Abstract
The tetraspan surface molecule MS4A4A is selectively expressed by cells of the monocyte-macrophage lineage(s), being induced during monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation, but not in dendritic cells. In vitro, MS4A4A is upregulated in macrophages by M2 or M2-like signals, including IL-4 and dexamethasone. In vivo, MS4A4A is expressed by human tissue resident macrophages, macrophages infiltrating the inflamed synovium in rheumatoid arthritis patients, and tumor-associated macrophages, and is induced in monocytes in patients treated with methylprednisolone. After macrophage engagement with Zymosan, an agonist of β-glucan receptor Dectin-1, MS4A4A colocalizes with Dectin-1 in the lipid rafts. In the absence of MS4A4A, activation of the Syk pathway downstream Dectin-1 is impaired, and the production of cytokines and reactive oxygen species is reduced. MS4A4A deficiency in macrophages has no impact on primary tumor growth, but compromises Dectin-1-driven NK cell-mediated resistance to metastasis. Thus, MS4A4A is a tetraspan molecule expressed during macrophage differentiation and M2/M2-like polarization that functionally interacts with Dectin-1 and is essential for full response by this innate immunity receptor, including NK cell-mediated resistance to metastasis.
Keywords: MS4A4A, tetraspanin, Dectin-1, macrophage, NK cell, tumor biology
Introduction
Macrophages are central players in the pathophysiology of infections and cancer, being capable of adapting to the local microenvironment assuming a range of different phenotypes. During infections, macrophages sense pathogens through pattern recognition receptors and by the release of immune mediators orchestrate the activation of proinflammatory immune responses. Briefly, and in parallel with the Th1/Th2 T cell polarization, the presence of Th1 cytokines and bacterial compounds promotes a classical activation of macrophages (M1), which are endowed with pro-inflammatory features, whereas upon exposure to Th2 stimuli macrophages acquire an alternative phenotype (M2) 1, 2. Macrophages also coordinate immune responses by complex bidirectional interplay with other immune cells. In tumors, in particular, Tumor-Associated Macrophages (TAM) establish a network with tumor and host cells supporting a protumoral microenvironment 3, 4, 5, 6. TAM promote tumor progression by different means, ranging from stimulation of angiogenesis to suppression of adaptive immune responses through the triggering of the activity of immune checkpoints, such as PD-L1, PD-L2, and VISTA 7. Based on this, targeting TAM represents a major therapeutic option under investigation 3. Several markers have been reported to identify specific macrophage subsets as well as distinct macrophage activation profiles 8, 9, 10. The present study was designed to investigate the expression and function in macrophages of the tetraspan molecule MS4A4A, which was shown by us and others to be part of the transcription signature of M2 polarized macrophages and TAM 8, 11, 12. Here we confirm and extend these previous observations, showing that MS4A4A is upregulated during monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation and polarization towards a M2/M2-like direction, is selectively expressed in tissue resident macrophages, in homeostatic as well as in inflammatory conditions, and ishighly expressed in TAM, both in humans and mice. We report that MS4A4A is functionally associated with Dectin-1 in macrophage lipid rafts and is required for the full activation of Syk-dependent signalling pathway and consequent production of cytokines and reactive oxygen intermediates upon Dectin-1 engagement. Though macrophage-selective genetic inactivation of Ms4a4a had no impact on primary mesenchymal carcinogenesis and transplanted tumor growth, we found that Ms4a4a-deficient macrophages are impaired in their ability to support Dectin-1-dependent cross-talk with NK cells, resulting in uncontrolled metastatic spread.
Materials And Methods
Cells
Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells were isolated from buffy coats of healthy donors and monocytes were obtained by serial centrifugation on Ficoll and Percoll density gradients (GE Healthcare Biosciences), in accordance with clinical protocols approved by the institutional Ethical Committee of the Humanitas Clinical and Research Center. Human macrophages were differentiated from monocytes by 7 days of culture with 100 ng/ml recombinant human (rh) M-CSF (R&D Systems) in RPMI 1640, 10% FBS, 1% L-glutamine, 1% penicillin/streptomycin (Lonza). Human dendritic cells were differentiated from monocytes by 7 days of culture with 50 ng/ml rhGM-CSF and 40 ng/ml rhIL-4. Macrophages were activated in vitro by 18/24 h incubation with either 100 ng/ml LPS purified from E. coli 055:B5 (Sigma-Aldrich) plus 20 ng/ml rhIFNγ (Peprotech) for M1 polarization, 20 ng/ml rhIL-4 (Peprotech) for M2 polarization, or 20 ng/ml rhIL-10 (Milteny Biotech), 10 ng/ml rhTGFβ (Miltenyi Biotech), or 10-6 M dexamethasone (Dex; Sigma-Aldrich). Murine bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDM) were generated by 6 days of culture with 20 ng/ml recombinant murine (rm) M-CSF (Miltenyi Biotech) and were cultured for 18 h with 100 ng/ml LPS plus 20 ng/ml rmIFNγ (R&D Systems) to induce M1 polarization or 20 ng/ml rmIL-4 (R&D Systems) to induce M2 polarization. TAM were isolated from tumors obtained injecting s.c. B16F1 (0.1 x 106) or Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC; 1 x 106) cells into C57BL/6J (Charles River Laboratories) or A498 human renal tumor cells (1 x 106) in NOD/scid/IL-2Rγnull mice (Jackson Laboratory). After mice were sacrificed (day 14 for LLC tumors, day 18 for A498 tumors, day 20 for B16F1 tumors), tumors were harvested and disaggregated by stirring in RPMI media containing 1 mg/ml collagenase A (Roche) and 0.1 mg/ml DNase I (Roche) for 30 min at 37°C, then 5% v/v FBS was added, the tumor suspension was filtered through a 100 μm cell strainer (BD Falcon) and washed with wash buffer (PBS containing 5% v/v FBS, 0.5 mM EDTA). Red blood cells were lysed and the tumor suspension was washed twice with wash buffer. Peritoneal exudate macrophages (PEC) from non-tumor mice were collected by peritoneal lavage with 5 ml ice-cold PBS. Tumor suspension cells and PEC were stained for F4/80 and CD11b and F4/80+/CD11b+ TAM and PEC were sorted using an Influx flow sorter (BD Bioscience) and immediately lysed for RNA extraction. To study Dectin-1 activity, cells were treated with 100 μg/ml Zymosan (InvivoGen), 100 μg/ml depleted Zymosan (InvivoGen), 100 μg/ml Curdlan (Wako Chemicals), 100 ng/ml LPS, 100 ng/ml PMA (Sigma-Aldrich), 100 ng/ml Pam3Cys (Enzo Life Science), 20 μg/ml fluorescein-conjugated Zymosan bioparticles (Molecular Probes), 5 x 106 A. fumigatus conidia-FITC, or 5 mM methyl-β-cyclodextrin (MβCD; Sigma-Aldrich). B16F1 and B16F10 cells were cultured in RPMI 1640, 10% FBS, 1% L-glutamine, 1% penicillin/streptomycin, 1% HEPES (Lonza). MC38 cells were cultured in Dulbecco's modified Eagle medium (DMEM; Lonza), 10% FBS, 1% L-glutamine, 1% penicillin/streptomycin, 1% sodium pyruvate, 1% non-essential amino acids (Lonza). SL4 cells were cultured in DMEM:F12 (1:1) medium (Lonza), 10% FBS, 1% L-glutamine, 1% penicillin/streptomycin. Chinese hamster ovary (CHO-K1) cells were grown in DMEM, 10% FBS, 100 U/ml penicillin/streptomycin, 25 mM HEPES (Gibco). Transfectants were obtained by lipofection with Lipofectamine 2000 according to manufacturer's instructions, and selected with 650 μg/ml G418 (Invitrogen).
Patients samples
Monocytes from patients with active severe Graves orbitopathy were collected before and 6 h after the first i.v. infusion of 1 g methylprednisolone. A signed informed consent for blood/serum collection and storage and for its use for research purposes was obtained by the Endocrinology Unit, Fondazione IRCCS Ca’ Granda Policlinico. In agreement with the institutional policy, the Ethical Committee approval was not requested as patients did not undergo tests or therapies other than those routinely proposed for their specific disease. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synovium samples were retrieved from early (<12 months symptoms) patients fulfilling the ACR/EULAR 2010 criteria 13 for RA diagnosis, recruited into the Pathobiology of Early Arthritis Cohort (PEAC; http://www.peac-mrc.mds.qmul.ac.uk/) at Bart’s Health NHS Trust in London. After obtaining written informed consent, patients underwent an ultrasound-guided needle synovial biopsy of the most inflamed accessible joint 14. Synovial tissue samples were immediately fixed in 4% formaldehyde (Merck) and subsequently paraffin-embedded. The study was approved by the institutional Ethical Committee (No. 05/Q0703/198). Histological analysis of normal and tumoral tissue samples was performed on material obtained from the Surgical Pathology Unit, ASST-Spedali Civili in Brescia. Experiments performed on archival material were approved by the institutional Ethical Committee (WV-Immunocancer 2014 to WV, IRB code NP906).
Immunohistochemical and immunofluorescence analysis
MS4A4A expression was analysed on 4-μm formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections of normal tissues (skin, lung, colon) and corresponding neoplastic samples (five melanomas, five lung adenocarcinomas, five colon adenocarcinomas) by staining with anti-human MS4A4A (rabbit polyclonal, dilution 1:4000; Sigma-Aldrich) and revealing using Novolink Polymer (Leica Biosystems) as secondary reagent. The chromogen reaction was developed using diaminobenzidine. For double immunostains, MS4A4A was combined with CD1c (clone OTI2F4; Abcam), CD163 (clone 10D6; Thermo Fisher Scientific), CD207 (clone 12D6; Vector Laboratories), and CD303 (clone 124B3.13; Dendritics). The second antibody reactivity was detected using a Mach 4 alkaline phosphatase system with Ferangi Blue (Biocare Medical) as chromogen. Slides were counterstained with haematoxylin. Omission of primary antibody was also performed as control staining. Immunostained sections were photographed using the DP73 Olympus digital camera mounted on the Olympus BX60 microscope and analysed by the acquisition software CellSens Standard. Images were then processed using Adobe Photoshop Cs4 Portable. MS4A4A expression on inflamed synovium was performed on 3-μm formalin-fixed paraffin embedded sections obtained from five patients by multiplex immunofluorescence staining using a tyramide signal amplification protocol and an anti-MS4A4A rabbit polyclonal anti human antibody (dilution 1:2000; Sigma-Aldrich) in combination with CD68 (mouse anti human IgG1, clone KP1; Dako), CD163 (mouse anti human IgG1, clone 10D6; Leica Biosystems), CD3 (mouse anti human IgG1, clone F7.2.38; Dako), CD20 (mouse anti human IgG2a, clone L26; Dako), and CD138 (mouse anti human IgG1, clone MI15; Dako). Matching isotypes were used as controls. Sections were incubated sequentially with MS4A4A, CD68 and either CD3, CD20, CD138, or CD163 at optimized concentrations. Briefly, after incubation with each primary antibody followed by the appropriate EnVision+ system HRP anti-mouse (Dako K4001) or anti-rabbit (Dako K4002) for 30 min, the Alexa Fluor 488-, Alexa Fluor 555- or Cy5-conjugated tyramide reagents (Invitrogen) were added per manufacturer instructions. Each primary antibody complex was stripped before the subsequent by microwaving the slides for 15 min at low power in citrate retrieval solution (pH 6). Nuclei were counterstained with 40,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI, 300 nM; Invitrogen) and mounted with ProLong Antifade Mountant (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Sections were imaged with the digital slide scanner Nanozoomer S60 (Hamamatsu Photonics). The quantification of CD68/MS4A4A/CD163+ cells was performed using the cell count plugin of the Image J software. TAM and NK infiltrating experimental metastasis were analysed on frozen sections (10-μm thick) obtained from tissue blocks of B16F1 metastasis-bearing lungs. Sections were thawed and fixed with 4% PFA for 5 min, washed and incubated for 15 min in PBS supplemented with 0.05% Tween-20, 2% BSA, 5% donkey serum (Sigma-Aldrich), and incubated for 1 h with purified polyclonal goat anti-mouse NKp46 (R&D System), rat anti mouse F4/80 (Serotech), and rabbit anti-mouse Ki-67 (Cell Signalling). After extensively wash, sections were incubated for 1 h with Alexa Fluor (488, 568, 647)-conjugated species-specific cross-adsorbed detection antibodies (Molecular Probes). Nuclei were stained using DAPI. Sections were mounted with 20 μl FluorSave reagent (Calbiochem). Fluorescent high-resolution images were acquired with a Leica SP8 STED 3X confocal microscope (Leica HC PL APO 60X/1.40 oil STED white objective system) and analysed by LAS-X software.
