Abstract
The canonical pathway of eicosanoid production in most mammalian cells is initiated by phospholipase A2-mediated release of arachidonic acid, followed by its enzymatic oxidation resulting in a vast array of eicosanoid products. However, recent work has demonstrated that the major phospholipase in mitochondria, iPLA2γ (patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 8 (PNPLA8)), possesses sn-1 specificity, with polyunsaturated fatty acids at the sn-2 position generating polyunsaturated sn-2-acyl lysophospholipids. Through strategic chemical derivatization, chiral chromatographic separation, and multistage tandem MS, here we first demonstrate that human platelet-type 12-lipoxygenase (12-LOX) can directly catalyze the regioselective and stereospecific oxidation of 2-arachidonoyl-lysophosphatidylcholine (2-AA-LPC) and 2-arachidonoyl-lysophosphatidylethanolamine (2-AA-LPE). Next, we identified these two eicosanoid-lysophospholipids in murine myocardium and in isolated platelets. Moreover, we observed robust increases in 2-AA-LPC, 2-AA-LPE, and their downstream 12-LOX oxidation products, 12(S)-HETE-LPC and 12(S)-HETE-LPE, in calcium ionophore (A23187)-stimulated murine platelets. Mechanistically, genetic ablation of iPLA2γ markedly decreased the calcium-stimulated production of 2-AA-LPC, 2-AA-LPE, and 12-HETE-lysophospholipids in mouse platelets. Importantly, a potent and selective 12-LOX inhibitor, ML355, significantly inhibited the production of 12-HETE-LPC and 12-HETE-LPE in activated platelets. Furthermore, we found that aging is accompanied by significant changes in 12-HETE-LPC in murine serum that were also markedly attenuated by iPLA2γ genetic ablation. Collectively, these results identify previously unknown iPLA2γ-initiated signaling pathways mediated by direct 12-LOX oxidation of 2-AA-LPC and 2-AA-LPE. This oxidation generates previously unrecognized eicosanoid-lysophospholipids that may serve as biomarkers for age-related diseases and could potentially be used as targets in therapeutic interventions.
Keywords: eicosanoid, platelet, aging, lysophospholipid, calcium, 2-arachidonoyl-lysophospholipids, iPLA2γ, myocardium, platelet-type 12-lipoxygenase (12-LOX), polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs)
Introduction
Lipoxygenases (LOXs)2 are a class of widely distributed nonheme iron-containing enzymes that catalyze the regio- and stereospecific peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids containing one or more (cis,cis)-1,4-pentadiene segments within the aliphatic chain (1–5). The primary products of LOX-catalyzed reactions are typically chiral fatty acid hydroperoxides, which are rapidly transformed intracellularly by peroxidases into their corresponding hydroxyl analogs. Both hydroperoxyl lipoxygenase products and their reduced hydroxyl counterparts have been shown to serve a plethora of signaling functions in multiple cell types, tissues, and disease states (6–11).
The most abundant source of 12-LOX is blood platelets (4). Similarly, the most thoroughly studied mammalian lipoxygenase is the human platelet-type 12-LOX, which initially abstracts hydrogen at the C10 position of arachidonic acid (AA). Next, the stereospecific incorporation of molecular oxygen occurs at the C12 position resulting in the production of 12(S)-hydroperoxy-eicosatetraenoic acid (12(S)-HpETE) (5). The hydroperoxide is readily reduced intracellularly to generate 12(S)-hydroxy-eicosatetraenoic acid (12-HETE) (12, 13). Both 12(S)-HpETE and 12(S)-HETE are potent signaling ligands for multiple cellular receptors (e.g. G protein–coupled receptors) and also participate in nonreceptor-mediated regulatory functions as well (14, 15). Previous work demonstrated that 12-HpETE and 12-HETE promote the formation/activation of intracellular signaling complexes (16, 17). In addition, 12-LOX product 12-HETE can be re-esterified into lysophospholipids by acyl-CoA–dependent acyltransferases generating oxidized phospholipids with their own repertoire of unique biologic properties (6, 18). For example, incorporation of hydroxylated acyl chain lipids into cellular phospholipids alters membrane bilayer molecular dynamics and has multiple effects on complex transmembrane protein assembly through serving as a molecular scaffold (19). Remarkably, 12-LOX loss of function, through either genetic ablation or by pharmacologic inhibition, can reverse islet β-cell dysfunction and restore normal insulin secretion (20–26). Moreover, 12-HETE activates platelets thereby serving as an autocrine and paracrine amplification cascade (27–31). Despite the profound biological and clinical importance of the downstream oxidized products of 12-LOX, investigations have been limited to previously known substrates for oxidation (i.e. arachidonic acid). Thus, the roles of 12-LOX in generating previously unknown metabolites that serve novel signaling functions remain to be clarified.
Recent structural studies of 12-LOX have revealed the fatty acid pentadiene target is positioned in close spatial proximity to the nonheme iron facilitating regiospecific hydrogen radicubal abstraction and stereospecific reaction of the radical intermediate with molecular oxygen to collectively result in the production of the chiral 12(S)-HpETE product (5, 24, 32, 33). Notably, the crystal structure of the 12-LOX catalytic domain possesses a U-shaped substrate-binding site that facilitates the precise positioning of the C10 hydrogens in arachidonic acid for the regioselective and stereospecific oxidization of AA resulting in the production of 12(S)-HpETE (32). The open U-shape substrate-binding site of 12-LOX appeared large enough to accommodate the associated polar head group of 2-AA-lysophospholipids. Accordingly, we hypothesized that the entry of the arachidonoyl moiety of 2-AA-lysophospholipids into the active site and stereospecific oxidation appeared likely. Furthermore, the presence of the zwitterionic polar head group in 2-AA-LPC or 2-AA-LPE may allow further molecular interactions to stabilize the arachidonate moiety of 2-AA-lysophospholipids in the active site.
Previously, we identified a novel calcium-independent phospholipase, phospholipase A2γ (also known as PNPLA8) that catalyzes the highly regioselective (over 90%) cleavage of phospholipids at the sn-1 position (with a polyunsaturated fatty acid at the sn-2 position) resulting in the generation of 2-acyl-lysophospholipids (34). To gain further insight into the role of iPLA2γ in cardiac function, we generated germline iPLA2γ−/− mice by eliminating the active site of the enzyme. Genetic ablation of iPLA2γ resulted in growth retardation, compromised thermal adaption to cold, reduced exercise endurance, and a surprising ability of iPLA2γ−/− mice to remain refractory to the development of obesity and insulin resistance during prolonged HF feeding. We did not observe significant changes of the longevity between WT and iPLA2γ−/− mice (35, 36). Moreover, lipidomic analysis revealed that genetic ablation of iPLA2γ−/− resulted in over a 60% decrease in the production of 2-[14C]arachidonoyl-LPC from 1-palmitoyl 2-[14C]arachidonoyl-PC in incubations with mitochondrial homogenates prepared from iPLA2γ−/− mice (35). The regiospecificity of iPLA2γ for the sn-1 position of polyunsaturated phospholipids suggested the existence of a previously unknown signaling pathway initiated by the generation of 2-arachidonoyl-lysophosphatidylcholine, which serves as a signaling node for multiple lipid 2nd messenger cascades (37, 38).
Herein, we report the ability of platelet-type 12-LOX to efficiently catalyze the regioselective and stereospecific oxidization of both 2-AA-LPC and 2-AA-LPE into 12(S)-HpETE-LPC and 12(S)-HpETE-LPE, which are readily reduced to 12(S)-HETE-LPC and 12(S)-HETE-LPE both in vitro and in vivo, respectively. In addition, we show that multiple eicosanoid-lysophospholipid molecular species are present in myocardium and platelets with dynamic alterations after cellular stimulation. Finally, we demonstrated that aging in mice is accompanied by increased levels of 12-HETE-LPC in serum that are attenuated by genetic ablation of iPLA2γ. Collectively, these results identify previously unknown iPLA2γ-initiated signaling pathways mediated by direct 12-LOX oxidation of 2-arachidonoyl-lysophospholipids to generate previously unrecognized eicosanoid-lysophospholipid metabolites in critical cells of the cardiovascular system that could potentially serve as biomarkers of disease and inflammation during aging.
Results
12-LOX efficiently catalyzes the regioselective and stereospecific oxidation of 2-AA-LPC and 2-AA-LPE to 12(S)-HpETE-lysophospholipids
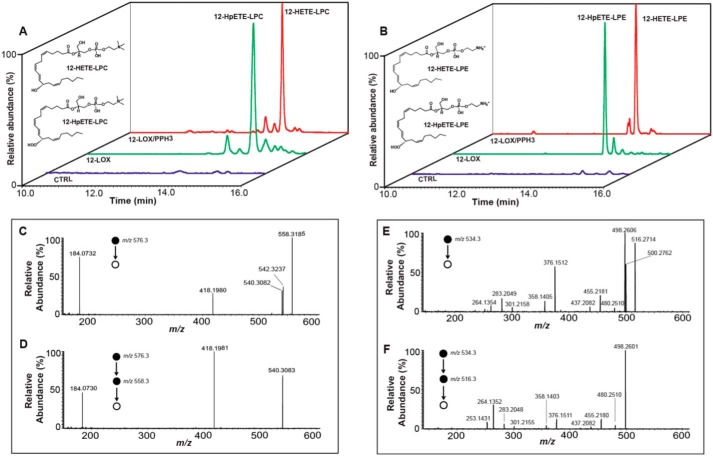
To test the hypothesis that 2-AA-lysophospholipids are efficient substrates for oxidation by 12-LOX, we first cloned, expressed, and purified recombinant human platelet-type 12-LOX as described under “Experimental procedures.” Additionally, we synthesized and purified 2-AA-LPC and 2-AA-LPE as previously described (34, 37–39). Next, we incubated 2-AA-LPC or 2-AA-LPE with purified 12-LOX. The reaction products were separated by HPLC and identified by high resolution high mass accuracy (HRAM) MS. Mass spectrometric analysis demonstrated the generation of previously unknown metabolites whose accurate masses and fragmentation patterns corresponded to the anticipated hydroperoxyl-oxidized eicosanoid-lysophospholipids (m/z 576.3291 for HpETE-LPC and m/z 534.2820 for HpETE-LPE, respectively) (Fig. 1, A and B). Multistage tandem MS with collision-induced dissociation (CID) fragmentation identified multiple informative fragment ions with the expected cleavage at the labile hydroperoxide bond and cleavage at the C12 position. Furthermore, accurate masses of the product ions were within 5 ppm of theoretical values and correspond to the likely fragmentation pathways (Figs. S1 and S2). Collectively, these experiments established the C12 regiochemistry of the 12-LOX–oxidized 2-AA-lysophospholipid products leading to their provisional assignments as 12-HpETE-LPC and 12-HpETE-LPE (Fig. 1, C–F).
