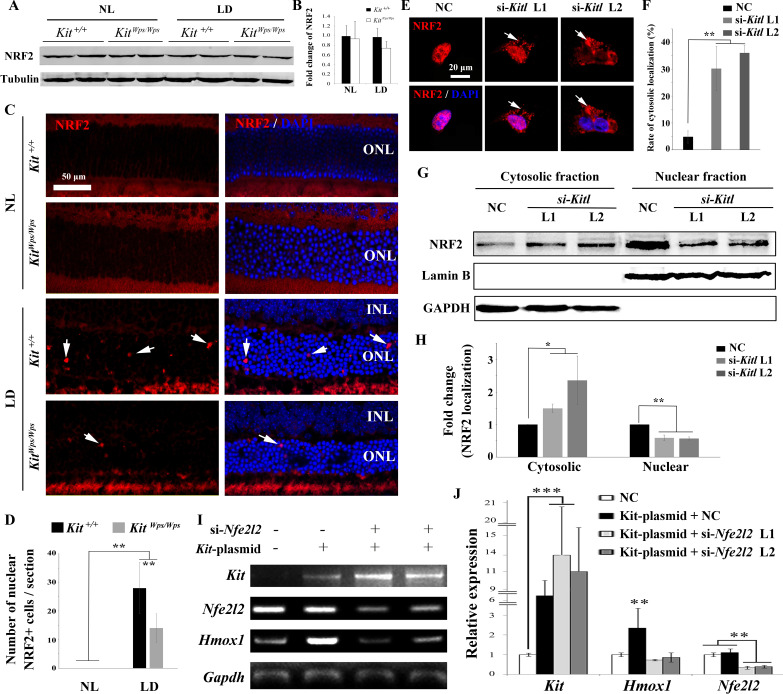
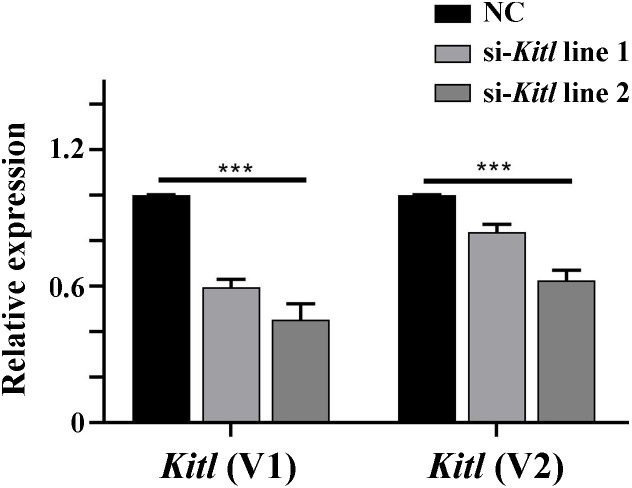
Figure 7. KIT signaling acts through the transcription factor NRF2 to regulate Hmox1 expression.
(A) Western blots for analyzing NRF2 expression in Kit+/+ and KitWps/Wps retinas under the indicated conditions. (B) The bar graph shows quantification of NRF2 expression in the indicated retinas. (C) Immunostaining of anti-NRF2 in Kit+/+ and KitWps/Wps retinas under the indicated conditions. The arrows point to nuclear signals of NRF2 in the ONL. (D) Quantification of the number of nuclear NRF2 positive cells in the retina. Note that LD induced nuclear accumulation of NRF2 in photoreceptor cells. (E–H) Analysis of subcellular localization of NRF2 in 661W photoreceptor cells treated with si-Kitl by immunostaining (E, and F) and western blot (G, and H). Note that knockdown of Kitl led to an increase in the proportion of cells with cytosolic NRF2. (I, J) Analyses of the regulation of HMOX1 in 661 W cells after overexpression of KIT together with si-Nfe2l2. The images of RT-PCR (I) and qPCR (J) show the expression levels of Kit, si-Nfe2l2, and Hmox1 under the indicated treatments. Note that upregulation of Hmox1 induced by overexpression of KIT was blocked by the knockdown of Nfe2l2. * indicates p<0.05, ** indicates p<0.01.