Abstract
Background:
Percent density (PD) is a strong risk factor for breast cancer that is potentially modifiable by lifestyle factors. PD is a composite of the dense (DA) and nondense (NDA) areas of a mammogram, representing predominantly fibroglandular or fatty tissues, respectively. Alcohol and tobacco use have been associated with increased breast cancer risk. However, their effects on mammographic density (MD) phenotypes are poorly understood.
Methods:
We examined associations of alcohol and tobacco use with PD, DA and NDA in a population-based cohort of 23,456 women screened using full-field digital mammography machines manufactured by Hologic or General Electric (GE). MD was measured using Cumulus. Machine-specific effects were estimated using linear regression, and combined using random effects meta-analysis.
Results:
Alcohol use was positively associated with PD (ptrend=0.01), unassociated with DA (ptrend=0.23), and inversely associated with NDA (ptrend=0.02) adjusting for age, BMI, reproductive factors, physical activity, and family history of breast cancer. In contrast, tobacco use was inversely associated with PD (ptrend=0.0008), unassociated with DA (ptrend=0.93), and positively associated with NDA (ptrend<0.0001). These trends were stronger in normal and overweight women than in obese women.
Conclusions:
These findings suggest that associations of alcohol and tobacco use with PD result more from their associations with NDA than DA.
Impact:
PD and NDA may mediate the association of alcohol drinking, but not tobacco smoking, with increased breast cancer risk. Further studies are needed to elucidate the modifiable lifestyle factors that influence breast tissue composition, and the important role of the fatty tissues on breast health.
Introduction
High percent density (PD) is common and is among the strongest risk factors for breast cancer.(1) The prevalence of heterogeneously dense or extremely dense breasts is between 40% to 60% of screening age women, and is estimated to account for up to one third of all breast cancer (BC) diagnoses.(2) PD decreases with age, body mass index (BMI), number of children, and menopause; and increases with age at menarche, age at first birth, and family history of breast cancer.(1,3,4) Of particular interest are modifiable exposures believed to alter PD, such as the use of menopausal hormone therapy (MHT), tamoxifen(5) and alcohol,(6) that could provide opportunities for women to reduce their BC risk. The dense area (DA) of the breast appears radiopaque on a mammogram and contains greater proportions of collagen, epithelial and stromal cells compared to the nondense area (NDA), which largely consists of fatty tissue.(7) Recent studies have shown that NDA is inversely associated with BC risk, independently of DA, suggesting that normal breast fat may play a protective role.(8,9) The underlying mechanisms through which mammographic density (MD) phenotypes are associated with BC risk are poorly understood.
Alcohol drinking has been consistently associated with increased BC risk.(10) Plausible mechanisms underlying this association include increased sex hormone levels and carcinogenic DNA damage with greater alcohol consumption.(11) Alcohol use has also been associated with higher PD,(6,12–15) but associations with absolute DA have been inconsistent.(13,15–21) It remains unknown whether alcohol influences PD by increasing DA or decreasing NDA because few prior studies have examined all three MD phenotypes. Tobacco smoke is an important human carcinogen that has been associated with increased breast cancer mortality,(22) but less consistently with breast cancer incidence.(23,24) Tobacco smoke is a complex mixture of chemicals with known carcinogenic and endocrine effects.(25) The effects of tobacco use on MD phenotypes are uncertain.(20,26–30)
Prior studies of alcohol and tobacco use have focused primarily on PD, due in part to the greater difficulty of quantitating the constituent measures of DA and NDA. However, to understand the mechanisms through which tobacco and alcohol influence PD, it is important to distinguish between their effects on the dense and nondense tissue components, which are likely to have distinct etiologies(31) as well as cellular interactions that influence the breast tissue microenvironment.(32) In addition, few prior studies have examined interactions between alcohol and tobacco, or potential modifiers of their effects, due to the large sample sizes required for adequate statistical power. Finally, most prior studies have utilized screen-film mammography, which has largely been replaced by full-field digital mammography (FFDM).
In this study, we examined associations of alcohol and tobacco use with quantitative measures of PD, DA and NDA in a population-based cohort of 23,456 women who underwent screening FFDM at Kaiser Permanente Northern California (KPNC) clinics using Hologic or General Electric (GE) machines. We further examined the combined effects of alcohol and tobacco use, and potential modification by BMI, menopausal status, and MHT use. To our knowledge, this is the largest study to date of alcohol and tobacco use and all three quantitative MD phenotypes measured on contemporary FFDM images.
Methods
Study population
This population-based study included non-Hispanic white women in the KPNC Research Program on Genes, Environment and Health (RPGEH) who participated in a genome-wide association study of mammographic density.(33,34) The study cohort has previously been described.(4,35,36) Briefly, eligible women were between the ages of 38 and 80 at mammography and had at least one screening FFDM exam during 2003–2013 at KPNC mammography clinics throughout Northern California, of which 36 clinics used Hologic (n=20,311) and 11 clinics used GE (n=3,881) FFDM machines. We excluded women with breast implants (3.6%), breasts that were too large to fit on a single image (1%), unreadable or unavailable images (2.6%), or history of bilateral breast cancer (0.06%) for whom no unaffected breast image was available for assessment.(4,35) Women with missing survey data for alcohol (n=686) or tobacco (n=701) were also excluded, yielding a final sample size of 23,456.