Figure 1.
Chemical characterization of 12-LOX mediated oxidation products of 2-AA-LPC and 2-AA-LPE. Purified recombinant human platelet-type 12-LOX (2 μg) was incubated with 2-AA-LPC (10 μm) or 2-AA-LPE (10 μm) in 100 mm Tris-HCl buffer (pH 7.2) at 30 °C for 5 min. The reaction was terminated by addition of methanol and acidified to pH 4 with glacial acetic acid. The reaction products were then purified by solid-phase extraction followed by separation on a C18 HPLC column prior to analysis utilizing an LTQ-Orbitrap mass spectrometer with a mass resolution of 30,000 at m/z 400 in the positive ion mode. A, extracted ion chromatograms (with a 3 ppm mass window) for the identified metabolic products of 12-HpETE-LPC (m/z 576.3296) and 12-HETE-LPC (m/z 560.3347) are shown; triphenylphosphine (PPH3) was used to reduce 12-HpETE-LPC to 12-HETE-LPC. CTRL, negative control reaction without 12-LOX. B, extracted ion chromatograms (with a 3 ppm mass window) for the identified metabolic products of 12-HpETE-LPE (m/z 534.2826) and 12-HETE-LPE (m/z 518.2877) are shown. PPH3 was used to reduce 12-HpETE-LPE to 12-HETE-LPE. CTRL, negative control reaction without 12-LOX, C, MS2 spectrum of the parent M+ ion (12-HpETE-LPC) at m/z 576.3. D, resultant MS3 spectrum of the fragment ions derived from the ion at m/z 558.3 (576.3 → 558.3). E, MS2 spectrum of the parent M+ ion (12-HpETE-LPE) at m/z 534.3. F, resultant MS3 spectrum of the fragment ions derived from the ion at m/z 516.3 (534.3 → 516.3). The chemical identities of the fragmentation product ions are described under supporting Figs. S1 and S2.
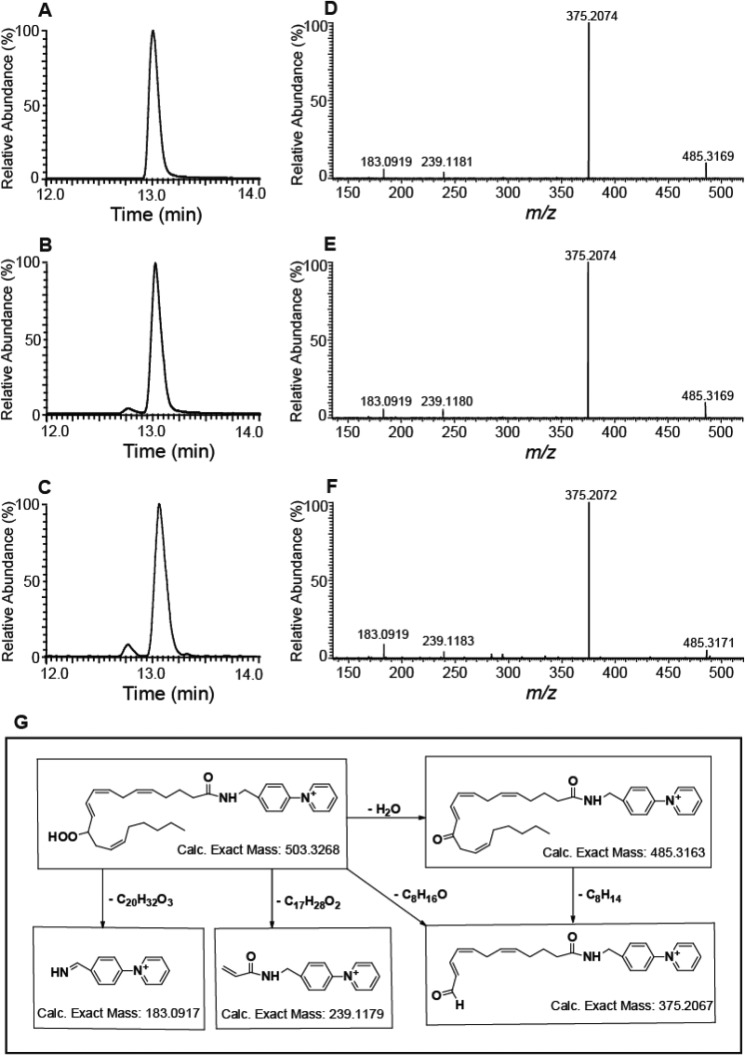
To further substantiate the proposed assignments by an independent method, we prepared and purified human recombinant cytosolic phospholipase A2α. Next, we treated the 12-LOX–generated eicosanoid-lysophospholipids with the purified recombinant cPLA2α to hydrolyze the sn-2 acyl chain (40–42). The released fatty acids were derivatized with N-(4-amino-methylphenyl)-pyridinium (AMPP), and the resultant AMPP-eicosanoids were separated by RP-HPLC prior to identification by HRAM MS (43). The elution times and fragmentation patterns of the AMPP-derivatized eicosanoids originating from the 12-LOX–generated eicosanoid-lysophospholipids were indistinguishable from authentic eicosanoid fatty acid standards, thereby confirming the proposed structural assignments (Fig. 2).
Figure 2.
Identification of the eicosanoid-lysophospholipids generated by 12-LOX–catalyzed oxidation of 2-AA-LPC and 2-AA-LPE. 12-LOX–generated eicosanoid-lysophospholipids were treated with cPLA2α and the resultant released eicosanoids were chemically derivatized with AMPP, separated on a C18 HPLC column and analyzed by MS. A, retention time chromatogram of standard reference of AMPP-derivatized 12-HpETE. B, retention time chromatogram of the AMPP-derivatized eicosanoid product generated by cPLA2α-mediated hydrolysis of the 12-LOX oxidation product of 2-AA-LPC. C, retention time chromatogram of the AMPP-derivatized eicosanoid product generated by cPLA2α-mediated hydrolysis of the 12-LOX oxidation product of 2-AA-LPE. D, MS/MS product ion spectrum of standard reference 12-HpETE derivatized with AMPP. E, MS/MS product ion spectrum of the eicosanoid-AMPP derivative obtained from 12-LOX–mediated oxidation of 2-AA-LPC. F, MS/MS product ion spectrum of the eicosanoid-AMPP derivative obtained from 12-LOX–mediated oxidation of 2-AA-LPE. G, proposed fragmentation pathways upon CID leading to the observed product ions for 12-HpETE-AMPP. The measured product ions' masses are within 2 ppm (parts per million) error relative to the calculated theoretical masses.
Determination of the chirality of 12-LOX–generated eicosanoid-lysophospholipids
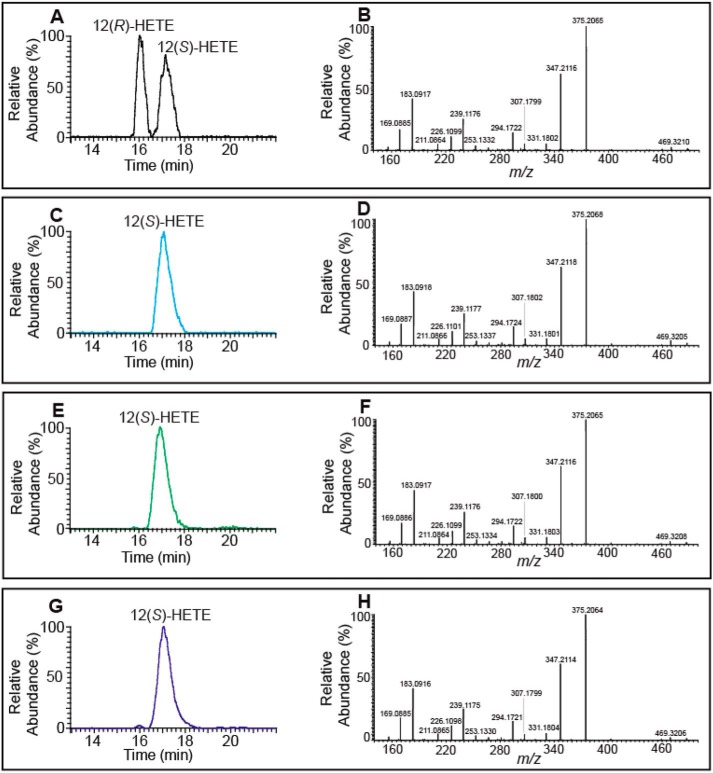
The stereochemistry of the 12-LOX–generated eicosanoid-lysophospholipid products were determined using chiral HPLC to separate the (R)- and (S)-stereoisomers of the AMPP-derivatized eicosanoids by comparisons with authentic standards. Mass spectrometric analysis of the separated reaction products revealed that 12-LOX–mediated oxidation of the arachidonoyl group of 2-AA-lysophospholipids yielded almost exclusively (>99%) the S-enantiomeric configuration (Fig. 3).
Figure 3.
Chiral-phase HPLC-MS analyses of the 12-HETE-AMPP derivatives generated by 12-LOX–catalyzed oxidation of 2-AA-LPC and 2-AA-LPE. 12-LOX generated hydroperoxy eicosanoid-lysophospholipids were treated with cPLA2α and then reduced by triphenylphosphine. Next, the resultant eicosanoid products were derivatized with AMPP and analyzed by chiral-phase HPLC-MS. A, chromatogram of standard racemic AMPP-derivatized 12(R/S)-HETE. B, MS/MS product ion spectrum of standard reference racemic AMPP-derivatized 12(R/S)-HETE. C, chromatogram of standard AMPP-derivatized 12(S)-HETE. D, MS/MS product ion spectrum of standard 12(S)-HETE; E, chromatogram of the AMPP-derivatized eicosanoid(s) originating from the 12-LOX oxidation products of 2-AA-LPC. F, MS/MS product ion spectrum of the AMPP-derivatized eicosanoid(s) originating from the 12-LOX oxidation products of 2-AA-LPC. G, chromatogram of the AMPP-derivatized eicosanoid(s) originating from the 12-LOX oxidation products of 2-AA-LPE. H, MS/MS product ion spectrum of the AMPP-derivatized eicosanoid(s) originating from the 12-LOX oxidation products of 2-AA-LPE.
Kinetics of 12-LOX–mediated oxidation of 2-AA-LPC and 2-AA-LPE
Next, we determined the apparent kinetic values of 12-LOX–mediated oxidation of both 2-AA-LPC and 2-AA-LPE substrates using substrate concentrations varying from 5 to 80 μm. The results (Table S1) revealed that human platelet-type 12-LOX is capable of metabolizing 2-AA-LPC more rapidly than 2-AA-LPE by a factor of 1.9. Mouse platelet 12-LOX also shows the similar trend of substrate preference but there is no statistically significant difference under the conditions examined.
