Abstract
We investigated a Q fever outbreak that occurred in an isolated area of the Amazon Rain Forest in French Guiana in 2014. Capybara fecal samples were positive for Coxiella burnetii DNA. Being near brush cutters in use was associated with disease development. Capybaras are a putative reservoir for C. burnetii.
Keywords: Q fever, Coxiella burnetii, capybara, Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris, infectious aerosols, brush cutter, weed cutter, grass trimmer, outbreak, Amazon Rain Forest, French Guiana, Comté River, military personnel, bacteria, zoonoses, pneumonia, multispacer sequence type 17, MST17, sylvatic cycle
Q fever is a cosmopolitan zoonosis caused by Coxiella burnetii, a gram-negative coccobacillus. Transmission occurs mainly through inhalation of contaminated particles present in the environment. Cattle, sheep, and goats constitute the main reservoirs worldwide, and afterbirth from infected animals is highly contagious.
The incidence of Q fever is particularly high in French Guiana, an overseas entity of France located in the Amazon region of South America between Suriname and the state of Amapá in Brazil. Disease in French Guiana is caused by a unique genotype, C. burnetii multispacer sequence type 17 (MST17) (1–3). The disparities in incidence between French Guiana and its neighboring countries suggest that Q fever incidence is underestimated in that part of the world, potentially because of misdiagnosis or the unavailability of diagnostic tools (4). Cases occur mainly in Cayenne, the capital of French Guiana, and the surrounding areas (5). Outbreaks beyond the outskirts of Cayenne have not been described. Studies of multiple domestic and wild fauna in French Guiana have only revealed the 3-toed sloth (Bradypus tridactylus) as a potential C. burnetii reservoir (6–9). However, another wild animal reservoir is highly suspected for this bacterium (4), and the epidemiologic cycle in French Guiana remains incomplete. In this article, we describe an outbreak that occurred in 2014 among French Navy service members in a remote area of French Guiana and the outbreak investigation findings, which implicated another species as a potential C. burnetii reservoir.
The Study
During August–September 2014, a total of 5 Q fever cases were diagnosed among 12 French Navy service members. All had been deployed for 3 days in mid-August to a carbet (an open-sided wooden shelter surrounded by forest) located on the Comté River, 30 km south of Cayenne (4°37′57.44′′N, 52°23′49.5′′W). Q fever diagnostic tests (Q Fever IFA IgM and Q Fever IFA IgG; Focus Diagnostics, http://www.focusdx.com; 100% sensitivity and 99% specificity to C. burnetii Nine Mile strain) were performed at the Institut Pasteur in Cayenne.
Patient interviews revealed that they had spent 3 days cleaning the carbet with brooms and clearing the surrounding area using a brush cutter (also known as a weed cutter or grass trimmer). No other common exposure was found. We performed a retrospective case–control study that included the 5 cases and 15 controls. Control participants had spent multiple days at the carbet during the 3-day cleanup (7 controls) or during the weeks just before or after the cleanup (8 controls) without developing any symptoms. We also administered a questionnaire to assess activities potentially associated with the C. burnetti exposure.
Given the unexpected location of this outbreak (i.e., in an isolated spot in the middle of the rain forest, far from Cayenne), we performed an environmental investigation for C. burnetti in late September. We sampled several possible sources in and around the carbet: dust from the storage area; soil from under the carbet; soil from burrows of small, nonflying mammals; mammal feces and bird and reptile droppings; and water from the sink, shower, shower water tank, and toilets (Figure 1). To sample small mammals around the carbet, we used 12 animal traps from BTT Mécanique (https://www.bttmecanique.fr), Tomahawk Live Trap (https://www.livetrap.com), and H.B. Sherman Traps, Inc. (https://www.shermantraps.com) per night for 5 nights. With all samples, we performed a quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) targeting IS1111 as previously described (10). We confirmed all positive results (i.e., DNA samples with a cycle threshold <35) using a second qPCR targeting the IS30a repeat sequence. We used another qPCR specific for C. burnetii MST17 to genotype C. burnetii DNA–positive samples (11).
Figure 1.