Mammographic density measurements
We obtained processed FFDM images for the closest screening exam following the RPGEH survey (n=23,323; 99.4%) when available, or prior to the survey date (n=133; 0.6%) otherwise, from the KPNC imaging archive. The average time interval from the survey date to the mammogram was 2.9 years. For women with a diagnosis of unilateral breast cancer (n=1918; 8.2%), we selected the image of the unaffected breast from the closest pre-diagnostic exam following the survey when available (n=592; 30.9%).(35) Sensitivity analyses were performed excluding women (n=1449; 6.2%) who were diagnosed with breast cancer before the mammogram and/or surveyed after the mammogram. For women without breast cancer, we selected the left breast image except in a random 10% subset of women for whom the right breast image was selected to blind the reader to the cancer status of images. All density measurements were performed using the cranio-caudal view. All FFDM images were down-sampled to a pixel size of 200 microns. Hologic images were denoised using a median filter with a radius of 3 pixels, as previously described.(35)
All MD measurements were performed by a single radiological technologist (RYL) trained by MJY and JAL in the use of the Cumulus6(37) software provided by MJY. Cumulus6 automatically detects the outer edge of the breast for most FFDM images. The reader is required to define the pectoral muscle boundary, and select the pixel intensity threshold for distinguishing the dense and nondense areas of the breast image. PD is computed by the DA divided by the total breast area, and NDA by the total area minus the DA. Reader reproducibility was assessed using random replicates within each image batch of up to 1100 images. The intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC) for PD, DA, and NDA were: 0.953, 0.927 and 0.996 for Hologic images; and 0.961, 0.940 and 0.995 for GE images, respectively.
Alcohol and tobacco use
Alcohol and tobacco use were ascertained from the survey administered at enrollment into RPGEH. Information on alcohol use was obtained from the following two survey questions. (1) On average, how many days a week do you have a drink containing alcohol? Responses ranged from 0 to 7. (2) On a typical day that you drink, how many drinks do you have? Responses ranged from 0 to 8 or more drinks. The number of alcoholic drinks consumed on a typical week, drinks per week (DPW), was estimated by the product of the responses to these two questions, and categorized into tertiles: none (0 DPW), moderate (1–4 DPW), or heavy (5+ DPW). Finer categories yielded similar associations, but resulted in small numbers in some exposure categories and less robust analyses of interactions and combined alcohol and tobacco effects. Tobacco use was determined based on the responses to the following questions: (1) Have you ever smoked one or more cigarettes per day for six months or longer? (2) Do you currently smoke or have you stopped smoking? (3) On average, how many packs of cigarettes do you (or did you) smoke per day (PPD)? Response options were: none, <0.5 packs, 0.5 to 1 pack, 1 to 1.5 packs, >1.5 packs. Tobacco use was categorized as: none, <½ PPD, ½−1 PPD, or 1+ PPD among women who smoked one or more cigarettes per day for six months or longer because only 3% of women reported smoking >1.5 PPD. We performed exploratory analyses to investigate associations of current or former tobacco use, and duration of smoking, with MD phenotypes.
Covariates
Model covariates were chosen a priori on the basis of known biologically plausible associations with MD and included: age at mammography, BMI at mammography, BMI at age 18, age at first birth, number of children, age at menarche, family history of breast cancer, menopausal status, MHT use within the five years prior to mammography, physical activity, and image batch. Age at mammography was determined based on date of birth and date of exam from the electronic health record (EHR). BMI was calculated using the height and weight recorded in the EHR for the patient visit closest to the mammography date. Late adolescent BMI was computed based on self-reported weight at age 18 and adult height recorded in the EHR. The KPNC pharmacy database, which records all dispensed outpatient and inpatient prescriptions, was used to determine MHT use within the 5 years prior to the mammography exam. Physical activity was defined as total Metabolic Equivalent (MET) hours per week and based on total MET-min/week = (8 × vigorous) + (4 × moderate) + (3.3 × walking) min/week.(38) Participants were asked how many days per week they did vigorous, moderate activity or walking, and how many minutes on average each time they did the activity.
We modeled the key covariates age and BMI using polynomial terms (age, age2, BMI, BMI2 and BMI3) to allow for non-linear relationships.(4) Age at menarche, age at first birth, number of children, family history of breast cancer, menopausal status, and MHT use within five years, were modeled categorically based on the RPGEH survey and EHR data.(4) To retain subjects with incomplete data for the model covariates, we included missing categories as indicated: late adolescent BMI (quartiles, missing), age at menarche (<11, 12–13, 14–15, 16+, missing), age at first birth (<20, 20–24, 25–29, 30–34, 35+ years, missing), parity (0, 1, 2, 3, 4+ children, missing), menopausal status (premenopausal, postmenopausal), MHT use (yes, no), first-degree relative with breast cancer (yes, no), physical activity (quartiles, missing). To evaluate effect modification, BMI strata were defined using the World Health Organization (WHO) categories of normal weight (18.5–24.9 kg/m2), overweight (25–29.9 kg/m2), and obese (≥30 kg/m2).
Statistical methods
We applied a square root transformation to PD, DA and NDA to reduce skew and heteroscedasticity of residuals in linear regression models. √DA and √NDA can be interpreted as the length (cm) of the side of a square area of dense or nondense tissue, respectively, whereas √PD can be interpreted as the width (cm) of the dense square within a 10 cm × 10 cm breast area.(39) To facilitate comparison to prior studies of quantitative area-based MD measures, we transformed the main parameter estimates back to units of % for PD and cm2 for DA and NDA using the delta method.(40) This nonlinear transformation depends on the baseline value of the original phenotype, and the overall means of 21.08%, 28.06 cm2, and 135.11 cm2 for PD, DA, and NDA, respectively, were used for this purpose.
