Abstract
Aim
To illustrate the [18F]FDG-PET/CT findings in patients affected by cancer with clinical diagnosis of Covid-19
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed the cases of patients who showed pulmonary involvement unrelated to cancer metastases on March 13 and 16 2020. We reviewed the scans, collected medical history, and exposure information.
Results
Among the 13 scans, we identified 5 cases with imaging findings suspicious for viral infection. Peripheral lung consolidations and/or ground-glass opacities in two or more lobes were found. Lung abnormalities displayed increased [18F]FDG uptake (SUVmax 4.3–11.3). All the patients on the day of PET/CT acquisition were asymptomatic, and they did not have fever or cough. In view of the PET/CT findings, home isolation, symptom surveillance, and treatment (in 3/5 patients) were indicated. At 1-week follow-up, 2/5 patients experienced the onset of mild respiratory symptoms.
Conclusions
The [18F]FDG-PET/CT can identify probable Covid-19 disease in the absence or before symptoms onset and can guide patient management. Nuclear medicine staff needs to be aware of the possibility of contact with patients affected by the SARS-CoV-2 infection even if they do not present any symptom. Therefore, safety measures need to be adopted for other patients and hospital staff in order to block the spread of infection.
Keywords: COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2, Coronavirus, FDG-PET/CT, Asymptomatic, Imaging
Introduction
Lombardy, a northern Italy region, is the economic driver of Italy and one of the most productive regions in Europe, with strong international links and a high-density population [1]. These facts could justify the high cost in terms of infected people and deaths the region is paying to the Covid-19 pandemic. As of March 30, 2020, among the 101,739 cases diagnosed in Italy, 42,161 were registered in Lombardy [2].
Clinical diagnosis is generally based on exposure history, clinical symptoms, results of blood, and biochemical tests. However, there is evidence that a substantial proportion of patients do not present any symptoms. Chest computed tomography (CT), which typically shows ground-glass opacities (GGOs) or bilateral pulmonary consolidations in multiple lobar and segmental areas, and [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET)/CT can reveal lung infection [3, 4].
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed the cases of patients who were referred to the Nuclear Medicine Department in Humanitas Gavazzeni on March 13 and 16 (Friday and Monday, respectively), 2020 during the Covid-19 outbreak in Bergamo area, Italy. We included those patients that showed pulmonary [18F]FDG-PET/CT abnormalities unrelated to cancer metastases. We collected medical history and exposure information, and we reviewed the scans. All the patients signed the informed consent for their data access and publication. The Humanitas Clinical and Research Center ethics committee approved the study.
Scanner and acquisition protocol
PET scans were acquired approximately 60 min after [18F]FDG administration (activity range 200–300 MBq, according to weight) in the fasting state. Images were obtained from the skull base to the tights using a Phillips Gemini LXL PET/CT with an integrated 16-slice CT. Reconstructed images were then displayed on a Philips Extended Workspace EBW-NM 2.0.2 workstation and interpreted by experienced nuclear medicine physicians (LS, MB).
Results
Among the 13 scans performed on March 13 and 16 (two working days), we identified 5 cases (38%). On the day of the scan, none of the patient presented fever or cough. We found irregular opacities (case 1), diffuse opacities with mild uptake (case 2), whole segment involvement (case 3), limited areas (case 4), and multiple foci (case 5) with a wide range of FDG uptake (4.3–11.3). The [18F]FDG PET/CT findings, clinical data, and epidemiological considerations strongly suggested a diagnosis of Covid-19 (Table 1). Based on FDG-PET/CT report, home isolation and symptom surveillance were indicated. In 3/5 patients, antibiotic therapy was prescribed to prevent bacterial superinfection.
Table 1.