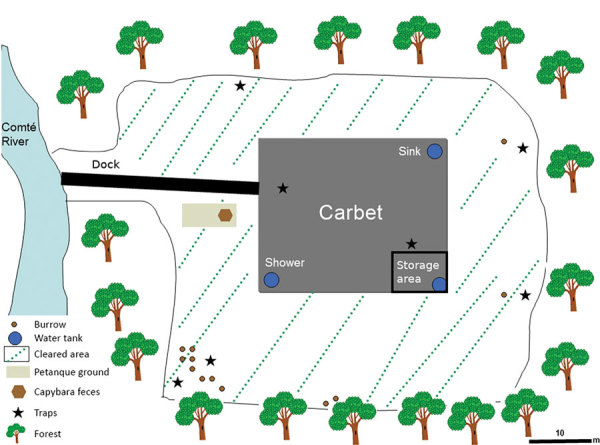
Sample collection and animal trap sites around carbet used in environmental investigation of Q fever outbreak near Comté River in the Amazon Rain Forest area of French Guiana, 2014.
We confirmed the 5 cases of acute Q fever (in 4 men and 1 woman of median age 27 [range 20–40] years) by serology (Table 1); the attack rate was 40% (5/12). Symptoms began 12–23 days after the stay; 4 patients had elevated fever (>39°C) and pneumonia with >1 lobe involved (Table 1). Each Q fever patient received 200 mg of doxycycline daily for 3 weeks. Outcomes were favorable, and none progressed to persistent focalized Q fever. The only risk factor found in univariate analysis was being close to the brush cutter during brush cutting (p = 0.03; Table 2).
Table 1. Characteristics of French Navy service members who had Q fever after visit to carbet along Comté River, Amazon Rain Forest, French Guiana, 2014–2015*.
| Patient no. | Age, y/sex | Dates of stay at carbet | Date of symptom onset | Date of serology | Phase I |
Phase II |
Clinical presentation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IgG | IgM | IgG | IgM | |||||||
| 1 | 21/M | 2014 Aug 15–17 | 2014 Sep 2 | 2014 Sep 9 | <50 | 800 | 50 | 100 | Fever, pneumonia, myalgia | |
| 2014 Sep 15 | <50 | >6,400 | 100 | 6,400 | ||||||
| 2 | 40/F | 2014 Aug 15–17 | 2014 Aug 29 | 2014 Sep 1 | <50 | <50 | <50 | <50 | Fever, pneumonia | |
| 2014 Sep 10 | <50 | 400 | 3,200 | 6,400 | ||||||
| 3 | 27/M | 2014 Aug 15–17 | 2014 Aug 31 | 2014 Sep 5 | <50 | <50 | <50 | 50 | Fever, pneumonia, myalgia | |
| 2014 Sep 17 | <50 | 6,400 | 800 | >6,400 | ||||||
| 4 | 20/M | 2014 Aug 15–17 | 2014 Aug 31 | 2014 Sep 26 | 100 | 800 | 200 | 800 | Fever, myalgia | |
| 5 | 28/M | 2014 Aug 15–17 | 2014 Sep 13 | 2014 Sep 18 | <50 | <50 | <50 | <50 | Fever, pneumonia, vomiting, diarrhea, myalgia | |
| 6 | 29/F | 2014 Dec 22 | 2015 Jan 14 | 2015 Jan 28 | 200 | 800 | 800 | 200 | Fever, pneumonia | |
| 2015 Feb 24 | 50 | 1,600 | 800 | 800 | ||||||
*We measured antibody concentrations against both antigenic variants (phase I and phase II) of Coxiella burnetii. High levels of phase II antibodies are found in acute Q fever, whereas high levels of IgG phase I antibodies are predominant in chronic Q fever.
Table 2. Univariate analysis of risk factors for acute Q fever development in outbreak near Comté River, Amazon Rain Forest, French Guiana, 2014*.