Linear regression models were used to evaluate the association of the exposure and outcomes, adjusted for covariates, separately for each FFDM machine manufacturer (Hologic or GE). Machine-specific estimates were then combined by restricted maximum likelihood (REML) random effects meta-analysis using the R metafor package. The REML random effects meta-analysis method may be more robust than the DerSimonian and Laird method in accounting for the error associated with parameter estimation when the number of study groups is small.(41) We used the Q statistic to test for study heterogeneity by machine type, and I2 to quantify the degree of heterogeneity.(42) We performed global tests for statistical interactions using a likelihood ratio test to compare the linear mixed-effects models with and without the interaction terms, where machine type was modeled as a random intercept and all other covariates were modeled as fixed effects using the R lme4 package. Mediation analyses were conducted to evaluate the relative contribution of DA and NDA to associations with PD.(43,44) Standard errors of the indirect effect estimates were computed using 2,000 bootstrap replicates, and the machine-specific effects were combined by REML random effects meta-analysis. All analyses were implemented in SAS version 9.4 (SAS Inc. Cary, NC) and R version 3.5 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria).
Results
Subject characteristics
The study included 23,456 women screened at KPNC clinics that used Hologic (84%) or GE (16%) FFDM machines (Table 1). Women screened at clinics using Hologic machines were 2.6 years older and had 0.8 kg/m2 higher BMI, on average, compared to women screened at clinics using GE machines. In addition, the Hologic cohort was slightly more likely to be postmenopausal, use MHT, and have higher parity and older age at first birth. The distributions of alcohol and tobacco use, and square-root transformed values of PD, DA and NDA were generally comparable in the Hologic and GE cohorts. PD was strongly correlated with DA (R = 0.8) and NDA (R = −0.8) as expected, and DA and NDA were moderately negatively correlated (R = −0.35) in both cohorts. Less than 3% of women were excluded because of missing alcohol or tobacco data, and these women did not have significantly different distributions of age, BMI or other covariates.
Table 1.
Study population characteristics, by digital mammography machine manufacturer.
| Characteristic | Hologic Study | GE Study | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N=19699 | N=3757 | |||
| n | % | n | % | |
| Age (years), mean ± SD | 61.9 | ± 8.6 | 59.3 | ± 8.9 |
| Age at Menarche (years) | ||||
| <11 | 4200 | 21.3 | 777 | 20.7 |
| 12–13 | 10729 | 54.5 | 2079 | 55.3 |
| 14–15 | 3417 | 17.4 | 635 | 16.9 |
| 16+ | 722 | 3.7 | 166 | 4.4 |
| Missing | 631 | 3.2 | 100 | 2.7 |
| BMI (kg/m2), mean ± SD | 27.7 | ± 6.2 | 26.9 | ± 5.8 |
| Late adolescent BMI (kg/m2), mean ± SD | ||||
| 1st quartile | 18.1 | ± 0.9 | 18.1 | ± 0.9 |
| 2nd quartile | 20.0 | ± 0.4 | 19.9 | ± 0.4 |
| 3rd quartile | 21.4 | ± 0.4 | 21.4 | ± 0.5 |
| 4th quartile | 25.0 | ± 3.1 | 24.9 | ± 3.4 |
| Missing, n | 1883 | 361 | ||
| Age at first birth (years) | ||||
| <20 | 2111 | 10.7 | 360 | 9.6 |
| 20–24 | 5516 | 28.0 | 990 | 26.4 |
| 25–29 | 4553 | 23.1 | 785 | 20.9 |
| 30–34 | 2267 | 11.5 | 411 | 10.9 |
| 35–40 | 926 | 4.7 | 177 | 4.7 |
| >40 | 209 | 1.1 | 36 | 1.0 |
| Missing | 2302 | 11.7 | 558 | 14.8 |
| Number of births | ||||
| None | 1815 | 9.2 | 440 | 11.7 |
| 1 | 3006 | 15.3 | 545 | 14.5 |
| 2 | 7633 | 38.8 | 1314 | 35.0 |
| 3 | 3409 | 17.3 | 608 | 16.2 |
| 4+ | 1648 | 8.4 | 309 | 8.2 |
| Missing | 2188 | 11.1 | 541 | 14.4 |
| MHT use within 5 years prior to mammogram | ||||
| Yes | 4662 | 23.7 | 1140 | 30.3 |
| No | 15037 | 76.3 | 2617 | 69.7 |
| Menopausal status | ||||
| Premenopause | 4676 | 23.7 | 1031 | 27.4 |
| Postmenopause | 15023 | 76.3 | 2726 | 72.6 |
| First-degree relative with breast cancer | ||||
| Yes | 1865 | 9.5 | 358 | 9.5 |
| No | 17834 | 90.5 | 3399 | 90.5 |
| Breast cancer diagnosis prior to mammogram | ||||
| Yes | 1127 | 5.7 | 199 | 5.3 |
| No | 18572 | 94.3 | 3558 | 94.7 |
| Physical activity (METs), mean ± SD | ||||
| 1st quartile | 61.7 | ± 69.4 | 64.7 | ± 70.0 |
| 2nd quartile | 411.8 | ± 122.1 | 413.6 | ± 120.0 |
| 3rd quartile | 953.1 | ± 204.0 | 950.5 | ± 196.8 |
| 4th quartile | 2243.9 | ± 749.9 | 2187.4 | ± 693.8 |
| Missing, n | 396 | 72 | ||
| Alcohol use (drinks per week) | ||||
| None | 7926 | 40.2 | 1487 | 39.6 |
| 1–4 | 6122 | 31.1 | 1116 | 29.7 |
| 5+ | 5651 | 28.7 | 1154 | 30.7 |
| Tobacco use (packs per day) | ||||
| Never | 11969 | 60.8 | 2264 | 60.3 |
| <1/2 | 2507 | 12.7 | 436 | 11.6 |
| 1/2–1 | 2980 | 15.1 | 607 | 16.2 |
| 1+ | 2243 | 11.4 | 450 | 12.0 |
| MD phenotypes, mean ± SD | ||||
| Percent density (%) | 20.4 | ± 14.9 | 24.4 | ± 17.1 |
| Dense area (cm2) | 27.9 | ± 17.9 | 29.0 | ± 20.9 |
| Nondense area (cm2) | 140.0 | ± 77.7 | 109.2 | ± 61.0 |
| MD phenotypes (square-root), mean ± SD | ||||
| Percent density | 4.2 | ± 1.6 | 4.6 | ± 1.8 |
| Dense area | 5.0 | ± 1.6 | 5.0 | ± 1.9 |
| Nondense area | 11.3 | ± 3.3 | 10.0 | ± 2.9 |
MD = Mammographic density; GE = General Electric; BMI = body mass index; MHT = menopausal hormone therapy; MET = metabolic equivalent; SD = standard deviation.