12-LOX–mediated oxidation of 2-AA-LPC and 2-AA-LPE is potently inhibited by ML355 (N-2-benzothiazolyl-4-[[(2-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)methyl] amino]-benzenesulfonamide)
Previous work has demonstrated that ML355 is a potent and selective inhibitor of 12-LOX–mediated generation of 12-HpETE from arachidonic acid (44). To further establish the role of 12-LOX in the oxidation of 2-AA-lysophospholipids, recombinant human or mouse platelet-type 12-LOX was preincubated with ML355 prior to addition of 2-AA-LPC or 2-AA-LPE substrates. Analysis of the reaction extracts by LC-MS demonstrated that production of 12-HpETE-LPC and 12-HpETE-LPE by either human or mouse platelet-type 12-LOX were dramatically inhibited (>80%) by ML355 (Fig. 4). Utilization of HRAM MS in conjunction with multistage tandem MS CID fragmentation analysis and pharmacologic inhibition collectively identify 12-LOX as an efficient enzymatic mediator of the production of the identified eicosanoid-lysophospholipids from 2-arachidonoyl-lysophospholipids. These novel moieties have the potential to serve as metabolic and signaling nodes for a wide range of eicosanoid phospholipids after acyl transferase activity (or transacylase activity) or alternatively through the release of nonesterified eicosanoids after hydrolysis.
Figure 4.
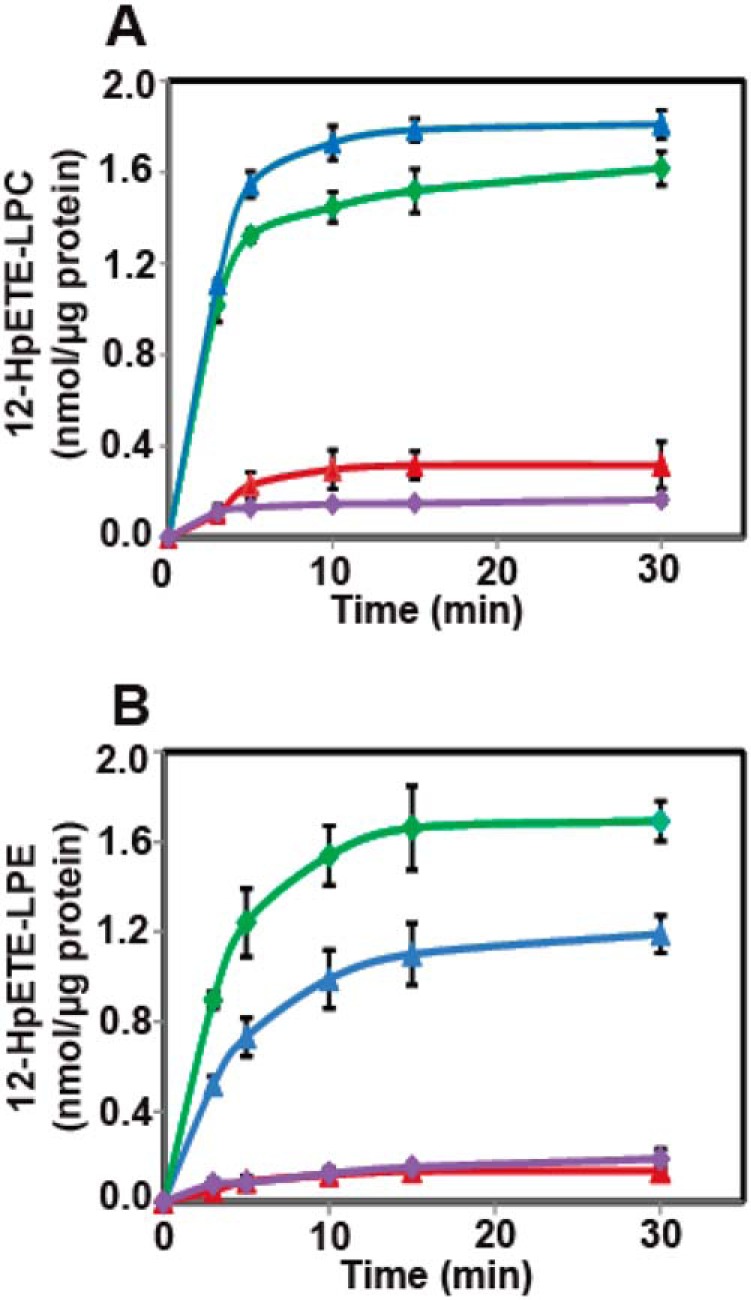
Platelet-type 12-LOX–mediated oxidation of 2-AA-LPC and 2-AA-LPE is inhibited by ML355. Purified recombinant human or mouse 12-LOX was incubated with either 2-AA-LPC (10 μm) or 2-AA-LPE (10 μm) at 30 °C for the indicated times. The reaction was then terminated with methanol and the resultant products were enriched by solid-phase extraction prior to analysis by LC-MS. For inhibition experiments, purified recombinant 12-LOX was preincubated with ML355 (1.0 μm) for 15 min prior to incubation with 2-AA-LPC or 2-AA-LPE. A, time course of 12-LOX–mediated oxidation of 2-AA-LPC and its inhibition by ML355 ((human 12-LOX (blue triangles), mouse 12-LOX (green diamonds); human 12-LOX with ML355 (red triangles), and mouse 12-LOX with ML355 (purple diamonds)). B, time course of 12-LOX–mediated oxidation of 2-AA-LPE and its inhibition by ML355 ((human 12-LOX (blue triangles), mouse 12-LOX (green diamonds), human 12-LOX with ML355 (red triangles), and mouse 12-LOX with ML355 (purple diamonds)). Data are expressed as mean ± S.E. of three replicate experiments.
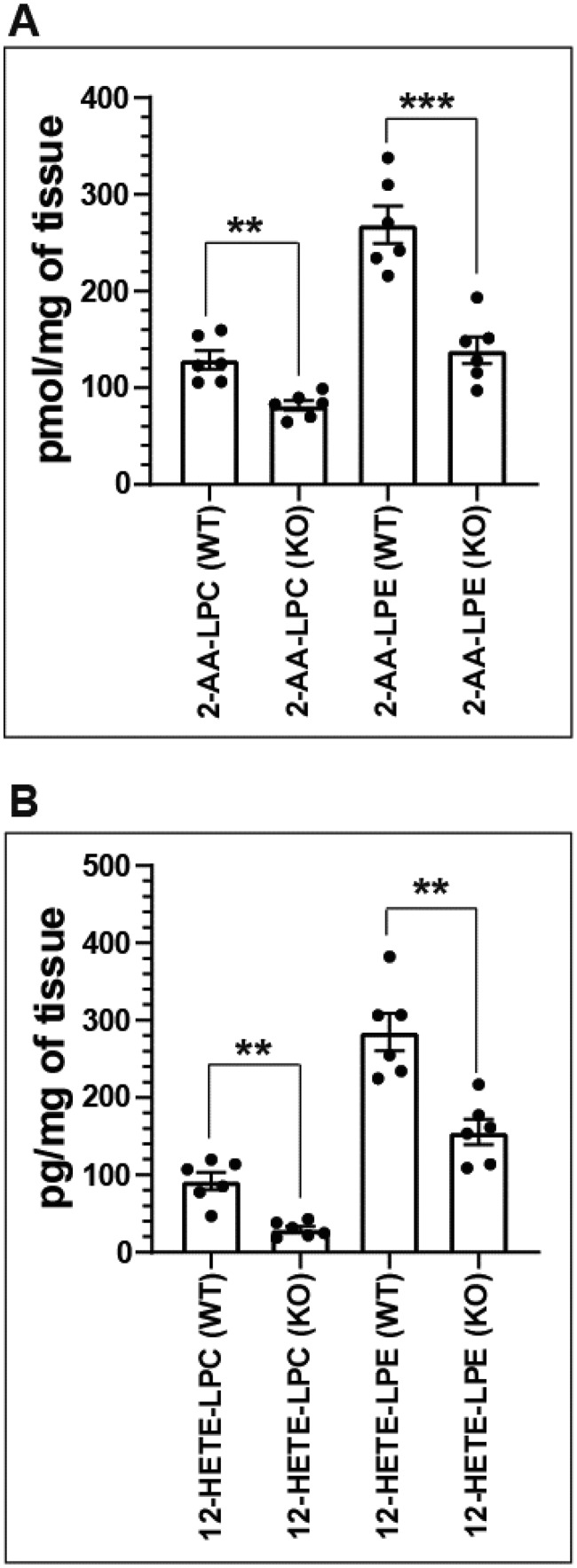
Genetic ablation of iPLA2γ markedly attenuates the production of 12-HETE-lysophospholipids in murine myocardium
To determine whether the identified 12-LOX–generated eicosanoid-lysophospholipids were present in murine myocardium and if their production depended upon iPLA2γ, we compared WT versus germline iPLA2γ−/− mice generated in our laboratory (35). Lipids from freshly isolated murine heart tissue of WT and germline iPLA2γ−/− mice were extracted using a modified Bligh and Dyer procedure, enriched for eicosanoid-lysophospholipids by solid-phase extraction, and analyzed by LC-MS/MS as described under “Experimental procedures.” Genetic ablation of iPLA2γ resulted in a marked reduction of both 2-AA-LPC and 2-AA-LPE in murine myocardium (Fig. 5A). Furthermore, the amounts of their respective 12-LOX oxidation products, 12-HETE-LPC and 12-HETE-LPE, were also markedly decreased in myocardial tissue from iPLA2γ−/− mice compared with their WT littermates (Fig. 5B). The results demonstrate that 12-HETE-lysophospholipids are present in murine myocardium and that their production is initiated by iPLA2γ.
Figure 5.
Genetic ablation of iPLA2γ markedly attenuates the production of 2-AA-lysophospholipids and 12-HETE-lysophospholipids in murine myocardium. Murine myocardial tissue was isolated from wildtype (WT) and iPLA2γ knockout (KO) mice and flash frozen in liquid nitrogen prior to lipid extraction using a modified Bligh and Dyer (56) procedure. The myocardial lipid extracts were purified by solid-phase extraction and analyzed by HPLC-MS/MS. A, contents of 2-AA-LPC and 2-AA-LPE in mouse heart tissue from WT and KO mice. B, contents of 12-HETE-LPC and 12-HETE-LPE in mouse heart tissue from WT and KO mice. Data are expressed as mean ± S.E. of six independent replicates. Statistical analyses were performed using an unpaired two-tailed Student's t test. p values for the bracketed data sets are as indicated (**, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001).
