Abstract
Since late December 2019, a new type of coronavirus (CIVID-19) causing a cluster of respiratory infections was first identified in Wuhan-China. And it disseminated to all countries. Generally, COVID-19 cases have fever, cough, respiratory distress findings (dyspnoea, intercostal retraction, cyanosis etc.). In this paper, we have presented an adult otitis media case whom infected with COVID-19, but she have not any classical COVID-19 symptoms.
Keywords: Coronavirus, COVID-19, Otitis media, X-ray, Reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction
1. Introduction
The detection of coronavirus that is the cause of severe acute respiratory syndrome, dates back to 1900s [1].
In December 2019, an outbreak of a coronavirus disease (COVID-19) originated from China and expeditiously distributed to all of world [2]. The WHO announced the COVID-19 as a pandemic disease on March 2020 [3]. We acknowledge that 80% of cases show with mild disease and the entire case-fatality rate is about 2.3% but goes to 14.8% in patients aged over 80 years [4].
Among adult patients, cardiovascular disease, hypertension and diabetes mellitus were the most usual inherent diseases. Fever (92.8%), cough (69.8%), dyspnoea (34.5%), myalgia (27.7%), headache (7.2%), diarrhoea (6.1%), rhinorrhoea (4.0%), sore throat (5.1%) and pharyngalgia in 17.4% are all published signs [5].
In the present case, we report a 35-year-old female patient with a previously undefined otalgia and tinnitus who was diagnosed with COVID-19 on physical examination, reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) tests and radiographic studies.
2. Case report
A 35-year-old female patient presented to our clinic with otalgia and tinnitus. She has not any published COVID-19 symptoms. The patient has not any comorbid diseases.
There was hyperemia and bulging tympanic membrane in her otorhinolaryngologic examination (Fig. 1 ). But there was mild rhonchi at lower part of thorax.
Fig. 1.
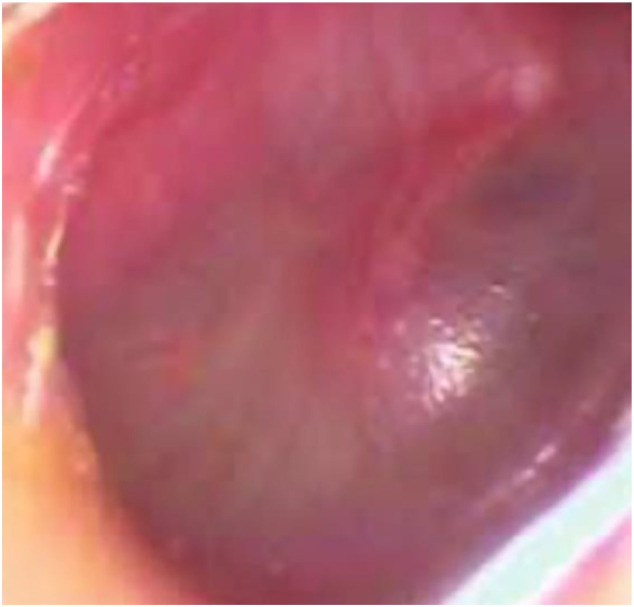
Otoscopic finding of ear.
The patient underwent audiometry and tympanometry tests. In terms of roncus detected in the examination, further examinations (chest X-ray, real-time reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)) were requested due to the pandemic status of world.
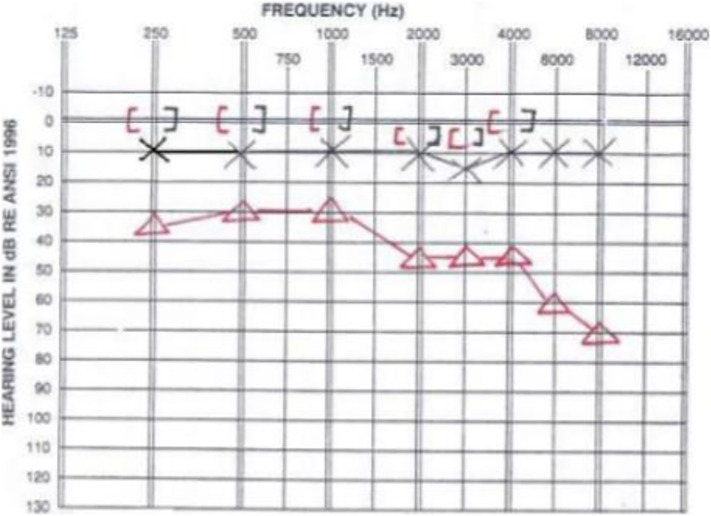
There was conductive hearing loss in audiometry and type-b appearance in tympanometry in right ear (Fig. 2 ). Also there was bilateral lung involvement in chest X-ray and positive RT-PCR result about COVID-19 (Fig. 3 ).
Fig. 2.
Audiometry of patient.
Fig. 3.
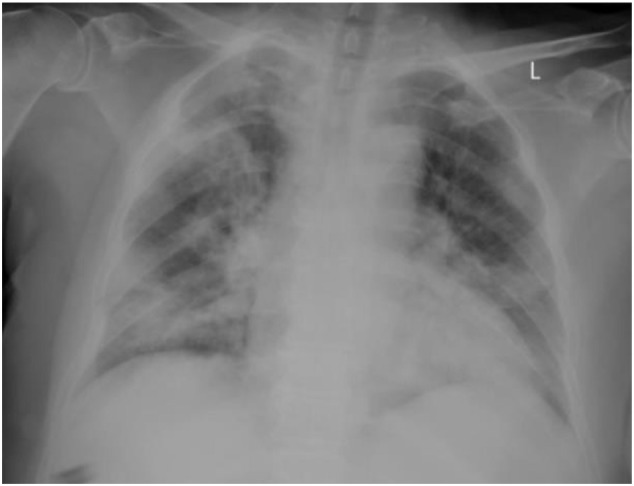
Chest X-ray of patient.
Antiviral treatment (75 mg of oseltamivir taken orally every 12 h, 7 days) was provided. The patient was kept at her home to continue the quarantine protocol for 14 days. The RT-PCR tests were repeated 7 and 13 days later. After the treatment, it was determined that the pcr test result was negative and the chest X-ray was normal.
3. Discussion
The outbreak of COVID-19 has become a clinical threat to the world. Our knowledge about COVID-19 is limited. Different methods including antiviral therapy and chloroquine therapy are tried worldwide. As with all pandemics, COVID-19 should be kept under close monitoring, as the more we learn about this novel virus. But clinicians must be kept in mind that COVID-19 can manifest itself with different findings, without the classic symptoms and complete body examination is most important in evaluation of patients.
References
- 1.Bradburne A.F. Sensitivity of L132 cells to some “new” respiratory viruses. Nature. 1969;221(5175):85–86. doi: 10.1038/221085a0. Jan 4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lai C.C., Shih T.P., Ko W.C., Tang H.J., Hsueh P.R. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19): the epidemic and the challenges. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020 Feb 17 doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.WHO Director-General's opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19. 11 March 2020. https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-remarks-at-the-media-briefing-on-covid-19---11-march-2020
- 4.Wu Z., McGoogan J.M. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA. 2020 doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.2648. Feb 24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Chen N., Zhou M., Dong X., Qu J., Gong F., Han Y. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study. Lancet. 2020;395:507–513. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]