Animal colonies
WT C57BL/6J mice were obtained by Charles River Laboratories (Calco, Italy). Mice with macrophage-specific Ms4a4a inactivation in C57BL/6J background were achieved breading mice carrying floxed Ms4a4a alleles (Ms4a4afl/fl; Ozgene) with mice expressing Cre under the control of the promoter of the lys2 gene, encoding for the myeloid-restricted lysozyme M protein (LysCre/+). Ms4a4afl/flLysCre/+ mice (here indicated as Ms4a4a-/-) were born in mendelian ratios, reproduced normally, and did not show significant differences in body weight compared to control floxed littermates (Ms4a4afl/flLys+/+, here used as WT animals). Ms4a4a-/- mice were co-housed with littermates in individually ventilated cages in a specific pathogen-free/viral antibody-free animal facility at Humanitas Clinical and Research Center. Clec7a-/- mice (here indicated as Dectin-1-/-) were obtained by Jackson Laboratory. To obtain double knock-out mice (here indicated as Ms4a4a x Dectin-1 KO), Dectin-1-/- mice were bred with Ms4a4afl/fl x ubiquitinCre/+ mice. Animals were housed in ventilated cages in a specific pathogen-free/viral antibody-free animal facility at Humanitas Clinical and Research Center. Experiments were performed using sex- and age-matched mice.
Experimental models
The 3-methylcholanthrene (3-MCA)-induced tumor model was performed as previously described 15. Briefly, 8 weeks old C57BL/6J male mice were subcutaneously injected in the right thigh with 100 μg 3-MCA (Sigma-Aldrich) dissolved in 100 μl corn oil and tumor progression was evaluated twice a week over the course of the following 5 months. In the melanoma B16F1 model, tumor dimension was monitored in mice s.c. injected with 0.1 x 106 B16F1 cells using the equation volume = πab2/6, where a and b are the lengths of the major and minor axes, as previously described 16. Lung metastasis were analysed in the lungs 10 days after i.v. injection with 0.3 x 106 B16F1 or B16F10 cells and 14 days after i.v. injection with 0.3 x 106 SL4 cells. To visualise metastasis, lungs from mice injected with SL4 were fixed and stained over night with Bouin’s Solution (Histoline). Liver metastasis were analysed 14 days after i.s. injection with 0.25 x 106 MC38 cells. For NK cell depletion in the melanoma model, mice were i.p. injected with 200 μg anti-NK1.1 (BioXcell) or its isotype control 3 days before and 100 μg anti-NK1.1 or isotype control 3 and 7 days after B16F1 cells injection and metastasis were evaluated at day 10. For NK cell depletion in the colon carcinoma model, mice were i.p. injected with 200 μg anti-NK1.1 (BioXcell) or its isotype control 5 and 3 days before and 3 and 7 and 10 days after MC38 cells injection and metastasis were evaluated at day 12. Animal procedures were reviewed and approved by the institutional Ethical Committee at Humanitas Clinical and Research Center and were in accordance with national (D.L. N. 116, G.U. suppl. 40, 18-2-1992 and N. 26, G.U. 4-3-2014) and international laws and policies (EEC Council Directive 2010/63/EU, OJ L 276/33 22-9-2010; National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, US National Research Council, 2011). The study was approved by the Italian Ministry of Health (approvals n. 89/2013-B issued on the 8/4/2013, 6B2B3.N.ERY issued on 06/12/2017, and 949/2018-PR issued on the 20/12/2018).
Split-ubiquitin assay
The split-ubiquitin assay was performed as previously described 17. Briefly, a split-ubiquitin NubG-X library from monocyte-derived human macrophages treated with 10-6 M Dex was directionally cloned into the prey vector pBT3-N and the bait protein MS4A4A cDNA was cloned into the bait vector pBT3-STE, in which the LexA-VP16-Cub cassette is fused to the N-terminus. The yeast strain NMY51 (MATa his3-200 trp1–901 leu2–3,112 ade2 LYS2::(lexAop)4-HIS3 ura3::(lexAop)8-LacZ ade2::(lexAop)8-ADE2 GAL4) was transformed using standard procedures 18. Transformants were grown on selective medium lacking leucine, tryptophan, histidine and adenine, with addition of 20 mM 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole. Positive clones were sequenced by colony PCR (pPR3N-FOR: 5’-GTCGAAAATTCAAGACAAGG-3’; pPR3N-REV: 5’-AAGCGTGACATAACTAATTAC-3’). Library plasmids were isolated from positive clones and retransformed into NMY51 to test bait dependency. Preys activating the histidine and adenine reporters in the presence of MS4A4A and not the empty pBT3-STE vector were considered as potential MS4A4A interactors.
Flow cytometry
For direct multi-color flow cytometry (FACS Canto II and LRS Fortessa; BD Bioscience), cells were incubated for 30 min at 4°C with directly conjugated anti-human antibodies (MS4A4A-PE, R&D System; CD3-FITC, BD Pharmigen; CD56-BV421, BioLegend; CD19-BV421, BD Pharmigen; CD14-FITC, BD Pharmigen; CD16-PE-Cy7, BD Pharmigen; CD11c-APC, BD Pharmigen; CD36-APC, BD Pharmingen; CD123-PE-Cy7, BD Pharmigen; CD163-AF700, BioLegend; CD206-FITC, BD Pharmingen; Dectin-1-PerCP Fluor 710, eBioscience; HLA-DR-APC-Cy7, BD Pharmigen) or anti-mouse antibodies (Dectin-1-PE, BioLegend; F4/80-PB, Serotech; F4/80-APC, eBioscience; CD45-BV605, BD Pharmingen; CD45-PerCP Cy5.5, BioLegend; CD45.2-FITC, eBioscience; CD45.2-APC-eFluor 780, eBioscience; NK1.1-PECF594 and NK1.1-PE, BD Pharmigen; CD3-APC, BD Pharmigen; CD3-APC-eFluor 780, eBioscience; CD107a-APC, BioLegend; DX-5-APC, eBioscience; CD4-FITC, BD Pharmigen; CD11b-PB, BD Pharmigen; CD11b-eFluor 450, eBioscience; B220-PE-Cy7, BD Pharmigen; Gr-1-PE, CD11c-PE-Cy7, BD Pharmigen; MHC Class II (I-A/I-E)-FITC, eBioscience; Ly6G-PE, BD Pharmigen; Ly6C-PerCP-Cy5.5 eBioscience; CD11c-Pe-Cy7, eBioscience; IFNγ AF700, BD Pharmingen) and their appropriate isotype controls. Live/dead cell discrimination was performed staining with the Zombie Aqua Fixable Viability Kit (Biolegend). For MS4A6A and MS4A7 surface staining, purified MS4A6A (Abnova) and MS4A7 (Novusbio) antibodies were used as primary antibodies and anti-human IgG-AF488 (Invitrogen) as secondary antibody. Wheat Germ Agglutinin AF594-conjugated (WGA; ThermoFisher) was used to detect N-acetylglucosamine residues on the surface of tumor cells. To block Fc receptors, a purified anti-mouse CD16/CD32 (BioLegend) was used. For intracellular staing, cells were permebilized and fixed using the FoxP3/Transcription Factor Staining Buffer Set (eBioscience). Phosphoproteins were detected as previously described 19 using the phospho-Syk-Tyr525/526 antibody (Cell Signalling) and the phospo-p38-Thr180/Tyr182 antibody (Cell Signalling) as primary antibodies and an anti-rabbit IgG AF647 as secondary antibody (Invitrogen) or the directly conjugated phospho-ERK-AF647 antibody (BD Pharmigen), according to protocols recommended by the manufacturers. To analyse immune cell infiltration, lungs were incubated for 1 h at 37°C in 1% DNAse I in HBSS supplemented with 1 mg/ml collagenase D (Roche) and then for 10 min in 5 mM EDTA on ice. The cell suspension was passed through a 70 μm filter, red cells were lysed with ACK (Lonza), and then cells were stained and analyzed by flow cytometry. Data were analyzed with FACS Diva (BD) and Flow Jo (Treestar) software. Gating strategies applied are reported in Figure S10.
Imaging analysis
Freshly isolated human monocytes were differentiated to macrophages directly on 14 mm diameter cover glasses (Menzel-Gläser) in 24 well plates and treated as described above. Cells were fixed with 4% PFA (Euromedex). For intracellular staining, cells were permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich), 2% BSA (Biosera), 5% goat serum (Dako) in PBS. Cells were then incubated for 18 h with a purified mouse anti-human MS4A4A MoAb (R&D System) and a purified goat anti-human Dectin-1 polyclonal (R&D System) and then for 1 h with Alexa Fluor (488, 647)-conjugated species-specific cross adsorbed detection antibodies (Molecular Probes). Nuclei were stained using DAPI. Lipid rafts were stained with the Vybrant Lipid Raft Labeling Kit, based on the cholera toxin subunit B (CT-B) labeled with the red-fluorescent Alexa Fluor 594 dye (Molecular Probes), following the manufacturer protocol. High-resolution images (1024 x 1024 pixels) were acquired with an Olympus Fluoview FV1000 laser scanning confocal microscope with 60X (N.A. 1.4) plan-apochromat oil immersion objective (Olympus) and analyzed with ImageJ software (NIH). Quantitative colocalization and statistical analysis were performed with Imaris Coloc 4.2 (Bitplane AG) software and FV1000 1.6 colocalization software (Olympus) and ImageJ Coloc2 plugin. Representative images were smoothed with a Gaussian filter and upscaled with bicubic interpolation (ImageJ). For stimulated emission depletion (STED) microscopy, human macrophages were stained with purified mouse anti-human MS4A4A MoAb (R&D System) and a purified goat anti human Dectin-1 polyclonal (R&D System) and then for 1 h with Alexa Fluor (568, 647)-conjugated species-specific cross-adsorbed detection antibodies (Molecular Probes). Lipid rafts were stained with the Vybrant Lipid Raft Labeling Kit, based on the CT-B labeled with the green-fluorescent Alexa Fluor 488 324 dye (Molecular Probes), following the manufacturer protocol. Mowiol was used as mounting medium. Alexa Fluor 488, 568 and 647 were excited with a 400 Hz white light laser tuned at 485/493, 561/569 and 635/643 nm, respectively, and emission was collected at 505-550, 580-620, and 650-700 nm, respectively. A gating between 0.4 to 7 ns was applied to avoid collection of reflection and autofluorescence and sequential acquisition was applied to avoid fluorescence overlap. The 775 nm CW-depletion laser (30% of power; ≈90 mW) was used for Alexa Fluor 488, 568 and 647 excitations. STED analysis was performed on ROI corresponding to the traced freehand area of the image of a single cell (3-5 ROIs per image) and xyz images (1928 x 1928 px; px size, 0.05 μm; vx size, 0.2 μm) were acquired in a z-stack (30-40 images; 0.2 μm slice) with a Leica SP8 STED 3X confocal microscope system adopting a Leica HC PL APO 100x/1.40 oil STED white objective at 706-929 mAU. CW-STED and gated CW-STED were applied to Alexa Fluor 488 and Alexa Fluor 568 and 647, respectively. A linear background subtraction was applied to all z-stack STED images. The colocalization rate was measured with the LASX software after a maximum intensity projection of the non-deconvolved images. Collected images were deconvolved with Huygens Professional software. To evaluate the interaction between MS4A4A and its putative partners, we investigated by Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy (FLIM) the Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) from an excited MS4A4A-eGFP donor molecule to ground state proximal acceptor molecules chimerized to the fluorescent protein mCherry 20. To this purpose, eGFP-MS4A4A and mCherry chimerized candidate partners were cotransfected in 2 x 105 CHO-K1 cells seeded onto poly-L-lysine treated coverslips, cells were fixed, irradiated with a 830 nm light to excite the donor, and imaged using a TriM Scope II two photon laser scanning microscope (LaVision Biotec) equipped with a 60X water immersion lens (LUMFL60x; Olympus). Light was separated using a IR700 long pass filter and detected with the FLIM X16 TCSPC module 350 (LaVision Biotec). FLIM data were fitted with single exponential and background correction using Imspector Pro (LaVision Biotech).
