Abstract
The protein coded by the open-reading-frame 3a of SARS coronavirus has been demonstrated to form a cation-selective channel that may become expressed in the infected cell. The activity of the channel is involved in the mechanism of virus release. Drugs that inhibit the ion channel can, therefore, inhibit virus release, and they could be a source for development of novel therapeutic antiviral agents. Various drugs found in Chinese herbs that are well known as anticancer agents also have an antiviral potency. Here we tested the flavonols kaempferol, kaempferol glycosides, and acylated kaempferol glucoside derivatives with respect to their potency to block the 3a channel. We used the Xenopus oocyte with a heterologously expressed 3a protein as a model system to test the efficacy of the flavonols. Some of these drugs turned out to be potent inhibitors of the 3a channel. The most effective one was the glycoside juglanin (carrying an arabinose residue) with an IC50 value of 2.3 µM for inhibition of the 3a-mediated current. Kaempferol derivatives with rhamnose residue also seem to be quite effective. We suggest that viral ion channels, in general, may be a good target for the development of antiviral agents, and that, in particular, kaempferol glycosides are good candidates for 3a channel proteins of coronaviruses.
Key words: coronavirus, virus release, ion channel, kaempferol derivatives, flavonoids
Abbreviations
- CoV
coronavirus
- ORF
open reading frame
- ORi
oocyte Ringerʼs
- G-ORi
ORi supplemented with gentamycin
- NMR
nuclear magnetic resonance
- SARS
severe acute respiratory syndrome
- S1
test solution without Ba2+
- S2
test solution with 10 mM Ba2+
Introduction
Various herbal antiviral drugs have been developed that interfere with the viral life cycle 1. During the first appearance of SARS about 50 % of the patients in mainland China were treated successfully with Chinese herbal medicine in addition to Western medicine 2, 3.
Several viruses encode for ion-selective channels that become incorporated into the membrane of the infected cell 4, 5, 6, 7. Activation of such channels seems to be involved in the process of virus production and release 8, 9, 10, 11, 12. Hence, inhibition of the ion channel activation will counteract virus production; this may allow the infected body to build up or strengthen its own immune system. The viral ion channel will, therefore, be a potential candidate for developing new antiviral drugs. The ORF 3a of SARS CoV encodes for an ion-permeable channel. We could previously demonstrate that micromolar concentrations of the anthraquinone emodin can inhibit the 3a channel activity with an IC50 value of only 20 µM and also inhibit coronavirus release with a similar sensitivity from infected cells 13. This indicates that the viral ion channel is an interesting target for antiviral drugs.
Emodine as well as various flavonoids (Fig. 1) are well known to act as anticancer drugs 14, 15, but they were also discussed as antiviral drugs 16. The flavonol kaempferol and its glycosides have been reported previously to have high antiviral activity 1, but effects on the intracellular events were favoured as an explanation 17, 18. Here we investigated whether the flavonol kaempferol and kaempferol glycosides can block the 3a channel. In addition, we tested a number of other flavonoids (Fig. 1). This manuscript extends preliminary data 1 to investigate the role of this class of compounds in more detail.
Fig. 1.
Structure of the flavonoids tested with respect to their effects on the 3a-mediated current. The flavonol kaempferol (1) and the kaempferol glycosides afzelin (2), juglanine (3), and tiliroside (4), as well as two tiliroside derivatives (5–6), the kaempferol triglycoside (7), the flavonol quercetin (8), the flavanone naringenin (9), and the isoflavone genistein (10). Rha stands for rhamnose and Araf for arabinofuranose. For their respective effects, compare Table 1.
