Abstract
Objective
To assess whether neuropathy with anti-myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) antibody may improve after treatment with ibrutinib, an oral inhibitor of Bruton tyrosine kinase, we prospectively treated with ibrutinib a cohort of 3 patients with anti-MAG neuropathy and Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM).
Methods
All 3 patients underwent bone marrow biopsy showing WM, with MYD88L265P mutated and CXCR4S338X wild type, and were started on ibrutinib 420 mg/die. Patients were assessed at baseline, at 3-6-9 months, and at 12 months in 2 patients with a longer follow-up, using Inflammatory Neuropathy Cause and Treatment (INCAT) Disability Score, INCAT sensory sum score, and Medical Research Council sum score. The modified International Cooperative Ataxia Rating Scale was performed in 2 patients, whereas it was not used in the patient with Parkinson disease as a major comorbidity. Responders were considered the patients improving by at least one point in 2 clinical scales.
Results
All the patients reported an early and subjective benefit, consistent with the objective improvement, especially of the sensory symptoms as shown by clinical scales. Treatment was well tolerated.
Conclusion
These preliminary data point to a possible efficacy of ibrutinib in anti-MAG antibody neuropathy, which is the most common disabling paraproteinemic neuropathy, where active treatment is eagerly needed.
Classification of evidence
This study provides Class IV evidence that for patients with anti-MAG antibody neuropathy, ibrutinib improves neuropathy symptoms.
Anti-myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) antibody neuropathy is a chronic sensorimotor demyelinating polyneuropathy associated with immunoglobulin M (IgM) monoclonal gammopathy, manifestation of either a monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) or of a non-Hodgkin lymphoma, such as Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM).1,2 Anti-MAG antibodies are pathogenic,3 and rituximab, a chimeric anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, is currently the standard treatment. However, rituximab provides benefit in less than 50% of patients,4 and repeated cycles are often necessary with progressive loss of benefit.
Recently, the discovery of the mutational profile of the MYD88 and CXCR4 genes has radically changed the diagnostic and prognostic evaluation of IgM monoclonal gammopathies. MYD88L265P has been found to be the most common mutation in WM and IgM-MGUS,5 conferring prosurvival stimuli to tumor cells through constitutive activation of the Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) and nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells signaling. Conversely, the less common CXCR4 mutations are associated with adverse prognosis. Ibrutinib, the first-in-class inhibitor of BTK, has already been shown to be efficacious in B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas including WM, especially in those harboring MYD88L265P mutation and CXCR4 gene wild-type.5,6
In the study by Treon et al.,5 9 of 63 patients, 3 of whom had anti-MAG antibodies, received ibrutinib for progressive neuropathy. Subjective improvement occurred in 5 patients and 4 remained stable. In a subsequent study,6 4 of 31 patients with WM had been treated with ibrutinib for neuropathy, 2 remained stable and 2 had subjective improvement starting from week 9, with subsequent complete recovery in one patient. Despite the possibility of hematologic evaluation might have lacked specific scales to grade the response of neuropathy, still these preliminary data are promising and show that ibrutinib does not worsen rather may improve neuropathy.
We report on 3 patients with anti-MAG antibody neuropathy who had been successfully treated with ibrutinib. Demographic and hematologic data are summarized in table 1. All patients had neurophysiologic evidence of sensory-motor demyelinating polyneuropathy, with secondary axonal damage involving distal motor fibers in one patient (1).
Table 1.
Clinical and biological characteristics of ibrutinib-treated patients
The patients were assessed with Inflammatory Neuropathy Cause and Treatment (INCAT) Disability Score,7 INCAT sensory sum score,8 and Medical Research Council sum score. The modified International Cooperative Ataxia Rating Scale9 was also performed in 2 patients (1 and 3) to evaluate tremor and gait, whereas it was not used in patient 2, who had Parkinson disease as a major comorbidity. Responders were considered those patients who improved by at least one point in 2 clinical scales. Data regarding clinical scales are summarized in table 2.
Table 2.