Alcohol use and mammographic density phenotypes
Associations of alcohol use with PD, DA and NDA in adjusted models were similar in the Hologic and GE cohorts (Supplementary Figure 1). There was no evidence of significant heterogeneity by machine type (Q statistic P >0.05), and I2 was below 50% for all effect estimates except for the highest category of alcohol use in the NDA model (I2 = 68%, P = 0.08). We found a positive trend (ptrend = 0.01) of higher PD with higher levels of alcohol use (Table 2). Specifically, women who reported drinking 5+ alcoholic beverages per week had higher PD than non-drinkers by approximately half a percent (95% confidence interval: 0.07, 0.83). However, alcohol use was not significantly associated with DA. In contrast, there was an inverse trend of lower NDA with higher levels of alcohol use (ptrend=0.02). Women who reported drinking 5+ alcoholic beverages per week had lower NDA than non-drinkers by approximately four cm2 (−7.06, −0.35).
Table 2.
Association of alcohol and tobacco use with mammographic density phenotypes.
| Percent Density (%) | Dense Area (cm2) | Nondense Area (cm2) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | β (95% CI) | p | β (95% CI) | p | β (95% CI) | p | |
| Alcohol use | ||||||||
| None | 9413 | 40.1 | Referent | |||||
| 1–4 DPW | 7238 | 30.9 | 0.08 (−0.58, 0.74) | 0.8073 | −0.30 (−1.29, 0.69) | 0.5542 | −1.94 (−3.41, −0.47) | 0.0098 |
| 5+ DPW | 6805 | 29.0 | 0.45 (0.07, 0.83) | 0.0195 | 0.28 (−0.41, 0.96) | 0.4250 | −3.71 (−7.06, −0.35) | 0.0314 |
| p for trend | 0.0149 | 0.2323 | 0.0189 | |||||
| Tobacco use | ||||||||
| Never | 14233 | 60.7 | Referent | |||||
| <1/2 PPD | 2943 | 12.6 | −0.02 (−0.48, 0.45) | 0.9436 | 0.69 (0.03, 1.34) | 0.0383 | 1.77 (−0.14, 3.69) | 0.0693 |
| 1/2–1 PPD | 3587 | 15.3 | −0.47 (−0.89, −0.04) | 0.0322 | 0.08 (−0.52, 0.68) | 0.7984 | 2.83 (0.64, 5.03) | 0.0110 |
| 1+ PPD | 2693 | 11.5 | −0.76 (−1.23, −0.28) | 0.0021 | −0.20 (−0.88, 0.49) | 0.5731 | 4.37 (2.33, 6.40) | <0.0001 |
| p for trend | 0.0008 | 0.9340 | <0.0001 | |||||
All models were adjusted for age, age2, BMI, BMI2, BMI3, late adolescent BMI, age at menarche, age at first birth, parity, menopausal status, menopausal hormone therapy (MHT) use, first-degree relative with breast cancer, physical activity, and image batch. Effects were estimated using separate linear regression models of the square-root transformed phenotype in the Hologic and GE cohorts, and combined using restricted maximum likelihood (REML) random effects meta-analysis. Coefficients (β) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were back-transformed to the original scale. DPW = drinks per week; PPD = packs per day; BMI = body mass index.
The association of alcohol use with higher PD was explained mostly by lower NDA, rather than higher DA. Specifically, the positive association of alcohol drinking with PD was no longer significant after adjusting for NDA, (ptrend=0.60), but was only slightly attenuated by adjusting for DA (ptrend=0.059). Consistent with these results, mediation analysis showed that the indirect effect of alcohol on PD through NDA was statistically significant (p=0.001), whereas the indirect effect through DA was not significant (p=0.88). Approximately 69% of the total effect of alcohol on PD was explained by NDA in the fully adjusted mediation model.
Stratification by BMI ( Figure 1, Supplementary Table 1) showed that alcohol use was positively associated with PD and inversely associated with NDA in overweight or normal weight women, but these associations were not statistically significant in obese women. The global tests of interactions between alcohol and BMI categories reached statistical significance for PD (Pinteraction=0.04) and NDA (Pinteraction=0.02). Stratification by menopausal status (Figure 1, Supplementary Table 2) showed that alcohol use was positively associated with PD, except for a nonsignificant inverse association among postmenopausal women who drank 1–4 DPW (Pinteraction=0.016). However, there was no evidence that menopausal status significantly modified the associations of alcohol use with either NDA or DA, suggesting that the interaction found for PD may be due to chance. Further stratification by MHT use among post-menopausal women (Figure 1, Supplementary Table 3) showed that the effects of alcohol were not significantly modified by MHT use for PD (Pinteraction=0.70), DA (Pinteraction =0.86), or NDA (Pinteraction=0.77).