Results and Discussion
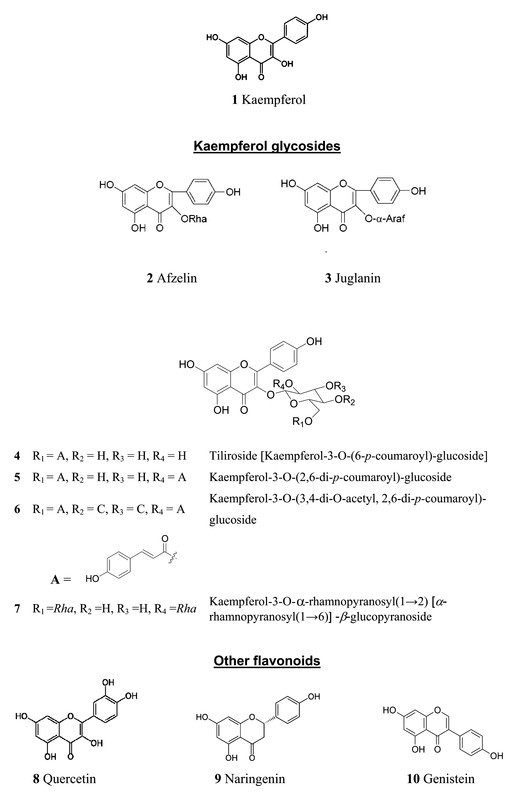
The flavonoids listed in Table 1 are well known for their anticancer activity, but also various antiviral effects have been reported 18, 19, 20. Here we investigated these drugs with respect to their efficacy to inhibit Ba2+-sensitive current. Fig. 2 a shows that 20 µM kaempferol reduced endogenous Ba2+-sensitive current. At − 100 mV the current was inhibited to 0.77 ± 0.08 (p < 0.01) of the control current in the absence of the drug. The degree of inhibition was independent of voltage.
Table 1 Effect of drugs on a 3a-mediated current. Current remaining in the presence of the respective drug concentration is expressed as ratio compared to control current in the absence of drug; values are given as mean ±SEM, based on n measurements. The values were determined from currents at − 100 mV. Two of the kaempferol glycosides were, in addition to 20 µM, also tested at 40 µM. Statistical difference from the control value was determined by t-test and is given by the p value; sns stands for statistically not significant (p > 0.2).
| Drug | Purity (%) | Concentration (µM) | Remaining current (relative to control) | n | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kaempferol glycosides | Kaempferol | > 97 | 20 | 0.82 ± 0.01 | 7 | < 0.01 |
| Juglanin | 98 | 20 10 | Complete inhibition 0.01 ± 0.06 | 5 | < 0.01 | |
| Tiliroside | > 95 | 20 | 0.48 ± 0.09 | 5 | < 0.01 | |
| Afzelin | 98 | 10 | 0.83 ± 0.01 | 5 | < 0.01 | |
| Kaempferol-3-O-(2,6-di-p-coumaroyl)-glucoside | > 95 | 20 (40) | No effect | 8 | sns | |
| Kaempferol-3-O-(3,4-diacetyl-2,6-di-p-coumaroyl)-glucoside | > 95 | 20 (40) | No effect | 8 | sns | |
| Kaempferol-3-O-α-rhamnopyranosyl(1 → 2) [α-rhamnopyranosyl(1 → 6)]-β-glucopyranoside | > 95 | 20 | 0.68 ± 0.11 | 4 | < 0.05 | |
| Other flavonoids | Quercetin | > 95 | 10 | 0.91 ± 0.10 | 8 | sns |
| Naringenin | 98 | 20 | 0.93 ± 0.05 | 4 | sns | |
| Genistein | > 96 | 20 | 0.91 ± 0.15 | 5 | sns |
Fig. 2.
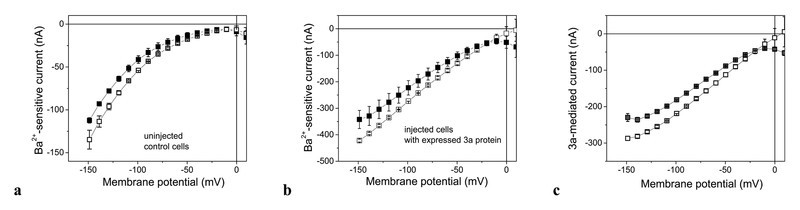
Effect of kaempferol on current-voltage (IV) curves of Ba2+-sensitive current. Open squares describe the current-voltage dependencies in the absence and filled squares in the presence of 20 µM kaempferol. a Endogenous currents, b currents of cells with heterologously expressed 3a protein, and c the 3a-protein-mediated current component (endogenous current subtracted). Data represent averages of n = 4 to 7 experiments ± SEM.
