Abstract
Conflicting results have been reported so far in pooled analyses and studies evaluating the optimum duration of dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) in acute coronary syndrome (ACS) patients. However, randomized clinical trials dedicated to this specific setting of higher thrombotic risk patients have only recently been completed, pointing at the noninferiority of a shorter strategy as compared to the traditional 12-month DAPT, furthermore allowing to reduce the risk of major bleeding complications. Therefore, a reconsideration of current clinical practice and guidelines should be certainly be advocated in light of the most recent updates, especially among ACS patients treated with percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and modern drug-eluting stents (DES). Our aim was to provide a comprehensive review of the available evidence on the optimal DAPT duration in ACS patients.
1. Background
Dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) using a combination of aspirin and a P2Y12 inhibitor (either a thienopyridine—clopidogrel or prasugrel—or ticagrelor) has represented the key point in the achievement of the significant prognostic improvements observed among patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) [1–3].
The European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the American College of Cardiology (ACC)/American Heart Association (AHA) recommend 12 months of DAPT after an acute cardiovascular event irrespective of the revascularization strategy, in both patients managed medically and those undergoing percutaneous coronary interventions [4, 5]. However, the latter certainly represents a higher thrombotic risk subgroup, where DAPT is mandatory in the first months after stent implantation until re-endothelization is complete, in order to prevent the device thrombosis and restenosis [6, 7].
Indeed, the recent achievements in stent technologies, with thinner struts, absent or bioresorbable polymer, and sharper imaging-assisted implantation techniques, have further improved clinical outcome with drug-eluting stents (DES), with reduced rates of restenosis and thrombotic complications, allowing a shorter DAPT duration (even as short as 1 month) [8–12].
However, whilst a progressive shortening of DAPT, driven by the DES technology is actually pursued in clinical practice, allowing to lower the rate of major bleeding complications, on the contrary, an opposite tendency towards a prolongation of the therapy has demonstrated additional anti-ischemic benefits in those higher risk patients, as those presenting with an ACS. The several trials and meta-analyses performed so far have failed to provide consistent indications on the optimal duration of DAPT in ACS [12–14], potentially due to the modest amount of data specifically addressing this population and in consideration of the use of the one-size-fits-all approach, not accounting for the significant heterogeneity of the bleeding and thrombotic risk in these patients.
The recent results of large-scale randomized trials [15, 16] evaluating the prognostic impact of a shorter vs. traditional 12-month DAPT in ACS patients undergoing coronary stenting with newer DES allow to reconsider the current therapeutic strategies in terms of antiplatelet treatment.
2. Dual Antiplatelet Therapy (DAPT) Duration in ACS: The Standard of 12 months
For many years, the administration of DAPT for a 12-month period after ACS has been indicated, primarily based on the CURE [17] trial, a study that was conducted 20 years ago and enclosing only a minority of patients treated with an early invasive revascularization strategy and even less receiving stent implantation. However, in that trial, the largest proportion of benefits among patients randomized to 1-year DAPT were observed before angiography in light of the earlier administration of clopidogrel as compared with those randomized to 1 month, while the difference between the two study groups became nonsignificant after 90 days after PCI.
In addition, the prolongation of DAPT has progressively required to deal with a higher occurrence of hemorrhagic events, being associated with impaired survival and enhanced ischemic complications.
In fact, in a substudy of the Acute Catheterization and Urgent Intervention Triage strategY (ACUITY) and Harmonizing Outcomes with RevasculariZatiON and Stents in Acute Myocardial Infarction (HORIZON-AMI) trials [18], including over 16,000 patients, the authors observed a strong independent relation of low hemoglobin levels and mortality, and similarly in the Paris registry [19], anemia emerged as the most important predictor of early DAPT discontinuation and recurrence of major cardiovascular events.
In addition, bleeding events certainly play an even greater role with more potent antiplatelet agents such as ticagrelor and prasugrel, resulting superior to clopidogrel in terms of platelet inhibition and antithrombotic protection in the respective PLATO [20] and TRITON-TIMI 38 [21] trials, being therefore currently indicated as a first-line strategy (class IA) over clopidogrel in the settings of ACS. However, higher percentages of non-CABG-related TIMI major bleeding events were observed in both PLATO (2.9 vs. 2.2%; p=0.003) and TRITON-TIMI 38 (2.4 vs. 1.8%; p=0.003) studies as compared with clopidogrel.
However, the efforts in reducing the duration of DAPT have been, so far, prevented by the fear of late (>30 days) and very late (>1 year) stent thrombosis, events that have prevented the spread of DES for many years. The development of newer generations of DES, with thinner struts, more predictable drug release, and lower grade of inflammation, thanks to biodegradable polymer or polymer-free technology, have allowed a faster re-endothelization, therefore reducing the rate of thrombotic complications to neglectable levels (<1%) and offering promising outcomes even with a shorter 1 to 6 months DAPT [12–16, 22].
Since 2012, after the publication of the PRODYGY trial [23], that randomized 2013 patients to 6 vs. 12 months of DAPT after PCI, further 14 trials have addressed the feasibility of reducing the period of DAPT [15, 16, 24–35], documenting the noninferiority of a shorter strategy as compared with the traditional 12 months in terms of anti-ischemic protection.
However, the limitations of the available studies have prevented, so far, the inclusion of these findings in routine clinical practice, in particular, the heterogeneity of the enrolled population and stent strategy, the nonuniformity of the primary endpoint, and the low ischemic events rate, conditioning the reduced power of these trials.
In the most recent guidelines, the optimal duration of DAPT has been lowered to at least 6 months only in stable patients although shorter or longer strategies could be reasonably considered according to patients' risk profile, requiring to balance between the thrombotic and hemorrhagic risk [4].