Gene expression analysis
For real-time PCR assay (qPCR), cells were lysed with QIAzol Reagent (Qiagen) and total RNA was extracted using miRNeasy mini kit (Qiagen). RNA was converted in cDNA using the High-Capacity cDNA Reverse Transcription Kit (Applied Biosystems) and quantification of the following transcripts was performed following the recommended protocols for SYBR Green Master Mix (Applied Biosystems): human MS4A4A (forward: 5’-CTGGGAAACATGGCTGTCATA-3’; reverse 5’-CTCATCAGGGCAGTCAGAATC-3’); murine Ms4a4a_CDS (forward: 5’-CTGCATAGGAGTATCCCTCTCT-3’; reverse 5’-GTCTCTGCCTTGGTAGGATTTG-3’), murine Ms4a4a_genotype (forward: 5’-TGTAATCGCCATCATGAACCT-3’; reverse 5’-GGGTATCCTATGTACACTGAAGAAG-3’); murine INAM (forward: 5′-GACACAGTTGGCCGAAGAGA-3′; reverse 5′-AACGCTGAGATTTCCTGCCA-3′); murine IL-12p40 (forward: 5’-GGAAGCACGGCAGCAGAATA-3’; reverse: 5’-AACTTGAGGGAGAAGTAGGAATGG-3’); murine IL-18 (forward: 5’-GACTCTTGCGTCAACTTCAAGG-3’; reverse: 5’-CAGGCTGTCTTTTGTCAACGA-3’); murine IL-15 (forward: 5’-CATTTTGGGCTGTGTCAGTGT-3’; reverse: 5’-ACTGGGATGAAAGTCACTGTCAGTG-3’). Results were normalized on human or murine GAPDH. qPCR was performed with the ViiA™ 7 Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems). To determine MS4A4A gene expression levels in different human tissues and cells lines and in different cancer types, the Laboratory for Systems Biology and Medicine RefExA database (http://sbmdb.genome.rcast.u-tokyo.ac.jp/refexa/main_search.jsp) and the Cancer Genome Atlas database (TCGA; dataset. https://doi.org/10.7908/C11G0KM9) through the Firebrowse repository (http://firebrowse.org/) were used. Gene expression levels as rsem values were downloaded and distribution boxplots were performed using the ggplot2 R package version 2.2.1. Correlation between MS4A4A and TAM markers were performed using the ‘rcorr’ function implemented in Hmisc R package version 4.0.3 adopting the Pearson’s correlation method. Significant correlations (p < 0.05) were plotted using the NMF R package version 0.20.6. Genes with a not significant correlation show a coefficient equal to zero. Mentioned source data are provided in Fig. S3.
NK cell functional assays
NK cell degranulation was investigated by the CD107a assay, as previously reported 21. Briefly, splenocytes isolated from Ms4a4a-/- and WT mice were treated for 18 h with 100 ng/ml rmIL-2 and co-cultured for 4 h with B16F1 or B16F10 cells (E:T ratio 12:1). Percentage of CD107a+ NK cells (Live/CD45+/CD3-/NK1.1+) was analysed by flow cytometry. IFNγ production was investigated on splenocytes isolated from Ms4a4a-/- and WT mice treated for 12 h with 50 ng/ml rmIL-2 and co-cultured for 4 h with B16F1 and additional 2 h with Golgi plug (BD Pharmingen). Percentage of IFNγ+ NK cells (Live/CD45+/CD3-/NK1.1+) was analysed by flow cytometry.
Macrophage functional assays
ROS production was investigated using the CellRox Deep Red reagent (Life Technologies) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Live-cell widefield microscopy was performed monitoring fluorescence at 350ex/461em (Hoechst) and 640ex/665em (CellROX) with a Cell-R epi-fluorescence microscope (Olympus). ROI were analysed using the Xcellence software (Olympus). Secreted cytokines were measured by ELISA (Duoset; R&D System).
Statistical analysis
Results were expressed as means ± SEM from multiple independent experiments. One way ANOVA and two-tailed Student’s t test were performed using Prism (GraphPad) and/or Excel (Microsoft) software. ROUT test was applied to determine outliers.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Results
MS4A4A expression is restricted to macrophages
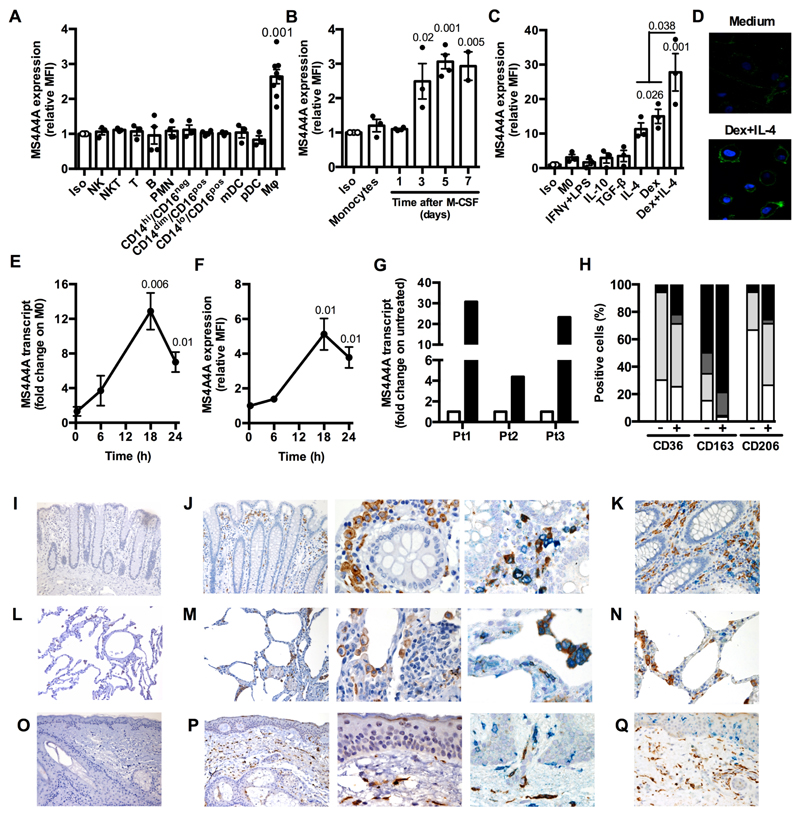
Transcriptomic data from us and others have previously identified MS4A4A as a putative marker of human macrophages undergoing IL-4-dependent alternative activation 8, 11. When investigated at the protein level by flow cytometry, macrophages were the only leukocyte population scoring positive, while circulating myeloid (PMN, monocyte subsets, myeloid and plasmacytoid dendritic cells) and lymphoid cells (NK, NKT, T, B) scored negative (Fig. 1A). Monocyte-derived dendritic cells did not express MS4A4A (Fig. S1A and S1B) and were also negative for MS4A6A and MS4A7, two other members of the MS4A family whose expression is associated to macrophages (Fig. S1E to S1H) 8. In vitro, MS4A4A expression progressively increased during M-CSF-dependent monocyte differentiation to macrophages (Fig. 1B). When regulation of MS4A4A expression in mature macrophages was investigated, we first confirmed its induction in alternative macrophages activated by IL-4, but not by other stimuli inducing M2-like phenotypes such as TGFβ and IL-10, and then identified glucocorticoid hormones (Dex) as a second potent inducer of MS4A4A expression, alone or in combination with IL-4 (Fig. 1C and 1D). As shown in Fig. 1E, the MS4A4A transcript was increased by Dex treatment at 18 h, when also a significant increase in MS4A4A protein expression was detected (Fig. 1F). Glucocorticoids were also demonstrated to act as potent MS4A4A inducers in vivo, as MS4A4A transcript levels were strongly upregulated in circulating monocytes isolated from Graves syndrome patients upon acute exposure to methylprednisolone (Fig. 1G). Conversely, Dex treatment was unable to induce expression of MS4A4A, MS4A6A, or MS4A7 in monocyte-derived dendritic cells (Fig. S1). Both in resting macrophages and more prominently in macrophages activated by Dex and IL-4 in combination, MS4A4A expression was significantly enriched in the CD163+ macrophage subset, while its expression did not correlate with CD36 and CD206 expression (Fig. 1H).
Figure 1. MS4A4A expression and its regulation in human macrophages.
A-C) Flow cytometry analysis of MS4A4A surface expression on human leukocyte subsets (A), on human monocytes during M-CSF-dependent differentiation to macrophages (B), and on differentiated macrophages in resting conditions (M0) and after treatment for 18 h with 20 ng/ml IFNγ plus 100 ng/ml LPS, 10 ng/ml IL-10, 20 ng/ml TGFβ, 20 ng/ml IL-4, 10-6 M Dex, or 20 ng/ml IL-4 + 10-6 M Dex (C). Data are represented as mean ± SEM of relative Mean Fluorescence Intensity (MFI, fold on isotype). Two experiments were performed (n = 3 - 8 for panel A, 3 - 5 for panel B, 3 for panel C). Statistical analysis by one-way ANOVA. Gating strategies used for panel 1A is shown in Figure S10A, for panels 1B and 1C in Figure S10B.
D) Immunofluorescence analysis of MS4A4A expression of human macrophages treated or not with 20 ng/ml IL-4 plus 10-6 M Dex for 18 h (lower and upper panel, respectively). DAPI staining of nuclei is shown in blue. Images are representative of one experiment out of 3 performed.
E-F) Time-course of MS4A4A transcript (E) and plasma membrane protein (F) in macrophages treated with 10-6 M Dex for the indicated time. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM of fold change (E) or relative MFI (F) on M0. Two experiments were performed (n = 3 for E and 5 for F). Statistical analysis by one sample Student’s t test.
G) Expression levels of MS4A4A transcript in monocytes isolated from three independent Graves orbitopathy patients (Pt) before and 6 h after the injection with 1 g methylprednisolone. Data are expressed as fold change on untreated cells (open columns).
H) Flow cytometry analysis of macrophages positive for membrane expression of MS4A4A and the other indicated M2 markers CD36, CD163, and CD206, in resting conditions (-) or after exposure for 18 h to 20 ng/ml IL-4 plus 10-6 M Dex. In each column, double negative cells are in white, MS4A4A single positive cells are in dark grey, cell only positive for the indicated marker are in light grey, double positive cells are in black. Two experiments were performed (n = 4 - 5). Gating strategy in Figure S10C.
I-Q) MS4A4A expression on formalin fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human colon (I-K), lung (L-N), and skin (O-Q). MS4A4A is visualized in brown (single staining in J-M-P, left and middle panels). In double-stained sections, MS4A4A expression (brown) was combined with CD163 (blue) in J-M-P right panels, CD1c (blue) in K, CD303 (blue) in N, and CD207 (blue) in Q. Omission of primary antibodies were used as negative control (I-L-O panels). Magnification: 100X (I-L-O and J-M-P left panels), 200X (K-N-Q) and 400X (J-M-P, middle and right panels). One set of images out of five healthy tissues analysed is shown.