In oocytes with expressed 3a protein, Ba2+-sensitive current was larger by a factor of about 3 to 5 than in control oocytes (compare Fig. 2 a and b). Kaempferol also affected this additional 3a-mediated current component (Fig. 2 b). After subtraction of the endogenous contribution (Fig. 2 c), the current at − 100 mV was reduced to 0.82 ± 0.10 of the current component in the absence of drug; this indicated that the endogenous and the 3a-mediated components exhibited similar sensitivity to kaempferol. This is in contrast to emodin which selectively inhibited the 3a-mediated current and at 20 µM already produced more than 50 % block (see 13). The poor solubility of kaempferol in water did not allow testing a higher concentration for evaluation of an IC50 value. We therefore did not further follow up the effect of kaempferol, but rather screened for the effect of various other flavonoids. In particular, the glycosides (Table 1) are water-soluble and in addition exhibit higher bioavailability 21.
In contrast to kaempferol, the tested kaempferol glycosides hardly affected Ba2+-sensitive endogenous current (for juglanin see, e.g., Fig. 3 a). In oocytes with an expressed 3a protein, stronger effects could be detected than with kaempferol (compare Table 1). Juglanin seemed to be the most potent kaempferol glycoside that gave complete inhibition at 20 µM; even 10 µM produced nearly complete inhibition. Therefore, we focussed on this drug for a more detailed analysis. Fig. 3 b illustrates the effect of two concentrations on the current-voltage dependencies of Ba2+-sensitive current in 3a protein-expressing oocytes. Already 2.5 µM exhibited a significant inhibition. The dependence of the 3a-mediated current component on juglanin concentration is shown in Fig. 3 c. The dashed line is a fit to the data of
Fig. 3.
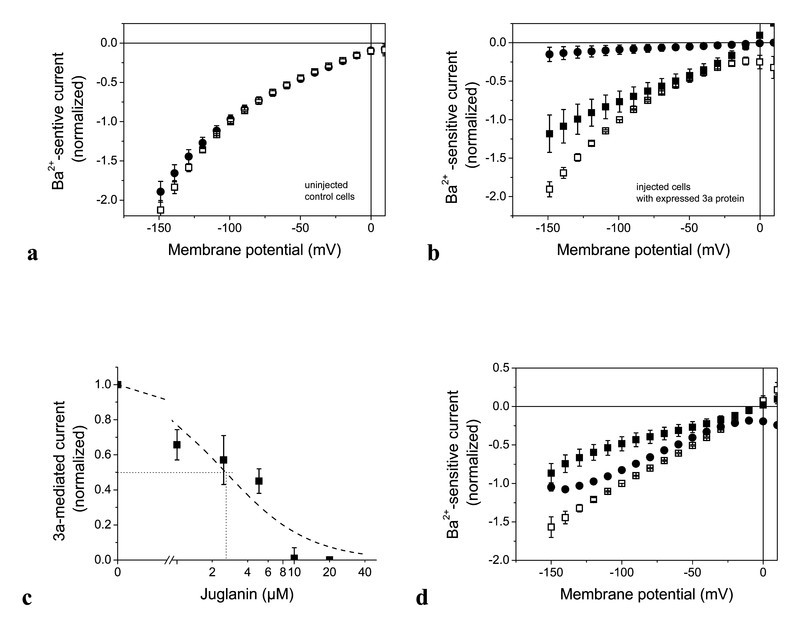
Effect of kaempferol glycosides on Ba2+-sensitive and 3a-mediated current. Results in the absence of drug are given by open squares and in the presence of drug by filled symbols. a Effect of 10 µM juglanin on current-voltage dependencies of Ba2+-sensitve current in control oocytes without a 3a protein. b Effect of 2.5 (filled squares) and 10 µM (filled circles) juglanin on 3a-mediated current that was determined as the difference of Ba2+-sensitive current in a 3a-expressing cells. Data points represent averages from 4–7 experiments ± SEM. c Inhibition of a 3-mediated current at − 100 mV by juglanin. The data points represent averages ± SEM of 5–17 measurements. The dashed line is an approximation of equ. 1 to the data points with n = 1.2 and K1/2 = 2.3 µM. d Effect of 20 µM tiliroside (squares) and 10 µM afzelin (circles) on voltage dependence of a Ba2+-sensitive current in 3a-expressing cell. Data points represent averages from 4–7 experiments ± SEM.