Figure 1. Associations of alcohol drinking with mammographic density phenotypes compared to non-drinkers, overall and stratified by BMI category, menopausal status, and use of menopausal hormone therapy.
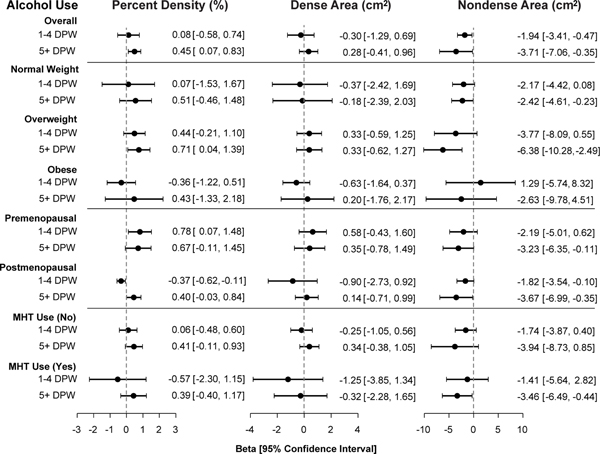
All models were adjusted for tobacco use, age, age2, BMI, BMI2, BMI3, late adolescent BMI, age at menarche, age at first birth, parity, menopausal status, menopausal hormone therapy (MHT) use, first-degree relative with breast cancer, physical activity, and image batch. Effects were estimated using separate linear regression models of the square-root transformed phenotype in the Hologic and GE cohorts, and combined using restricted maximum likelihood (REML) random effects meta-analysis. Coefficients (β) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were back-transformed to the original scale. DPW = drinks per week.
Tobacco use and mammographic density phenotypes
Associations of tobacco use with PD, DA and NDA in adjusted models were similar in the Hologic and GE cohorts (Supplementary Figure 1). There was no evidence of significant heterogeneity by machine type (Q statistic P >0.05 and I2 <20%). Tobacco use was inversely associated with PD and positively associated with NDA (Table 2). Women who reported smoking ½−1 PPD and 1+ PPD, respectively, had lower PD by approximately half (−0.89, −0.04) and three-quarters (−1.23, −0.28) of a percent than non-smokers (ptrend= 0.0008). Tobacco use was not significantly associated with DA (ptrend = 0.93), except for a small positive association in the lowest (<½ PPD) category that is likely due to chance. In contrast, women who reported smoking ½−1 PPD and 1+ PPD, respectively, had higher NDA by approximately three (0.64, 5.03) and four (2.33, 6.40) cm2 compared to non-smokers (ptrend<0.0001).
The association of tobacco use with lower PD was explained mostly by higher NDA, rather than lower DA. Specifically, the inverse association of smoking with PD was no longer significant after adjusting for NDA (ptrend=0.74), but remained significant after adjusting for DA (ptrend<0.0001). Consistent with these results, mediation analysis showed that the indirect effect of smoking on PD through NDA was statistically significant (p<0.0001), whereas the indirect effect through DA was not significant (p=0.39). Approximately 83% of the total effect of smoking on PD was explained by NDA in the fully adjusted mediation model.
Exploratory analyses of smoking status indicated that the inverse association with PD and positive association with NDA were stronger among current (3.8%) vs. former (35.4%) smokers (Supplementary Table 4). Exploratory analyses of smoking duration showed that women who smoked for >15 years (16.3%) had significantly lower PD, and women who smoked for >5 years (29.2%) had significantly higher NDA (Supplementary Table 4). These results indicate that the associations with PD and NDA may be stronger among current smokers who have smoked for at least five years.
Stratification by BMI (Figure 2, Supplementary Table 1) showed that the inverse association of tobacco use with PD was strongest in overweight women, whereas no statistically significant trends were found in obese or normal weight women. Similarly, the positive association of tobacco use with NDA was stronger in normal (ptrend=0.0015) and overweight (ptrend<0.0001) women than in obese women (ptrend=0.69). Global tests of the interaction of tobacco and BMI categories were statistically significant for PD (Pinteraction=0.0017) and NDA (Pinteraction<0.0001), suggesting that estimated associations with tobacco use are attenuated in obese women. Stratification by menopausal status (Figure 2, Supplementary Table 2) showed that the association of tobacco use with PD (Pinteraction=0.50) and NDA (Pinteraction=0.24) were similar in premenopausal and postmenopausal women. Stratification by MHT use in postmenopausal women (Figure 2, Supplementary Table 3) likewise yielded no evidence of significant modification of tobacco effects.
Figure 2. Associations of tobacco smoking with mammographic density phenotypes compared to non-smokers, overall and stratified by BMI category, menopausal status, and use of menopausal hormone therapy.