Calcium ionophore stimulates the production of 12-HETE-lysophospholipids in murine platelets, which is inhibited by genetic knockout of iPLA2γ
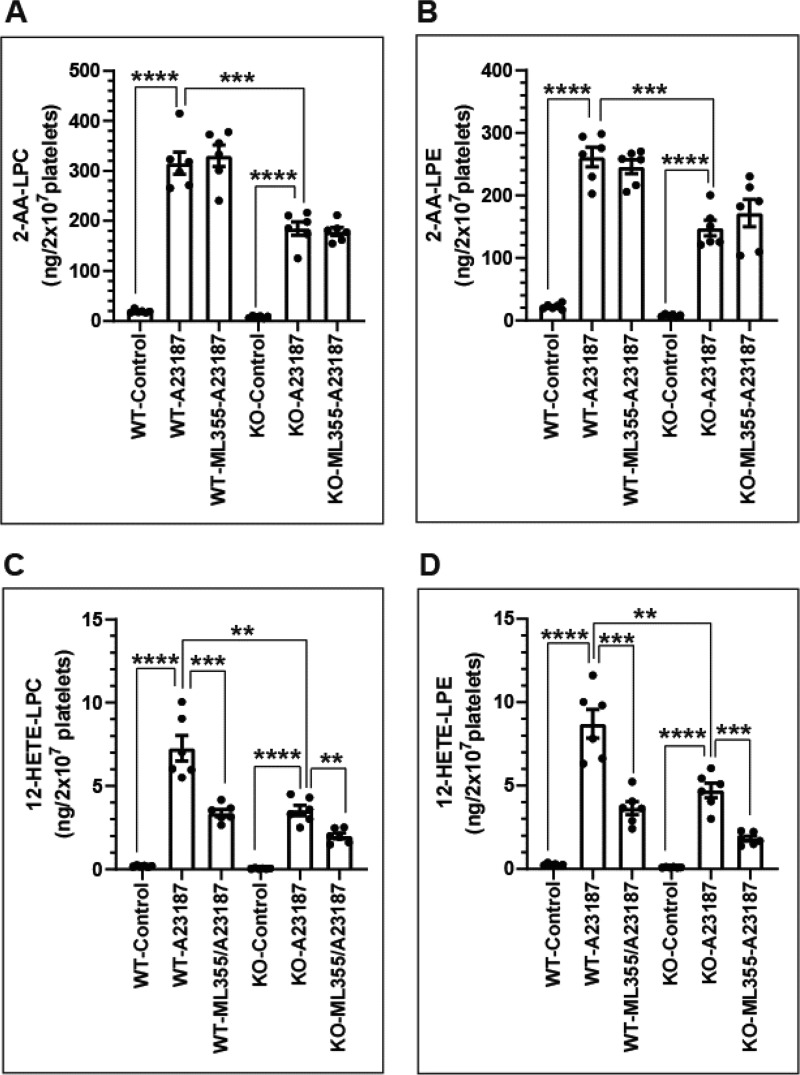
Next, to mechanistically identify the role of iPLA2γ in the release of 2-AA-lysophospholipids and subsequent production of 12-LOX eicosanoid-lysolipids in intact platelets, we stimulated murine platelets with calcium ionophore. Platelets from WT and germline iPLA2γ−/− mice were treated with either the vehicle (DMSO) alone or the calcium ionophore A23187 (1.0 μm). Ionophore-mediated calcium influx induced a robust increase in the levels of both 2-AA-LPC and 2-AA-LPE in WT platelets, which was markedly decreased in iPLA2γ knockout platelets in comparisons to WT littermate controls (Fig. 6, A and B). Notably, abundant amounts of 1-AA-LPC and 1-AA-LPE were also detected in platelets under the experimental conditions employed (Fig. S3). Previous work has indicated that the rate of α-hydroxy migration from the sn-2 carbon to the sn-1 carbon is influenced by multiple factors including pH and ionic strength (45). In the current work, we investigated acyl migration for 2-AA-LPC and 2-AA-LPE at selected pH values (Fig. S4). The results demonstrated that the acyl migration rate from the sn-2 position to the sn-1 position is highly dependent upon the pH of the solution. Although we cannot entirely rule out the direct synthesis of 1-AA-LPC and 1-AA-LPE in vivo (i.e. di-AA-PC and di-AA-PE, which can be hydrolyzed by PLA2 enzymes (e.g. cPLA2α) to generate 1-AA-LPC and 1-AA-LPE), we conclude that the majority of the 1-AA-lysophospholipids detected in platelets likely result from the cellular synthesis of 2-AA-lysophospholipids followed by nonenzymatic α-hydroxyl acyl migration.
Figure 6.
Calcium-dependent generation of 12-HETE-lysophospholipids in murine platelets isolated from WT and iPLA2γ−/− (KO) mice stimulated with calcium ionophore A23187. Washed platelets were incubated in the absence or presence of the calcium ionophore A23187 (1.0 μm) at 37 °C for 15 min prior to extraction of lipids using a modified Bligh and Dyer (56) procedure and analysis by HPLC-MS/MS. For inhibition experiments, ML355 (10 μm) was preincubated for 15 min prior to addition of A23187. A and B, content of 2-AA-LPC (A) and 2-AA-LPE (B) in the absence (DMSO) (Control) or presence (A23187) of calcium ionophore A23187 or ML355 and A23187 (ML355-A23187) in platelets from WT or KO mice. C and D, content of 12-HETE-LPC (C) and 12-HETE-LPE (D) in the absence (DMSO) (Control) or presence (A23187) of calcium ionophore A23187 or ML355 and A23187 (ML355-A23187) in platelets from WT or KO mice. Data are expressed as mean ± S.E. of six independent replicates. Statistical analyses were performed using an unpaired two-tailed Student's t test. Statistically significant p values are as indicated above the bracketed data sets (**, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001).
Importantly, the generation of 12-HETE-lysophospholipids in platelets was increased by the influx of calcium ion, which induced a robust increase in the levels of both 12-HETE-LPC and 12-HETE-LPE in WT platelets (Fig. 6, C and D). In stark contrast, genetic ablation of iPLA2γ markedly decreased the calcium-stimulated production of 12-LOX–derived eicosanoid-lysophospholipids in iPLA2γ−/− platelets relative to WT littermate controls (Fig. 6, C and D). Moreover, ML355 did not change the production of 2-AA-LPC and -LPE, but it significantly inhibited the production of 12-HETE-LPC and -LPE (Fig. 6).
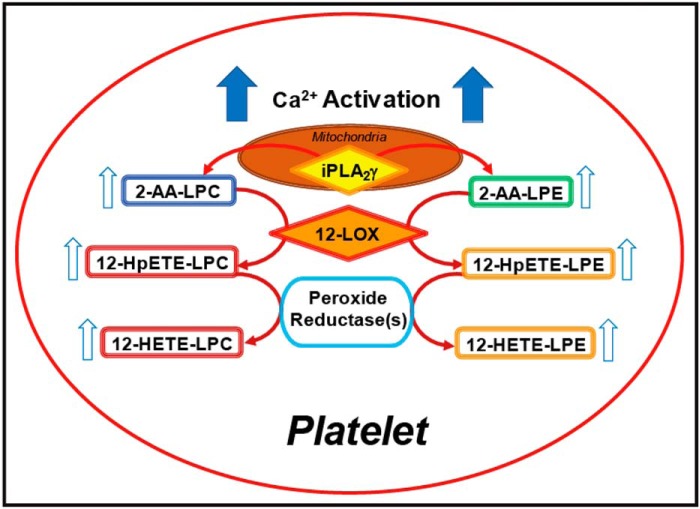
Because calcium activates iPLA2γ to produce 2-AA-lysophospholipids from arachidonate-containing phospholipids (37), these results indicate that the production of 2–12–HETE-lysophospholipids in platelets is initiated by iPLA2γ–mediated PLA1 hydrolysis of AA-phospholipids to produce 2-AA-lysophospholipids that can then be directly oxidized by 12-LOX to generate 2–12–HETE-lysophospholipids (Fig. 7). Furthermore, these results suggest that 12-HETE or its lysophospholipid derivatives released from parent phospholipids may participate in either autocrine or paracrine amplification cascades.
Figure 7.
Proposed pathways of iPLA2γ initiated production of arachidonate-containing lysophospholipids for 12-LOX–mediated generation of eicosanoid-lysophospholipids in murine platelets. Calcium-mediated activation of mitochondrial iPLA2γ results in the production of 2-AA-LPC and 2-AA-LPE, which are substrates for platelet-type 12-LOX for oxidation to 12-HpETE-LPC and 12-HpETE-LPE, respectively. The resulting hydroperoxide lysophospholipids are subsequently reduced to their corresponding hydroxyl molecular species by peroxide reductases (e.g. GSH peroxidases).
