1, Eb can be simplified as Eb ≈ 3/4πχ, which is proved to be valid for few-layer BP10. The sheet polarizability χ relates to the dielectric screening of electron-hole interactions. In the case of Fig. 2, few-layer BP is supported by a PDMS substrate, which introduces additional dielectric screening. Thus, both of the substrate and the material itself contribute to the screening. In view of this, the sheet polarizability χ is replaced by an effective value for N-layer BP, expressed as χeff = χ0 + Nχ1, with χ0 = 6.5 Å and χ1 = 4.5 Å describing the screening effect from the PDMS substrate and single-layer BP, respectively, based on our previous study10. Thus, we have σI ∝ 1/(χ0 + Nχ1). With this relation, it is clear that the exciton absorption increases as the layer number decreases, though it is not as dramatic as ~1/N. We use this relation to fit the data for E11, as shown in Fig. 3a, the overall agreement is much better than the 1/N scaling. The basic behavior is well captured by the modified model, though the agreement with experimental data is still not so excellent. The deviation is mainly caused by the experimental uncertainty in determining the optical conductivity, especially for thinner BP samples, which are expected to be more susceptible to the environment. The substrate plays a role in reducing the exciton binding energy, hence the integrated absorption. For free-standing BP, this model also gives a scaling of 1/N (ref. 10), consistent with the previous prediction for QWs. For E22 resonances, the exciton absorption increases with the decrease of layer number as well, as also shown in Fig. 3a. It should be noted that, the thickness dependence of exciton absorption in BP is even qualitatively quite different from that in traditional QWs. For the latter, the absorption reaches maximum at certain thickness and decreases again with decreasing thickness, due to the exciton wavefunction leakage into the barriers in the ultrathin limit27,28. Such scenario becomes more evident in shallow QWs. The hard confinement in atomically thin BP definitely distinguishes it from traditional QWs. From this perspective, atomically thin BP provides us unique opportunities to examine this new type of QWs.
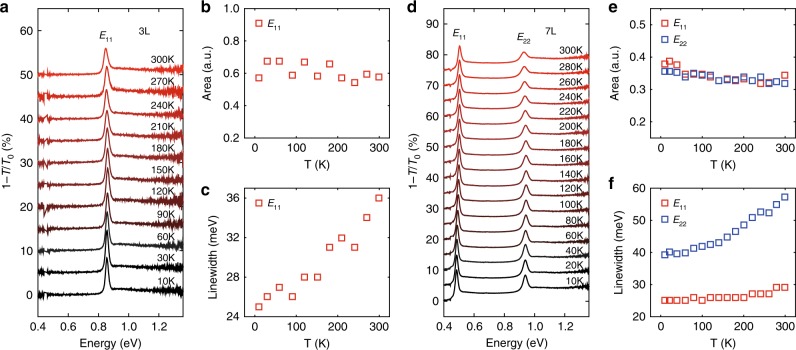
The frequency-integrated conductivity of excitons is robust against temperature, although the linewidth is typically vulnerable to various factors. Since the aforementioned PDMS substrate thermally expands (contracts) during the heating (cooling) process, significant strain effects can be introduced to few-layer BP samples during temperature-dependent measurements, overwhelming the pure temperature effect. Therefore, we transferred few-layer BP samples to quartz substrates with a much smaller thermal expansion coefficient, so that the strain effect can be ignored30. Fig 4a, d show the IR extinction spectra of a 3 L and 7 L BP at varying temperatures from 10 K to 300 K, respectively. To improve the ratio of signal-to-noise for such measurements, the incident IR beam size was set to be larger than the sample size. Thus, the absolute intensity of exciton absorption is underestimated, but it’s legitimate to compare the integrated area of exciton peaks for the same sample at different temperatures, which is directly related to the exciton oscillator strength. To quantitatively probe the temperature effect, the integrated area and linewidth of exciton peaks are extracted from spectral fitting using Eq. (3) in Methods. Clearly, the exciton width increases with temperature both for E11 and E22 as expected (Fig. 4c, f). Such scenario is common in semiconductors, which is attributed to the enhanced electron-phonon scattering channels at elevated temperature31,32. The integrated areas of exciton peaks, on the other hand, are nearly independent on the temperature, as shown in Fig. 4b, e. The slight deviation from a constant may arise from the experimental uncertainty and data fitting procedure. A recent study shows that for typical semiconductors, in the incoherent region of light-matter interactions, the integrated exciton absorption only depends on the radiative decays, rather than the scattering decays, hence the absorption is independent of temperature33. This is exactly the case for our observations. Since the integrated exciton intensity is proportional to the exciton binding energy, our results indicate that the exciton binding energy is almost a constant within the tested temperature range.