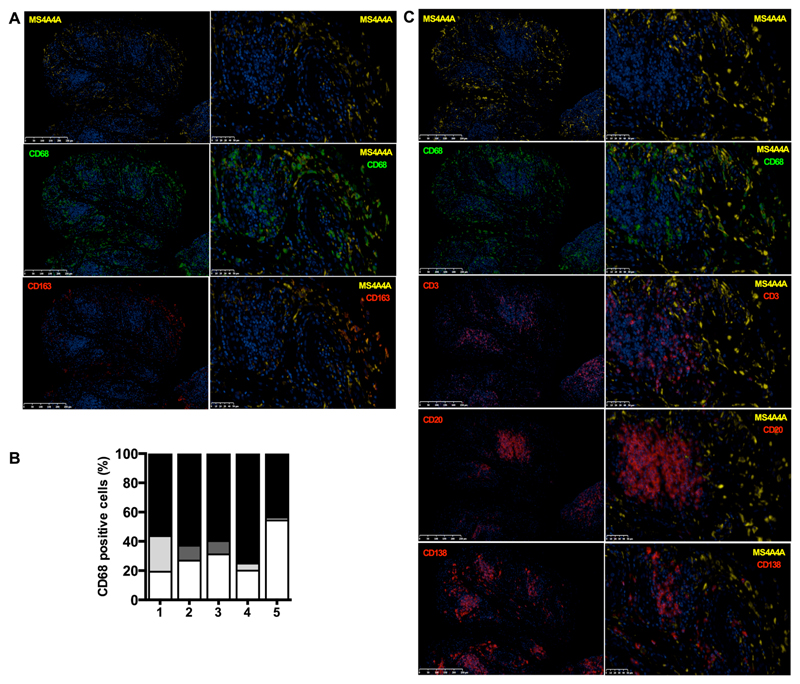
To define MS4A4A expression in tissues, we first interrogated the public gene expression database RefExA, which indicated expression of the MS4A4A transcript in several normal human tissues. However, when the search was conducted at the cell level, MS4A4A expression was again restricted to macrophages (Fig. S2A and S2B). In agreement with this, immunohistochemical analysis detected MS4A4A expression in several human tissues, including colon, lung, and skin (Fig. 1I to 1Q). Also in vivo, combined staining confirmed that MS4A4A expression was restricted to the CD163+ macrophages (Fig. 1J, 1M, and 1P). Importantly, lung plasmacytoid dendritic cells (CD303+), colon dendritic cells (CD1c+), and skin Langerhans cells (CD207+) did not express MS4A4A (Fig. 1K, 1N, and 1Q). Finally, when MS4A4A expression was investigated in the synovium of early rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, a prototypic chronic inflammatory condition, MS4A4A resulted again predominantly expressed by a subset of CD163+ macrophages (Fig. 2A and 2B) and was not detected in CD3+ T cells, CD20+ B cells, or CD138+ plasma cells (Fig. 2C) infiltrating the inflamed synovium. Taken together, these results indicate that both in normal and in chronic inflammatory conditions MS4A4A expression is restricted to tissue resident macrophages, where it is upregulated by IL-4 and glucocorticoid hormones.
Figure 2. MS4A4A expression is restricted to CD163+ macrophages in inflamed synovium.
A and C) Representative immunofluorescence images of MS4A4A expression on formalin fixed paraffin-embedded sections of synovial tissue from early RA patients. MS4A4A staining is visualized in yellow, CD68 in green; CD3, CD20, CD138 and CD163 are visualised in red. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI and visualised in blue. Matching isotype control antibodies were used as negative control. Magnification: 15X (left panels) and 40X (right panels).
B) Percentage of synovial macrophages (CD68+ cells) from early RA patients positive for MS4A4A and/or CD163, quantified by immunofluorescence in five individual RA patients (Pt 1 to 5). In each column, macrophages double negative for MS4A4A/CD163 are in white, MS4A4A single positive macrophages are in dark grey, CD163 single positive macrophages are in light grey, and MS4A4A/CD163 double positive macrophages are in black.
MS4A4A is expressed in tumor-associated macrophages (TAM) but is not functionally relevant for their protumoral function
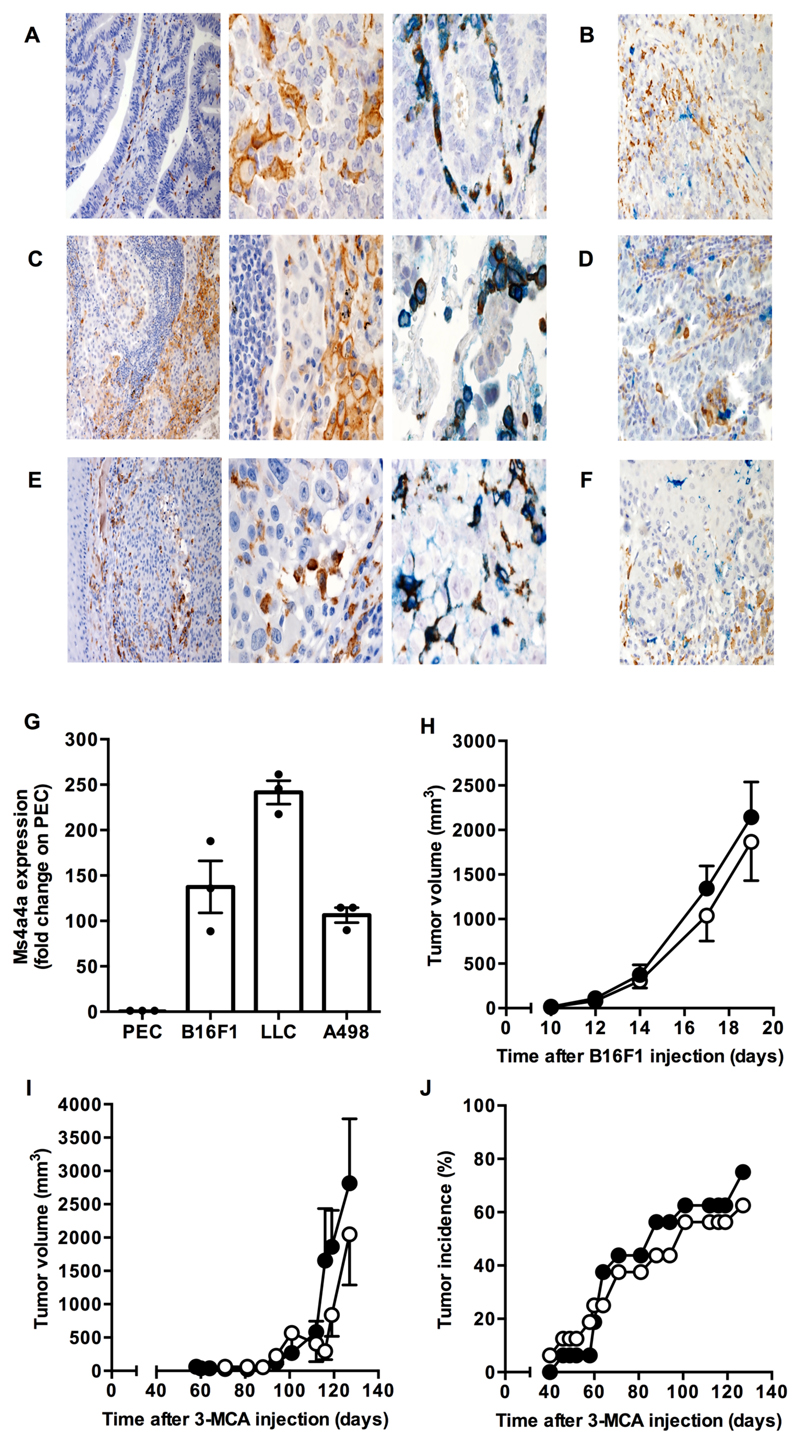
The gene expression database TCGA also reported the MS4A4A transcript signature in a large number of human tumors (Fig. S3A and S3B). Consistent with this, immunohistochemical analysis detected MS4A4A expression in colon and lung tumors, as well as in melanoma, and combined analysis confirmed that its expression was restricted to CD163+ TAM (Fig. 3A, 3C, 3E, and S3C), in agreement with results obtained on in vitro differentiated human macrophages and in inflamed synovium (Fig. 1H and 2A-B, respectively). A strong correlation between transcript levels encoding MS4A4A and CD163 and, to minor extent, other M2/TAM markers, was also evident in the TCGA cancer dataset (Fig. S3B). Importantly, also tumor-associated dendritic cells did not express MS4A4A (Fig. 3B, 3D, and 3F).
Figure 3. Ms4a4a is expressed in murine TAM but is dispensable for primary tumor growth.
A-F) MS4A4A expression on formalin fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human colon adenocarcinoma (A-B), lung adenocarcinoma (C-D), and melanoma (E-F). MS4A4A is visualized in brown (single staining A-C-E, left and middle panels). In double-stained sections, MS4A4A expression (brown) was combined with CD163 (blue) in A-C-E right panels, CD1c (blue) in B, CD303 (blue) in D, and CD207 (blue) in F. Magnification: 100X (A-C-E left panels), 200X (B-D-F) and 400X (A-C-E, middle and right panels). One set of images out of five cancer tissues analysed is shown.
G) Expression levels of the Ms4a4a transcript in murine TAM isolated from B16F1 tumors, Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC) tumors, and human renal cancer cell A498 tumor xenografts. Data are normalized to actin and expressed as mean ± SEM of Ms4a4a relative expression in TAM compared to corresponding PEC, used as control. Results pooled data (n = 4 - 7 mice per group) from one representative experiment out of three run in triplicate for A498 model and from one experiment (n = 3 mice per group) for LLC and B16F1 models. Gating strategy for cell sorting is shown in Figure S10D.
H) Tumor growth curve in Ms4a4a-/- (open symbol) and WT (closed symbol) mice upon s.c. injection of B16F1 melanoma cells. Two experiments were performed (n = 11); mean ± SEM. No statistical difference by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test.
I-J) Tumor volume (I) and incidence (J) of 3-methylcholanthrene-induced fibrosarcoma in Ms4a4a-/- (open symbol) and WT (closed symbol) mice. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 16). No statistical difference by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test.
As the absence of a specific antibody prevented us from investigating at the protein level the expression of Ms4a4a, the murine homologue of human MS4A4A, we evaluated its expression at the transcript level by qPCR. Consistent with results obtained in the human setting, macrophages were the only leukocyte population present in mouse spleen with detectable Ms4a4a transcript levels (Fig. S4A), and exposure to IL-4 or Dex, alone or in combination, strongly augmented its expression, while the M1 polarizing treatment IFNγ plus LPS was inactive (Fig. S4B). In line with high expression levels of MS4A4A detected by immunohistochemistry in human TAM, we detected elevated levels of the murine Ms4a4a transcript in murine TAM isolated from animals bearing LCC and B16F1 tumors, as well as xenograft tumors of the human kidney cancer cell line A498 grown in NOD/scid/IL-2Rγnull mice (Fig. 3G).
As Ms4a4a was highly expressed in murine TAM, we investigated its functional relevance for carcinogenesis and tumor progression in different tumoral experimental models. To this purpose, mice with macrophage-selective deletion of Ms4a4a were generated by breeding Ms4a4afl/fl and LysCre/+ animals. Ms4a4a expression was successfully abrogated in BMDM of Ms4a4afl/flLysCre/+ animals (indicated here as Ms4a4a-/- ; Fig. S4C), with no apparent phenotype or impact on the development for any immune subset (Fig. S4D). When animals were tested, we found no difference in appearance, incidence, and growth of primary tumors in mice having Ms4a4a competent or incompetent macrophages, neither in the B16F1 transplanted tumor model (Fig. 3H) nor in a model of mesenchymal carcinogenesis based on 3-MCA exposure (Fig. 3I and 3J). We conclude that, though highly expressed in TAM, Ms4a4a has no functional relevance for their ability to promote primary tumor growth, at least under the experimental conditions tested.