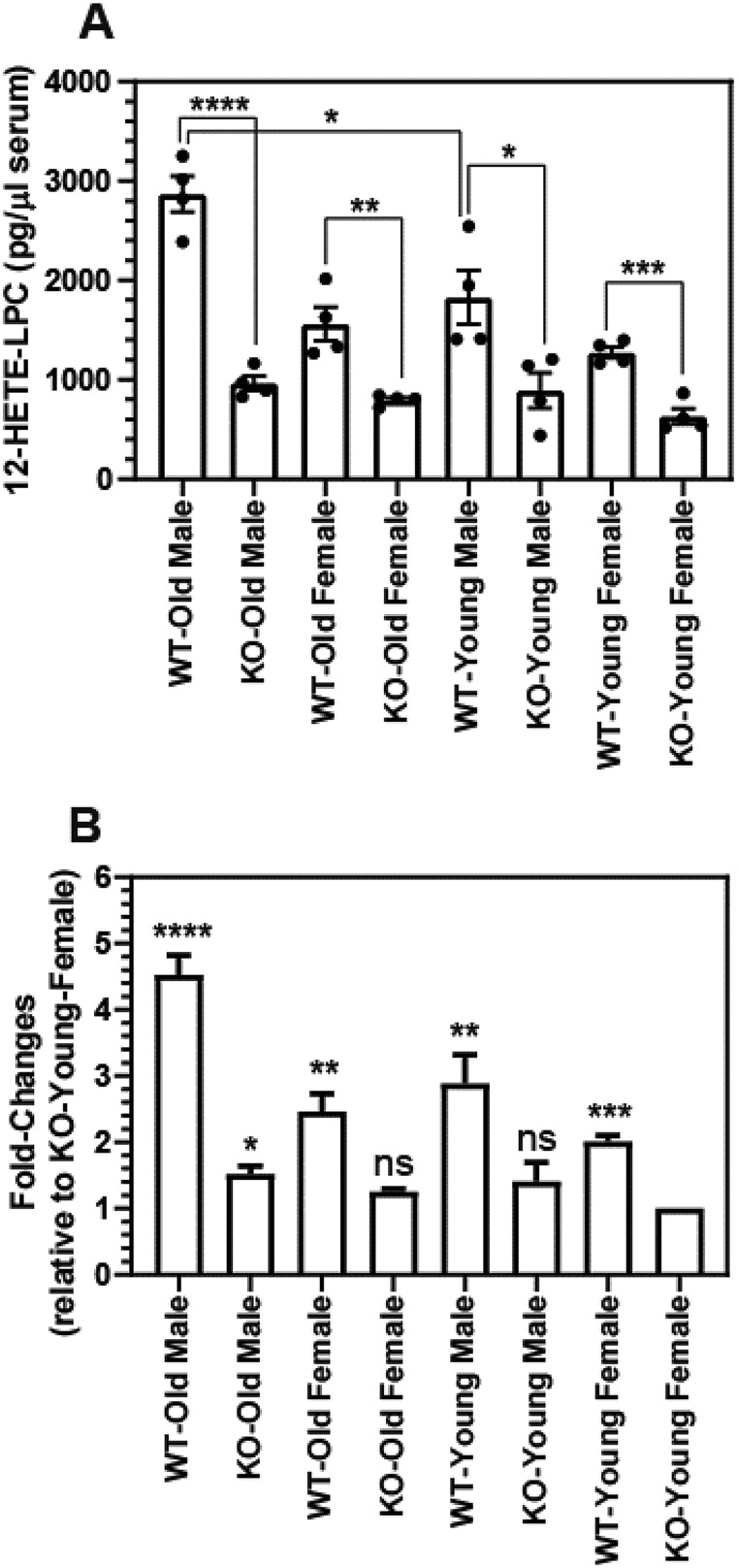
Eicosanoid-lysophospholipids increase with aging in murine serum, demonstrate gender-related differences, and are markedly attenuated in iPLA2γ−/− mice
Aging is known to result in substantial changes in serum lipids (46, 47) and sex differences in free eicosanoids production have been observed (48, 49). However, alterations in eicosanoid-lysophospholipid levels during aging or comparisons of male versus female mice have not been previously made. To gain insight into potential age- and gender-related changes in eicosanoid-lysophospholipid levels, we analyzed the amount of 12-HETE-LPC in serum from young (3-month-old) and old (10-month-old) male and female WT and iPLA2γ−/− mice. Notably, a 2-fold increase in serum 12-HETE-LPC was observed in 10-month-old male mice compared with 3-month-old male mice (Fig. 8). Furthermore, serum 12-HETE-LPC was markedly attenuated in iPLA2γ−/− male mice (∼65% decrease) relative to WT controls (Fig. 8). In contrast, we identified only modestly increased amounts of 12-HETE-LPC in serum from female mice during aging. Genetic ablation of iPLA2γ in female mice resulted in similar decreases relative to their WT controls as observed in the serum of male mice (Fig. 8). Collectively, these results demonstrate that aging is accompanied by marked increases in 12-HETE-LPC in male murine serum and imply that 12-HETE-LPC may serve as a gender-specific biomarker for various age-associated diseases.
Figure 8.
Altered levels of 12-HETE-LPC in the serum of old and young male and female WT and iPLA2γ−/− (KO) Mice. Murine serum was collected from young (3 months) and old (10 months) WT and iPLA2γ KO male and female mice. Serum lipids were extracted using a modified Bligh and Dyer (56) procedure. The lipid extracts were purified by solid-phase extraction and analyzed for the content of 12-HETE-LPC by HPLC-MS/MS. Data are expressed as mean ± S.E. of four independent replicates. Statistical analyses were performed using an unpaired two-tailed Student's t test. A, content of 12-HETE-LPC. Statistically significant p values are indicated above the bracketed data sets; B, fold-changes relative to KO-Young females. Statistically significant p values are indicated relative to the KO-Young female. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.005; ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001.
Discussion
Previously, we demonstrated that calcium ion induces the activation of iPLA2γ leading to the production of 2-AA-LPC and 2-AA-LPE (37). Remarkably 2-arachidonoyl-lysophospholipids were directly oxidized by cyclooxygenase-2 to produce multiple eicosanoid-lysophospholipids including those containing either prostaglandin (e.g. prostaglandin E2) or other hydroxylated polyunsaturated aliphatic acyl chains (e.g. 11(R)-HETE and 15-HETE) that are major participants in signaling processes (38). These findings led us to investigate whether 2-arachidonoyl-lysophospholipids were substrates for the platelet-type 12-lipoxygenase, which is the predominant 12-LOX in most cellular systems (50). In the present study, we expressed and purified recombinant human platelet-type 12-LOX and demonstrated that 12-LOX regioselectively and stereospecifically oxidizes multiple classes of 2-AA-lysophospholipids to their corresponding 12(S)-HETE-lysophospholipid derivatives. Intriguingly, 2-arachidonoyl-glycerol was not detectably oxidized by platelet-type 12-LOX (51). In stark contrast, 2-AA-LPC and 2-AA-LPE are efficiently oxidized by platelet-type 12-LOX. This difference demonstrates an interesting substrate specificity of platelet-type 12-LOX suggesting that additional interaction sites for suitable orientation and efficient catalysis by platelet 12-LOX is necessary.
To mechanistically identify the enzyme(s) responsible for the production of these previously unknown natural products, a mouse model with germline ablation of exon 5 (encoding the active site) of iPLA2γ was utilized (35). Upon stimulation with calcium ionophore, the production of both 2-AA-LPC and 2-AA-LPE were dramatically increased in WT platelets. Parallel increases were also observed in 12-HETE-LPC and 12-HETE-LPE in WT platelets stimulated with calcium ionophore. In contrast, the synthesis of 2-AA-LPC, 2-AA-LPE, 12-HETE-LPC, and 12-HETE-LPE were significantly decreased after ionophore stimulation of platelets from iPLA2γ−/− mice compared with their WT controls. Moreover, ML355 significantly inhibited the production of 12-HETE-lysolipids; but the production of 2-AA-LPC and -LPE were not changed. These findings suggest a sequential process initiated by calcium-mediated activation of iPLA2γ to produce 2-AA-lysophospholipids followed by their subsequent 12-LOX-catalyzed oxidation to generate 12-(S)-HETE-lysophospholipids.
Oxidized lysophospholipids are anticipated to undergo rapid lateral motion in the membrane facilitating two-dimensional interactions to engage biological partners (e.g. receptors, ion channels, etc.). Furthermore, because the membrane limits 3D spatial interactions, membranes can serve as scaffolds for complex assemblies of biomolecules (19, 52, 53). Thus, 12(S)-HETE-lysophospholipids are predicted to have potent pleiotropic effects on cellular membrane structure, molecular dynamics, dipole interactions, membrane potentials, and scaffolds in addition to serving as potential ligands to cellular receptors.
Moreover, we note that these oxidized lysophospholipids are also excellent substrates for sn-1 acyltransferases and transacylases, which result in the production of oxidized phospholipids that have emerged as potent signaling molecules in many systems (54). We suggest that multiple discrete eicosanoid-lysophospholipids generate a rich repertoire of molecular entities that can interact with specific receptors, differently modulate membrane surface charge and protein dynamics, and potentially serve as DAMPs (damage-associated molecular patterns) or DAMP precursors to facilitate specific cellular receptors in injured tissues. The difficulty to demonstrate a bona fide interaction due to the rapidly changing products of this class of lipids should be recognized. We have begun the synthesis of a nonhydrolyzable analog as well as an analog missing the sn-1 hydroxyl to address this important point.
Previously, we demonstrated that the sn-1 vinyl ether linkage of plasmenylcholine and plasmenylethanolamine containing arachidonic acid at the sn-2 position can be oxidatively cleaved by oxidized cardiolipin-activated cytochrome c to yield 2-AA-LPC and 2-AA-LPE, respectively (i.e. plasmalogenase activity) (55). Thus, in addition to the production of 2-AA-lysophospholipids by iPLA2γ, it seems likely that a portion of the 2-arachidonoyl-lysophospholipids and their corresponding 12-LOX oxidation products observed in iPLA2γ−/− platelets is due to cleavage of the vinyl ether linkage of plasmenylethanolamine, which is rich in platelet membranes. Alternatively, other PLA1 activities, either known or as yet undiscovered, may contribute to the generation of sn-2-arachidonoyl-lysophospholipids. Additionally, these studies also demonstrate that eicosanoid-lysophospholipids can be directly hydrolyzed by a variety of intracellular phospholipases (e.g. cPLA2α) and lysophospholipases resulting in the liberation of nonesterified eicosanoids that are known to possess potent effects in multiple disease states including diabetes, cancer, cardiovascular disease, and endothelial dysfunction (6–8).
Collectively, the present study identifies previously unknown signaling metabolites emanating from the iPLA2γ-mediated sn-1 hydrolysis of arachidonate-containing phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine. The resultant 2-arachidonoyl-lysophospholipids are subsequently oxidized directly by 12-LOX to generate eicosanoid-lysophospholipids (Fig. 7). Furthermore, our results demonstrate that aging is associated with marked alterations in 12-HETE-lysophospholipid levels in murine serum that were markedly attenuated by iPLA2γ genetic ablation. Finally, our results identify high concentrations of eicosanoid-lysolipids in murine serum that are age and gender selective. Thus, these moieties or their downstream metabolites can potentially provide new biomarkers for discovery of age-related disease states such as Alzheimer's disease.
Experimental procedures
Expression and purification of human platelet-type 12-LOX
Human platelet-type 12-LOX containing an N-terminal (His)6 tag was constructed and inserted into the BamHI-HindIII sites of pFastbac1 (Invitrogen) by GenScript. The sequence and orientation verified the identity of the recombinant pFastBac1 containing human ALOX12, which was transfected into DH10Bac cells (InVitrogen). The Bac-to-Bac Baculovirus Expression System (Invitrogen) was subsequently utilized for bacmid preparation and CellFECTIN-mediated transfection of Spodoptera frugiperda (Sf9) cells to produce recombinant baculovirus, which was then amplified and titered by the Neutral Red agar overlay method according to the manufacturer's protocol (Invitrogen). Expression of the N-terminal His-tagged 12-LOX was initiated by infection of 100 ml of Sf9 cells (1 × 106 cells/ml) with recombinant virus at a multiplicity of infection of 1. After incubation for 68 h at 27 °C, the cells were pelleted by centrifugation at 900 × g for 10 min at 4 °C, resuspended in 2 ml of ice-cold hypotonic 0.1 × PBS with swelling on ice for 2 min. Swelling was then stopped by addition of 2 ml of ice-cold hypertonic 2× PBS containing 10 mm imidazole (pH 7.4), 40 μl of 0.1 m phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, and 2 μl of 10 mg/ml leupeptin. The Sf9 cells were then sonicated (20 × 1-s bursts utilizing a Vibra-cell sonicator at 50% output). After adding 10 μl of DNase I (1.0 unit/μl) and 40 μl of 20% Tween 20, the Sf9 cells were sonicated again (10 × 1-s bursts at 50% output), incubated for 5 min on ice, and centrifuged at 15,000 × g for 15 min at 4 °C. The supernatant was removed and the NaCl concentration was adjusted to 300 mm.