At a concentration of about 2.3 µM juglanin, 50 % inhibition (IC50) was obtained. Hence juglanin is about one order of magnitude more potent to block 3a-protein channel than emodine 13. With an even higher IC50 value of 200 µM, emodine was shown to inhibit interaction between virus and host cell, which was considered to be a potent mechanism in herbal treatment of SARS 22. The higher sensitivity of the 3a channel makes this protein an even more interesting target for drug development.
Two other tested kaempferol glycosides, tiliroside and afzelin, were less potent than juglanin but were nevertheless as effective as emodine. Tiliroside at 20 µM produced a block to 0.48 ± 0.09 (Table 1 and Fig. 3 d); at the same concentration, juglanin completely blocked the 3a-mediated current (Table 1 and Fig. 3 b and d). A similar degree of inhibition as with 20 µM kaempferol was obtained with only 10 µM of afzelin (inhibition to 0.83 ± 0.01) compared to the current in the absence of drug (Table 1 and Fig. 3 d).
In a series of experiments, we also tested the acylated kaempferol derivatives kaempferol-3-O-(2,6-di-p-coumaroyl)-glucopyranoside and kaempferol-3-O-(3,4-diacetyl-2,6-di-p-coumaroyl)-glucoside, which all had an additional p-coumaroyl group (see Fig. 1). At 20 µM, both derivatives showed no effect on Ba2+-sensitive current. Even at concentrations up to 40 µM (Table 1), no significant inhibition could be detected. On the other hand, in a few orientating experiments, we found that the kaempferol triglycoside kaempferol-3-O-α-rhamnopyranosyl(1 → 2)[α-rhamnopyranosyl(1 → 6)]-β-glucopyranoside exhibited about 30 % inhibition at 20 µM (Table 1); this was similar to the effect of afzelin which was also applied at 20 µM in two of these experiments. Interestingly, both drugs are characterized by rhamnose residues (see Fig. 1).
As another flavonol, we tested the effect of quercetin, which was reported to also act as an effective drug against virus infections including SARS CoV 23. We found that the 3a-mediated current was not significantly affected by 10 µM quercetin (see Table 1); concentrations even up to 50 µM hardly affected the 3a-mediated current. Also the quercetin derivative with an arabinofuranoside, avicularin (not shown), was without any effect.
The flavanone naringenin and the isoflavone genistein are also known for their antiviral potency (see, e.g., 24, 25, 26), but neither naringenin nor genistein exhibited any significant modulation of the 3a-mediated current (see Table 1).
Though the flavonols quercetin and avicularin, the flavanone naringenin, and the isoflavone genistein do not affect the activity of the 3a protein, the flavonol kaempferol exhibits a clear inhibition of the 3a-mediated current; the kaempferol glycosides are even more potent inhibitors thus suggesting an importance of sugar residues. The most potent drug was the kaempferol glycoside juglanin with an arabinose residue. Interestingly, the kaempferol glycoside afzelin and the triglycoside with rhamnose residues seem also to be quite effective. In addition to the higher effectivity of the flavonoid glycosides to inhibit the 3a protein ion channel, they show higher solubility in water with higher bioactivity 19, 21.
Though flavonoid glycosides may be absorbed in the small intestine, biodegradation will limit their therapeutical application, and levels in plasma are probably below 1 µM 21. An important task for developing new antiviral drugs will therefore have to focus on improving bioactivity 27; several strategies have been tackled for increasing bioavailability including drug delivery and metabolic stability (compare 19, 21, 27, 28).
Activity of the 3a protein results in ion channel gating which allows small cations to cross the membrane. Although the channel shows selectivity for K+, also Na+ can penetrate with slightly lower permeability 11. As a consequence, activity of channel openings will lead to membrane depolarization, and activation of L-type Ca2+ channels 29 to an elevation of intracellular Ca2+ 30. This could account for the 3a-protein-dependent release of CoV from infected cells via exocytosis. Indeed, inhibition of 3a channel activity blocks virus release; this could be demonstrated by suppression of 3a expression as well as pharmacological inhibition of the 3a channel 11, 13. This reduction in virus production offers the body the chance to adjust its immune system to counteract the viral attack. Inhibition of ion channels encoded by other viruses could also be demonstrated to inhibit the respective virus production 31, 32, 33.
As a conclusion, we suggest that emodin and kaempferol could form the basis for the development of new antiviral drugs with higher bioavailability. In particular, the glycosides of kaempferol seem to be highly potent candidates for development as anti-coronaviral agents. The fact that these drugs not only block the 3a channel, thus counteracting virus production, but that they also interfere with other steps of the viral life cycle 20 emphasises the importance of multi-target drugs.
