The incidence of Covid-19 is rapidly growing worldwide. In Italy, as of April 3,, 119,827 cases have been reported with a toll death of 14,681 [1]; in Lombardy, the number of cases was 47,520, with 8311 deaths [2].
Early identification of SARS-CoV-2 infection is important for the safety of patients and health workers. Imaging can play a role in the diagnosis of Covid-19 [3, 4].
A 73-year-old male from Bergamo (Italy) was admitted to the National Cancer Institute of Milan, for curative surgery of a 22.5 × 14.2 × 19 cm vascular tumour, intermediate risk, of the right retroperitoneum. At admission, he was asymptomatic, and during hospitalization, he progressively developed fever (up to 38 °C) and hypoxemia. Temporal track of clinical data, laboratory tests and imaging findings (both computed tomography (CT) and [18F]fluoro-deoxyglucose ([18F]FDG) positron emission tomography (PET)/CT), retrospectively retrieved, are reported in the Figure. Imaging suggested viral infection. Diagnosis was obtained by means of reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction on rhino pharyngeal swab. Subsequently, the patient was transferred to a Covid-19 dedicated hospital; surgery was postponed. We could not reach the patient for consent; local ethics committee approved the publication.
Epidemiological data, worldwide and at local level, need to be considered when approaching a patient with respiratory symptoms. Neoplastic disease may constitute a risk factor and also a confounding factor. It is important to recognize Covid-19 as early as possible for optimal patient management and ensure hospital staff and patient’s safety. Imaging demonstrated Covid-19 even in the presence of mild symptoms. In view of its high sensitivity, imaging may be considered for anticipating diagnosis and safety interventions. Early after image acquisition, scans should be reviewed to identify suspected Covid-19 cases. High-resolution CT of the thorax during PET acquisition could improve lung abnormalities detection.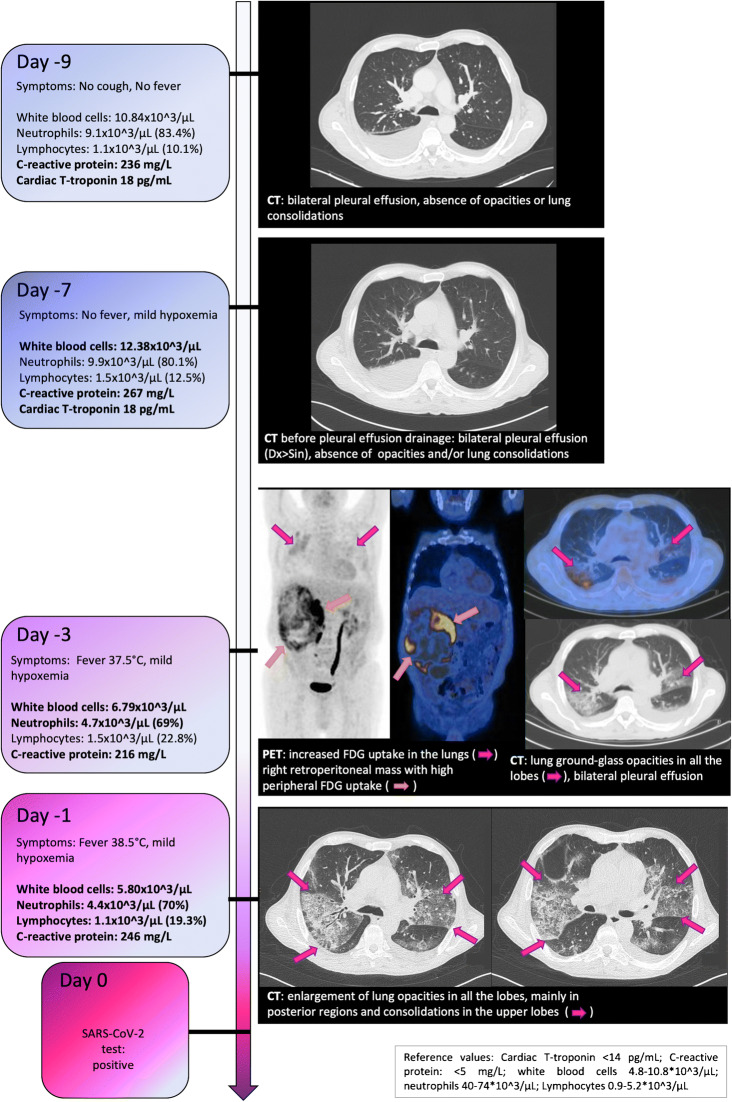
Authors’ contribution
MK and AA conceptualized the paper, GS, BP and AM evaluated and reported the imaging findings, AG managed patient treatment and diagnostic work-up, MK drafted the manuscript, and all the authors revised and commented on the paper and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Data availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Compliance with ethical standards
Consent and ethics
The Ethics Committee of the Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Naziuonale dei Tumori authorized the publication on March 20, 2020. The patient could not be reached, and therefore, the Ethics Committee waived the patient consent for publication in fully anonymized form.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
This article is part of the Topical Collection on infection and inflammation.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/ accessed on Apr 3rd, 2020.
- 2.http://www.protezionecivile.gov.it/media-comunicazione/comunicati-stampa/-/content-view/view/1242651 , accessed on Apr 3rd, 2020.
- 3.Xu Xi, Yu Chengcheng, Qu Jing, Zhang Lieguang, Jiang Songfeng, Huang Deyang, Chen Bihua, Zhang Zhiping, Guan Wanhua, Ling Zhoukun, Jiang Rui, Hu Tianli, Ding Yan, Lin Lin, Gan Qingxin, Luo Liangping, Tang Xiaoping, Liu Jinxin. Imaging and clinical features of patients with 2019 novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging. 2020;47(5):1275–1280. doi: 10.1007/s00259-020-04735-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Qin Chunxia, Liu Fang, Yen Tzu-Chen, Lan Xiaoli. 18F-FDG PET/CT findings of COVID-19: a series of four highly suspected cases. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging. 2020;47(5):1281–1286. doi: 10.1007/s00259-020-04734-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.