| Exposure type | Cases, n = 5, no. (%) | Controls, n = 15, no. (%) | Crude OR (95% CI) | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Using brush cutter | 2 (40) | 3 (20) | 2.52 (0.15–36.3) | 0.56 |
| Being close to brush cutter while in use | 5 (100) | 5 (33) | NA (1.20–NA) | 0.03 |
| Collecting or moving wood | 4 (80) | 11 (73) | 1.43 (0.09–89.2) | 1 |
| Collecting freshly cut grass | 0 | 2 (13) | 0 (0–16.8) | 1 |
| Cleaning dust on furniture | 2 (40) | 11 (73) | 0.26 (0.02–3.19) | 0.29 |
| Sweeping carbet | 3 (60) | 13 (87) | 0.25 (0.01–4.79) | 0.25 |
| Using shower inside carbet | 3 (60) | 4 (27) | 3.81 (0.31–62.5) | 0.29 |
| Walking around carbet | 2 (40) | 5 (33) | 1.31 (0.08–16.0) | 1 |
| Stirring soil | 1 (20) | 1 (7) | 3.24 (0.04–293) | 0.45 |
| Cleaning animal droppings | 0 | 7 (47) | 0 (0–1.81) | 0.11 |
*NA, not applicable; OR, odds ratio.
We failed to capture any small mammals during the 5-day sampling period. All qPCR tests performed with dust, soil samples, water samples, bird and reptile droppings, and fecal samples taken from burrows (attributable to small mammals) were negative for C. burnetti DNA. However, fresh mammal fecal samples were positive for C. burnetii (cycle threshold 31) and later genotyped as MST17. These fecal samples were identified by 3 independent experts as originating from capybaras (Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris, the world’s largest rodent; Figure 2), which were often found laying a few meters from the carbet. We did not perform DNA testing to confirm species origin, but capybara feces are distinctive and easily identified by their descriptions in the literature (12,13).
Figure 2.

Feces of capybara (Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris) (A) and image of capybara (B), French Guiana. The length of the middle fingernail, which is often used in the field for feces measurement, is 12 mm. Photographs by Nicolas Defaux, http://www.photographienature.com.
To prevent further Q fever cases, the carbet was closed for 4 months. In late December 2014, eight service members were sent to clean up the grounds surrounding the carbet. Instructions were issued to wear personal protective equipment (coveralls, gloves, and an FFP [filtering face piece] 2) during the operation. Only 1 young woman did not comply with the instructions for wearing the mask because she did not use the brush cutter herself; 3 weeks later, she had Q fever pneumonia (Table 1). None of the other service members got sick.
Conclusions
In total, 5 of 6 Q fever patients had pneumonia, confirming the virulence of MST17, the sole genotype found in French Guiana (3). This Q fever outbreak occurred outside of Cayenne and suburban areas, in the Amazon Rain Forest. These results confirm wildlife exposure and a sylvatic transmission cycle for C. burnetii MST17. In this outbreak, the capybara appeared to excrete C. burnetii in its feces, which caused environmental contamination that persisted for several months; alternatively, the environment might have still been infectious months later because of recontamination. Other wild animals in the Amazon Rain Forest might also be able to excrete C. burnetii (14,15), so the sites of future outbreaks cannot be predicted. The hazard of a C. burnetii infection probably exists throughout the entire rain forest because no barriers limit animal mobility in this environment.
Overlap between the sylvatic cycle and risky human activities led to this Q fever outbreak, and the availability of diagnostic tools led to its detection. Diagnostic tool availability could explain the lack of detection elsewhere in the Amazon region. Our case–control study found that being close to the brush cutter during its operation was associated with disease development. The unfortunate incident responsible for the sixth case 4 months after the initial outbreak confirmed this association; this incident demonstrated that the brush cutter, a tool commonly used for gardening in French Guiana, generated an infectious aerosol when used to cut vegetation near contaminated soil. This incident also demonstrated that wearing an FFP2 is effective protection against infection in cases of exposure to C. burnetii infectious aerosols. Outbreaks occur when human activities lead to aerosolization of elements in the environment contaminated during the sylvatic cycle. As shown by this report, we cannot control sylvatic cycle transmission, but protective measures implemented during risky activities can prevent infections in humans.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Denis Blanchet, Benoit de Thoisy, and Sébastien Briolant for their help with this study; Nicolas Defaux for kindly providing the photo of the capybara; Mael Dewynter, Olivier Tostain, and Guillaume Feuillet for the species identification; and Alain Berlioz-Arthaud for performing the IFA tests.
This work was supported by the French Military Health Service.
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest. The opinions or assertions expressed here are the personal views of the authors and should not be considered official or as a reflection of the views of the French Military Health Service.
Biography
Dr. Christen works at Laveran Military Teaching Hospital, Marseille, France, and has worked in French Guiana. His research interests include the epidemiology of tropical diseases.