Patient characteristics and FDG-PET/CT imaging findings
| Patient n° | Sex | Age | Comorbidities | Symptoms | Exposure | Imaging | Follow-up at 1 week | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N° of affected lobes | CT features (GGO or consolidative opacities) | SUVmax | LN (Y/N) | LN (SUV max) | Other findings | Symptoms therapy | ||||||
| 1 | F | 45 | Colon cancer | None | Family | 5 | Consolidative opacities | 4.3 | Y | 4.5 | Left pelvic lesion | No symptoms Antibiotic therapy |
| 2 | M | 67 | Rectal cancer Diabetes | None | Not known | 3 | GGO | 4.3 | N | – | Osteolytic lesion of the ischiatic right bone | Fever Mild respiratory symptoms Antibiotic therapy |
| 3 | F | 44 | Submandibular salivary gland cancer | None | Not known | 2 | Consolidative opacities and GGO | 11.3 | Y | 3.7 | Left laterocervical adenopathies | No symptoms, No therapy Husband hospitalized for respiratory symptoms |
| 4 | F | 56 | Ovary carcinoma | None | Not known | 3 | GGO | 5.3 | Y | 3.0 | Left laterocervical inflammatory uptake | No Symptoms, No therapy |
| 5 | M | 70 | Squamous cell cancer and nodal metastases from CUP, prostate cancer | None | Not known | 4 | GGO | 4.9 | Y | 3.0 | Right laterocervical swelling | Fever mild respiratory symptoms Antibiotic therapy |
CUP, cancer of unknown primary; F, female; GGO, ground glass opacities; LN, lymph node uptake; M, male; SUVmax, maximum standardized uptake value
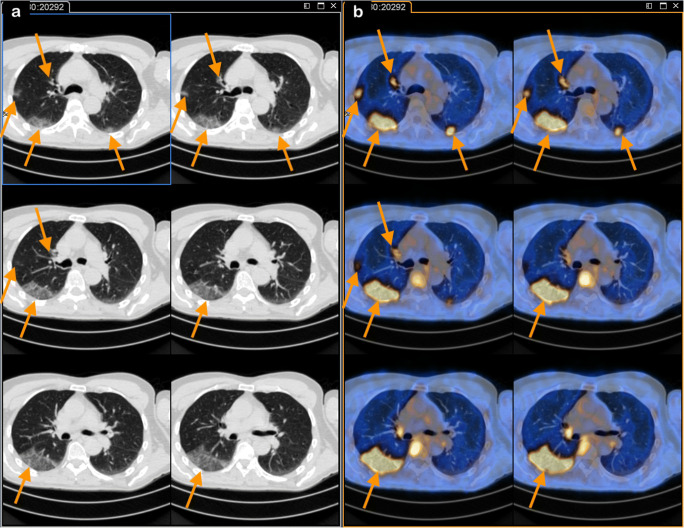
Case 1
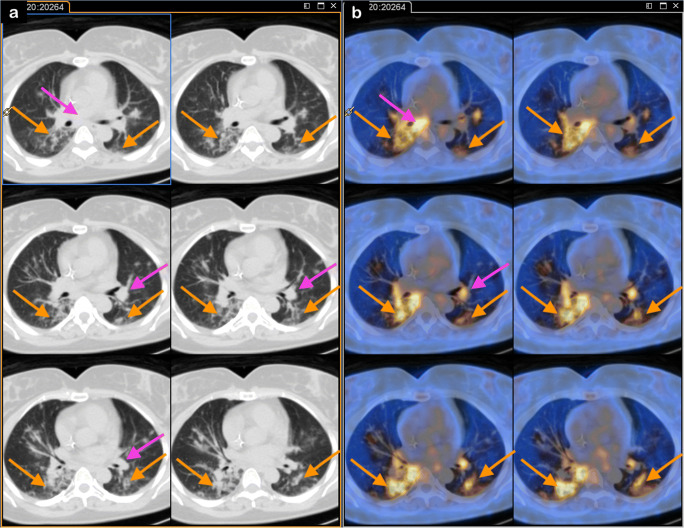
A 45-year-old female, affected by relapsed colon cancer (G2, pT3N1 at diagnosis), performed an [18F]FDG-PET/CT to assess response to chemotherapy. The patient reported low-grade fever until 10 days before PET/CT, treated with antibiotic therapy. On the day of the scan, the patient did not present any respiratory symptom and did not have fever (Fig. 1). Modest mediastinal nodal uptake was visible (pink arrows). One week after [18F]FDG PET/CT, the patient did not report any symptoms, but antibiotic therapy was prescribed.
Fig. 1.
PET/CT (axial CT—panel a; axial fused PET/CT—panel b) showed multiple bilateral interstitial infiltrates (right upper, middle and lower, and left upper and lower lobes—orange arrows) with increased [18F]FDG uptake (SUVmax 4.3)
Case 2
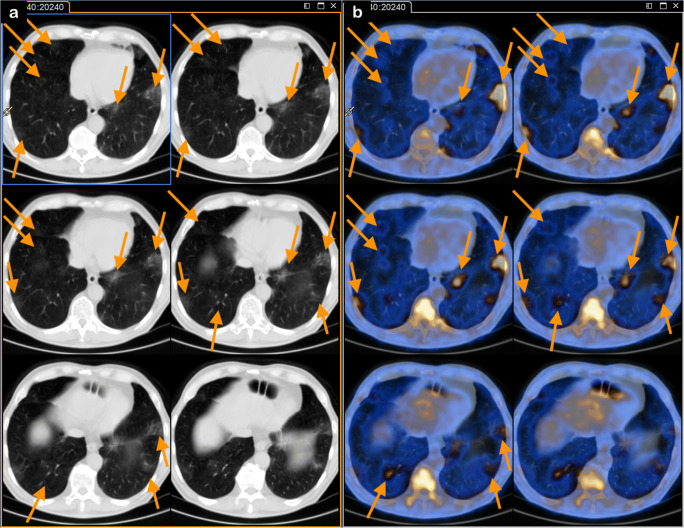
A 67-year-old male affected by metastatic adenocarcinoma of the rectum (G2, pT2N1aM1—bone) recently (February 14, 2020) operated on, was referred for the [18F]FDG-PET/CT for staging purpose. The patient reported low-grade fever until 4 days before PET/CT. On the day of the scan, the patient did not present any respiratory symptom and did not have fever (Fig. 2). At 1-week follow-up, the patient reported the onset of fever and mild respiratory symptoms in the days following FDG PET/CT, for which antibiotic therapy was prescribed.