Purification of the recombinant 12-LOX was performed using nickel-nitrilotriacetic acid (Ni-NTA) metal-affinity chromatography per the manufacturer's protocol (Thermo Scientific number 88225). Briefly, the protein extract was loaded onto a Ni-NTA column that was pre-equilibrated with 3 × 10 ml of 2× PBS containing 25 mm imidazole (pH 7.4). After washing the column 6 times with 7.0 ml of 2× PBS containing 25 mm imidazole (pH 7.4) to remove nonspecifically bound proteins, the His-tagged 12-LOX was fractionally eluted with 9 × 1.0 ml of ice-cold 2× PBS containing 150 mm imidazole (pH 7.4). The presence of the recombinant 12-LOX was confirmed by ECL Western blot analysis using an anti-(His)6 mAb.
Expression and purification of human cPLA2α
The cDNA encoding human cPLA2α was subcloned to engineer a 6-residue histidine tag, His6, at the C terminus for purification using Ni-NTA affinity chromatography. Briefly, Sf9 cells (5 × 100-ml suspension cultures at 1 × 106 cells/ml) were infected with baculovirus-encoding recombinant cPLA2α(His)6 baculovirus (multiplicity of infection ∼1). After incubation at 27 °C for 72 h, the Sf9 cells expressing cPLA2α(His)6 were centrifuged (600 × g for 10 min) to remove the cell media. The resultant cell pellets were resuspended in 20 ml of lysis buffer (20 mm potassium Pi, pH 8.0, containing 2 mm imidazole, 10% glycerol, 5 μg/ml of leupeptin, 5 μg/ml of aprotinin), sonicated (20–25 bursts, 30% power), and centrifuged (600 × g for 5 min). The supernatant was removed (saved) and the remaining cell pellets were sonicated (20–25 bursts, 30% power) in an additional 20 ml of lysis buffer. The cell homogenates were then pooled and centrifuged (100,000 × g for 1 h) to obtain the cytosolic fraction. The cytosol containing cPLA2α(His)6 was diluted 1:1 in 20 mm potassium Pi (pH 8.0), 2 mm imidazole, 500 mm NaCl, 10% glycerol (Buffer A) and applied to a 3 ml of Ni-NTA column equilibrated with 20 mm potassium Pi (pH 8.0), 2 mm imidazole, 250 mm NaCl, 10% glycerol (Buffer B). After washing the column with 30 ml of Buffer A containing 10 mm imidazole, bound proteins were eluted with 20 mm potassium Pi (pH 8.0), 250 mm imidazole, 500 mm NaCl, 10% glycerol. Eluted proteins were dialyzed overnight against 10 mm Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) containing 0.1 mm EDTA and 10% glycerol. The dialyzed proteins containing cPLA2α(His)6 were next applied to a MonoQ FPLC column equilibrated with the same buffer. After washing the MonoQ column with 10 mm Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) containing 0.1 mm EDTA, and 10% glycerol, bound cPLA2α(His)6 was eluted with a 0–1.0 m NaCl linear gradient and assayed for activity using 1-palmitoyl-2-[1-14C]arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine in the presence of 50 mm Tris-HCl (pH 7.6) containing 1 mm CaCl2. Following addition of glycerol to 20%, active fractions were flash frozen in liquid N2 and stored at −80 °C prior to use.
Kinetic analysis of the 12-LOX–mediated oxidation of 2-AA-LPC or 2-AA-LPE
Time course experiments
Human or mouse platelet-type recombinant 12-LOX (mouse platelet-type 12-LOX was purchased from Cayman Chemicals Co., Ann Arbor, MI) (2 μg) was incubated with either 2-AA-LPC or 2-AA-LPE (10 μm) in 400 μl of 100 mm Tris-HCl buffer (pH 7.2) containing 10% glycerol at 30 °C for various times. The reaction was then terminated by adding 100 μl of methanol, acidified to pH 4 with glacial acetic acid and applied to a Strata-X solid-phase extraction cartridge previously preconditioned with 3 ml of methanol and equilibrated with 3 ml of 20% methanol, 80% H2O. After washing with H2O, the reaction products were eluted with methanol and analyzed by LC-MS methods as described below.
Inhibition of 12-LOX by ML355
Human or mouse platelet-type recombinant 12-LOX (2 μg) was incubated with ML355 (ML355 was purchased from Cayman Chemicals) (1.0 μm) in 400 μl of 100 mm Tris-HCl buffer (pH 7.2) containing 10% glycerol at 23 °C for 15 min. 2-AA-LPC or 2-AA-LPE were then added and the reactions were incubated for various times at 30 °C before termination with acidified methanol. The reaction products were isolated, concentrated, and purified by solid-phase extraction using Strata-X columns as described above and analyzed by LC-MS as described below.
Substrate concentration dependence experiments
Human or mouse platelet-type recombinant 12-LOX (2 μg) was incubated with varying concentrations of 2-AA-LPC or 2-AA-LPE (5 to 80 μm) in 400 μl of 100 mm Tris-HCl buffer (pH 7.2) containing 10% glycerol in a 30 °C water bath for 2 min. The reactions were then terminated, and the reaction products were analyzed by LC-MS as described below. The kinetic values of Km and Vmax were determined from a nonlinear least-squares best-fit of the data to the Michaelis-Menten equation using GraphPad Prism (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA).
Hydrolysis of eicosanoid-lysophospholipids by cPLA2α and identification of the released eicosanoid products
The eicosanoid-lysophospholipid products generated by 12-LOX were incubated with purified cPLA2α (5 μg) in 200 μl of HEPES buffer (10 mm HEPES, pH 7.4, 100 mm KCl, 0.5 mm CaCl2, and 10% glycerol) for 15 min at 37 °C. Reactions were stopped by addition of 50 μl of methanol followed by acidification of the reaction mixture to pH 4 with glacial acetic acid. Terminated reactions were immediately applied to a Strata-X solid-phase extraction cartridge (60 mg/ml) that had been previously preconditioned with 3 ml of methanol followed by sequential washing with 3 ml of 10% methanol, 90% H2O. After washing with 3 ml of H2O, the oxidized fatty acid metabolites were eluted with 2 × 0.5-ml volumes of methanol containing 1% glacial acetic acid. The combined acidified methanol eluates were evaporated to dryness using a SpeedVac concentrator prior to charge-switch derivatization with AMPP. Derivatization with AMPP was performed as previously described (43). Briefly, 20 μl of ice-cold acetonitrile/N,N-dimethylformamide (4:1, v/v) and 20 μl of ice-cold 640 mm (3-(dimethylamino)propyl)ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride in HPLC grade water were added to the dried residue in a sample vial. The vial was briefly vortexed and 40 μl of 5 mm N-hydroxyl benzotriazole and 15 mm AMPP in acetonitrile were added, vortexed, and placed in a 60 °C water bath for 30 min. Samples were then analyzed by LC-MSn using “C18 reverse phase HPLC-tandem MS” and “chiral-phase HPLC-tandem MS” (see below).
C18 reverse phase HPLC-tandem MS (LC-MSn)
LC-MSn analyses were performed using an LTQ-Orbitrap mass spectrometer (Thermo Scientific, San Jose, CA) equipped with a Surveyor HPLC system (Thermo Scientific). Briefly, solid-phase extractions of the 12-lipoxygenase reaction mixtures utilizing 2-AA-LPC or 2-AA-LPE as a substrate were separated on a C18 reversed phase column (Ascentis Express, 2.7-μm particles, 150 × 2.1 mm) at 23 °C using a linear gradient of solvent A (0.1% glacial acetic acid in water) and solvent B (0.1% glacial acetic acid in acetonitrile) at a flow rate of 0.2 ml/min. The following solvent gradient program was used: 0.0–5.0 min, 25% B; 5.0–7.0 min, 25–35% B; 7.0–20.0 min, 35–60% B; 20.0–20.1 min, 60–100% B; 20.1–28.0 min, 100% B; 28.0–28.1 min, 100% B to 25% B followed by 10 min isocratic re-equilibration at 25% B. The sample injection volume was 10 μl and the autosampler tray temperature was maintained at 4 °C throughout the analysis. Mass spectrometric analyses were performed using an LTQ-Orbitrap mass spectrometer. The LTQ ion source was operated in the positive ion mode at sheath, auxiliary, and sweep gas flows (arbitrary units) of 40, 5, and 1, respectively. The capillary temperature was set to 275 °C, and the electrospray voltage was 4.1 kV. Capillary voltage and tube lens voltage were set at 30 and 110 V, respectively. The mass spectrometer was calibrated using the manufacturer's recommended positive mode calibration solution containing l-methionyl-arginyl-phenylalanyl-alanine acetate, Ultramark 1621, and caffeine. Resolving powers (at m/z 400 Th) of 30,000 in full scan mode and in MS/MS mode were used. The mass accuracy was within 5 ppm at mass values from m/z 130 to 2000. For MS/MS analyses, a normalized collision energy of 30% was applied and the activation time was set at 30 ms with an activation parameter of q = 0.25. Data acquisition was performed using an Xcalibur operating system, version 2.1 (Thermo Scientific).
Chiral-phase HPLC-tandem MS
Chiral-phase LC-MSn analyses employing reverse phase LC were performed using an LTQ-Orbitrap mass spectrometer (Thermo Scientific) with a Surveyor HPLC system (Thermo Scientific). Briefly, AMPP-derivatized eicosanoids were injected and separated on a Chiralpak® AD-RH chiral-phase HPLC column (5.0-μm particles, 150 × 2.1 mm) at 23 °C using a linear gradient of solvent A (0.1% glacial acetic acid in water) and solvent B (0.1% glacial acetic acid in acetonitrile) at a flow rate of 0.2 ml/min. The following solvent gradient program was used: 0.0–1.0 min, 5–22% B; 1.0–7.0 min, 22–26% B; 7.0–7.1 min, 26–40% B; 7.1–20.0 min, 40–60% B; 20.0–21.0 min, 60–100% B; 21.0–29.0 min, 100% B prior to isocratic re-equilibration at 5% B for 10 min. The sample injection volume was 10 μl and the autosampler tray temperature was maintained at 4 °C throughout the analysis. Mass spectrometric analysis conditions were identical to those described above under “C18 reverse phase HPLC-tandem MS (LC-MSn).”