Fig. 4. Temperature dependence of the optical absorption.
IR extinction spectra of a 3 L and d 7 L BP on quartz substrates at varying temperatures from 10 K to 300 K, respectively. The spectra are vertically offset for clarity. Integrated area of the exciton peaks of b 3 L and e 7 L BP as a function of temperature, respectively. Linewidth of the exciton peaks of c 3 L and f 7 L BP as a function of temperature, respectively. Data are extracted from spectral fitting using Eq. (3) in Methods.
Continuum absorption
Next, we will focus on the layer dependence of the absorption due to the continuum transition. As seen in Fig. 2, a relatively flat response can be observed in the σ(ħω) spectra above the ground state exciton energy, mainly associated with the continuum band-to-band transitions (labeled as Tjj) and possibly excited excitonic states10. A closer examination of Fig. 2 shows that the continuum absorption is not strictly a constant but decreases gradually with increasing photon energy. For simplicity, we focus on the continuum absorption close to the band edge (ħω ≈ Eg), indicated by the red (blue) arrows for T11 (T22) transitions in Fig. 2. The results are summarized in Fig. 3b as a function of layer number N, they approximately follow a constant value despite of the experimental uncertainty. This means that the absorption due to the bandgap continuum transitions is almost the same, regardless of the thickness of BP samples.
According to the Fermi’s golden rule, if a light beam with frequency ω and linear polarization along is normally incident to a direct-gap 2D system, the dimensionless absorption A(ħω) due to a pair of conduction and valence bands can be expressed as (in SI units)34
| 1 |
where ε0 is the vacuum permittivity, m0 is the free electron mass, and Ar is the area of the 2D material. The momentum matrix element is defined as , with as the momentum operator. and is the wave vector.
It first looks like that the absorption is strongly band parameter dependent, since the terms of and DOS are involved in Eq. (1). Surprisingly, the absorption in isotropic graphene1,2 and InAs QWs35 are found to be universal, indicating that there is a cancelling mechanism between these two terms. For massless graphene, which has a unique linear energy dispersion near the Dirac point (vF is the Fermi velocity), the cancelation is exact with no frequency dependence, leading to a well-defined universal absorption quanta πα, where α = e2/4πε0ħc is the fine structure constant (~1/137)36. For anisotropic 2D massive semiconductors (see Supplementary Note 2 for details), based on the perturbation theory34, it is obtained that , and , where μx(y) is the reduced effective mass in the AC (ZZ) direction. With these, and also taking into account the degrees of spin and valley degeneracy of gs and gv, we thus have
| 2 |
where Θ(ħω − Eg) is the step function, describing the 2D joint DOS, and Eg is the bandgap. This indicates that most of the band parameter dependent terms are perfectly canceled out, leaving behind the frequency dependent term ω and the band anisotropy term . Our observations in few-layer BP can be well explained by Eq. (2): (i) above the bandgap ħω > Eg, the absorption gradually decreases as the photon energy increases; (ii) near the bandgap ħω ≈ Eg, with gs = 2, gv = 1 for BP20, Eq. (2) gives a value of (or equals to the optical conductivity ), slightly deviating from the universal value πα. The prefactor originates from the band anisotropy, which is nearly layer-independent for 2–7 L BP17. When μx = μy, it collapses to the isotropic case36; (iii) with the photon energy higher than the second subband transition (T22), additional contribution in absorption shows up with another step height of .
Discussion
As a simple explanation of what we observed for both exciton and electron-hole continuum transitions, we can revisit the 2D band structure of few-layer BP. Due to the strong coupling between layers, the conduction and valence bands split into multiple 2D subbands with sizable energy spacing (for the case with sample thickness below 10 L)15. If we focus on the bandgap continuum transition, no matter the thickness or how many subbands in total, the relevant ones are only c1 and v1 subbands. As a consequence, one can not expect more absorption with photon energy right above the bandgap when the layer number increases, given that only the first pair of 2D subbands is involved and the 2D joint DOS typically barely vary. Therefore the increase of sample thickness does not cause enhanced absorption for the continuum. However, on the other hand, the excitonic effect weakens with increasing layer number due to weaker confinement in the z direction, which actually decreases the exciton absorption. This can qualitatively explain the findings in Fig. 3. This argument applies to other 2D materials as well. For MoS2, the electronic bands associated with direct-gap exciton at K point show almost no splitting when the layer number increases from 1 to 2 (or other thickness)37. The degenerate subbands certainly double the DOS and the exciton absorption can increase accordingly, giving an opposite trend compared to BP. As for N-layer graphene, in spite of the complexity of the very low energy band structure, in the range from visible to near-IR, N pairs of subbands are involved in the optical absorption and each pair contributes an absorption quanta πα1,2. While for N-layer BP, if we only focus on the bandgap region, only one pair of subbands is involved and one absorption step is contributed, regardless of the thickness. Of course, if we increase the photon energy, more and more subbands are counted in and the absorption increases step by step. Eventually the continuum absorption is comparable to that of N-layer graphene. Therefore, counting the 2D subbands does give us a good estimation of absorption in different 2D systems36.