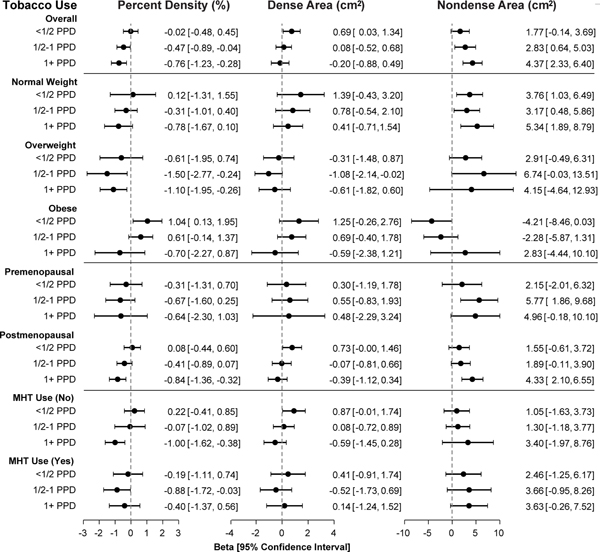
All models were adjusted for tobacco use, age, age2, BMI, BMI2, BMI3, late adolescent BMI, age at menarche, age at first birth, parity, menopausal status, menopausal hormone therapy (MHT) use, first-degree relative with breast cancer, physical activity, and image batch. Effects were estimated using separate linear regression models of the square-root transformed phenotype in the Hologic and GE cohorts, and combined using restricted maximum likelihood (REML) random effects meta-analysis. Coefficients (β) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were back-transformed to the original scale. PPD = packs per day.
Sensitivity and exploratory analyses of alcohol and tobacco use
Exploratory analyses of alcohol and tobacco use stratified by both menopausal status and BMI were comparable to the results stratified by BMI only, although the sample size and statistical power were reduced in each substratum. Among both premenopausal (Supplementary Table 5) and postmenopausal (Supplementary Table 6) women who were overweight or normal weight, alcohol use was inversely associated with NDA, and tobacco use was positively associated with NDA, whereas no significant trends were found in obese women. Sensitivity analyses (Supplementary Table 7) excluding 1449 (6.2%) women who were diagnosed with breast cancer before the mammogram and/or surveyed after the mammogram showed no meaningful differences compared with the main results including all 23,456 women (Table 2 and Supplementary Table 8). These results indicated that associations of alcohol and tobacco use with MD phenotypes were not unduly influenced by breast cancer treatment or reverse temporality.
Combined effects of alcohol and tobacco use
In light of the opposite directions of association of tobacco and alcohol use with MD phenotypes, and the correlation between the two behaviors, it is important to consider their combined effects. Comparison of adjusted models including both alcohol and tobacco to models with only one of the two exposures showed evidence of negative confounding (Supplementary Table 8). Specifically, the magnitude of the effects for the most extreme categories of alcohol (5+ DPW) and tobacco use (1+PPD) on PD and NDA increased by >10% when both exposures were included in the model. We found no evidence of departure from an additive model (pinteraction=0.98) for the combined effects of alcohol and tobacco use on MD phenotypes (Supplementary Table 9). Specifically, for NDA the effects of heavy alcohol use in non-smokers, and heavy tobacco use in non-drinkers, were of similar magnitude and in opposite directions, and no significant association was found among women with heavy use of both alcohol and tobacco.
Discussion
In this large population-based study of 23,456 women, we found that alcohol use was positively associated with PD, unassociated with DA, and inversely associated with NDA, whereas tobacco use was inversely associated with PD, unassociated with DA, and positively associated with NDA. These associations were strongest among normal and overweight women, and were attenuated in obese women. We did not find evidence of interactions between alcohol and tobacco use, nor modification of their effects by menopausal status and MHT use. This study provides evidence that associations of alcohol and tobacco use with PD may be mediated mostly through their associations with NDA rather than DA, and motivates future studies to examine the biological role of breast adipocytes in mammographic density and breast cancer risk.
Comparison to prior studies
The finding that higher alcohol consumption is associated with higher PD is consistent with a recent meta-analysis of 11 studies that reported a significant difference in PD of 0.84% when comparing the highest with the lowest categories of alcohol use.(6) In a subset of 5 studies(13,15–18) with absolute DA measurements, a positive association was found overall.(6) However, the three positive studies had a combined sample size of 542,(13,15,16) whereas the two studies with no significant overall associations were comparatively larger studies of 1147 and 2251 women, respectively, in Sweden(17) and Norway.(18) Two more recent Scandinavian studies found that alcohol use was positively associated with fully automated measures of DA (20) or dense volume (21) in models adjusted only for age, BMI, and menopausal status (20) or with additional adjustment for education and number of pregnancies.(21) To our knowledge, only two previous studies have examined alcohol use in relation to NDA.(17,19) Consistent with our findings, both studies reported nonsignificant positive associations with PD, null associations with DA, and significant inverse associations with NDA. NDA was 10.6 cm2 lower when comparing ≥10 grams of alcohol per day with none,(17) and 0.41 lower on the square-root scale when comparing ≥5 grams of alcohol per day with none among 2,100 post-menopausal women within the Nurses’ Health Study.(19) These reported effect sizes were larger than our parameter estimates of −0.16 (−3.71 cm2) for NDA and 0.05 (0.45%) for PD comparing 5+ DPW with none, which could be due in part to our tighter adjustment for BMI using three polynomial terms instead of a single linear term, or differences in the alcohol consumption categories.
The finding that tobacco use was associated with lower PD is consistent with most prior studies.(14,21,26,27,45–48) The few studies that reported null associations used dichotomous measures of tobacco use and PD,(28–30) which could have obscured a dose-response relationship. To our knowledge, only one prior study of 1,147 women in Sweden examined associations of tobacco use with NDA in addition to PD and DA.(17) Although no significant associations were reported, NDA was 2.3 cm2 higher comparing current with never smokers.(17) Women in the Swedish study had a similar prevalence of smoking, but lower smoking intensity (8.5% >0.5 PPD) than in our study (26.5% >0.5 PPD), which may explain the larger NDA difference of 5.4 cm2 comparing current with never smokers in our study.