MS4A4A colocalizes with Dectin-1 in lipid rafts
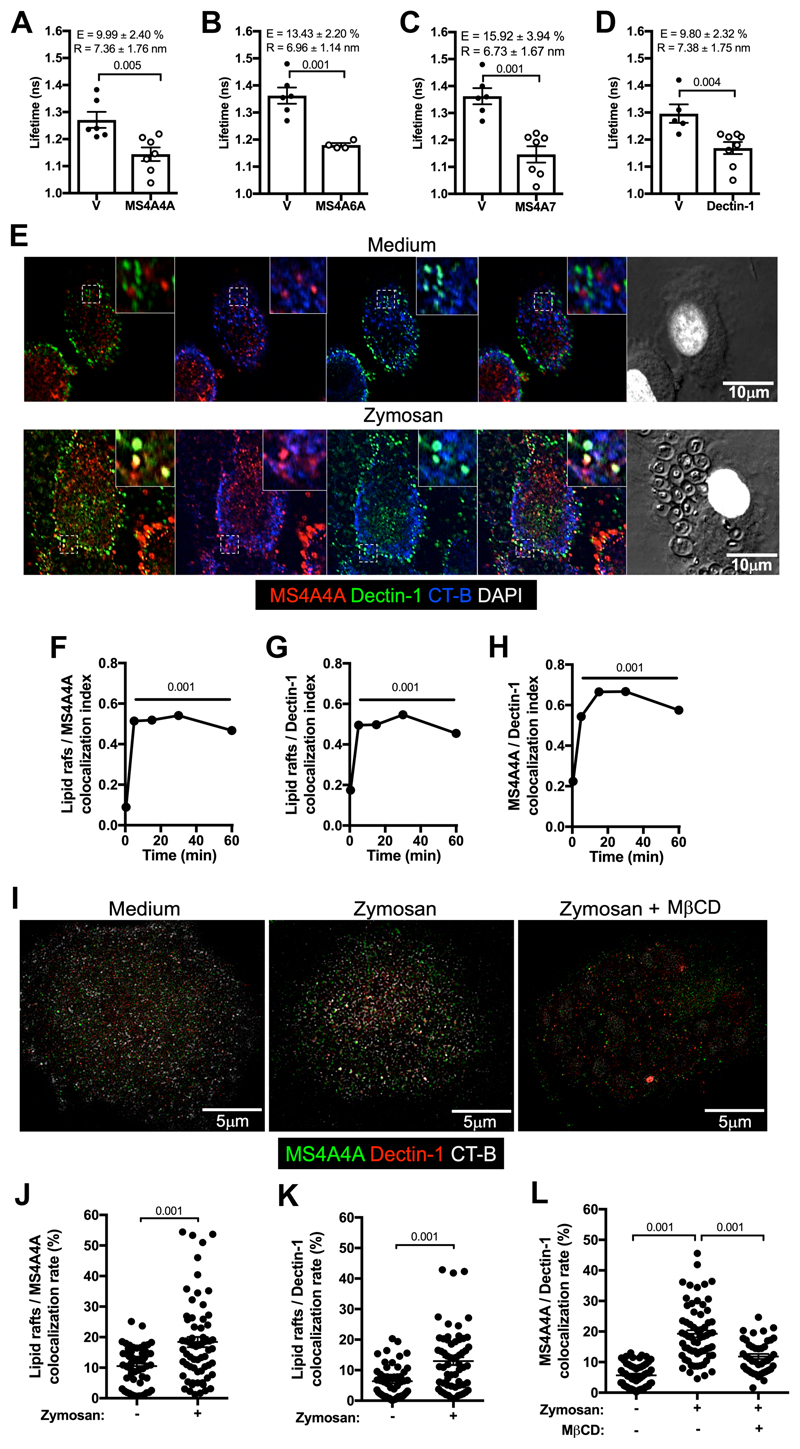
In search for a functional role of MS4A4A in macrophages, we considered the structural homology of MS4A proteins with tetraspanins, which are known to engage latero-lateral interactions with other membrane proteins and influence their functional properties 22, 23. By performing a split-ubiquitin yeast two-hybrid screening, an approach previously applied to identify partners of other MS4A members 17, we identified membrane proteins interacting with MS4A4A. These included MS4A4A itself as well as MS4A6A and MS4A7, two other MS4A family members highly expressed in alternative macrophages 8, suggesting that on the macrophage plasma membrane these three MS4A members may interact among themselves. MS4A4A interaction with these proteins was validated by FLIM-FRET analysis (Fig. 4A to 4C). On the opposite, FLIM-FRET experiments did not confirm the interaction of MS4A4A with the tetraspanins CD63 (Förster radius 1.24 ± 0.15 vs 1.27 ± 0.06 for vector and MS4A4A transfected cells, respectively; p > 0.05) and CD9 (Förster radius 1.28 ± 0.06 vs 1.26 ± 0.05 for vector and MS4A4A transfected cells, respectively; p > 0.05). Candidate MS4A4A interactors also included the membrane receptor Dectin-1, whose interaction with MS4A4A was confirmed by FLIM-FRET (Fig. 4D). Flow cytometry analysis indicated that macrophages had high co-expression levels of MS4A4A and Dectin-1, both under resting conditions and upon Dex treatment (Fig. S1I and S1J), and confocal microscopy experiments revealed that MS4A4A and Dectin-1 colocalization was significantly increased by the Dectin-1 agonist Zymosan (Fig. 4E and 4H). Zymosan also induced a significant increase in the colocalization index of both MS4A4A and Dectin-1 with the lipid rafts tracer CT-B (Fig. 4E to 4G). Super-resolution STED microscopy further confirmed increased colocalization of MS4A4A and Dectin-1 upon Zymosan stimulation, as well as increased colocalization of both proteins with CT-B (Fig. 4I to 4K). Interestingly, treatment with the cholesterol-depleting agent MβCD completely abrogated the Zymosan-induced increase in Dectin-1 colocalization with MS4A4A (Fig. 4I to 4L). Taken together, these results indicate that, upon exposure to Dectin-1 agonists, MS4A4A and Dectin-1 colocalizes in lipid rafts on the macrophage plasma membrane, suggesting a functional relevance of MS4A4A on Dectin-1 signalling.
Figure 4. MS4A4A and Dectin-1 associate in lipid rafts after Zymosan engagement.
A-D) FLIM-FRET analysis of eGFP mean fluorescence lifetime in CHO-K1 cells expressing eGFP-MS4A4A alone (V) or in combination with mCherry-MS4A4A (panel A), mCherry-MS4A6A (panel B), mCherry-MS4A7 (panel C), and mCherry-Dectin-1 (panel D). FRET efficiency (E) and Förster radius (R), which expresses the distance between the molecules, are indicated. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 4 - 7).
E-H) Colocalization of MS4A4A and Dectin-1 in lipid rafts (stained with cholera toxin; CT-B) in human macrophages treated or not with 100 μg/ml Zymosan analysed by immunofluorescence. Panel E shows images referring to the 30 min time point in one experiment out of 3 analysed, panels F to H report kinetics of colocalization of MS4A4A in lipid rafts, Dectin-1 in lipid rafts, and MS4A4A and Dectin-1, respectively. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI and visualised in white. Results are shown as mean ± SEM of the colocalization index (Manders coefficient) in 20÷78 cells analysed. Error bars are included in symbols. Statistical analysis in comparison with time 0 was performed by one-way ANOVA.
I-L) Super-resolution stimulated emission depletion microscopy (STED) analysis of MS4A4A and Dectin-1 in lipid rafts (stained with CT-B) in human macrophages treated or not for 15 min with 100 μg/ml Zymosan alone or in combination with 5 mM methyl-β-cyclodextrin. Panel I shows images referring to one experiment representative of 2 analysed. Panels J to L report the colocalization rate (%) of MS4A4A in lipid rafts, Dectin-1 in lipid rafts, and MS4A4A and Dectin-1, respectively. Results are shown as mean ± SEM of the colocalization rate in 20÷33 cells analysed. Statistical analysis by two-tailed unpaired (Mann-Whitney) Student’s t test (J and K) and one-way ANOVA (L).
Ms4a4a is dispensable for Dectin-1-dependent phagocytosis but is required for its signalling activity
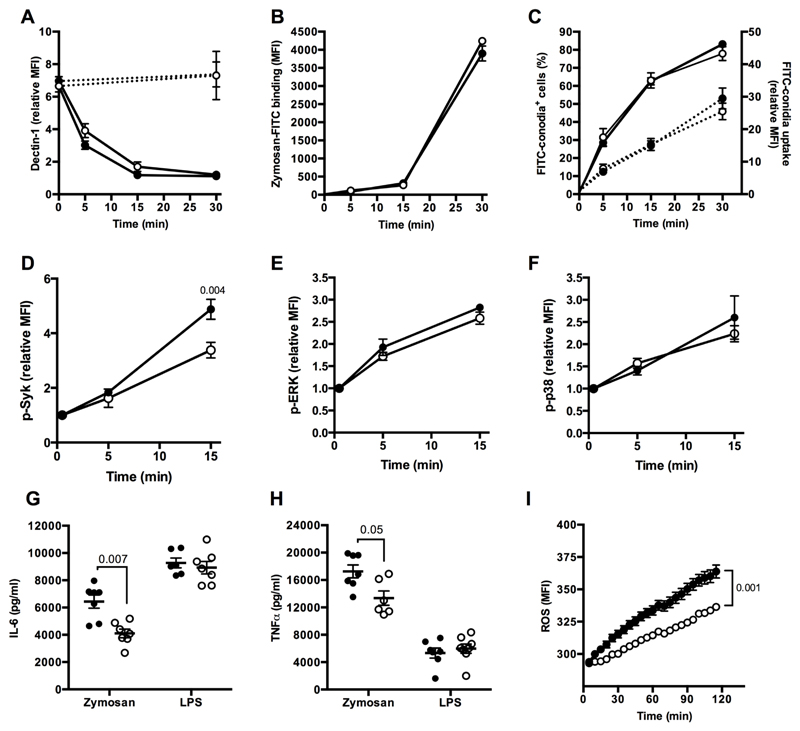
We then investigated the role of Ms4a4a in Dectin-1 functions. Similar levels of Dectin-1 expression were detected on BMDM generated from Ms4a4a-/- and WT mice, and no difference was observed in the rate of Dectin-1 internalization induced by its agonist Zymosan (Fig. 5A). Similarly, binding of Zymosan-FITC particles was identical in BMDM generated from Ms4a4a-/- and WT animals (Fig. 5B). Ms4a4a expression was also not relevant for Dectin-1 internalization and phagocytosis when A. fumigatus conidia were used (Fig. 5C).
Figure 5. MS4A4A is required for Dectin-1 signalling.
A) Dectin-1 surface expression on BMDM from Ms4a4a-/- (open symbol) and WT (closed symbol) mice, primed for 18 h with 10 ng/ml GM-CSF, upon stimulation for the indicated times with 100 μg/ml Zymosan (solid line) or 100 ng/ml LPS (dashed line). Data are represented as relative mean ± SEM of Mean Fluorescence Intensity (MFI, fold on isotype) in F4/80+ cells. Time 0: n = 15 for WT and 25 for Ms4a4a-/-; 5 min: n = 11 for WT and 20 for Ms4a4a-/-; 15 min: n = 4 for WT and 5 for Ms4a4a-/-; 30 min: n = 4 for WT and 3 for Ms4a4a-/-; 30 min with LPS: n = 6 for WT and 5 for Ms4a4a-/-. Five experiments were performed. Gating strategy in Figure S10E.
B) Binding of Zymosan-FITC to Ms4a4a-/- (open symbol) and WT (closed symbol) BMDM. Data are represented as mean ± SEM of Mean Fluorescence Intensity (MFI; n = 4 - 6).
C) Phagocytosis of A. Fumigatus conidia-FITC by Ms4a4a-/- (open symbol) and WT (closed symbol) BMDM. Data are represented as mean ± SEM of percentage (left y axis, solid lines) and relative MFI (fold on untreated; right y axis, dotted lines) of FITC+ cells gated on F4/80+ cells. Three experiments were performed (n= 6 for WT and 8 for Ms4a4a-/- at all time points). Gating strategy in Figure S10F.
D-F) Syk (D), ERK (E) and p38 (F) phosphorylation in BMDM from Ms4a4a-/- (open symbol) and WT (closed symbol) mice primed for 18 h with 10 ng/ml GM-CSF and stimulated or not for indicated times with 100 μg/ml Zymosan. Data are represented as mean ± SEM of relative Mean Fluorescence Intensity (MFI, fold on untreated). Five experiments (n = 4 - 12) for panel D; three experiments (n = 4 - 7) for panel E; four experiments (n = 4 - 8) for panel F. Statistical analysis by two-tailed unpaired (Mann-Whitney) Student’s t test. Gating strategies in Figure S10G, S10H, and S10I.
G-H) Secretion of IL-6 (G) and TNFα (H) by BMDM from Ms4a4a-/- (open symbols) and WT (closed symbols) mice primed for 18 h with 10 ng/ml GM-CSF and stimulated for 6 h with 100 μg/ml Zymosan or 100 ng/ml LPS (used as positive control). Cytokine levels in untreated cells were below detection limit. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. Four experiments were performed (n = 6 - 7 for panel G and n = 6 - 8 for panel H). Statistical analysis by two-tailed unpaired (Mann-Whitney) Student’s t test.
