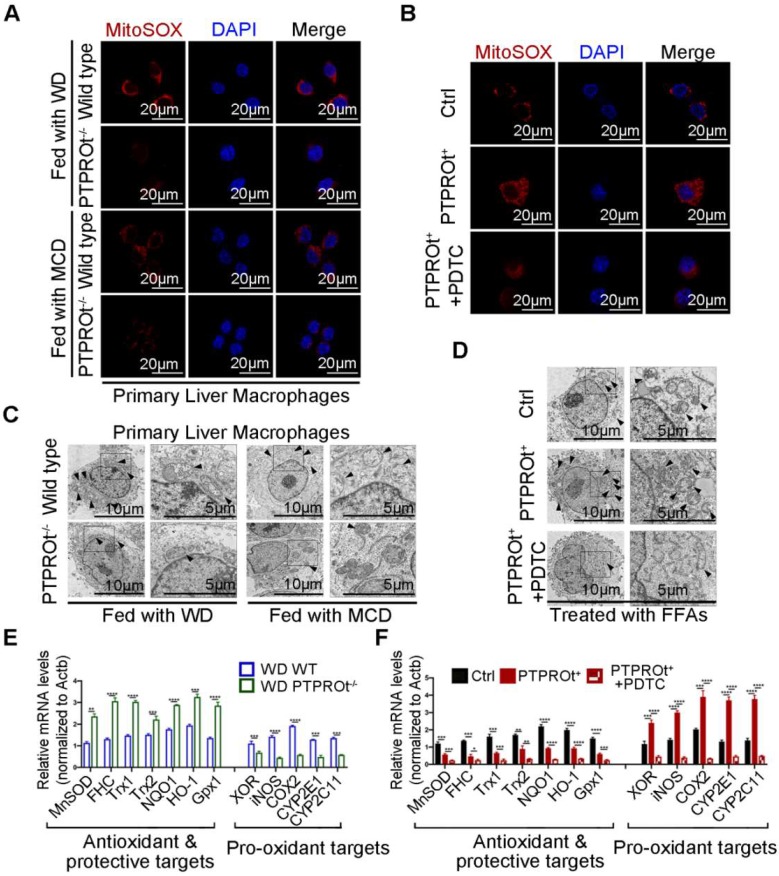
Figure 3.
PTPROt deficiency in liver macrophages suppresses the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) by inhibiting NF-κB, which reduces pro-oxidant gene expression and promotes antioxidant gene expression. A. Fluorescence microscopy of ROS (identified with MitoSOX) in primary liver macrophages isolated from the mice described in Figure 1A, B. DAPI, DNA-binding dye. Bar = 20 μm. B. Fluorescence microscopy of ROS (MitoSOX) in RAW-Ctrl or RAW-PTPROt+ cells treated with free fatty acids (FFAs), with or without pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC) for 24 hr. DAPI, DNA-binding dye. Bar= 20 μm. C. Transmission electron microscopy of primary liver macrophages isolated from the mice described in Figure 1A, B. The arrows indicate mitochondria in liver marcophages. Bar (left) = 10 μm, Bar (right) = 5 μm. D. Transmission electron microscopy of RAW-Ctrl or RAW-PTPROt+ cells treated with FFAs, with or without PDTC for 24 hr. The arrows indicate mitochondria in liver marcophages. Bar (left) = 10 μm, Bar (right) = 5 μm. E. RT-qPCR results showing the relative mRNA levels of antioxidant and protective targets (MnSOD, FHC, Trx1, Trx2, NQO1, HO-1 and Gpx1) and pro-oxidant targets (XOR, iNOS, COX2, CYP2E1 and CYP2C11) in primary liver macrophages isolated from the mice described in Figure 1A, B. F. RT-qPCR results showing the relative mRNA levels of antioxidant & protective targets (MnSOD, FHC, Trx1, Trx2, NQO1, HO-1 and Gpx1) and pro-oxidant targets (XOR, iNOS, COX2, CYP2E1 and CYP2C11) in RAW-Ctrl and RAW-PTPROt+ cells treated with FFAs, with or without PDTC for 24 hr. Abbreviations: DAPI: 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; FFAs: Free Fatty Acids; MCD: Methionine-choline-deficient; PDTC: Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate; WD: Western diet; MitoSOX: Mitochondrial Superoxide Indicator.