Hypothesized mechanisms
The associations of alcohol and tobacco use with NDA in this study were unlikely to be explained by residual confounding by BMI, which reflects overall weight rather than adipose tissue distribution, because we adjusted for BMI using a flexible nonlinear model with three polynomial terms, and also adjusted for quartiles of BMI at age 18, in all models. Moreover, stratification by BMI showed that the associations of alcohol and tobacco use with NDA persisted even in normal or overweight women, within a narrow BMI range that was further adjusted using the same saturated covariate model. The attenuated associations with NDA found in obese women may have been due to smaller numbers, greater measurement error,(49) or biological differences in this subgroup.
The associations of alcohol and tobacco use with MD phenotypes may be mediated partly through their effects on sex hormone levels. Alcohol use has been shown to increase estrogen signaling via upregulation of aromatase expression and activity, increased estrogen receptor expression and activity, and decreased hepatic clearance of circulating estrogens.(50,51) In contrast, tobacco use has been reported to have anti-estrogenic effects via increased hepatic metabolism due to the induction of cytochrome P450 enzymes, and decreased bioavailability due to aromatase inhibition and increased sex hormone binding globulin levels.(25,52) Estrogen has been hypothesized to increase DA and thereby PD by stimulating the proliferation of mammary cells.(53) Moreover, estrogen is known to regulate adipose tissue metabolism, and has been shown to decrease adipose tissue mass by decreasing lipogenesis and stimulating lipolysis,(54,55) which plausibly could decrease the adipose tissues of the breast. Consistent with this hypothesis, menopause which naturally reduces sex hormone levels has been associated with decreased PD and DA, as well as increased NDA, independently of age and BMI.(3,56) The effects of sex hormones on breast tissue composition are likely to be mediated not only through direct effects on epithelial cells, stromal cells and adipocytes but also through their cellular interactions.(32)
The associations of alcohol and tobacco use with BMI-adjusted NDA may also be mediated through their effects on lipid metabolism, weight change and adipose tissue distribution. Alcohol drinking has been associated with higher high density lipoprotein (HDL) levels,(57) and cigarette smoking with lower HDL levels(58) in women. Furthermore, higher HDL levels have been associated with higher PD(57,59) and lower NDA,(60) supporting the hypothesis that alcohol and tobacco use may influence MD phenotypes through their effects on lipid metabolism. Moderate alcohol use has also been associated with decreased weight in women,(61) believed to be due to the higher metabolic demands of microsomal ethanol oxidation, the primary route through which women process alcohol.(62) Furthermore, weight loss has been associated with decreased NDA, independently of BMI and waist circumference.(63) In contrast, smoking cessation has been associated with weight gain in women, whereas current smokers tend to have lower weight compared with never smokers.(64) Over 90% of the smokers in this study were former smokers, and weight gain is another plausible mechanism for the association of tobacco use with higher BMI-adjusted NDA. Adipose tissues are also a source of estrogens, particularly in postmenopausal women,(65) which could counter the antiestrogenic effects of smoking and contribute to the weaker associations of smoking with NDA found in obese premenopausal and postmenopausal women.
Strengths and limitations
This large population-based study had high statistical power to detect modest associations of alcohol and tobacco use with MD phenotypes. RPGEH participants were unselected for breast cancer or other disease phenotypes, which improves the generalizability of the study findings. Quantitative measures of PD, DA and NDA were centrally measured from contemporary FFDM images using the well-established Cumulus(37) method, and were highly reproducible. Nonetheless, we cannot exclude the possibility that measurement error could have obscured modest associations of alcohol or tobacco use with DA. The inclusion of all three MD phenotypes in this study was an important strength because it enabled disentangling the effects of alcohol and tobacco use on the dense and nondense tissue components of the breast that are combined in the PD measure.
A limitation of this study is that minority women were not included because it was ancillary to a genome-wide association study. Future studies in minority women are needed. There was also potential for recall bias in the alcohol and tobacco information collected on the RPGEH survey. However, the resulting misclassification is likely to be non-differential with respect to MD phenotypes and lead to bias towards the null hypothesis. Like most studies, we did not have detailed information regarding smoking and drinking behaviors over the life course, such as age at initiation and cessation, which would enable more precise evaluation of associations with cumulative exposures or the timing of the exposure on MD phenotypes. We also did not have measures of adiposity, other than breast fat and BMI, and were unable to assess the extent to which associations with BMI-adjusted NDA were correlated with fat depots outside of the breast.
Conclusions
This large population-based study confirms that alcohol drinking is associated with a modest increase in PD, and provides significant evidence that this association may result mostly from lower amounts of nondense fatty tissues in the breast, rather than higher amounts of dense fibroglandular tissues. These findings are consistent with the association of alcohol drinking with increased breast cancer risk being mediated in part through lower NDA, and supports a protective role of breast adipocytes in maintaining healthy breasts. This study also provides significant evidence that tobacco smoking is associated with a modest decrease in PD, mainly through its association with higher NDA. Different components of tobacco smoke may have either carcinogenic or antiestrogenic effects, complicating the relationship of smoking with breast cancer risk. Our findings suggest that any association of tobacco smoking with increased BC risk is unlikely to be mediated through MD phenotypes. Future studies of modifiable lifestyle factors and mammographic density, which include NDA as well as PD and DA, are needed to improve our understanding of the underlying biology, and enable better preventive interventions to reduce breast cancer risk.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the KPNC members who generously agreed to participate in the RPGEH. We thank Mark Westley, Marvella Villaseñor, Marc Sofilos, Shannon Walters, Anoma Gunasekara, and Gordon Mawdsley for their technical expertise and assistance. The study was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health: R01CA166827 (W. Sieh, L.A. Habel), R01CA168893 (L.A. Habel), and R01CA237541 (W. Sieh, L.A. Habel). The RPGEH was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health RC2AG036607, Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, Ellison Medical Foundation, Wayne and Gladys Valley Foundation, and Kaiser Permanente National and Regional Community Benefit Programs. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the sponsors.