I) ROS production by BMDM from Ms4a4a-/- (open symbol) and WT (closed symbol) mice stimulated with 100 μg/ml Zymosan. Data are represented as MFI ± SEM (n = 6). Statistical analysis by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test.
In order to investigate the relevance of Ms4a4a for Dectin-1 signalling, phosphorylation of Syk, p38 and ERK was assessed in BMDM generated from Ms4a4a-/- and WT mice. While all three pathways were activated upon Zymosan challenge, Syk phosphorylation, but not ERK and p38 phosphorylation, was significantly reduced in Ms4a4a-/- as compared to WT BMDM (Fig. 5D to 5F). The same results were obtained when the Dectin-1-specific agonists depleted Zymosan and Curdlan were used, but not when BMDM were stimulated with LPS or PMA (Fig. S5A to S5D). Neither p38 nor ERK phosphorylation were influenced by Ms4a4a expression with any stimuli used (Fig. S5E and S5F). In accordance with reduced Syk phosphorylation, upon Zymosan challenge Ms4a4a-/- BMDM released less cytokines (e.g. IL-6 and TNFα; Fig. 5G and 5H, respectively) and produced less ROS (Fig. 5I). The same defect was observed when depleted Zymosan and Curdlan were used (Fig. S5G and S5J, S5H and S5K, respectively). Of note, the absence of Ms4a4a did not impact on cytokine production by BMDM stimulated with TLR agonists, such as LPS (Fig. 5G to 5I) or Pam3Cys (Fig. S5I and S5L).
Taken together, these results indicate that Ms4a4a is dispensable for Dectin-1-mediated microbial recognition and phagocytosis, but is required to support optimal Syk phosphorylation and production of inflammatory cytokines and ROS following Dectin-1 engagement.
Ms4a4a contributes to Dectin-1-mediated protection against metastasis
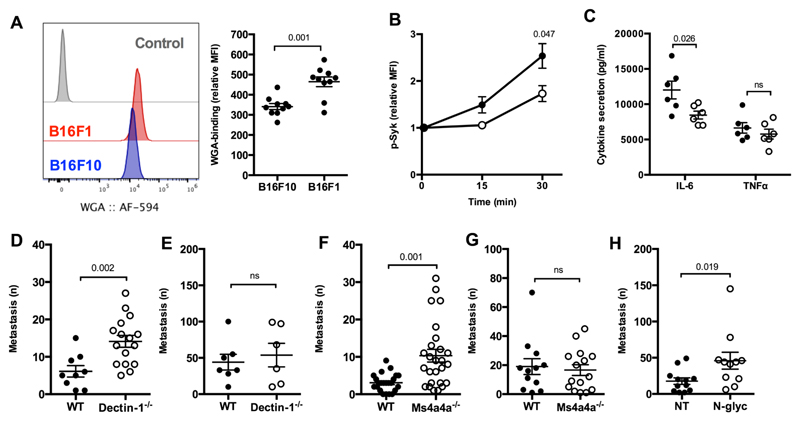
Dectin-1 has recently been shown to allow dendritic cell/macrophage-dependent recognition of tumor-associated molecular patterns on some tumor cells 16. This Dectin-1-mediated recognition pathway was shown to have an impact on the metastatic potential of the low metastatic B16F1 cells. Conversely, this pathway had no relevance for the metastatic potential of the highly metastatic B16F10 melanoma cells, which were found negative for the appropriate N-glycan structures recognized by Dectin-1 16. In accordance with this evidence, we observed a higher binding of WGA, which recognizes N-acetylglucosamine residues, on the surface of B16F1 cells as compared to B16F10 cells (Fig. 6A). As shown for the pathogen-derived Dectin-1 agonists (see Fig. 5 and S5), also the tumor B16F1 cells were able to trigger Syk phosphorylation and cytokine production by BMDM, both of which were reduced in Ms4a4a-/- as compared to WT cells (Fig. 6B and 6C).
Figure 6. Ms4a4a regulates Dectin-1 recognition and control of B16F1 metastasis.
A) WGA binding on the surface of B16F1 and B16F10 cells assessed by flow cytometry. Data are shown as representative dot plot (left) and mean ± SEM of relative Mean Fluorescence Intensity (MFI, fold on unstained; right). Six experiments were performed (n = 10). Statistical analysis by two-tailed unpaired (Mann-Whitney) Student’s t test. Gating strategy in Figure S10J.
B) Syk phosphorylation in BMDM from Ms4a4a-/- (open symbol) and WT (closed symbol) mice primed for 18 h with 10 ng/ml GM-CSF and cocultured or not for indicated times with B16F1 apoptotic cells (heat-shocked by 5 min at 65°C and 5 min on ice) at 1:1 ratio. Data are represented as mean ± SEM of relative Mean Fluorescence Intensity (MFI, fold on unstained). Three experiments (n = 6 - 11). Statistical analysis by two-tailed unpaired (Mann-Whitney) Student’s t test. Gating strategy in Figure S10K.
C) Secretion of indicated cytokines by BMDM from Ms4a4a-/- (open symbol) and WT (closed symbol) mice primed for 18 h with 10 ng/ml GM-CSF and cocultured with B16F1 cells for 6 h. Cytokine levels in untreated cells were below detection limit. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Two experiments (n = 5 - 6). Statistical analysis by two-tailed unpaired (Mann-Whitney) Student’s t test.
D-E) Number of metastatic foci in lungs from Dectin-1-/- (open symbol) and WT (closed symbol) mice upon i.v. injection of B16F1 (D) or B16F10 (E) melanoma cell lines. Results are reported as mean ± SEM. Three experiments for B16F1 cells (n = 9 for WT; n = 16 for Dectin-1-/-), one experiment for B16F10 cells (n = 7 for WT; n = 6 for Dectin-1-/-). Statistical analysis by two-tailed unpaired (Mann-Whitney) Student’s t test.
F-G) Number of metastatic foci in lungs from Ms4a4a-/- (open symbol) and WT (closed symbol) mice upon i.v. injection of B16F1 (F) or B16F10 (G) melanoma cell lines. Results are reported as mean ± SEM. Five experiments for B16F1 cells (n = 23 for WT; n = 26 for Ms4a4a-/-), three experiments for B16F10 cells (n = 12 for WT; n = 15 for Ms4a4a-/-). Statistical analysis by two-tailed unpaired (Mann-Whitney) Student’s t test.
H) Number of metastatic foci in lungs from WT mice upon i.v. injection of B16F1 treated for 1 h with 25 U/ml N-glycosidase F (N-Glyc, open symbol) or buffer (NT, closed symbol). Results are expressed as mean ± SEM. Two experiments were performed (n = 12 for NT; n = 11 for N-glyc). Statistical analysis by two-tailed unpaired (Mann-Whitney) Student’s test.
Prompted by this observation, we assessed the relevance of Dectin-1 and Ms4a4a expression in macrophages for the metastatic potential in vivo of B16F1 and B16F10 cells. In agreement with observations from Chiba and colleagues 16, B16F1 cells showed a significant higher metastatic potential in Dectin-1-/- animals compared to WT mice, whereas no difference was observed in the number of metastasis generated by B16F10 cells (Fig. 6D and 6E, respectively). Similarly to previous observations on Dectin-1 16, Ms4a4a deletion had no effect on the metastatic spreading of B16F10, but resulted in a significant increase in the number of B16F1 metastasis, whose metastatic potential became comparable to that of B16F10 (Fig. 6F, 6G, and S6A). Of note, the number of B16F1 metastases was not further increased when Ms4a4a x Dectin-1 double KO animals were used, consistent with the idea the two molecules cooperate in a common recognition mechanism (Fig. S6B). Importantly, the increased B16F1 metastatic spreading observed in the absence of Dectin-1 or Ms4a4a was also evident when N-glycans-depleted B16F1 cells were injected in WT animals (Fig. 6H). Similar experiments were then performed with two colon carcinoma cell lines with different metastatic potential. As observed for B16 cells, the low metastatic MC38 cells showed high WGA binding levels and an increased number of metastasis when injected in both Dectin-1-/- and Ms4a4a-/- mice as compared to WT mice (Fig. S7A, S7B, and S7D). Conversely, the highly metastatic SL4 cells, which showed lower WGA binding as compared to MC38 (Fig. S7A), generated the same number of metastasis in both Dectin-1-/- and Ms4a4a-/- animals compared to WT animals (Fig. S7C and S7E). Taken together, these results suggest that expression of Ms4a4a on macrophages is required for Dectin-1-mediated control of metastatic spreading of highly N-glycosylated tumor cells.
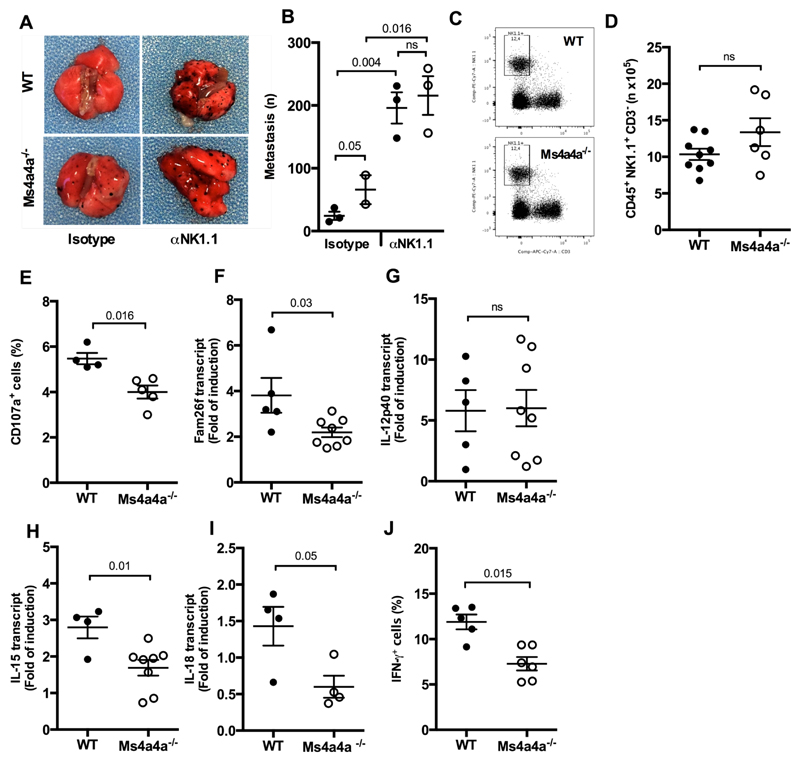
In vitro experiments have identified NK cells as effector cells in B16F1 killing 16. Consistent with this, NK cell depletion by the use of a αNK1.1 antibody resulted in a significant increase in B16F1 lung metastasis and abrogated the difference observed between Ms4a4a-/- and WT animals (Fig. 7A and 7B). Conversely, NK cell depletion did not abrogate the difference observed in the number of MC38 liver metastasis, opening new insights on a possible direct control of metastatic spread by Ms4a4a+ macrophages in the liver (Fig. S7D). Confocal microscopy analysis showed that in B16F1 lung metastasis NK cells and macrophages were located in close proximity, suggesting a possible cross-talk between NK cells and macrophages in tumors (Fig. S6C). Based on this, we then investigated the role of Ms4a4a in NK cell the activation. Though Ms4a4a deletion had no impact on the abundace of NK cells and macrophages in the lungs bearing B16F1 metastatic lesions (Fig. 7C and 7D for NK cells; Fig. S6D to S6G for macrophages), macrophage expression of Ms4a4a was required for optimal recognition by NK cells of tumor targets as NK cell cytotoxicity, assessed in vitro as the frequency of CD107a+ cells in a degranulation assay, was significantly lower when B16F1 cells were cultured with splenocytes from Ms4a4a-/- mice as compared to the WT counterpart (Fig. 7E). Of note, this defective activation of NK cells was not observed when B16F10 cells were used as targets (Fig. S6H). Chiba and colleagues proposed that Dectin-1 triggering by tumor cells induces expression on macrophage plasma membrane of IFN regulatory factor 3-dependent NK-activating molecule (INAM, also known as Fam26f), which in turn promotes NK cell activation leading to tumor cell killing 16. Consistent with this, induction of INAM transcript in BMDM cocultured with B16F1 cells was defective when Ms4a4a-deficient cells were used (Fig. 7F). A similar defect was observed when other Dectin-1 ligands were used, but not when BMDM were activated using LPS (Fig. S6I to S6K). The absence of Ms4a4a also affected the cytokine profile induced in BMDM by tumor cell recognition. While induction of IL-12p40 after B16F1 engagement did not require Ms4a4a expression on BMDM (Fig. 7G), we detected significant lower levels of both IL-15 and IL-18 transcripts (Fig. 7H and 7I, respectively), a defect also evident when BMDM were stimulated with Zymosan (Fig. S6L). Consistent with this, IFNγ production by NK cells was significant lower when B16F1 cells were cocultured with Ms4a4a-/- splenocytes as compared to WT littermates (Fig. 7J). Taken together, these results are consistent with a non-redundant role of Ms4a4a expression in macrophages in controlling tumor metastatization by supporting a Dectin-1-dependent recognition of N-glycans on tumor cells and triggering NK cell-mediated tumor cell killing.