On the contrary, the traditional period of 12-month DAPT is still recommended in ACS patients, not accounting for the results of the recent studies, due to the modest amount of available literature. In fact, in previous trials, patients presenting for an acute event represented only 20–30% of the study population, as underlined in Table 1. However, it is also indicated that “in specific clinical scenarios, this standard DAPT duration can be shortened (<12 months) or extended (>12 months).” Nevertheless, the exact definition for these scenarios is still unclear.
Table 1.
Characteristics of randomized studies comparing different durations of dual antiplatelet therapy.
| Study | Antiplatelet treatment | ACS patients (n/N) | Primary efficacy endpoint | Primary efficacy result | Primary safety endpoint | Primary safety result | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strategy shorter DAPT | Months | Strategy longer DAPT | Months | ||||||
| RESET | ASA + clopidogrel | 3 | ASA + clopidogrel | 12 | 601/2117 | Composite death from all-cause myocardial infarction or stent thrombosis | — | TIMI | — |
| ISAR-SAFE | ASA + clopidogrel | 6 | ASA + clopidogrel | 12 | 1601/4000 | Composite of death, myocardial infarction, stent thrombosis, stroke, or TIMI major bleedings | — | TIMI | — |
| DAPT STEMI | ASA + prasugrel, ticagrelor (preferred above clopidogrel) | 6 | ASA + prasugrel, ticagrelor (preferred above clopidogrel) | 12 | 870/870 | All-cause mortality, myocardial infarction, any revascularization, stroke, TIMI major bleeding | — | TIMI/BARC 3 | — |
| I-LOVE-IT 2 | ASA + clopidogrel | 6 | ASA + clopidogrel | 12 | 1496/1829 | Composite of cardiac death, target vessel myocardial infarction (TVMI), or clinically indicated target lesion revascularization (CI-TLR) | — | BARC 3–5 | — |
| REDUCE | ASA + prasugrel, ticagrelor (preferred above clopidogrel) | 3 | ASA + prasugrel, ticagrelor (preferred above clopidogrel) | 12 | 1496/1496 | All-cause death, MI, ST, stroke, TVR, or bleeding | — | BARC 2–5 | — |
| SMART DATE | ASA + any P2Y12 inhibitor | 6 | ASA + any P2Y12 inhibitor | 12 | 1000/1297 | A composite of all-cause mortality, myocardial infarction, and cerebrovascular events) | — | BARC 2–5 | — |
| EXCELLENT | ASA + clopidogrel | 6 | ASA + clopidogrel | 12 | 744/1443 | Composite of cardiac death, myocardial infarction, or target vessel revascularization | — | TIMI | — |
| IVUS XL | ASA + clopidogrel | 6 | ASA + clopidogrel | 12 | 687/1400 | Composite of cardiac death, myocardial infarction, stroke, or TIMI major bleeding | — | TIMI | — |
| OPTIMIZE | ASA + clopidogrel | 3 | ASA + clopidogrel | 12 | 996/3119 | Composite of death from any cause, MI, stroke, or major bleeding | — | Intracranial, intraocular, or retroperitoneal hemorrhage; clinically overt blood loss resulting hemoglobin decrease >3 g/dL, any hemoglobin decrease >4 g/dL, or transfusion of 1 unit of packed red blood cells or whole blood; or intracranial hemorrhage or bleeding causing hemodynamic compromise and requiring intervention | — |
| SECURITY | ASA + any P2Y12 inhibitor | 6 | ASA + any P2Y12 inhibitor | 12 | 442/1399 | Composite of cardiac death, MI, stroke, definite or probable stent thrombosis or bleeding academic consortium criteria (BARC) type 3 or 5 bleeding | — | BARC 3–5 | — |
| NIPPON | ASA + clopidogrel (prasugrel) | 6 | ASA + clopidogrel (prasugrel) | 18 | 1079/3307 | All-cause death, Q-wave or non-Q-wave MI, cerebrovascular events, and major bleeding events | — | Modified REPLACE-2 criteria | — |
| STOPDAPT 2 | ASA + clopidogrel | 1 | ASA + clopidogrel | 12 | 1140/3009 | Composite of cardiac death, MI, stroke, definite or probable stent thrombosis or TIMI major/minor bleeding |

|
TIMI |

|
| SMART CHOICE | ASA + any P2Y12 inhibitor | 3 | ASA + any P2Y12 inhibitor | 12 | 1736/2993 | All-cause death, MI, or stroke | — | BARC 2–5 |

|
| DES LATE-DATE | ASA + clopidogrel | 12 | ASA + clopidogrel | 24 | 3063/5045 | Composite of death resulting from cardiac causes, myocardial infarction, or stroke | — | TIMI |

|
| ARCTIC interruption | ASA + clopidogrel (75 or 150 mg) or prasugrel | 12 | ASA + clopidogrel (75 or 150 mg) or prasugrel | 24 | 323/1286 | Any death, myocardial infarction, stent thrombosis, stroke, or TIA, urgent revascularization | — | STEEPLE | — |
| DAPT study | ASA + clopidogrel/prasugrel | 12 | ASA + clopidogrel/prasugrel | 30 | 3576/9961 | Stent thrombosis |

|
GUSTO | — |
| Italic/italic+ | ASA | 6 | ASA + clopidogrel (prasugrel, ticagrelor) | 12 | 792/1850 | Composite of death, MI, emergency TVR, stroke, or major bleeding | — | TIMI | — |
| TWILIGHT | ASA + ticagrelor (then ticagrelor) | 3 | ASA + ticagrelor | 12 | 7119/7119 | Death from any cause, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal stroke | — | BARC 2, 3–5 |

|