Fig. 2.
PET/CT (axial CT—panel a; axial fused PET/CT—panel b) showed bilateral ground glass opacities (right lower and left upper and lower lobes—orange arrows), especially in the left 100 lung, with increased [18F]FDG uptake (SUVmax 4.3)
Case 3
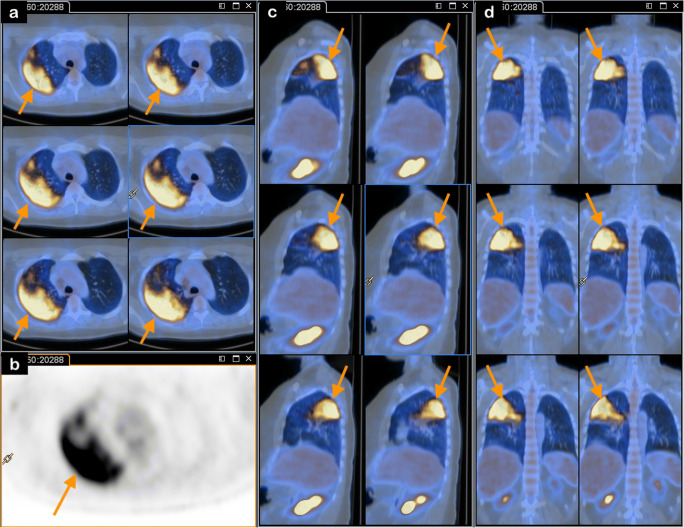
A 44-year-old female affected by salivary gland carcinoma surgically removed and treated with adjuvant radiotherapy performed a follow-up [18F]FDG-PET/CT. On the day of the scan and in the previous months, the patient did not present any respiratory symptoms and did not have fever (Fig. 3). Faint mediastinal nodal uptake was detected. One week after [18F]FDG-PET/CT, the patient did not report any symptoms or need for therapy. However, the husband was hospitalized for respiratory symptoms consistent with Covid-19.
Fig. 3.
On the scan (axial fused PET/CT—panel a; axial PET—panel b; sagittal fused PET/CT—panel c; coronal fused PET/CT—panel d) increased [18F]FDG uptake (SUVmax 11.3) was visible on the lung opacities of the right upper (orange arrows) and modest uptake in the lower lobes
Case 4
A 56-year-old female affected by bilateral clear cells ovary carcinoma (G3, pT1cNx, FIGO IIIC) and endometrial adenocarcinoma (G1, pT1bNx, FIGO IB) performed an [18F]FDG-PET/CT for treatment response assessment. On the day of the scan and in the previous months, the patient did not present any respiratory symptoms and did not have fever (Fig. 4). One week after [18F]FDG PET/CT, the patient did not report any symptoms or need for therapy.
Fig. 4.