General animal studies
Animal protocols were conducted in strict accordance with the National Institutes of Health guidelines for humane treatment of animals and were reviewed and approved by the Animal Studies Committee of Washington University.
Murine myocardium sample preparation and analysis of eicosanoid-lysophospholipids
Murine heart tissue samples from control C57BL/6 and iPLA2γ−/− mice (35) were rapidly removed, flash frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored at −180 °C prior to analysis for eicosanoid-lysophospholipids. Myocardial tissues were extracted using a modified Bligh and Dyer (56) procedure. Briefly, ∼40 mg of tissue was extracted by addition of 3 ml of ice-cold CH3OH/CHCl3 (1:2 (v/v) containing 2% glacial acetic acid) followed directly by addition of 17:0-LPC as an internal standard. Next, the samples were homogenized using a Polytron homogenizer at 0–4 °C and 1 ml of ice-cold H2O was added prior to separation of the organic and aqueous phases by centrifugation at 1,500 × g for 15 min. The CHCl3 layer was transferred to a new tube, whereas the aqueous layer was re-extracted by subsequent addition of 2 ml of CHCl3, vortexing, and phase separation by centrifugation at 1,500 × g for 15 min. The CHCl3 extracts were combined, evaporated under a nitrogen stream, and resuspended in 100 μl of 80% methanol in water prior to LC-MS/MS analyses as described above.
Murine serum sample preparation and analysis of eicosanoid-lysophospholipids
Serum samples from 10- or 3-month-old control C57BL/6 mice and iPLA2γ−/− mice (35) were prepared by centrifugation of the blood collected from submandibular veins at 1,500 × g for 10 min after incubation for 30 min at room temperature. The serum was quickly removed and 10 μl of fresh serum were used for lipid extractions using a modified Bligh and Dyer procedure (56) and analysis by HPLC-MS/MS as described above.
Isolation and activation of platelets
Blood from control C57BL/6 and iPLA2γ−/− mice (35) was obtained by intracardiac puncture from euthanized mice. About 0.8 ml of blood was drawn into a syringe containing 0.15 ml of 3.8% sodium citrate to prevent platelet activation. The blood was then centrifuged at 150 × g for 10 min at room temperature, and the platelet-rich-plasma was subsequently centrifuged at 250 × g for 5 min to remove residual red blood cells. The purified platelet-rich-plasma was spun at 1,500 × g for 10 min, and the pellet was resuspended in Tyrode's buffer containing 0.38% sodium citrate. The platelets were pelleted by centrifuging at 800 × g for 10 min, resuspended in Tyrode's buffer containing 1.0 mm CaCl2 and incubated at 37 °C in the presence or absence of A23817 (1.0 μm) for 15 min. For inhibition experiments, ML355 (10 μm) was preincubated with the isolated platelets for 15 min prior to addition of A23187. Lipids were then extracted using a modified Bligh and Dyer (56) procedure and analyzed by HPLC-MS/MS as described above.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using the two-tailed Student's t test. p values of less than 0.05 were considered to be statistically significant. All data are reported as the mean ± S.E. unless otherwise noted.
Data availability
All data presented in this paper are contained within the manuscript.
Author contributions
X. L. and R. W. G. conceptualization; X. L. and B. G. D. resources; X. L. data curation; X. L., C. M. J., and R. W. G. formal analysis; X. L. and R. W. G. supervision; X. L. validation; X. L. and R. W. G. investigation; X. L. visualization; X. L. and R. W. G. methodology; X. L., C. M. J., and R. W. G. writing-original draft; X. L., B. G. D., and R. W. G. writing-review and editing; R. W. G. funding acquisition; R. W. G. project administration; H. F. S. prepared human platelet recombinant 12-LOX proteins; generated and provided iPLA2γ knockout mice for murine heart and platelet experiments; S. G. and B. G. D. provided iPLA2γ knockout mice for murine heart and platelet experiments; C. M. J. prepared human recombinant cPLA2α protein.
Supplementary Material
This work was supported, in whole or in part, by National Institutes of Health Grants RO1HL118639 and R01HL133178 (to R. W. G.). The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
This article contains Figs. S1–S4.
- 12-LOX
- 12-lipoxygenase
- iPLA2γ
- calcium-independent phospholipase A2γ
- cPLA2α
- cytosolic phospholipase A2α
- PPH3
- triphenylphosphine
- AA-LPC
- arachidonoyl-lysophosphatidylcholine
- AA-LPE
- arachidonoyl-lysophosphatidylethanolamine
- 12-HETE
- 12-hydroxy-eicosatetraenoic acid
- 12-HpETE
- 12-hydroperoxy-eicosatetraenoic acid
- ML355
- N-2-benzothiaoly-4-[[(2-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]amino]-benzenesulfonamide
- HRAM
- high resolution high mass accuracy
- CID
- collision-induced dissociation
- Ni-NTA
- nickel-nitrilotriacetic acid
- AA
- arachidonic acid.
References
- 1. Hamberg M., and Hamberg G. (1980) On the mechanism of the oxygenation of arachidonic acid by human platelet lipoxygenase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 95, 1090–1097 10.1016/0006-291X(80)91584-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Yamamoto S. (1992) Mammalian lipoxygenases: molecular structures and functions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1128, 117–131 10.1016/0005-2760(92)90297-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Brash A. R. (1999) Lipoxygenases: occurrence, functions, catalysis, and acquisition of substrate. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 23679–23682 10.1074/jbc.274.34.23679 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Haeggström J. Z., and Funk C. D. (2011) Lipoxygenase and leukotriene pathways: biochemistry, biology, and roles in disease. Chem. Rev. 111, 5866–5898 10.1021/cr200246d [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Newcomer M. E., and Brash A. R. (2015) The structural basis for specificity in lipoxygenase catalysis. Protein Sci. 24, 298–309 10.1002/pro.2626 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Morgan A. H., Dioszeghy V., Maskrey B. H., Thomas C. P., Clark S. R., Mathie S. A., Lloyd C. M., Kühn H., Topley N., Coles B. C., Taylor P. R., Jones S. A., and O'Donnell V. B. (2009) Phosphatidylethanolamine-esterified eicosanoids in the mouse: tissue localization and inflammation-dependent formation in Th-2 disease. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 21185–21191 10.1074/jbc.M109.021634 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Kuhn H., Banthiya S., and van Leyen K. (2015) Mammalian lipoxygenases and their biological relevance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1851, 308–330 10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.10.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Moon S. H., Liu X., Cedars A. M., Yang K., Kiebish M. A., Joseph S. M., Kelley J., Jenkins C. M., and Gross R. W. (2018) Heart failure-induced activation of phospholipase iPLA2γ generates hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids opening the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. J. Biol. Chem. 293, 115–129 10.1074/jbc.RA117.000405 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Tersey S. A., Bolanis E., Holman T. R., Maloney D. J., Nadler J. L., and Mirmira R. G. (2015) Minireview: 12-lipoxygenase and islet beta-cell dysfunction in diabetes. Mol. Endocrinol. 29, 791–800 10.1210/me.2015-1041 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Dobrian A. D., Lieb D. C., Cole B. K., Taylor-Fishwick D. A., Chakrabarti S. K., and Nadler J. L. (2011) Functional and pathological roles of the 12- and 15-lipoxygenases. Prog. Lipid Res. 50, 115–131 10.1016/j.plipres.2010.10.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Ackermann J. A., Hofheinz K., Zaiss M. M., and Krönke G. (2017) The double-edged role of 12/15-lipoxygenase during inflammation and immunity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1862, 371–381 10.1016/j.bbalip.2016.07.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Hamberg M., and Samuelsson B. (1974) Prostaglandin endoperoxides: novel transformations of arachidonic acid in human platelets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 71, 3400–3404 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3400 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Siegel M. I., McConnell R. T., Porter N. A., and Cuatrecasas P. (1980) Arachidonate metabolism via lipoxygenase and 12L-hydroperoxy-5,8,10,14-icosatetraenoic acid peroxidase sensitive to anti-inflammatory drugs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 77, 308–312 10.1073/pnas.77.1.308 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Ruzicka T. (1992) The role of the epidermal 12-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid receptor in the skin. Eicosanoids 5, S63–S65 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Guo Y., Zhang W., Giroux C., Cai Y., Ekambaram P., Dilly A. K., Hsu A., Zhou S., Maddipati K. R., Liu J., Joshi S., Tucker S. C., Lee M., and Honn K. V. (2011) Identification of the orphan G protein-coupled receptor GPR31 as a receptor for 12-(S)-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 33832–33840 10.1074/jbc.M110.216564 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Herbertsson H., Kühme T., Evertsson U., Wigren J., and Hammarström S. (1998) Identification of subunits of the 650 kDa 12(S)-HETE binding complex in carcinoma cells. J. Lipid Res. 39, 237–244 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Liu B., Khan W. A., Hannun Y. A., Timar J., Taylor J. D., Lundy S., Butovich I., and Honn K. V. (1995) 12(S)-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid and 13(S)-hydroxy-octadecadienoic acid regulation of protein kinase C-α in melanoma cells: role of receptor-mediated hydrolysis of inositol phospholipids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 92, 9323–9327 10.1073/pnas.92.20.9323 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Thomas C. P., Morgan L. T., Maskrey B. H., Murphy R. C., Kühn H., Hazen S. L., Goodall A. H., Hamali H. A., Collins P. W., and O'Donnell V. B. (2010) Phospholipid-esterified eicosanoids are generated in agonist-activated human platelets and enhance tissue factor-dependent thrombin generation. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 6891–6903 10.1074/jbc.M109.078428 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Isaacson Y., Sherbourne C. D., Gross R. W., and Stenson W. F. (1990) The synthesis and molecular dynamics of phospholipids having hydroxylated fatty acids at the sn-2 position. Chem. Phys. Lipids 52, 217–226 10.1016/0009-3084(90)90117-A [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Hussain H., Shornick L. P., Shannon V. R., Wilson J. D., Funk C. D., Pentland A. P., and Holtzman M. J. (1994) Epidermis contains platelet-type 12-lipoxygenase that is overexpressed in germinal layer keratinocytes in psoriasis. Am. J. Physiol. 