| GLOBAL LEADERS | ASA + ticagrelor (then ticagrelor) | 1 | ASA + ticagrelor or clopidogrel | 12 | 7487/15968 | All-cause mortality or new nonfatal, centrally adjudicated Q-wave MI | — | BARC 3–5 |

|
In the multicenter DAPT STEMI trial [15], a total of 870 STEMI patients treated with primary angioplasty and RESOLUTE Onyx Stent who were taking DAPT and were event-free at six months were randomized 1 : 1 to single antiplatelet therapy or to DAPT for an additional six months. New ADP antagonists were similarly used in both groups (58%). All patients who were randomized were then followed for another 18 months (i.e., 24 months after the primary PCI). The primary endpoint (composite of all-cause mortality, any MI, any revascularization, stroke, and TIMI major bleeding at 18 months after randomization) occurred in 4.8% of patients receiving single antiplatelet therapy vs. 6.6% of patients receiving DAPT (pnon-inferiority = 0.004). In the multicenter SMART DATE trial [24], a total of 2712 ACS patients treated with PCI and DES with permanent (Xience or RESOLUTE Onyx) or bioresorbable (ORSIRO) polymer were randomly assigned to 6-month DAPT (n = 1357) and 12-month or longer DAPT (n = 1355). Clopidogrel was used in 79.7% of patients in the 6-month DAPT and in 81.8% of patients in the 12-month DAPT. The primary endpoint (composite of all-cause death, MI, or stroke at 18 months) occurred in 4.7% with the 6-month DAPT and in 4.2% with the 12-month DAPT (pnon-inferiority = 0.03). Although all-cause mortality did not differ significantly between 6-month DAPT and 12-month DAPT (2.6% vs. 2.9%, p = 0.90) and neither did stroke (0.8% vs. 0.9%, p = 0.84) and ST (1.1% vs. 0.7%, p = 0.32), MI occurred more frequently in the 6-month DAPT than in the 12-month DAPT group (1.8% vs. 0.8%; p = 0.02). No significant difference was observed in the rate of BARC type 2–5 bleeding between the two groups (2.7% vs. 3.9%; p = 0.09).
The REDUCE trial [16] compared a very short DAPT (3 months) vs. a standard 12-month DAPT strategy in a total of 1496 ACS patients successfully treated with a new-generation DES (COMBO), including almost 50% STEMI patients and large use of new ADP antagonists (almost 60%). Differently from the DAPT STEMI but similarly to the SMART DATE, patients were randomized during initial hospitalization.
In this study, a 3-month DAPT strategy was not inferior to 12-month DAPT with regards to the primary endpoint (composite of mortality, MI, ST, stroke, TVR, or bleeding (BARC II, III, and V)). Similar outcome between the two groups was observed at 2-year follow-up (11.6% vs. 12.1%, respectively) and also confirmed in the per-protocol analysis, actual treatment analysis, and for major subgroups such as age, diabetic status, gender, type of ACS (STEMI vs. NSTEMI/ACS), and kidney function.
No significant differences were observed in the secondary endpoints (mortality, MI, ST, TVR, and bleedings) although cardiac mortality and stent thrombosis were numerically higher in the three-month DAPT group.
In a recent comprehensive meta-analysis restricted to ACS, including 17,941 patients [12], a shorter DAPT strategy was associated with a nonsignificant reduction in bleedings, whereas no difference in cardiovascular mortality, MI, and ST was observed with a shorter vs. standard 12-month DAPT (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
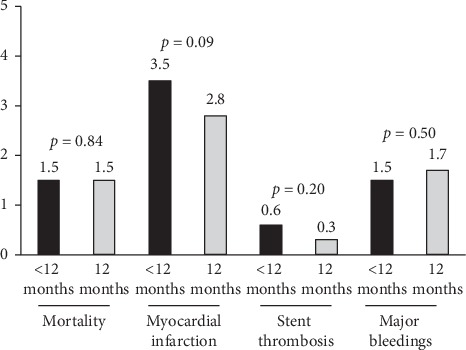
Bar graph showing the rate of major clinical events in clinical trials comparing 12-month dual antiplatelet strategy (DAPT) vs. a shorter strategy followed by ASA alone.
Several trials have recently investigated a short DAPT strategy with the drop of aspirin that has been claimed as the major determinant of gastrointestinal bleeding complications. The GLOBAL LEADERS trial [36] compared 1-month DAPT followed by 23-month ticagrelor vs. standard 12-month DAPT. This trial included 130 secondary/tertiary care hospitals in different countries, with 15,991 unselected patients with stable coronary artery disease or ACS undergoing PCI. The non-prespecified, post hoc analysis restricted to ACS patients, including 7487 patients (3750 assigned to 1-month DAPT followed by ticagrelor therapy and 3737 to standard 1-year DAPT), has been recently published. Between 31 and 365 days after randomization, the primary outcome (composite of all-cause death or new Q-wave myocardial infarction) occurred in 55 patients (1.5%) in the experimental group and in 75 patients (2.0%) in the reference group (HR = 0.73; p=0.07); investigator-reported Bleeding Academic Research Consortium-defined bleeding type 3 or 5 occurred in 28 patients (0.8%) with 1-month DAPT and in 54 patients (1.5%) with 1-year DAPT (HR = 0.52; p=0.004) (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
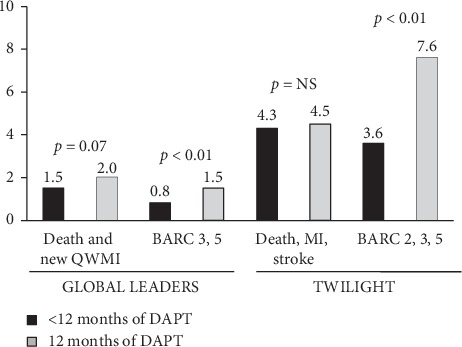
Bar graph showing the rate of major clinical events in clinical trials comparing 12-month dual antiplatelet strategy (DAPT) vs. a shorter strategy followed by ticagrelor alone.