The [18F]FDG-PET/CT CT (axial CT—panel a; axial fused PET/CT—panel b) showed bilateral subpleural ground glass opacities (right upper and lower and left lower lobes) with focally increased [18F]FDG uptake (SUVmax 5.3) (orange arrows)
Case 5
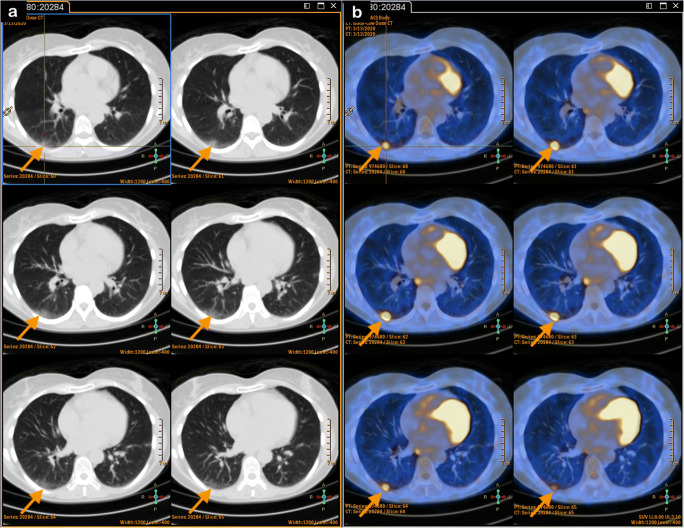
A 70-year-old male, diagnosed with squamous cell cancer latero-cervical nodal metastases, was referred for an [18F]FDG-PET/CT for staging of unknown primary tumor. The patient reported low-grade fever until 4 days before PET/CT without respiratory symptoms. On the day of the scan, the patient did not present any respiratory symptom and did not have fever (Fig. 5). At 1-week follow-up, the patient reported the onset of fever and mild respiratory symptoms in the days following [18F]FDG PET/CT, antibiotic therapy was prescribed.
Fig. 5.
PET/CT (axial CT—panel a; axial fused PET/CT—panel b) showed lung ground-glass opacities in the right upper, middle, lower lobe, and left inferior lobe (SUVmax 4.9) (orange arrows)
SARS-CoV-2 test has not been performed as per local protocol since the patients did not present symptoms. Indeed, in this kind of patients, SARS-CoV-2 test may produce false negative results in a substantial proportion of cases [5]. The diagnosis was based on the epidemiological considerations (being Bergamo area with the highest Covid-19 incidence) and imaging findings.
Discussion
Highly suggestive findings of Covid-19 include pulmonary round-glass opacities and consolidations, in more than two segments, mainly bilateral; the opacities can present as circumscribed areas of involving a whole segment/lobe; pulmonary abnormalities display moderate to high FDG uptake (SUVmax range 4.3–11.3). Nodal uptake can also be visualized.
In areas with high Covid-19 prevalence, the nuclear medicine staff also needs to be aware of the possibility of contact with patients affected by the SARS-CoV-2 infection even if they do not present any symptom. Therefore, safety measures need to be adopted for other patients and hospital staff in order to block the spread of infection. Cancer patients, particularly those under anticancer treatment, are potentially more susceptible for a severe infection. Therefore, strict measures to prevent virus transmission need to be put in place in institutions where cancer patients are referred to [6].
[18F]FDG-PET/CT findings identified probable cases in early phase of disease even before symptoms onset, with relevant impact on patient management, and population safety.
Authors’ contribution
MK, LS, and EB conceptualized the paper; LS and MB evaluated and reported the imaging findings; SCD managed patient treatment and diagnostic work-up; MK drafted the manuscript; and all the authors revised and commented on the paper and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Data availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
Compliance with ethical standards
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Consent and ethics
Informed consent was obtained from all the patients for access to their data and publication. The Humanitas Clinical and Research Center ethics committee approved the study.
Footnotes
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Infection and inflammation.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.https://www.assolombarda.it/centro-studi/booklet-italy-lombardy-and-milan-ndeg-08-october-2019, accessed on Mar 22nd, 2020.
- 2.http://www.protezionecivile.gov.it/media-comunicazione/comunicati-stampa/-/content-view/view/1240371 , accessed on Mar 30th, 2020.
- 3.Qin Chunxia, Liu Fang, Yen Tzu-Chen, Lan Xiaoli. 18F-FDG PET/CT findings of COVID-19: a series of four highly suspected cases. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging. 2020;47(5):1281–1286. doi: 10.1007/s00259-020-04734-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Xu Xi, Yu Chengcheng, Qu Jing, Zhang Lieguang, Jiang Songfeng, Huang Deyang, Chen Bihua, Zhang Zhiping, Guan Wanhua, Ling Zhoukun, Jiang Rui, Hu Tianli, Ding Yan, Lin Lin, Gan Qingxin, Luo Liangping, Tang Xiaoping, Liu Jinxin. Imaging and clinical features of patients with 2019 novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging. 2020;47(5):1275–1280. doi: 10.1007/s00259-020-04735-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Xie X, Zhong Z, Zhao W, Zheng C, Wang F, Liu J. Chest CT for typical 2019-nCoV pneumonia: relationship to negative RT-PCR testing. Radiology. 2020. 10.1148/radiol.2020200343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 6.Ueda M, Martins R, Hendrie PC, McDonnell T, Crews JR, Wong TL, et al. Managing cancer care during the COVID-19 pandemic: agility and collaboration toward a common goal. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw. 2020;20:1–4. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2020.7560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.