Footnotes
Suggested citation for this article: Christen JR, Edouard S, Lamour T, Martinez E, Rousseau C, de Laval F, et al. Capybara and brush cutter involvement in Q fever outbreak in remote area of Amazon Rain Forest, French Guiana, 2014. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020 May [date cited]. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2605.190242
These senior authors contributed equally to this article.
References
- 1.Epelboin L, Chesnais C, Boullé C, Drogoul A-S, Raoult D, Djossou F, et al. Q fever pneumonia in French Guiana: prevalence, risk factors, and prognostic score. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;55:67–74. 10.1093/cid/cis288 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Pfaff F, François A, Hommel D, Jeanne I, Margery J, Guillot G, et al. Q fever in French Guiana: new trends. Emerg Infect Dis. 1998;4:131–2. 10.3201/eid0401.980124 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Mahamat A, Edouard S, Demar M, Abboud P, Patrice J-Y, La Scola B, et al. Unique clone of Coxiella burnetii causing severe Q fever, French Guiana. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013;19:1102–4. 10.3201/eid1907.130044 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Epelboin L, Nacher M, Mahamat A, Pommier de Santi V, Berlioz-Arthaud A, Eldin C, et al. Q fever in French Guiana: tip of the iceberg or epidemiological exception? PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016;10:e0004598. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004598 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Tran A, Gardon J, Weber S, Polidori L. Mapping disease incidence in suburban areas using remotely sensed data. Am J Epidemiol. 2002;156:662–8. 10.1093/aje/kwf091 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Pommier de Santi V, Marié J-L, Briolant S, Mahamat A, Djossou F, Epelboin L, et al. Q fever in French Guiana: a specific epidemiological context [in French]. Bull Acad Vet Fr. 2016;169:148–54. 10.4267/2042/61397 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gardon J, Héraud JM, Laventure S, Ladam A, Capot P, Fouquet E, et al. Suburban transmission of Q fever in French Guiana: evidence of a wild reservoir. J Infect Dis. 2001;184:278–84. 10.1086/322034 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Davoust B, Marié J-L, Pommier de Santi V, Berenger J-M, Edouard S, Raoult D. Three-toed sloth as putative reservoir of Coxiella burnetii, Cayenne, French Guiana. Emerg Infect Dis. 2014;20:1760–1. 10.3201/eid2010.140694 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Pommier de Santi V, Briolant S, Mahamat A, Ilcinkas C, Blanchet D, de Thoisy B, et al. Q fever epidemic in Cayenne, French Guiana, epidemiologically linked to three-toed sloth. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2018;56:34–8. 10.1016/j.cimid.2017.12.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Edouard S, Mahamat A, Demar M, Abboud P, Djossou F, Raoult D. Comparison between emerging Q fever in French Guiana and endemic Q fever in Marseille, France. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2014;90:915–9. 10.4269/ajtmh.13-0164 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.D’Amato F, Eldin C, Georgiades K, Edouard S, Delerce J, Labas N, et al. Loss of TSS1 in hypervirulent Coxiella burnetii 175, the causative agent of Q fever in French Guiana. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2015;41:35–41. 10.1016/j.cimid.2015.04.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chame M. Terrestrial mammal feces: a morphometric summary and description. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2003;98(Suppl 1):71–94. 10.1590/S0074-02762003000900014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Mendes A, Nogueira-Filho SLG. Feeds and nutrition of farmed capybaras. In: Moreira JR, Ferraz KMPMB, Herrera EA, Macdonald DW, editors. Capybara: biology, use and conservation of an exceptional neotropical species. New York: Springer; 2013.. p. 261–74. 2012 Jul 2 [cited 2019 Jun 7]. 10.1007/978-1-4614-4000-0_15 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Rozental T, Ferreira MS, Guterres A, Mares-Guia MA, Teixeira BR, Gonçalves J, et al. Zoonotic pathogens in Atlantic Forest wild rodents in Brazil: Bartonella and Coxiella infections. Acta Trop. 2017;168:64–73. 10.1016/j.actatropica.2017.01.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ferreira MS, Guterres A, Rozental T, Novaes RLM, Vilar EM, Oliveira RC, et al. Coxiella and Bartonella spp. in bats (Chiroptera) captured in the Brazilian Atlantic Forest biome. BMC Vet Res. 2018;14:279. 10.1186/s12917-018-1603-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