Figure 7. Expression of Ms4a4a in macrophages is required for NK-mediated Dectin-1-triggered protection against metastasis.
A-B) Representative images (A) and number of metastatic foci (B) in lungs from Ms4a4a-/- (open symbol) and WT (closed symbol) mice injected i.v. with B16F1 cells upon NK cell depletion. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM. Two experiments performed (n = 2 - 3 for each group). Statistical analysis by one-way ANOVA and unpaired Student’s t test.
C-D) Representative dot plots (C) and numbers (D) of NK cell infiltrating the lungs of Ms4a4a-/- (open symbol) and WT (closed symbol) mice injected i.v. with B16F1 cells. Data are represented as mean ± SEM of absolute numbers (n) of Live/CD45+/CD3-/NK1.1+ cells. Three experiments were performed (n = 9 for WT and 6 for Ms4a4a-/-). Statistical analysis by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. Gating strategy in Figure S10M.
E) Degranulation of NK cells after engagement with B16F1 cells. Data are represented as mean ± SEM of percentage of CD107a+ NK cells gated on Live/CD45+/CD3-/NK1.1+ splenocytes. Two experiments were performed (n = 4 for WT and 5 for Ms4a4a-/-). Statistical analysis by two tailed unpaired (Mann-Whitney) Student’s t test. Gating strategy in Figure S10L.
F-I) Transcript abundance of INAM (Fam26f; F), IL-12p40 (G), IL-15 (H), and IL-18 (I) in Ms4a4a-/- (open symbol) and WT (closed symbol) BMDM primed with 10 ng/ml rmGM-CSF cocultured for 24 h with B16F1 apoptotic cells (heat-shocked by 5 min at 65°C and 5 min on ice). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM of fold of induction. Two experiments were performed for panel F (n = 5 for WT and 8 for Ms4a4a-/-), G (n = 5 for WT and 8 for Ms4a4a-/-), H (n = 4 for WT and 8 for Ms4a4a-/-), and I (n = 4 for WT and 4 for Ms4a4a-/-). Statistical analysis by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test.
J) IFNγ production by NK cells after engagement with B16F1 cells. Data are represented as mean ± SEM of percentage of IFNγ+ NK cells gated on Live/CD45+/CD3-/NK1.1+ splenocytes. Two experiments were performed (n = 5 for WT and 6 for Ms4a4a-/-). Statistical analysis by two tailed unpaired (Mann-Whitney) Student’s t test. Gating strategy in Figure S10L.
Discussion
MS4A4A is a member of the MS4A family, encoded in a 600 Kb region on chromosome 11q12-13 in human and chromosome 19 in mouse genome 24, 25. MS4A4A has been reported by us and by others as a macrophage-restricted transcript associated with M2/M2-like polarization, and genome-wide association studies have correlated SNP variants within the MS4A4A/MS4A6A locus with late onset Alzheimer’s disease 26 and cutaneous systemic sclerosis 27. Recent studies have described MS4A4A as a chemosensor expressed by necklace sensory neurons 28 and as a partner of the receptor tyrosine kinase KIT in mast cells 29, but its function in macrophages is unknown.
MS4A proteins are characterized by a common structural organization based on four putative highly hydrophobic transmembrane domains, two extracellular loops, and short cytoplasmic N- and C-terminals, tightly resembling tetraspanins 30, 31, 32. Tetraspanins, a large family of cell-surface proteins with a similar structural organization, are known to establish homo and heterocomplexes called tetraspanin-enriched microdomains in which they engage lateral interactions with different partners, influencing their trafficking and signalling properties 23, 33, 34, 35, 36. Of note, some MS4A proteins, including CD20/MS4A1, FcεR1β/MS4A2, and the highly MS4A4A-related protein MS4A4B, have been shown to enter oligomeric complexes in lipid rafts, where they interact and influence signalling properties of associated partners 17, 37, 38, 39. Furthermore, MS4A4A has been reported to regulate the signalling activity of the receptor tyrosine kinase KIT controlling its endocytic recycling and degradation pathways by a mechanism that involves colocalization of KIT with caveolin-1 in lipid rafts in mast cells 29. Here we have demonstrated that, after Dectin-1 engagement by Zymosan, Dectin-1 and MS4A4A translocate in lipid rafts on macrophage plasma membrane. Of note, Dectin-1 has already been reported to interact with tetraspanins, which control its availability on the plasma membrane and the amount of cytokines produced after Zymosan engagement 40, 41. Finally, we also provide evidence of MS4A4A association with itself and with MS4A6A and MS4A7, other two MS4A family members with a macrophage-restricted expression pattern, and showed that in the absence of MS4A4A expression the signalling properties of Dectin-1 are affected. Taken together, our results suggest that these three MS4A proteins may contribute to the organization on the plasma membrane of macrophages of specific microdomains where signalling properties of membrane receptors, including Dectin-1, are regulated.
Dectin-1 is a pattern recognition receptor belonging to the non-classical C-type lectin receptors family 42. Dectin-1 plays a pivotal role in controlling a wide range of fungal infections, including species of Candida, Aspergillus, Pneumocystis, and Coccidioides 42, 43, 44, but more recently its role in the resistance to a broader range of microorganisms, in autoimmunity, and in tumor cell recognition has also been recognized 45. The signalling activity of Dectin-1 after ligand engagement requires clustering into a phagocytic synapse 19 and results in enhanced phagocytosis and respiratory burst activity and secretion of several cytokines, including IL-6 and TNFα 46, 47, 48. The Dectin-1 signalling pathway in macrophages is still ill-defined 49, 50, 51. It has however been demonstrated Dectin-1 signaling activity in macrophages is delayed as compared to dendritic cells, and that it leads to both Syk-independent and Syk-dependent signalling pathways, which control phagocytosis and production of effector molecules (cytokines and ROS), respectively 49, 52, 53, 54. Our evidence that MS4a4a-deficient macrophages show normal phagocytic properties but reduced Syk phosphorylation and impaired cytokine and ROS production indicates that MS4A4A is functionally relevant for the Syk-dependent signalling pathway in macrophages. In macrophages, MS4A4A expression was significantly increased by IL-4 and, intriguingly, glucocorticoids. In patients with Graves disease treated with methylprednisolone, induction of MS4A4A was observed in circulating monocytes, thus providing an in vivo confirmation of the regulation found in vitro. Glucocorticoid hormones are potent regulators of immunity and inflammation and macrophages are a prime target for their action under physiological and pharmacological conditions 55. Glucocorticoid hormones not only suppress inflammatory cytokines production, but also orchestrate tissue remodeling and reshape macrophage functions with the induction of antiinflammatory molecules such as the IL-1 decoy receptor IL-1R2 56 and selected chemokines 57. Moreover, glucocorticoid hormones have been suggested to set components of the innate immune system in an alert mode, priming for immediate/early responses to pathogens 55. Given the coupling of MS4A4A with a microbial sensor, its induction could be a component of this early aspect of the pathophysiology of glucocorticoid hormones. Irrespective of its significance, monocyte expression of MS4A4A could serve as a biomarker of the response of mononuclear phagocytes to these agents.
Macrophages have been shown to promote activation of NK cells anti-tumoral activities through direct cell-cell contacts or soluble mediators, including IL-15 and IFNβ 21, 58, 59. In this setting, recent evidence in a melanoma model indicates that macrophage recognition of tumor cell-associated molecular patterns via Dectin-1 is associated with reduction of tumor burden and metastatic spreading due to the activation of cytotoxic NK cells 16. NK cells are known to play a major role in resistance against hematologic neoplasms, while their role in solid tumors is usually considered less relevant 60, 61. Recent results challenge this long held view by showing that inactivation of the NK cell checkpoint IL-1R8 unleashes NK cell mediated resistance against carcinogenesis at NK cell-rich anatomical sites, such as liver and lung 62. In line with this general view, results reported here indicate that when macrophages are engaged via Dectin-1 with B16F1 melanoma cells, the absence of MS4A4A impairs their ability to upregulate INAM, secrete IFNγ-inducing cytokines, and trigger NK cell-mediated cytotoxic response, thus hampering NK cell ability to control tumor metastatization to the lung. Considering these evidence and the observation that MS4A4A is barely detectable in the various subsets of circulating monocytes and induced during their differentiation to macrophages, we conclude that MS4A4A expression on TAM is likely required to support the interaction between NK cells and TAM observed in metastatic foci, where this cross-talk activates NK cells-mediated tumor cell killing. MS4A4A therefore does not contribute to the protumoral functions of TAM infiltrating primary tumors and conversely its expression in macrophages at metastatic sites is required for appropriate NK-mediated anti-tumoral functions. These results are well in line with previous results by us and others showing that the organ immunological context is indeed a key determinant of effective antitumor effector mechanisms 63, with divergent impact of immune manipulations on primary versus metastatic tumors 64, 65.
Several studies are ongoing with the aim of targeting TAM as a promising immune strategy to impact on tumor biology 3, 66, 67. MS4A4A belongs to the same protein family of CD20 (also known as MS4A1) and as mentioned the two proteins share a similar protein structural organization 24. Thus, from a translational perspective, as CD20 targeting by monoclonal antibodies has proven to be effective for the treatment of hematological and autoimmune disorders 68, 69, our discovery of MS4A4A as a new M2/TAM marker raises the interesting possibility that it may represent a valid target for TAM depletion, though the anti-tumoral effect has to be balanced with the negative impact on metastasis spreadin we have shown here. Finally, targeting the MS4A4A/Dectin-1 interaction may allow fine tuning of uncontrolled, pathogen-triggered innate immune responses.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
Authors thank Cecilia Garlanda and Marinos Kallikourdis (Humanitas Clinical and Research Center) for providing cDNAs of murine leukocyte subsets, Tatsuro Irimura (Juntendo University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan) and Raffaella Giavazzi (Mario Negri Institute, Milan, Italy) for providing MC38 and SL4 cells. Technical assistance from Alessandro Fontanini, Chiara Perrucchini, Tilo Schorn, Remi Porte, and Fabio Pasqualini is acknowledged. Antonio Inforzato (Humanitas Clinical and Research Center), Andreas Diefenbach (Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Germany), and Luise Florin (University Medical Centre of the Johannes Gutenberg University, Mainz, Germany) are gratefully acknowledged for their support and discussion.
Financial support from Fondazione Cariplo (grant n. 2015-0564 to AM), Cluster Alisei (MEDINTECH CTN01_00177_962865 to AM), the European Research Council (grant no. 669415 - PHII to AM), the Italian Association for Cancer Research (AIRC IG-2016 grant n. 19014 to AM; AIRC 5X1000 grant n. 21147 to AM; AIRG IG-2016 grant n. 19213 to ML), Medical Research Council (Pathobiology of Early Arthrytis Cohort – PEAC grant n. 36661 to CP), and Arthritis Research UK Experimental Treatment Centre (grant n. 20022 to CP). IM was supported by a “Mario and Valeria Rindi” fellowship and a “Fellowship for abroad” from the Italian Foundation for Cancer Research, and by a European Federation of Immunological Societies-IL short-term fellowship. RSG was supported by a PhD studentship (PD/BD/114138/2016) from Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia, Purtugal. FT and SKB were supported by an ARAP fellowship and by core-funding from SIgN - A*STAR, Singapore. SL was supported by Fondazione Beretta, Italy.