The TWILIGHT trial [37] included patients undergoing PCI who were at high risk for ischemic or hemorrhagic complications and who completed a 3-month course of dual antiplatelet therapy with ticagrelor plus aspirin. They were, thereafter, randomized to single antiplatelet therapy (SAPT) with ticagrelor or DAPT up to 12-month follow-up. The primary endpoint was the occurrence of BARC 2, 3, or 5, whereas the secondary endpoint was the combined occurrence of all-cause death, nonfatal MI, or stroke. Out of 7119 patients enrolled in the study, 4614 had ACS. In this population, SAPT, as compared with DAPT, was associated with a significant reduction in the primary safety endpoint (3.6% vs. 7.6%; p < 0.01), without any difference in the secondary endpoint (4.3% vs. 4.5%) (Figure 2).
3. Prolonged DAPT beyond 1 Year after ACS for Secondary Prevention
In the last few years, several trials and meta-analyses have addressed different strategies of DAPT duration, attempting to decrease either the ischemic or the hemorrhagic complications and improve the outcomes of ACS patients.
In particular, the option of prolonging the treatment with DAPT beyond 12 months has been explored in different trials [38–40], based on the observations in older studies that first-generation DES was associated with a significantly higher risk of very late ST. In the International Drug-Eluting Stent Event Registry of Thrombosis (DESERT), in fact, the majority of ST events occurred after 1 year (75%) and continued to be observed for as long as 7.3 years [41]. Similarly, the large National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Dynamic Registry reported a significant 4-year reduction of mortality in patients with extended DAPT after DES implantation [42].
On the contrary, in the large nonrandomized registry, the Coronary Revascularization Demonstrating Outcome (CREDO)-Kyoto Registry Cohort-2 [43], prolonged thienopyridine therapy beyond 1 year did not reduce ischemic events, but showed a trend toward increased bleeding. A similar risk was also underlined in the Dual Antiplatelet Therapy (DAPT) Study [40], an international multicenter, randomized trial that compared 30 with 12 months of dual antiplatelet therapy after PCI, where the continuation of treatment beyond 12 months was associated with a reduction in ischemic events (stent thrombosis and myocardial infarction), but also increased noncardiovascular death, potentially driven by a marked raise in hemorrhagic complications. Moreover, almost 50% of these who avoided myocardial infarctions were nonstent related, and therefore associated to the prevention of “de novo” events, with no final impact on survival, as concluded also by subsequent meta-analyses [44], thus leaving considerable uncertainty with respect to the appropriateness of the extension of DAPT beyond the recommended period except than in selected subsets of patients at very high risk of recurrent ACS.
However, none of these studies specifically addressed to the ACS population and neither conducted with newer generations of DES.
In the Dual Antiplatelet Therapy (DAPT) trial [40], a total of 9961 patients undergoing DES implantation were randomly assigned at 1-year follow-up to continue thienopyridine treatment up to 30 months or to receive placebo. Prolonged DAPT was associated with reduced stent thrombosis (0.4% vs. 1.4%; p < 0.001) and major adverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events (4.3% vs. 5.9%; p < 0.001). The rate of myocardial infarction was lower with prolonged DAPT than with placebo (2.1% vs. 4.1%; p < 0.001). However, prolonged DAPT was associated with higher all-cause mortality (2.0% vs. 1.5%; p=0.05) and moderate or severe bleeding (2.5% vs. 1.6%; p=0.001), as in Figure 3. A post hoc analysis showed less benefits in thrombotic complications with prolonged DAPT in patients receiving new-generation DES (Xience) as compared with first-generation SES or PES (p int = 0.048). Besides, another subanalysis showed that the reduction of MACCE for prolonged DAPT was greater for MI patients (3.9% vs. 6.8%; p < 0.001) compared with those with no MI (4.4% vs. 5.3%; p=0.08; interaction p=0.03) [45].
Figure 3.
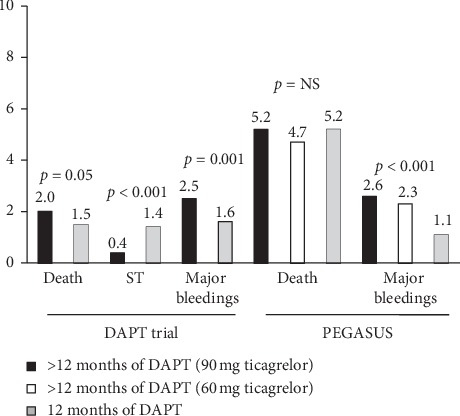
Bar graph showing the rate of major clinical events in clinical trials comparing 12-month dual antiplatelet strategy (DAPT) vs. a longer (>12 months) strategy.
In the PEGASUS trial [46], a total of 21,162 patients with a previous (1 to 3 years earlier) myocardial infarction were randomly assigned 1 : 1 : 1 fashion to ticagrelor 90 mg twice daily, ticagrelor 60 mg twice daily, or placebo and followed up for a median of 33 months. The primary efficacy end point was the composite of cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, or stroke. The primary safety end point was thrombolysis in myocardial infarction (TIMI) major bleeding.
As displayed in Figure 3, the two ticagrelor doses each reduced, as compared with placebo, the rate of the primary efficacy end point (composite of cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, or stroke) (p=0.008; p=0.004). Rates of TIMI major bleeding were higher with ticagrelor (2.60% with 90 mg and 2.30% with 60 mg) than with placebo (1.06%) (p < 0.001 for each dose vs. placebo). An overall similar all-cause mortality was observed in the three groups.