Clinical scales at the baseline and the follow-up of ibrutinib-treated patients
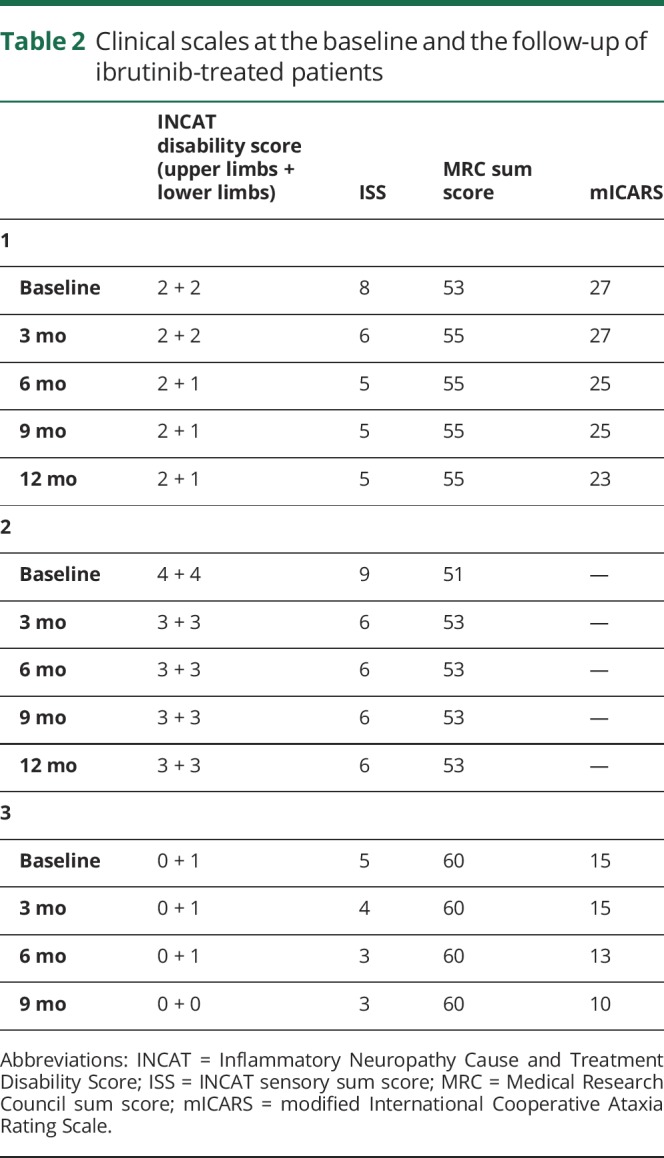
Patient 1 is a 73-year-old man, with a long history (from 2008) of anti-MAG antibody neuropathy. He had undergone therapy with plasma exchange, IV immunoglobulins, and rituximab with only partial benefit. After worsening, in December 2018, bone marrow biopsy (BMB) showed WM, with MYD88L265P mutation and a lack of CXCR4S338X. Ibrutinib 420 mg/die was started in January 2019. At baseline, he presented with distal weakness and hypoesthesia at the lower limbs, loss of vibration sense up to the knee, lower limbs areflexia, and upper limbs tremor (table 2). After 1 and 3 months of treatment, there was a slight improvement in touch sensation at the feet and in motor deficit at the toes (table 2). After 6 months, further improvement in touch sensation and distal motor deficit occurred, whereas tremor persisted. The clinical benefit was stable at 12 months (table 2). Monoclonal protein and IgM levels decreased. Anti-MAG antibodies decreased at 3 months but gradually increased thereafter (table 1).
Patient 2 is a 80-year-old man, affected with anti-MAG antibody neuropathy and Parkinson disease. BMB showed WM harboring MYD88L265P and unmutated CXCR4 gene. He started ibrutinib 420 mg/die in February 2019. At baseline, there was a severe sensory-motor impairment at 4 limbs (distal lower limbs and grip strength deficit, hypoesthesia and loss of vibration sense up to the knee, lower limbs areflexia, postural tremor at upper limbs, table 2). After 1 and 3 months of treatment, a slight improvement in sensory signs and symptoms occurred, with vibration sense and reflexes reappearing at the knees (table 2). The improvement was maintained 12 months later. Monoclonal protein and IgM levels steadily decreased, whereas the antibody titers decreased at 3 months and then increased thereafter (table 1).
Patient 3 is a 74-year-old woman with WM and anti-MAG neuropathy since 2015. She was treated in 2016 with cyclophosphamide and rituximab, with clinical stability. In 2018, for progressive worsening of gait instability (frequent falls) and lower limbs dysesthesias (table 2), she underwent BMB that confirmed WM with MYD88L265P mutation and unmutated CXCR4 gene. The patient started ibrutinib 420 mg/die in May 2019, and at the 1- and 3-month follow-ups, she already reported subjective improvement of touch sensation at the lower limbs (table 2). At the 6-month evaluation, she reported dramatic improvement in gait stability that further improved at month 9 (table 2). Monoclonal protein and IgM levels steadily decreased, whereas the antibody titers decreased at 3 months and then increased thereafter (table 1).
Therapy was well tolerated, and none developed atrial fibrillation or infections. All patients are currently still receiving treatment.
Discussion
Anti-MAG antibody neuropathy is a slowly progressive neuropathy that may become disabling when sensory ataxia worsens or motor impairment occurs. Efficacy after treatment with rituximab is reported only in approximately half of the patients, highlighting the unmet need for effective therapeutic options. The discovery of the mutational profile of the MYD88 and CXCR4 genes10 have opened new potential therapeutic avenues. Data from previous hematologic studies5,6 were also encouraging regarding neuropathies, including those associated with anti-MAG antibodies.