In summary, we have determined the optical conductivity of 2–7 L BP using IR absorption spectroscopy. Our results reveal that the exciton absorption increases as the layer number decreases, a direct consequence of enhanced excitonic effects in reduced dimensionality. Moreover, the absorption from the continuum states near the band edge exhibits a layer-independent value. Few-layer BP provides us an ideal platform to probe the dimensional effect on the strength of optical absorption from bound (exciton) and unbound (continuum) states in the same material. The highly enhanced exciton absorption of atomically thin BP, which tends to host high density of optical excitations, may open up new possibilities for applications in nonlinear optics and quantum optics. Our results are expected to stimulate further theoretical interests in anisotropic 2D materials.
Methods
Sample preparation
Few-layer BP samples were prepared by a modified mechanical exfoliation method38. Firstly, a piece of bulk BP crystal (HQ Graphene Inc.) was cleaved several times using a Scotch tape. Secondly, the tape containing BP flakes was slightly pressed against a PDMS substrate of low viscosity and then peeled off rapidly. Some thin BP flakes with relatively large area and clean surface were left on the PDMS substrate. To achieve high optical quality, the samples on PDMS were directly used for room-temperature IR measurements, without any additional sample transfer process. Supplementary Fig. 1 shows an example of a 3 L BP on PDMS. The negligible Stokes shift indicates good sample quality. To avoid sample degradation in air, the samples were prepared in a N2 glove box with O2 and H2O levels lower than 1 ppm, and then loaded into a cryostat purged with N2 for subsequent IR measurements. The cryostat is only for sample protection instead of temperature control. The layer number and crystal orientation of BP were readily identified using polarized IR spectroscopy15.
Polarized IR spectroscopy
The IR extinction (1 − T/T0) spectra of few-layer BP were measured using a Bruker FTIR spectrometer (Vertex 70 v) equipped with a Hyperion 2000 microscope, as illustrated in Fig. 1d. A tungsten halogen lamp was used as the light source to cover the broad spectral range of 0.4–1.36 eV with 1 meV resolution, in combination with a liquid nitrogen cooled Mercury-Cadmium-Telluride (MCT) detector. The lower bound cutoff photon energy is restricted by the substrate. The linearly polarized incident light was obtained after the IR beam passing through a broadband ZnSe grid polarizer, then was focused on BP samples using a ×15 IR objective. For room-temperature measurements, the aperture size was set to be smaller than the sample size to make sure the IR beam all goes through the sample. A spectrum was typically acquired over 1000 averages to improve the signal-to-noise ratio.
Low temperature IR measurements
For low temperature measurements, few-layer BP samples were transferred from PDMS to quartz substrate, to avoid the significant strain effect of PDMS during the heating (cooling) process, since the latter has a much smaller thermal expansion coefficient. Then, the samples were loaded into a liquid He cooled cryostat, with the temperature range from 10 K (or lower) to 300 K. To improve the signal-to-noise ratio, the aperture size was set to be larger than the sample size.
Data analysis
Generally, homogeneous broadened lineshape is characterized by a Lorentzian function. However, for the E11 peaks in Fig. 2, attempts failed to fit the lineshape using a single Lorentzian function, since the high-energy tail deviates the spectrum from the ideal lineshape, especially for thinner BP. Similar observations have been reported in QWs39–41, the exciton absorption (or emission) lineshape is slightly asymmetric, exhibiting a Lorentzian and an exponential slope at the low- and high-energy side, respectively. This is caused by the so-called “exciton localization effect”, as a consequence of spatial inhomogeneity39. Nevertheless, such imperfection will not affect our determination of the integrated areas of exciton peaks.