266, C243–C253 10.1152/ajpcell.1994.266.1.C243 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Liagre B., Vergne P., Rigaud M., and Beneytout J. L. (1997) Expression of arachidonate platelet-type 12-lipoxygenase in human rheumatoid arthritis type B synoviocytes. FEBS Lett. 414, 159–164 10.1016/S0014-5793(97)00904-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Virmani J., Johnson E. N., Klein-Szanto A. J., and Funk C. D. (2001) Role of “platelet-type” 12-lipoxygenase in skin carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett. 162, 161–165 10.1016/S0304-3835(00)00634-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Garreta A., Val-Moraes S. P., García-Fernandez Q., Busquets M., Juan C., Oliver A., Ortiz A., Gaffney B. J., Fita I., Manresa À., and Carpena X. (2013) Structure and interaction with phospholipids of a prokaryotic lipoxygenase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FASEB J. 27, 4811–4821 10.1096/fj.13-235952 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Yeung J., and Holinstat M. (2011) 12-Lipoxygenase: a potential target for novel anti-platelet therapeutics. Cardiovasc. Hematol. Agents Med. Chem. 9, 154–164 10.2174/187152511797037619 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Ma K., Xiao A., Park S. H., Glenn L, Jackson L., Barot T., Weaver J. R., Taylor-Fishwick D. A., Luci D. K., Maloney D. J., Mirmira R. G., Imai Y., and Nadler J. L. (2017) 12-Lipoxygenase inhibitor improves functions of cytokine-treated human islets and type 2 diabetic islets. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 102, 2789–2797 10.1210/jc.2017-00267 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Tersey S. A., Maier B., Nishiki Y., Maganti A. V., Nadler J. L., and Mirmira R. G. (2014) 12-Lipoxygenase promotes obesity-induced oxidative stress in pancreatic islets. Mol. Cell. Biol. 34, 3735–3745 10.1128/MCB.00157-14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Yeung J., Tourdot B. E., Fernandez-Perez P., Vesci J., Ren J., Smyrniotis C. J., Luci D. K., Jadhav A., Simeonov A., Maloney D. J., Holman T. R., McKenzie S. E., and Holinstat M. (2014) Platelet 12-LOX is essential for FcγRIIα-mediated platelet activation. Blood 124, 2271–2279 10.1182/blood-2014-05-575878 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Adili R., Holman T. R., and Holinstat M. (2015) Novel 12-LOX inhibitor ML355 attenuates platelet reactivity and impairs thrombus growth, stability and vessel occlusion in vivo. Blood 126, 3442 10.1182/blood.V126.23.3442.3442 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Adili R., Tourdot B. E., Mast K., Yeung J., Freedman J. C., Green A., Luci D. K., Jadhav A., Simeonov A., Maloney D. J., Holman T. R., and Holinstat M. (2017) First selective 12-LOX inhibitor, ML355, impairs thrombus formation and vessel occlusion in vivo with minimal effects on hemostasis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 37, 1828–1839 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.309868 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Tourdot B. E., and Holinstat M. (2017) Targeting 12-lipoxygenase as a potential novel antiplatelet therapy. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 38, 1006–1015 10.1016/j.tips.2017.08.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Ikei K. N., Yeung J., Apopa P. L., Ceja J., Vesci J., Holman T. R., and Holinstat M. (2012) Investigations of human platelet-type 12-lipoxygenase: role of lipoxygenase products in platelet activation. J. Lipid Res. 53, 2546–2559 10.1194/jlr.M026385 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Xu S., Mueser T. C., Marnett L. J., and Funk M. O. (2012) Crystal structure of 12-lipoxygenase catalytic-domain-inhibitor complex identifies a substrate-binding channel for catalysis. Structure 20, 1490–1497 10.1016/j.str.2012.06.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Kobe M. J., Neau D. B., Mitchell C. E., Bartlett S. G., and Newcomer M. E. (2014) The structure of human 15-lipoxygenase-2 with a substrate mimic. J. Biol. Chem. 289, 8562–8569 10.1074/jbc.M113.543777 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Yan W., Jenkins C. M., Han X., Mancuso D. J., Sims H. F., Yang K., and Gross R. W. (2005) The highly selective production of 2-arachidonoyl lysophosphatidyl-choline catalyzed by purified calcium-independent phospholipase A2γ. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 26669–26679 10.1074/jbc.M502358200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Mancuso D. J., Sims H. F., Han X., Jenkins C. M., Guan S. P., Yang K., Moon S. H., Pietka T., Abumrad N. A., Schlesinger P. H., and Gross R. W. (2007) Genetic ablation of calcium-independent phospholipase A2γ leads to alterations in mitochondrial lipid metabolism and function resulting in a deficient mitochondrial bioenergetic phenotype. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 34611–34622 10.1074/jbc.M707795200 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Mancuso D. J., Sims H. F., Yang K., Kiebish M. A., Su X., Jenkins C. M., Guan S., Moon S. H., Pietka T., Nassir F., Schappe T., Moore K., Han X., Abumrad N. A., and Gross R. W. (2010) Genetic ablation of calcium-independent phospholipase A2γ prevents obesity and insulin resistance during high fat feeding by mitochondrial uncoupling and increased adipocyte fatty acid oxidation. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 36495–36510 10.1074/jbc.M110.115766 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Moon S. H., Jenkins C. M., Liu X., Guan S., Mancuso D. J., and Gross R. W. (2012) Activation of mitochondrial calcium-independent phospholipase A2γ (iPLA2γ) by divalent cations mediating arachidonate release and production of downstream eicosanoids. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 14880–14895 10.1074/jbc.M111.336776 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Liu X., Moon S. H., Jenkins C. M., Sims H. F., and Gross R. W. (2016) Cyclooxygenase-2 mediated oxidation of 2-arachidonoyl-lysophospholipids identifies unknown lipid signaling pathways. Cell Chem. Biol. 23, 1217–1227 10.1016/j.chembiol.2016.08.009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Creer M. H., and Gross R. W. (1985) Separation of isomeric lysophospholipids by reverse phase HPLC. Lipids 20, 922–928 10.1007/BF02534778 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Pete M. J., and Exton J. H. (1996) Purification of a lysophospholipase from bovine brain that selectively deacylates arachidonoyl-substituted lysophosphatidylcholine. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 18114–18121 10.1074/jbc.271.30.18114 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Pete M. J., Wu D. W., and Exton J. H. (1996) Subcellular fractions of bovine brain degrade phosphatidylcholine by sequential deacylation of the sn-1 and sn-2 positions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1299, 325–332 10.1016/0005-2760(95)00225-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Dennis E. A., Cao J., Hsu Y. H., Magrioti V., and Kokotos G. (2011) Phospholipase A2 enzymes: physical structure, biological function, disease implication, chemical inhibition, and therapeutic intervention. Chem. Rev. 111, 6130–6185 10.1021/cr200085w [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Liu X., Moon S. H., Mancuso D. J., Jenkins C. M., Guan S., Sims H. F., and Gross R. W. (2013) Oxidized fatty acid analysis by charge switch derivatization, selected reaction monitoring, and accurate mass quantitation. Anal. Biochem. 442, 40–50 10.1016/j.ab.2013.06.014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Luci D. K., Jameson J. B. 2rd, Yasgar A., Diaz G., Joshi N., Kantz A., Markham K., Perry S., Kuhn N., Yeung J., Kerns E. H., Schultz L., Holinstat M., Nadler J. L., Taylor-Fishwick D. A., Jadhav A., Simeonov A., Holman T. R., and Maloney D. J. (2014) Synthesis and structure-activity relationship studies of 4-((2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzyl)amino)benzenesulfonamide derivatives as potent and selective inhibitors of 12-lipoxygenase. J. Med. Chem. 57, 495–506 10.1021/jm4016476 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Rouzer C. A., Ghebreselasie K., and Marnett L. J. (2002) Chemical stability of 2-arachidonylglycerol under biological conditions. Chem. Phys. Lipids 119, 69–82 10.1016/S0009-3084(02)00068-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Dorninger F., Moser A. B., Kou J., Wiesinger C., Forss-Petter S., Gleiss A., Hinterberger M., Jungwirth S., Fischer P., and Berger J. (2018) Alterations in the plasma levels of specific choline phospholipids in Alzheimer's disease mimic accelerated aging. J. Alzheimers Dis. 62, 841–854 10.3233/JAD-171036 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Morris J. K., Piccolo B. D., John C. S., Green Z. D., Thyfault J. P., and Adams S. H. (2019) Oxylipin profiling of Alzheimer's disease in nondiabetic and type 2 diabetic elderly. Metabolites 9, 177 10.3390/metabo9090177 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Pace S., Sautebin L., and Werz O. (2017) Sex-biased eicosanoid biology: Impact for sex differences in inflammation and consequences for pharmacotherapy. Biochem. Pharmacol. 145, 1–11 10.1016/j.bcp.2017.06.128 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Pace S., Rossi A., Krauth V., Dehm F., Troisi F., Bilancia R., Weinigel C., Rummler S., Werz O., and Sautebin L. (2017) Sex differences in prostaglandin biosynthesis in neutrophils during acute inflammation. Sci. Rep. 7, 3759 10.1038/s41598-017-03696-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Shayman J. A. (2016) Adding lyso-lipids to arachidonate metabolism sets the stage for new biology. Cell Chem. Biol. 23, 1175–1176 10.1016/j.chembiol.2016.10.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Moody J. S., Kozak K. R., Ji C., and Marnett L. J. (2001) Selective oxygenation of the endocannabinoid 2-arachidonylglycerol by leukocyte-type 12-lipoxygenase. Biochemistry 40, 861–866 10.1021/bi002303b [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Heffern C. T., Pocivavsek L., Birukova A. A., Moldobaeva N., Bochkov V. N., Lee K. Y., and Birukov K. G. (2013) Thermodynamic and kinetic investigations of the release of oxidized phospholipids from lipid membranes and its effect on vascular integrity. Chem. Phys. Lipids 175–176, 9–19 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Asai Y., and Watanabe S. (2000) Formation and stability of the dispersed particles composed of retinyl palmitate and phosphatidylcholine. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 5, 39–45 10.1081/PDT-100100517 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Liu G. Y., Moon S. H., Jenkins C. M., Sims H. F., Guan S., and Gross R. W. (2019) Synthesis of oxidized phospholipids by sn-1 acyltransferase using 2–15-HETE lysophospholipids. J. Biol. Chem. 294, 10146–10159 10.1074/jbc.RA119.008766 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Jenkins C. M., Yang K., Liu G., Moon S. H., Dilthey B. G., and Gross R. W. (2018) Cytochrome c is an oxidative stress-activated plasmalogenase that cleaves plasmenylcholine and plasmenylethanolamine at the sn-1 vinyl ether linkage. J. Biol. Chem. 293, 8693–8709 10.1074/jbc.RA117.001629 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Bligh E. G., and Dyer W. J. (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 37, 911–917 10.1139/o59-099 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
All data presented in this paper are contained within the manuscript.