Materials and Methods
Expression of 3a protein in Xenopus oocytes
To investigate effects of kaempferol and its derivatives on the 3a protein of SARS-CoV, we used the Xenopus oocyte for heterologous expression and applied voltage-clamp techniques (for details see 11, 13). Females of the clawed toad Xenopus laevis (Maosheng Bio-Technology Com.) were anaesthetized with tricane (1 g/L H2O, MS222; Sandoz) or in ice water. Parts of the ovary were removed and treated with 0.3 units/mL Liberase (Roche) or with 1 mg/mL Collagenase (Sigma) for 3 to 4 h to remove enveloping tissue and to obtain isolated oocytes. The entire procedure follows standard protocols including care of laboratory animals that have been established according to German Animal Protection Law. For expression of 3a protein, oocytes of stage V or VI 34 were selected and injected with 20 or 30 ng cRNA for 3a protein (for details see 11) (at 1 ng/nL) two to three days before the experiments; uninjected oocytes served as controls. The cells were stored for 2 days at 19 °C in oocyte Ringerʼs-like solution (G-ORi, see solutions). Experiments were performed at room temperature (24–26 °C).
Solutions
Standard ORi solution contained: 90 mM NaCl, 2 mM KCl, 2 mM CaCl2, and 5 mM Hepes (adjusted to pH 7.4 with Tris). For cell incubation, the ORi was supplemented with 70 µg/L gentamycin (G-ORi).
Since the 3a protein channel showed high permeability to K+ 11, the test solution without Ba2+ (S1) contained: 100 mM KCl, 2 mM MgCl2, and 5 mM Hepes (pH 7.4); because the Xenopus oocytes express endogenous Ca2+-activated K+ and Cl− channels, Ca2+ was omitted from the bath solutions (but replaced by Mg2+) to reduce these background currents. Test solution S2 contained 10 mM BaCl2 in addition. The change in osmolarity due to addition of BaCl2 did not affect the membrane currents. The difference between the current measured in S1 and S2 was considered as the Ba2+-sensitive current component. Both solutions, S1 and S2, contained some DMSO (see below).
All stock solutions of drugs were made up in DMSO. Kaempferol was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich; two probes of the kaempferol glycosides (juglanin, kaempferol-3-O-α-L-arabinofuranoside, and afzelin, kaempferol-3-O-α-L-rhamnoside) were kindly provided by Prof. X. Hao and Dr. Y. Wang, Kunming, China, or bought from BioBioPHa.
Kaempferol acylated glucosides were previously isolated from polar extracts from the leaves of the plant Quercus ilex L. 35; the kaempferol triglycoside was an isolate from Viola odorata L. 36. Isolation was carried out mainly by column chromatography on Sephadex LH-20 and silica gel. The structure of the compounds was established by NMR experiments. The purity was checked by NMR and high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array detector and was over 95 %. Quercetin and naringenin were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, and genistein from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. The purities of all drugs are listed in Table 1.
Voltage–clamp experiments
We applied conventional two-electrode voltage clamp using Turbo TEC-03 with CellWorks software (NPI Electronic) to measure the current mediated by SARS-3a protein. This method allowed directly monitoring modulations of the ion channel function under various conditions including inhibition by drugs. Previously, we had successfully applied this method to show that emodin (purity > 95 %) inhibits ion flow through the 3a protein ion channel 13. To determine steady-state current–voltage dependencies (IV curves), membrane currents were averaged during the last 20 ms of 200 ms, rectangular voltage pulses from − 150 to + 30 mV in 10-mV increments; the pulses were applied from a holding potential of − 60 mV. To avoid changes at the bath electrodes due to changes in Cl− activity, the electrodes were uncoupled from the bath via ORi-filled channels.
Current mediated by the 3a protein can be blocked by Ba2+ 11. Therefore, we determined Ba2+-sensitive current as the difference of steady-state current in the presence and absence of 10 mM BaCl2 (see Solutions). Since oocytes which did not express 3a protein also exhibited some Ba2+-sensitive current contribution, this endogenous component was determined in uninjected control cells and used for subtraction from total Ba2+-sensitive current of the injected oocytes from the same batch. The difference was considered to represent 3a-mediated current.