References
- 1.Biswas SK, Mantovani A. Macrophage plasticity and interaction with lymphocyte subsets: cancer as a paradigm. Nat Immunol. 2010;11:889–896. doi: 10.1038/ni.1937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Murray PJ, et al. Macrophage activation and polarization: nomenclature and experimental guidelines. Immunity. 2014;41:14–20. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.06.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Mantovani A, Marchesi F, Malesci A, Laghi L, Allavena P. Tumour-associated macrophages as treatment targets in oncology. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2017;14:399–416. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2016.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Noy R, Pollard JW. Tumor-associated macrophages: from mechanisms to therapy. Immunity. 2014;41:49–61. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.06.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ruffell B, Affara NI, Coussens LM. Differential macrophage programming in the tumor microenvironment. Trends Immunol. 2012;33:119–126. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2011.12.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sica A, et al. Macrophage polarization in tumour progression. Semin Cancer Biol. 2008;18:349–355. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2008.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gabrilovich DI, Ostrand-Rosenberg S, Bronte V. Coordinated regulation of myeloid cells by tumours. Nat Rev Immunol. 2012;12:253–268. doi: 10.1038/nri3175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Martinez FO, Gordon S, Locati M, Mantovani A. Transcriptional profiling of the human monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation and polarization: new molecules and patterns of gene expression. J Immunol. 2006;177:7303–7311. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.10.7303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Martinez FO, et al. Genetic programs expressed in resting and IL-4 alternatively activated mouse and human macrophages: similarities and differences. Blood. 2013;121:e57–69. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-06-436212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Varol C, Mildner A, Jung S. Macrophages: development and tissue specialization. Annu Rev Immunol. 2015;33:643–675. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-032414-112220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sanyal R, et al. MS4A4A: a novel cell surface marker for M2 macrophages and plasma cells. Immunol Cell Biol. 2017;95:611–619. doi: 10.1038/icb.2017.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Solinas G, Germano G, Mantovani A, Allavena P. Tumor-associated macrophages (TAM) as major players of the cancer-related inflammation. J Leukoc Biol. 2009;86:1065–1073. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0609385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Aletaha D, et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:2569–2581. doi: 10.1002/art.27584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kelly S, et al. Ultrasound-guided synovial biopsy: a safe, well-tolerated and reliable technique for obtaining high-quality synovial tissue from both large and small joints in early arthritis patients. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74:611–617. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bonavita E, et al. PTX3 is an extrinsic oncosuppressor regulating complement-dependent inflammation in cancer. Cell. 2015;160:700–714. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chiba S, et al. Recognition of tumor cells by Dectin-1 orchestrates innate immune cells for anti-tumor responses. Elife. 2014;3:e04177. doi: 10.7554/eLife.04177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Howie D, et al. MS4A4B is a GITR-associated membrane adapter, expressed by regulatory T cells, which modulates T cell activation. J Immunol. 2009;183:4197–4204. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0901070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Woods RA, Gietz RD. High-efficiency transformation of plasmid DNA into yeast. Methods Mol Biol. 2001;177:85–97. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-210-4:085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Goodridge HS, et al. Differential use of CARD9 by dectin-1 in macrophages and dendritic cells. J Immunol. 2009;182:1146–1154. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.182.2.1146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Millington M, et al. High-precision FLIM-FRET in fixed and living cells reveals heterogeneity in a simple CFP-YFP fusion protein. Biophys Chem. 2007;127:155–164. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2007.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mattiola I, et al. Priming of Human Resting NK Cells by Autologous M1 Macrophages via the Engagement of IL-1beta, IFN-beta, and IL-15 Pathways. J Immunol. 2015;195:2818–2828. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Charrin S, et al. Lateral organization of membrane proteins: tetraspanins spin their web. Biochem J. 2009;420:133–154. doi: 10.1042/BJ20082422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Levy S, Shoham T. The tetraspanin web modulates immune-signalling complexes. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:136–148. doi: 10.1038/nri1548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Adra CN, et al. Cloning of the cDNA for a hematopoietic cell-specific protein related to CD20 and the beta subunit of the high-affinity IgE receptor: evidence for a family of proteins with four membrane-spanning regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994;91:10178–10182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.21.10178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hupp K, Siwarski D, Mock BA, Kinet JP. Gene mapping of the three subunits of the high affinity FcR for IgE to mouse chromosomes 1 and 19. J Immunol. 1989;143:3787–3791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hollingworth P, et al. Common variants at ABCA7, MS4A6A/MS4A4E, EPHA1, CD33 and CD2AP are associated with Alzheimer's disease. Nat Genet. 2011;43:429–435. doi: 10.1038/ng.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Rice LM, et al. A longitudinal biomarker for the extent of skin disease in patients with diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67:3004–3015. doi: 10.1002/art.39287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Greer PL, et al. A Family of non-GPCR Chemosensors Defines an Alternative Logic for Mammalian Olfaction. Cell. 2016;165:1734–1748. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Cruse G, et al. The CD20 homologue MS4A4 directs trafficking of KIT toward clathrin-independent endocytosis pathways and thus regulates receptor signaling and recycling. Mol Biol Cell. 2015;26:1711–1727. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E14-07-1221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Eon Kuek L, Leffler M, Mackay GA, Hulett MD. The MS4A family: counting past 1, 2 and 3. Immunol Cell Biol. 2016;94:11–23. doi: 10.1038/icb.2015.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ishibashi K, Suzuki M, Sasaki S, Imai M. Identification of a new multigene four-transmembrane family (MS4A) related to CD20, HTm4 and beta subunit of the high-affinity IgE receptor. Gene. 2001;264:87–93. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(00)00598-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Liang Y, Tedder TF. Identification of a CD20-, FcepsilonRIbeta-, and HTm4-related gene family: sixteen new MS4A family members expressed in human and mouse. Genomics. 2001;72:119–127. doi: 10.1006/geno.2000.6472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Berditchevski F, Odintsova E. Tetraspanins as regulators of protein trafficking. Traffic. 2007;8:89–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2006.00515.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Boucheix C, Rubinstein E. Tetraspanins. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2001;58:1189–1205. doi: 10.1007/PL00000933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hemler ME. Tetraspanin functions and associated microdomains. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:801–811. doi: 10.1038/nrm1736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Tarrant JM, Robb L, van Spriel AB, Wright MD. Tetraspanins: molecular organisers of the leukocyte surface. Trends Immunol. 2003;24:610–617. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2003.09.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Dombrowicz D, et al. Allergy-associated FcRbeta is a molecular amplifier of IgE- and IgG-mediated in vivo responses. Immunity. 1998;8:517–529. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80556-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Petrie RJ, Deans JP. Colocalization of the B cell receptor and CD20 followed by activation-dependent dissociation in distinct lipid rafts. J Immunol. 2002;169:2886–2891. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.6.2886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Polyak MJ, Li H, Shariat N, Deans JP. CD20 homo-oligomers physically associate with the B cell antigen receptor. Dissociation upon receptor engagement and recruitment of phosphoproteins and calmodulin-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:18545–18552. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M800784200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Mantegazza AR, et al. CD63 tetraspanin slows down cell migration and translocates to the endosomal-lysosomal-MIICs route after extracellular stimuli in human immature dendritic cells. Blood. 2004;104:1183–1190. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-01-0104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Meyer-Wentrup F, et al. Dectin-1 interaction with tetraspanin CD37 inhibits IL-6 production. J Immunol. 2007;178:154–162. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.1.154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Taylor PR, et al. Dectin-1 is required for beta-glucan recognition and control of fungal infection. Nat Immunol. 2007;8:31–38. doi: 10.1038/ni1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Hardison SE, Brown GD. C-type lectin receptors orchestrate antifungal immunity. Nat Immunol. 2012;13:817–822. doi: 10.1038/ni.2369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Wuthrich M, Deepe GS, Jr, Klein B. Adaptive immunity to fungi. Annu Rev Immunol. 2012;30:115–148. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-020711-074958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Dambuza IM, Brown GD. C-type lectins in immunity: recent developments. Curr Opin Immunol. 2015;32:21–27. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2014.12.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Brown GD. Dectin-1: a signalling non-TLR pattern-recognition receptor. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6:33–43. doi: 10.1038/nri1745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.del Fresno C, et al. Interferon-beta production via Dectin-1-Syk-IRF5 signaling in dendritic cells is crucial for immunity to C. albicans. Immunity. 2013;38:1176–1186. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.05.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Willment JA, Brown GD. C-type lectin receptors in antifungal immunity. Trends Microbiol. 2008;16:27–32. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2007.10.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Brubaker SW, Bonham KS, Zanoni I, Kagan JC. Innate immune pattern recognition: a cell biological perspective. Annu Rev Immunol. 2015;33:257–290. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-032414-112240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Rogers NC, et al. Syk-dependent cytokine induction by Dectin-1 reveals a novel pattern recognition pathway for C type lectins. Immunity. 2005;22:507–517. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2005.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Zanoni I, et al. CD14 controls the LPS-induced endocytosis of Toll-like receptor 4. Cell. 2011;147:868–880. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.09.051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Dennehy KM, et al. Syk kinase is required for collaborative cytokine production induced through Dectin-1 and Toll-like receptors. Eur J Immunol. 2008;38:500–506. doi: 10.1002/eji.200737741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Herre J, et al. Dectin-1 uses novel mechanisms for yeast phagocytosis in macrophages. Blood. 2004;104:4038–4045. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-03-1140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Underhill DM, Rossnagle E, Lowell CA, Simmons RM. Dectin-1 activates Syk tyrosine kinase in a dynamic subset of macrophages for reactive oxygen production. Blood. 2005;106:2543–2550. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-03-1239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Cain DW, Cidlowski JA. Immune regulation by glucocorticoids. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017;17:233–247. doi: 10.1038/nri.2017.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Colotta F, et al. Interleukin-1 type II receptor: a decoy target for IL-1 that is regulated by IL-4. Science. 1993;261:472–475. doi: 10.1126/science.8332913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Kodelja V, et al. Alternative macrophage activation-associated CC-chemokine-1, a novel structural homologue of macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha with a Th2-associated expression pattern. J Immunol. 1998;160:1411–1418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Bellora F, et al. The interaction of human natural killer cells with either unpolarized or polarized macrophages results in different functional outcomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:21659–21664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1007654108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Michel T, Hentges F, Zimmer J. Consequences of the crosstalk between monocytes/macrophages and natural killer cells. Front Immunol. 2012;3:403. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Gorelik E, Wiltrout RH, Okumura K, Habu S, Herberman RB. Role of NK cells in the control of metastatic spread and growth of tumor cells in mice. Int J Cancer. 1982;30:107–112. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910300118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Morvan MG, Lanier LL. NK cells and cancer: you can teach innate cells new tricks. Nat Rev Cancer. 2016;16:7–19. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2015.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Molgora M, Barajon I, Mantovani A, Garlanda C. Regulatory Role of IL-1R8 in Immunity and Disease. Front Immunol. 2016;7:149. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Molgora M, et al. IL-1R8 is a checkpoint in NK cells regulating anti-tumour and anti-viral activity. Nature. 2017;551:110–114. doi: 10.1038/nature24293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Mantovani A, Giavazzi R, Polentarutti N, Spreafico F, Garattini S. Divergent effects of macrophage toxins on growth of primary tumors and lung metastases in mice. Int J Cancer. 1980;25:617–620. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910250511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Massara M, et al. ACKR2 in hematopoietic precursors as a checkpoint of neutrophil release and anti-metastatic activity. Nat Commun. 2018;9 doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03080-8. 676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Majety M, Runza V, Lehmann C, Hoves S, Ries CH. A drug development perspective on targeting tumor-associated myeloid cells. FEBS J. 2018;285:763–776. doi: 10.1111/febs.14277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Ries CH, et al. Targeting tumor-associated macrophages with anti-CSF-1R antibody reveals a strategy for cancer therapy. Cancer Cell. 2014;25:846–859. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2014.05.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Franks SE, Getahun A, Hogarth PM, Cambier JC. Targeting B cells in treatment of autoimmunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 2016;43:39–45. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2016.09.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Salles G, et al. Rituximab in B-Cell Hematologic Malignancies: A Review of 20 Years of Clinical Experience. Adv Ther. 2017;34:2232–2273. doi: 10.1007/s12325-017-0612-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.