To determine the integrated conductivity (σI), the E11 peaks in Fig. 2 are fitted using a documented model, which was first proposed by Schnabel et al.39, and has been successfully applied to QW-like structures40,41. This model is analytically expressed as:
| 3 |
The first part is a Lorentzian function, describing the symmetric lineshape with area of LS and linewidth of γL. ∆ = ħω − ħω0, with ħω0 denoting the average transition energy between the conduction and valence subbands. The second part describes the asymmetric lineshape, γ is the linewidth and η describes the asymmetric broadening by exciton localization, LA is the spectral weight. We use Eq. (3) to fit the E11 peaks. As shown in Fig. 2 (red curves), the general agreement is excellent, except for a small discrepancy at the high-energy end of the peaks, given that the excited excitonic states (2 s or 3 s states) and the continuum absorption are also involved in this spectral region. While E22 peaks (blue curves) can be well fitted only using the symmetric part (Lorentzian function). The integrated conductivities shown in Fig. 3a are extracted from the fitted peaks. In addition, as indicated by the extracted parameter η for each layer thickness (Supplementary Fig. 4), we can see that thinner BP exhibits larger asymmetry. This is reasonable, since thinner BP is more sensitive to the underlying substrate and environment.
Supplementary information
Acknowledgements
H.Y. is grateful to the financial support from the National Young 1000 Talents Plan, National Science Foundation of China (grants: 11874009, 11734007), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (grants: 2016YFA0203900 and 2017YFA0303504), Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDB30000000), and the Oriental Scholar Program from Shanghai Municipal Education Commission. M.H. is grateful to the financial support from the Initiative Funds for Shenzhen High Class University (grant: G02206301). G.Z. acknowledges the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant: 11804398), Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi (grant: 2020JQ-105), Open Research Fund of State Key Laboratory of Surface Physics and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities. Part of the experimental work was carried out in Fudan Nanofabrication Lab.
Author contributions
H.Y. and G.Z. initiated the project and conceived the experiments. G.Z. prepared the samples and performed the room-temperature IR measurements. G.Z., M.H., and S.H. performed the low temperature IR measurements with assistance from F.W., Q.X., C.S., C.W., and Y.L. G.Z., M.H., and H.Y. performed the data analysis and co-wrote the manuscript. H.Y. supervised the whole project. All authors commented on the manuscript.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Peer review information Nature Communications thanks Robert Bogdanowicz, Bo Gao, and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Peer review reports are available.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Mingyuan Huang, Email: huangmy@sustech.edu.cn.
Hugen Yan, Email: hgyan@fudan.edu.cn.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information is available for this paper at 10.1038/s41467-020-15699-7.
References
- 1.Nair RR, et al. Fine structure constant defines visual transparency of graphene. Science. 2008;320:1308. doi: 10.1126/science.1156965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Mak KF, et al. Measurement of the optical conductivity of graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008;101:196405. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.101.196405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ju L, et al. Graphene plasmonics for tunable terahertz metamaterials. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011;6:630. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2011.146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Yan H, et al. Tunable infrared plasmonic devices using graphene/insulator stacks. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012;7:330. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2012.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Li ZQ, et al. Dirac charge dynamics in graphene by infrared spectroscopy. Nat. Phys. 2008;4:532. doi: 10.1038/nphys989. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Stauber T, Peres NMR, Geim AK. Optical conductivity of graphene in the visible region of the spectrum. Phys. Rev. B. 2008;78:085432. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.78.085432. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ye Z, et al. Probing excitonic dark states in single-layer tungsten disulphide. Nature. 2014;513:214. doi: 10.1038/nature13734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chernikov A, et al. Exciton binding energy and nonhydrogenic Rydberg series in monolayer WS2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014;113:076802. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.113.076802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.He K, et al. Tightly bound excitons in monolayer WSe2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014;113:026803. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.113.026803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Zhang G, et al. Determination of layer-dependent exciton binding energies in few-layer black phosphorus. Sci. Adv. 2018;4:eaap9977. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aap9977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Rodin AS, Carvalho A, Castro Neto AH. Excitons in anisotropic two-dimensional semiconducting crystals. Phys. Rev. B. 2014;90:075429. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.90.075429. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chaves A, Low T, Avouris P, Çakır D, Peeters FM. Anisotropic exciton Stark shift in black phosphorus. Phys. Rev. B. 2015;91:155311. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.91.155311. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Mak KF, Sfeir MY, Misewich JA, Heinz TF. The evolution of electronic structure in few-layer graphene revealed by optical spectroscopy. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2010;107:14999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1004595107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mak KF, Lee C, Hone J, Shan J, Heinz TF. Atomically thin MoS2: a new direct-gap semiconductor. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010;105:136805. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.105.136805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Zhang G, et al. Infrared fingerprints of few-layer black phosphorus. Nat. Commun. 2017;8:14071. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Li L, et al. Direct observation of the layer-dependent electronic structure in phosphorene. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017;12:21. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2016.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Qiao J, Kong X, Hu ZX, Yang F, Ji W. High-mobility transport anisotropy and linear dichroism in few-layer black phosphorus. Nat. Commun. 2014;5:4475. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Tran V, Soklaski R, Liang Y, Yang L. Layer-controlled band gap and anisotropic excitons in few-layer black phosphorus. Phys. Rev. B. 2014;89:235319. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.89.235319. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Querry, M. R. Optical Constants of Minerals and Other Materials from the Millimeter to the Ultraviolet (Chemical Research, Development Engineering Center, Aberdeen, 1987).