Nevertheless, more complex patients were excluded from these studies, such as those with a high bleeding risk or those with more advanced coronary disease, including patients with left main disease or multivessel CAD and incomplete revascularization.
Thus, based on the current findings, a standard 12-month DAPT cannot certainly be systematically applied to all ACS patients, whilst an individualized therapy of shortened or extended therapy according to patients' risk profile should be advocated.
In fact, the current guidelines do recommend a prolonged DAPT in patients at high risk for thrombotic complications but with low bleeding risk (class 2A).
However, further large-scale studies will allow to better define the criteria for the stratification of the patients and tailoring of DAPT.
4. DAPT Optimization in Special Populations: Towards and Individualized DAPT Duration
In the last decades, the complexity of patients admitted for an ACS has progressively increased. In fact, with the progressive ageing of the population, among 30% of patients with an acute ischemic event are in advanced age, displaying a higher rate of comorbidities, such as diabetes, renal failure, and a more severe coronary disease, therefore requiring extensive stenting and the management of difficult anatomies. Thus, both thrombotic and bleeding risk are enhanced among these patients, challenging the optimization of DAPT.
Several studies have attempted so far to identify the best criteria for the selection of the optimal DAPT duration. In particular, several risk scores have been developed, derived from large randomized trials, although the majority were developed for the prediction of events occurring mainly during hospital stay or soon after discharge. The newer “DAPT score” [47], derived from the 11,648 patients enrolled in the Dual Antiplatelet Therapy study (DAPT) trial, may be useful for decisions about extending DAPT in patients treated with coronary stent implantation, suggesting that a prolonged > 12-month therapy may be favorable for those with a score ≥2. Diabetes mellitus, current cigarette use, prior PCI or prior MI, congestive heart failure or left ventricular ejection fraction <30%, MI at presentation, vein graft PCI, and stent diameter <3 mm increase the thrombotic risk, while a score reduction is warranted by advanced age, especially for patients >75 years of age. On the contrary, for the prediction of bleedings, the most recent score endorsed by guidelines is represented by the PRECISE-DAPT (PREdicting bleeding Complications In patients undergoing Stent implantation and subsEquent Dual Anti-Platelet Therapy) [48], enclosing a five-item (age, CrCl, hemoglobin, white blood cell count, and prior spontaneous bleeding) prediction algorithm for out-of-hospital bleeding in patients treated with DAPT. It was observed that among patients deemed at high bleeding risk (PRECISE-DAPT score ≥ 25), prolonged DAPT was associated with no ischemic benefit but a remarkable bleeding burden leading to an NNT for harm of 38, whilst a PRECISE-DAPT score <25 was associated with a significant reduction in ischemic endpoints.
Nevertheless, the exact prognostic role of these scores in the context of real-life ACS patients, often displaying a greater complexity as compared with subjects enrolled in randomized clinical trials, is still unknown.
In addition, it should be accounted that about one-third of ACS patients nowadays displays an indication to oral anticoagulation [1, 49–51], increasing the hemorrhagic risk and therefore raising uncertainty not only on the timing of DAPT discontinuation but also on the optimal combination of the antithrombotic and antiplatelet agents and the selection of the drug to be dismissed.
In fact, recently completed trials have introduced the opportunity of an aspirin-free dual therapy in post-PCI patients [36, 37, 49–53], providing comparable mortality and a reduction in major bleedings as compared with triple therapy, introducing the concept that ASA could be no more a pillar treatment in coronary disease, especially in the era of novel oral anticoagulants (Figure 4).
Figure 4.
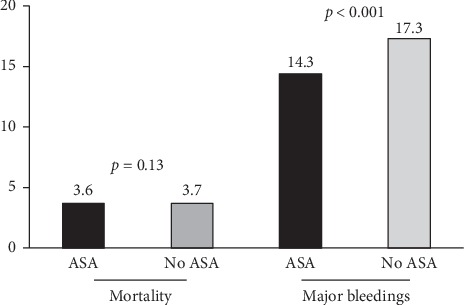
Bar graph showing the rate of major clinical events (mortality and major bleedings) with ASA-free or traditional dual antiplatelet strategy (DAPT) in patients receiving concomitant oral anticoagulation.
The WOEST trial [52] was the pioneer trial in the proposition of an aspirin-free strategy after PCI in AF patients (vitamin K antagonists and clopidogrel). In this trial including 573 patients, a dual therapy strategy was associated with a significant reduction in major bleeding complications without any excess in thrombotic complications as compared with triple therapy.
In the RE-DUAL PCI [49], patients were randomized to either dabigatran plus P2Y12 inhibitor or to a triple therapy with warfarin. However, in the warfarin arm, DAPT was continued for a maximum of three months, with a subsequent drop of ASA, in ACS patients, that represented 52% of the study population.
Similarly, the PIONEER AF-PCI [50] that enrolled about half of the patients with ACS showed a comparable efficacy, but a reduction of major bleedings, with rivaroxaban plus a P2Y12 inhibitor for 12 months as compared with warfarin plus DAPT. However, in this study, the duration of triple therapy was planned for 1, 6, or 12 months, with warfarin plus ASA being continued thereafter.
Analogous conclusions were reached also in the most recent AUGUSTUS trial [51], enclosing 37.3% of ACS patients treated with PCI and 23.9% of ACS patients medically managed that were randomized to P2Y12 plus apixaban or warfarin, with or without ASA.
The advantages of a dual therapy with NOAC and ADP antagonists, as compared with triple therapy with VKA have been confirmed with edoxaban in the recent ENTRUST-AF PCI trial [53].
However, the large heterogeneity of the strategies proposed for the management of these high-bleeding risk subjects, as described in Table 2, has not led so far to a joint agreement in terms of triple therapy, especially in ACS patients.