We have reported on the first 3 patients treated with ibrutinib, 2 after the loss of response to rituximab. All the patients reported an early and subjective benefit, especially of the sensory symptoms, which has also been supported by the objective improvement of at least one point in 2 neurologic scales. Less perception of benefit after therapy was reported by the oldest patient, who had a concomitant disabling Parkinson disease. To note, an early improvement was also recorded in patient 1, who had a long history of anti-MAG antibody neuropathy with poor response to previous treatments. The biological effect of ibrutinib was demonstrated by the steady decrease of the IgM levels and of the monoclonal component. Surprisingly (but consistently), the anti-MAG antibody titer decreased at the 3 months follow-up but at subsequent evaluation, increased regardless of the IgM level and of clinical improvement.
It is well known that the severity of the neuropathy does not correlate with the anti-MAG antibody titer, which also does not correlate with the paraprotein entity. Furthermore, if despite the halving of the monoclonal paraprotein, the antibody titer persists elevating, it is likely that the quantity of the antibody-producing cells is low compared with the whole paraprotein. Another possibility is that ibrutinib may succeed in eliminating the WM malignant cells, but it is less active in the lymphoplasmocytes producing anti-MAG antibodies. The possibility of serum factors that influence the in vitro antibody binding or the assays' variability because of the differences in the ELISA plates or their handling, or standard curves generated by positive controls, should also be considered. Finally, the lymphoplasmocytes that produce the anti-MAG antibodies may have a survival advantage, explaining why only less than 50% of anti-MAG neuropathy patients respond to rituximab or eventually relapse.
Our preliminary data in 3 patients point to a possible efficacy of ibrutinib in anti-MAG antibody neuropathy, which is the most common disabling paraproteinemic neuropathy.
Glossary
- BMB
bone marrow biopsy
- BTK
Bruton tyrosine kinase
- IgM
immunoglobulin M
- INCAT
Inflammatory Neuropathy Cause and Treatment
- MAG
myelin-associated glycoprotein
- MGUS
monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance
- WM
Waldenström macroglobulinemia
Appendix. Authors
Study funding
A. Visentin received a research fellowship from RCV—Ricerca per Credere nella Vita.
Disclosure
F. Castellani, A. Visentin, M. Campagnolo, A. Salvalaggio, M. Cacciavillani, C. Candiotto, and R. Bertorelle report no disclosures. L. Trentin received research founding by Janssen. C. Briani reports no disclosures. Go to Neurology.org/NN for full disclosures.
References
- 1.Latov N, Sherman WH, Nemni R, et al. Plasma-cell dyscrasia and peripheral neuropathy with a monoclonal antibody to peripheral-nerve myelin. N Engl J Med 1980;303:618–621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Briani C, Visentin A, Campagnolo M, et al. Peripheral nervous system involvement in lymphomas. J Peripher Nerv Syst 2019;24:5–18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Dalakas MC. Advances in the diagnosis, immunopathogenesis and therapies of IgM-anti-MAG antibody-mediated neuropathies. Ther Adv Neurol Disord 2018;11:1756285617746640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lunn MP, Nobile-Orazio E. Immunotherapy for IgM anti-myelin-associated glycoprotein paraprotein-associated peripheral neuropathies. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2016;10:CD002827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Treon SP, Tripsas CK, Meid K, et al. Ibrutinib in previously treated Waldenström's macroglobulinemia. N Engl J Med 2015;372:1430–1440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dimopoulos MA, Trotman J, Tedeschi A, et al. Ibrutinib for patients with rituximab-refractory Waldenström's macroglobulinaemia (iNNOVATE): an open-label substudy of an international, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2017;18:241–250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hughes R, Bensa S, Willison H, et al. ; Inflammatory Neuropathy Cause and Treatment (INCAT) Group. Randomized controlled trial of intravenous immunoglobulin versus oral prednisolone in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Ann Neurol 2001;50:195–201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Merkies IS, Schmitz PI, van der Mechè FG, van Doorn PA. Psychometric evaluation of a new sensory scale in immune-mediated polyneuropathies. Inflammatory Neuropathy Cause and Treatment (INCAT) Group. Neurology 2000;54:943–949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Schmahmann JD, Gardner R, MacMore J, Vangel MG. Development of a brief ataxia rating scale (BARS) based on a modified form of the ICARS. Mov Disord 2009;24:1820–1828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Vos JM, Notermans NC, D'Sa S, et al. High prevalence of the MYD88 L265P mutation in IgM anti-MAG paraprotein-associated peripheral neuropathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2018;89:1007–1009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



