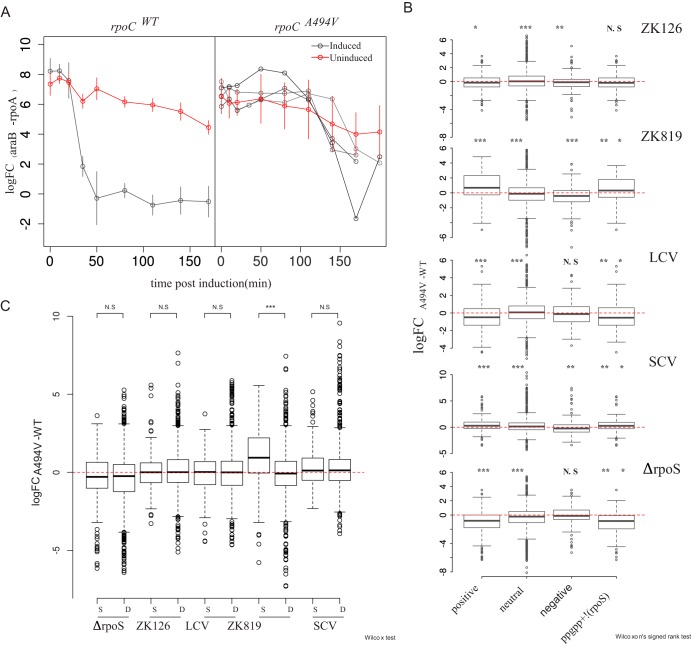
FIG 7.
rpoCA494V mutation affects global gene expression states. (A) Semiquantitative estimation of araB expression by RT-PCR in rpoCWT (left) and rpoCA494V (right) in the ZK819 background, after induction with 100 mM l-arabinose. Error bars indicate standard deviations (n = 4). Individual replicates have been shown separately for the rpoCA494V strain to emphasize the biological variation observed in the induction pattern in mutant strain compared to wild type. Threshold cycle values from araB mRNA were normalized with that of constitutively expressing rpoA gene. araB measurements from uninduced cultures as controls are shown in red. (B) Differential expression of positive, negative, and neutrally regulated targets of ppGpp between rpoCA494V and rpoCWT in different backgrounds (noted in top right of each figure). To control for the behavior of a large number of genes controlled by both σS and ppGpp, differential expression of genes which are upregulated by ppGpp but are not σS targets was taken into account. (C) Differential expression of σS and σD target genes between rpoCA494V and rpoCWT in different backgrounds. Wilcoxon’s test was used to test significance of the difference in median expression values. P value scale: ***, <0.001; **, <0.01; *, <0.05.