To correct for possible drift with time, Ba2+-sensitive current was calculated according to:
or
IS1 and IS2 stand for current measurements in the absence and presence of the Ba2+, respectively, the subscripts before and after refer to measurements before and after the measurement with the respective other solution. For a typical experiment, either of the following sequences of solutions was used for perfusing the chamber with the oocyte:
S1 → S2 → S1 → S1+ → S2+ → S1+ → S1 → S2 → S1
S2 → S1 → S2 → S2+ → S1+ → S2+ → S2 → S1 → S2.
The + sign indicates solutions with the respective drug.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the technical assistance from Huiming Du during the various steps of this project. SS, DS, and WS thank Prof. Gu Quanbao for helpful discussions. The work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, 2012CB518502). We also gratefully acknowledge the support from Green Valley Holding Co, Shanghai.
Footnotes
Conflict of Interest All authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.Schwarz S, Sauter D, Lu W, Wang K, Sun B, Efferth T, Schwarz W. Coronaviral ion channels as target for Chinese herbal medicine. Forum Immunopathol Dis Ther. 2012;3:1–13. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Zhang M M, Liu X M, He L. Effect of integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine on SARS: A review of clinical evidence. World J Gastroenterol. 2004;10:3500–3505. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i23.3500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Liu X M Zhang M M He L Li Y P Kang Y K Chinese herbs combined with Western medicine for severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) Cochrane Database Syst Rev 20061CD004882 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Fischer W B, Thiel G, Fink R HA. Viral membrane proteins. Eur Biophys J. 2010;39:1041–1042. doi: 10.1007/s00249-009-0525-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Krüger J, Fischer W B. Assembly of viral membrane proteins. J Chem Theor Comput. 2009;5:2503–2513. doi: 10.1021/ct900185n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wang K, Xie S, Sun B. Viral proteins function as ion channels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1808:510–515. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2010.05.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Fischer W B, Wang Y T, Schindler C, Chen C Y. Burlington: Elsevier Inc./Academic Press; 2012. Mechanism of function of viral channel protein and implications for drug development; pp. 259–321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Liang X, Li Z Y. Ion channels as antivirus targets. Virol Sin. 2010;25:267–280. doi: 10.1007/s12250-010-3136-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kelly M L, Cook J-A, Brown-Augsburger P, Heinz B A, Smith M C, Pinto L H. Demonstrating the intrinsic ion channel activity of virally encoded proteins. FEBS Lett. 2003;552:61–67. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(03)00851-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Montal M. Structure-function correlates of Vpu, a membrane protein of HIV-1. FEBS Lett. 2003;552:47–53. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(03)00849-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lu W, Zheng B J, Xu K, Schwarz W, Du L Y, Wong C KL, Chen J D, Duan S M, Deubel V, Sun B. Severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus 3a protein forms an ion channel and modulates virus release. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:12540–12545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0605402103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Schwarz S, Sauter D, Lu W, Wang K, Sun B, Efferth T, Schwarz W. Coronaviral ion channels as target for Chinese herbal medicine. Forum Immunopathol Dis Ther. 2012;3:1–13. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Schwarz S, Wang K, Yu W, Sun B, Schwarz W. Emodin inhibits current through SARS-associated coronavirus 3a protein. Antivir Res. 2011;90:64–69. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2011.02.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Tan W, Lu J, Huang M, Li Y, Chen M, Wu G, Gong J, Zhong Z, Xu Z, Dang Y, Guo J, Chen X, Wang Y. Anti-cancer natural products isolated from Chinese medicinal herbs. Chin Med. 2011;6:27. doi: 10.1186/1749-8546-6-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lown J W. Anthracycline and anthraquinone anticancer agents: Current status and recent developments. Pharmacol Ther. 1993;60:185–214. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(93)90006-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Naithani R, Huma L C, Holland L E, Shukla D, McCormick D L, Mehta R G, Moriarty R M. Antiviral activity of phytochemicals: A comprehensive review. Minirev Med Chem. 2008;8:1106–1133. doi: 10.2174/138955708785909943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lyu S-Y, Rhim J-Y, Park W-B. Antiherpetic activities of flavonoids against herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) and type 2 (SV-2) in vitro. Arch Pharm Res. 2005;28:1293–1301. doi: 10.1007/BF02978215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Mitrocotsa D, Mitaku S, Axarlis S, Harvala C, Malamas M. Evaluation of the antiviral activity of kaempferol and its glycosides against human cytomegalovirus. Planta Med. 2000;66:377–379. doi: 10.1055/s-2000-8550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Nijveldt R J, van Nood E, van Hoorn D EC, Boelens P G, van Norren K, Leeuwen P AM. Flavonoids: a review of probable mechanisms of action and potential applications. Am J Clin Nutr. 2001;74:418–425. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/74.4.418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kaul T N, Middleton E, Ogra P L. Antiviral effect of flavonoids on human viruses. J Med Virol. 1985;15:71–79. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890150110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hollman P CH. Absorption, bioavailability, and metabolism of flavonoids. Pharm Biol. 2004;42:74–83. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ho T W, Wu S L, Chen J C, Li C C, Hsiang C Y. Emodin blocks the SARS coronavirus spike protein and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 interaction. Antivir Res. 2007;74:92–101. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2006.04.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Chen L, Li J, Luo C, Liu H, Xu W, Chen G, Liew O W, Zhu W, Push C M, Shen X, Jiang H. Binding interaction of quercetin-3-β-galactoside and its synthetic derivatives with SARS-CoV 3 CLpro: Structure activity relationship studies reveal salient pharmacophore features. Bioorg Med Chem. 2006;14:8295–8306. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2006.09.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lyu S Y, Rhim J Y, Park W B. Antiherpetic activities of flavonoids against herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) and type 2 (HSV-2) in vitro. Arch Pharm Res. 2005;28:1293–1301. doi: 10.1007/BF02978215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Liu A L, Wang H D, Lee S MY, Wang Y T, Du G H. Structure-activity relationship of flavonoids as influenza virus neuraminidase inhibitors and their in vitro anti-viral activities. Bioorg Med Chem. 2008;16:7141–7147. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2008.06.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Evers D L, Chao C F, Wang X, Zhang Z, Huong S M, Huang E S. Human cytomegalovirus-inhibitory flavonoids: Studies on antiviral activity and mechanism of action. Antiviral Res. 2005;68:124–134. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2005.08.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Thilakarathna S H, Rupasinghe H PV. Flavonoid bioavailability and attempts for bioavailability enhancement. Nutrients. 2013;5:3387. doi: 10.3390/nu5093367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Walle T. Absorption and metabolism of flavonoids. Free Radic Biol Med. 2004;36:829–837. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.01.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lu W, Xu K, Sun B. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer; 2010. SARS accessory proteins ORF3a and 9b and their functional analysis; pp. 167–175. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Zhou Y, Frey T K, Yang J J. Viral calciomics: Interplays between Ca2+ and virus. Cell Calcium. 2009;46:1–17. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2009.05.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Wilson L, Gage P, Ewart G. Hexamethylene amiloride blocks E protein ion channels and inhibits coronavirus replication. Virology. 2006;353:294–306. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.05.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Luscombe C A, Huang Z H, Murray M G, Miller M, Ilkinson J, Ewart G D. A novel Hepatitis C virus p 7 ion channel inhibitor, BIT225, inhibits bovine viral diarrhea virus in vitro and shows synergism with recombinant interferon-α-2b and nucleoside analogues. Antivir Res. 2010;86:144–153. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2010.02.312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Xie S Q, Wang K, Yu W, Lu W, Xu K, Wang J, Ye B, Schwarz W, Jin Q, Sun B. DIDS blocks a chloride-dependent current that is mediated by the 2B protein of enterovirus 71. Cell Res. 2011;21:1271–1275. doi: 10.1038/cr.2011.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Dumont J N. Oogenesis in “Xenopus laevis” (Daudin): I. Stages of oocyte development in laboratory maintained animals. J Morphol. 1972;136:153–180. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051360203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Karioti A, Bilia A R, Skaltsa H. Quercus ilex L.: A rich source of polyacylated flavonoid glucosides. Food Chem. 2010;123:131–142. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Karioti A, Furlan C, Vincieri F F, Bilia A R. Analysis of the constituents and quality control of Viola odorata aqueous preparations by HPLC-DAD and HPLC-ESI-MS. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011;399:1715–1723. doi: 10.1007/s00216-010-4473-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