Table 2.
Characteristics of randomized studies comparing different antiplatelet strategies in association with direct oral anticoagulants or vitamin K antagonists (VKA).
| Study | Antiplatelet treatment | ACS patients (n/N) | Primary efficacy endpoint | Primary efficacy result | Primary safety endpoint | Primary safety result | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strategy shorter DAPT | Months | Strategy longer DAPT | Months | ||||||
| PIONEER AF-PCI | Rivaroxaban 15 + clopidogrel (ticagrelor/prasugrel allowed < 15%) or | 12 months | VKA + DAPT | 1, 6, or 12 months | 1096/1415 | Death from cardiovascular cause, myocardial infarction, or stroke | — | Clinically significant bleeding |

|
| WOEST | Causes myocardial infarction or stroke |

|
All bleeding events (TIMI criteria) |

|
|||||
| ENTRUST-AF PCI | VKA + clopidogrel | 1 month after BMS and 12 months after DES | VKA + ASA + clopidogrel | 1 month after BMS and 12 months after DES | 155/563 | Stroke, death, myocardial infarction, stent thrombosis, and target vessel revascularization | — | Clinically relevant bleeding | — |
| RE-DUAL PCI | Edoxaban 60 mg + clopidogrel ticagrelor/prasugrel allowed < 10%) | 12 months | VKA + ASA + clopidogrel ticagrelor/prasugrel allowed < 15%) | 12 months (ASA min 1 month) | 777/1506 | Cardiovascular death, stroke, systemic embolic events (SEE), myocardial infarction, and definite stent thrombosis | — | ISTH major or clinically relevant nonmajor bleedings |

|
| AUGUSTUS | Dabigatran 110 or 150 mg BID + clopidogrel or ticagrelor | 6 months | VKA + ASA + clopidogrel or ticagrelor | 6 months | 1744/3489 | Thromboembolic events, death, or unplanned revascularization | — | ISTH major or clinically relevant nonmajor bleedings |

|
5. Future Perspectives
Real-life experience has pointed at the presence of several clinical and angiographic factors which should be acknowledged for the estimation of the balance between the thrombotic and the ischemic risk in ACS patients, therefore for the planning of the optimal duration of DAPT. Evidence from the recent studies has clearly shown that technological improvements and the broad spectrum of pharmacological adjuncts nowadays offer a wide range of combinations, allowing to tailor the antithrombotic therapy according to patients' risk profile.
Therefore, it appears that an individualized approach of shortening or prolonging DAPT according to the patients' characteristics should be recommended. Due to current evidences, it is undoubtful that a shorter DAPT strategy may be reasonable among ACS patients, potentially leaving a standard 12-month or longer therapy to high-risk patients with extensive coronary disease, complex anatomy, and percutaneous intervention, and therefore at high risk for thrombotic complications, in the presence of low risk of bleedings. Due to the results of the GLOBAL LEADERS and TWILIGHT trial [36, 37], it may be questioned whether aspirin is still needed in the treatment of ACS in the era of new ADP antagonists. Further investigations are certainly needed to solve this issue.
While many trials [49–53] have recently demonstrated that a dual therapy (NOAC and ADP antagonists) may be the preferred strategy after percutaneous intervention in patients needing chronic oral anticoagulation, further investigations are certainly warranted in ACS patients.
Future large dedicated studies will certainly help to define the criteria that should be accounted for the stratification of the patients and for the weighting of the ischemic and hemorrhagic risk that should guide an optimal tailored antiplatelet therapy.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.Levine G. N., Bates E. R., Blankenship J. C., et al. 2011 ACCF/AHA/SCAI guideline for percutaneous coronary intervention: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions. Circulation. 2011;23:E574–E651. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0b013e31823ba622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Verdoia M., Schaffer A., Barbieri L., et al. Benefits from new ADP antagonists as compared with clopidogrel in patients with stable angina or acute coronary syndrome undergoing invasive management. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology. 2014;63(4):339–350. doi: 10.1097/fjc.0000000000000052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Mehta S. R., Bainey K. R., Cantor W. J., et al. 2018 Canadian Cardiovascular Society/Canadian Association of Interventional Cardiology focused update of the guidelines for the use of antiplatelet therapy. Canadian Journal of Cardiology. 2018;34(3):214–233. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2017.12.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Valgimigli M., Bueno H., Byrne R. A., et al. 2017 ESC focused update on dual antiplatelet therapy in coronary artery disease developed in collaboration with EACTS: the task force for dual antiplatelet therapy in coronary artery disease of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and of the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS) European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery. 2018;39(3):213–260. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Amsterdam E. A., Wenger N. K., Brindis R. G., et al. 2014 AHA/ACC guideline for the management of patients with non- ST-elevation acute coronary syndromes: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American heart Association task force on practice guidelines. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2014;64(24):e139–e228. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2014.09.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Verdoia M., Sartori C., Pergolini P., et al. Prevalence and predictors of high-on treatment platelet reactivity with ticagrelor in ACS patients undergoing stent implantation. Vascular Pharmacology. 2016;77:48–53. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2015.04.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.De Luca G., Dirksen M. T., Spaulding C., et al. Time course, predictors and clinical implications of stent thrombosis following primary angioplasty. Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 2013;110(4):826–833. doi: 10.1160/th13-02-0092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.De Luca G., Dirksen M. T., Spaulding C., et al. Drug-eluting stent in primary angioplasty (DESERT) cooperation. Archives of Internal Medicine. 2012;172:611–621. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2012.758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Habib A., Finn A. V. Endothelialization of drug eluting stents and its impact on dual anti-platelet therapy duration. Pharmacological Research. 2015;93:22–27. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2014.12.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Garot P., Morice M.-C., Tresukosol D., et al. 2-year outcomes of high bleeding risk patients after polymer-free drug-coated stents. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2017;69(2):162–171. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2016.10.