- 20.Low T, et al. Tunable optical properties of multilayer black phosphorus thin films. Phys. Rev. B. 2014;90:075434. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.90.075434. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lin C, Grassi R, Low T, Helmy AS. Multilayer black phosphorus as a versatile mid-infrared electro-optic material. Nano Lett. 2016;16:1683. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b04594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.de Sousa DJP, de Castro LV, da Costa DR, Pereira JM, Low T. Multilayered black phosphorus: From a tight-binding to a continuum description. Phys. Rev. B. 2017;96:155427. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.96.155427. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Masumoto Y, Matsuura M, Tarucha S, Okamoto H. Direct experimental observation of two-dimensional shrinkage of the exciton wave function in quantum wells. Phys. Rev. B. 1985;32:4275. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.32.4275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Masselink WT, et al. Absorption coefficients and exciton oscillator strengths in AlGaAs-GaAs superlattices. Phys. Rev. B. 1985;32:8027. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.32.8027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Feldmann J, et al. Linewidth dependence of radiative exciton lifetimes in quantum wells. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1987;59:2337. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.59.2337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bastard G, Mendez EE, Chang LL, Esaki L. Exciton binding energy in quantum wells. Phys. Rev. B. 1982;26:1974. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.26.1974. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zhang B, Kano SS, Shiraki Y, Ito R. Reflectance study of the oscillator strength of excitons in semiconductor quantum wells. Phys. Rev. B. 1994;50:7499. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.50.7499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Iotti RC, Andreani LC. Crossover from strong to weak confinement for excitons in shallow or narrow quantum wells. Phys. Rev. B. 1997;56:3922. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.56.3922. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Olsen T, Latini S, Rasmussen F, Thygesen KS. Simple screened hydrogen model of excitons in two-dimensional materials. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016;116:056401. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.116.056401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Huang S, et al. Strain-tunable van der Waals interactions in few-layer black phosphorus. Nat. Commun. 2019;10:2447. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10483-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Selig M, et al. Excitonic linewidth and coherence lifetime in monolayer transition metal dichalcogenides. Nat. Commun. 2016;7:13279. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Dey P, et al. Optical coherence in atomic-monolayer transition-metal dichalcogenides limited by electron-phonon interactions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016;116:127402. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.116.127402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Horng, J. et al. Perfect absorption by an atomically thin crystal. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.00884v1.
- 34.Chuang, S. L. Physics of Photonic Devices (John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, 2009).
- 35.Fang H, et al. Quantum of optical absorption in two-dimensional semiconductors. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2013;110:11688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1309563110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Stauber T, Noriega-Pérez D, Schliemann J. Universal absorption of two-dimensional systems. Phys. Rev. B. 2015;91:115407. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.91.115407. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Splendiani A, et al. Emerging photoluminescence in monolayer MoS2. Nano Lett. 2010;10:1271. doi: 10.1021/nl903868w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Castellanos-Gomez A, et al. Isolation and characterization of few-layer black phosphorus. 2D Mater. 2014;1:025001. doi: 10.1088/2053-1583/1/2/025001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Schnabel RF, et al. Influence of exciton localization on recombination line shapes: InxGa1−xAs/GaAs quantum wells as a model. Phys. Rev. B. 1992;46:9873. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.46.9873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Leosson K, Jensen JR, Langbein W, Hvam JM. Exciton localization and interface roughness in growth-interrupted GaAs/AlAs quantum wells. Phys. Rev. B. 2000;61:10322. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.61.10322. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Naeem A, et al. Giant exciton oscillator strength and radiatively limited dephasing in two-dimensional platelets. Phys. Rev. B. 2015;91:121302(R). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.91.121302. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.