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Buccheri S., Franchina G., Romano S., et al. Clinical outcomes following intravascular imaging-guided versus coronary angiography-guided percutaneous coronary intervention with stent implantation. JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions. 2017;10(24):2488–2498. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2017.08.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Verdoia M., Khedi E., Ceccon C., Suryapranata H., De Luca G. Duration of dual antiplatelet therapy and outcome in patients with acute coronary syndrome undergoing percutaneous revascularization: a meta-analysis of 11 randomized trials. International Journal of Cardiology. 2018;264:30–38. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2018.02.095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Barillà F., Pelliccia F., Borzi M., et al. Optimal duration of dual anti-platelet therapy after percutaneous coronary intervention: 2016 consensus position of the Italian Society of Cardiology. Journal of Cardiovascular Medicine. 2017;18(1):1–9. doi: 10.2459/JCM.0000000000000434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bavishi C., Trivedi V., Singh M., Katz E., Messerli F. H., Bangalore S. Duration of dual antiplatelet therapy in patients with an acute coronary syndrome undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. The American Journal of Medicine. 2017;130(11):1325.e1–1325.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2017.05.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kedhi E., Fabris E., van der Ent M., et al. Six months versus 12 months dual antiplatelet therapy after drug-eluting stent implantation in ST-elevation myocardial infarction (DAPT-STEMI): randomised, multicentre, non-inferiority trial. BMJ. 2018;363:p. k3793. doi: 10.1136/bmj.k3793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.De Luca G., Damen S. A., Camaro C., et al. Final results of the randomised evaluation of short-term dual antiplatelet therapy in patients with acute coronary syndrome treated with a new generation stent (REDUCE) trial. EuroIntervention. 2019;15(11):e990–e998. doi: 10.4244/EIJ-D-19-00539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mehta S. R., Yusuf S., Peters R. J., et al. Effects of pretreatment with clopidogrel and aspirin followed by long-term therapy in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: the PCI-CURE study. The Lancet. 2001;358(9281):527–533. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(01)05701-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Brener S. J., Mehran R., Dangas G. D., et al. Relation of baseline hemoglobin levels and adverse events in patients with acute coronary syndromes (from the acute catheterization and urgent intervention triage strategy and harmonizing outcomes with revascularization and stents in acute myocardial infarction trials) The American Journal of Cardiology. 2017;119(11):1710–1716. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2017.02.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Baber U., Mehran R., Giustino G., et al. Coronary thrombosis and major bleeding after PCI with drug-eluting stents. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2016;67(19):2224–2234. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2016.02.064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wallentin L., Becker R. C., Budaj A., et al. Ticagrelor versus clopidogrel in patients with acute coronary syndromes. New England Journal of Medicine. 2009;361(11):1045–1057. doi: 10.1056/nejmoa0904327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wiviott S. D., Braunwald E., McCabe C. H., et al. Prasugrel versus clopidogrel in patients with acute coronary syndromes. New England Journal of Medicine. 2007;357(20):2001–2015. doi: 10.1056/nejmoa0706482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Palmerini T., Benedetto U., Biondi-Zoccai G., et al. Long-term safety of drug-eluting and bare-metal stents. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2015;65(23):2496–2507. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2015.04.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Costa F., Vranckx P., Leonardi S., et al. Impact of clinical presentation on ischaemic and bleeding outcomes in patients receiving 6- or 24-month duration of dual-antiplatelet therapy after stent implantation: a pre-specified analysis from the PRODIGY (Prolonging Dual-Antiplatelet Treatment after Grading Stent-Induced Intimal Hyperplasia) trial. European Heart Journal. 2015;36(20):1242–1251. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hahn J.-Y., Song Y. B., Oh J.-H., et al. 6-month versus 12-month or longer dual antiplatelet therapy after percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with acute coronary syndrome (SMART-DATE): a randomised, open-label, non-inferiority trial. The Lancet. 2018;391(10127):1274–1284. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(18)30493-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kim B.-K., Hong M.-K., Shin D.-H., et al. A new strategy for discontinuation of dual antiplatelet therapy. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2012;60(15):1340–1348. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2012.06.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Schulz-Schupke S., Byrne R. A., Ten Berg J. M., et al. ISAR-SAFE: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of 6 vs. 12 months of clopidogrel therapy after drug-eluting stenting. European Heart Journal. 2015;36(20):1252–1263. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Qi J., Li Y., Li J., et al. Safety and efficacy of 6-month versus 12-month dual antiplatelet therapy in patients after implantation of multiple biodegradable polymer-coated sirolimus-eluting coronary stents: insight from the I-LOVE-IT 2 trial. Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions. 2017;89(S1):555–564. doi: 10.1002/ccd.26947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Gwon H.-C., Hahn J.-Y., Park K. W., et al. Six-month versus 12-month dual antiplatelet therapy after implantation of drug-eluting stents. Circulation. 2012;125(3):505–513. doi: 10.1161/circulationaha.111.059022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Feres F., Costa R. A., Abizaid A., et al. Three vs twelve months of dual antiplatelet therapy after zotarolimus-eluting stents: the OPTIMIZE randomized trial. JAMA. 2013;310:2510–2522. doi: 10.1001/jama.2013.282183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Colombo A., Chieffo A., Frasheri A., et al. Second-generation drug-eluting stent implantation followed by 6- versus 12-month dual antiplatelet therapy. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2014;64(20):2086–2097. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2014.09.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Nakamura M., Iijima R., Ako J., et al. Dual antiplatelet therapy for 6 versus 18 months after biodegradable polymer drug-eluting stent implantation. JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions. 2017;10(12):1189–1198. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2017.04.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hong S.-J., Shin D.-H., Kim J.-S., et al. 6-Month versus 12-month dual-antiplatelet therapy following long everolimus-eluting stent implantation. JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions. 2016;9(14):1438–1446. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2016.04.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Hahn J.-Y. P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy versus dual antiplatelet therapy in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: the SMART-CHOICE randomized, open-label, noninferiority trial. Proceedings of the American College of Cardiology (ACC) 68th Annual Scientific Session and Expo; March 2019; New Orleans, LA, USA. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Watanabe H. One-month dual antiplatelet therapy followed by clopidogrel monotherapy versus standard 12-month dual antiplatelet therapy with clopidogrel after drug-eluting stent implantation: STOPDAPT-2 trial. Proceedings of the American College of Cardiology (ACC) 68th Annual Scientific Session and Expo; March 2019; New Orleans, LA, USA. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Gilard M., Barragan P., Al Noryani A., Noor H., Majwal T. Is 6 months DAPT after coronary stenting not inferior to 24 months? The italic/italic + randomized trial. Results of the one year primary endpoint. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2015;65(8):777–786. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2014.11.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Tomaniak M., Chichareon P., Onuma Y., et al. Benefit and risks of aspirin in addition to ticagrelor in acute coronary syndromes. JAMA Cardiology. 2019;4(11):p. 1092. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2019.3355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Mehran R., Baber U., Sharma S. K., et al. Ticagrelor with or without aspirin in high-risk patients after PCI. New England Journal of Medicine. 2019;381(21):2032–2042. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1908419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Collet J.-P., Silvain J., Barthélémy O., et al. Dual-antiplatelet treatment beyond 1 year after drug-eluting stent implantation (ARCTIC-Interruption): a randomised trial. The Lancet. 2014;384(9954):1577–1585. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(14)60612-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lee C. W., Ahn J.-M., Park D.-W., et al. Optimal duration of dual antiplatelet therapy after drug-eluting stent implantation. Circulation. 2014;129(3):304–312. doi: 10.1161/circulationaha.113.003303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Mauri L., Kereiakes D. J., Yeh R. W., et al. Twelve or 30 months of dual antiplatelet therapy after drug-eluting stents. New England Journal of Medicine. 2014;371(23):2155–2166. doi: 10.1056/nejmoa1409312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Waksman R., Kirtane A. J., Torguson R., et al. Correlates and outcomes of late and very late drug-eluting stent thrombosis. JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions. 2014;7(10):1093–1102. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2014.04.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Mulukutla S. R., Marroquin O. C., Vlachos H. A., et al. Benefit of long-term dual anti-platelet therapy in patients treated with drug-eluting stents: from the NHLBI dynamic registry. The American Journal of Cardiology. 2013;111(4):486–492. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2012.10.030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Natsuaki M., Morimoto T., Furukawa Y., et al. Late adverse events after implantation of sirolimus-eluting stent and bare-metal stent. Circulation: Cardiovascular Interventions. 2014;7(2):168–179. doi: 10.1161/circinterventions.113.000987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Navarese E. P., Andreotti F., Schulze V., et al. Optimal duration of dual antiplatelet therapy after percutaneous coronary intervention with drug eluting stents: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ. 2015;350(25):p. h1618. doi: 10.1136/bmj.h1618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Yeh R. W., Kereiakes D. J., Steg P. G., et al. Benefits and risks of extended duration dual antiplatelet therapy after PCI in patients with and without acute myocardial infarction. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2015;65(20):2211–2221. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2015.03.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Bonaca M. P., Bhatt D. L., Cohen M., et al. Long-term use of ticagrelor in patients with prior myocardial infarction. New England Journal of Medicine. 2015;372(19):1791–1800. doi: 10.1056/nejmoa1500857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Yeh R. W., Secemsky E. A., Kereiakes D. J., et al. Development and validation of a prediction rule for benefit and harm of dual antiplatelet therapy beyond 1 year after percutaneous coronary intervention. JAMA. 2016;315(16):1735–1749. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.3775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Choi S. Y., Kim M. H., Cho Y. R., et al. Performance of PRECISE-DAPT score for predicting bleeding complication during dual antiplatelet therapy. Circulation: Cardiovascular Interventions. 2018;11(12) doi: 10.1161/circinterventions.118.006837.e006837 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Cannon C. P., Lip G. Y. H., Oldgren J. Dual antithrombotic therapy with dabigatran after PCI in atrial fibrillation. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2018;378(378):485–486. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1715183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Gibson C. M., Mehran R., Bode C., et al. Prevention of bleeding in patients with atrial fibrillation undergoing PCI. New England Journal of Medicine. 2016;375(25):2423–2434. doi: 10.1056/nejmoa1611594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Lopes R. D., Heizer G., Aronson R., et al. Antithrombotic therapy after acute coronary syndrome or PCI in atrial fibrillation. New England Journal of Medicine. 2019;380(16):1509–1524. doi: 10.1056/nejmoa1817083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Dewilde W. J., Oirbans T., Verheugt F. W., et al. Use of clopidogrel with or without aspirin in patients taking oral anticoagulant therapy and undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: an open-label, randomised, controlled trial. The Lancet. 2013;381(9872):1107–1115. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(12)62177-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Vranckx P., Valgimigli M., Eckardt L., et al. Edoxaban-based versus vitamin K antagonist-based antithrombotic regimen after successful coronary stenting in patients with atrial fibrillation (ENTRUST-AF PCI): a randomised, open-label, phase 3b trial. The Lancet. 2019;394(10206):1335–1343. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(19)31872-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