Abbreviations:
- BC
Breast cancer
- BMI
Body mass index
- DA
Dense area
- DPW
Drinks per week
- EHR
Electronic health record
- FFDM
Full-field digital mammography
- GE
General Electric
- HDL
High density lipoprotein
- ICC
Intraclass correlation coefficient
- KPNC
Kaiser Permanente Northern California
- MD
Mammographic density
- MET
Metabolic equivalent of task
- MHT
Menopausal hormone therapy
- NDA
Nondense area
- PD
Percent density
- PPD
Packs per day
- REML
Restricted maximum likelihood
- RPGEH
Research Program on Genes, Environment and Health
- WHO
World Health Organization
Footnotes
Conflicts of interest: The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.Boyd NF, Rommens JM, Vogt K, Lee V, Hopper JL, Yaffe MJ, et al. Mammographic breast density as an intermediate phenotype for breast cancer. Lancet Oncol 2005;6(10):798–808 doi 10.1016/S1470-2045(05)70390-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Engmann NJ, Golmakani MK, Miglioretti DL, Sprague BL, Kerlikowske K, Breast Cancer Surveillance C. Population-Attributable Risk Proportion of Clinical Risk Factors for Breast Cancer. JAMA Oncol 2017;3(9):1228–36 doi 10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.6326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Burton A, Maskarinec G, Perez-Gomez B, Vachon C, Miao H, Lajous M, et al. Mammographic density and ageing: A collaborative pooled analysis of cross-sectional data from 22 countries worldwide. PLoS Med 2017;14(6):e1002335 doi 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Alexeeff SE, Odo NU, Lipson JA, Achacoso N, Rothstein JH, Yaffe MJ, et al. Age at Menarche and Late Adolescent Adiposity Associated with Mammographic Density on Processed Digital Mammograms in 24,840 Women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2017;26(9):1450–8 doi 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-17-0264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cuzick J, Warwick J, Pinney E, Duffy SW, Cawthorn S, Howell A, et al. Tamoxifen-Induced Reduction in Mammographic Density and Breast Cancer Risk Reduction: A Nested Case-Control Study. J Natl Cancer I 2011;103(9):744–52 doi 10.1093/jnci/djr079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ziembicki S, Zhu J, Tse E, Martin LJ, Minkin S, Boyd NF. The Association between Alcohol Consumption and Breast Density: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Cancer Epidem Biomar 2017;26(2):170–8 doi 10.1158/1055-9965.Epi-16-0522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ghosh K, Brandt KR, Reynolds C, Scott CG, Pankratz VS, Riehle DL, et al. Tissue composition of mammographically dense and non-dense breast tissue. Breast Cancer Res Tr 2012;131(1):267–75 doi 10.1007/s10549-011-1727-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pettersson A, Hankinson SE, Willett WC, Lagiou P, Trichopoulos D, Tamimi RM. Nondense mammographic area and risk of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 2011;13(5):R100 doi 10.1186/bcr3041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Pettersson A, Graff RE, Ursin G, Santos Silva ID, McCormack V, Baglietto L, et al. Mammographic density phenotypes and risk of breast cancer: a meta-analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst 2014;106(5) doi 10.1093/jnci/dju078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hamajima N, Hirose K, Tajima K, Rohan T, Calle EE, Heath CW Jr., , et al. Alcohol, tobacco and breast cancer--collaborative reanalysis of individual data from 53 epidemiological studies, including 58,515 women with breast cancer and 95,067 women without the disease. Br J Cancer 2002;87(11):1234–45 doi 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Singletary KW, Gapstur SM. Alcohol and breast cancer: review of epidemiologic and experimental evidence and potential mechanisms. JAMA 2001;286(17):2143–51 doi 10.1001/jama.286.17.2143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.McDonald JA, Goyal A, Terry MB. Alcohol Intake and Breast Cancer Risk: Weighing the Overall Evidence. Curr Breast Cancer Rep 2013;5(3) doi 10.1007/s12609-013-0114-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Flom JD, Ferris JS, Tehranifar P, Terry MB. Alcohol intake over the life course and mammographic density. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2009;117(3):643–51 doi 10.1007/s10549-008-0302-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Cabanes A, Pastor-Barriuso R, Garcia-Lopez M, Pedraz-Pingarron C, Sanchez-Contador C, Vazquez Carrete JA, et al. Alcohol, tobacco, and mammographic density: a population-based study. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2011;129(1):135–47 doi 10.1007/s10549-011-1414-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Frydenberg H, Flote VG, Larsson IM, Barrett ES, Furberg AS, Ursin G, et al. Alcohol consumption, endogenous estrogen and mammographic density among premenopausal women. Breast Cancer Res 2015;17:103 doi 10.1186/s13058-015-0620-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Quandt Z, Flom JD, Tehranifar P, Reynolds D, Terry MB, McDonald JA. The association of alcohol consumption with mammographic density in a multiethnic urban population. BMC Cancer 2015;15:1094 doi 10.1186/s12885-015-1094-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Brand JS, Czene K, Eriksson L, Trinh T, Bhoo-Pathy N, Hall P, et al. Influence of lifestyle factors on mammographic density in postmenopausal women. PLoS One 2013;8(12):e81876 doi 10.1371/journal.pone.0081876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Qureshi SA, Couto E, Hofvind S, Wu AH, Ursin G. Alcohol intake and mammographic density in postmenopausal Norwegian women. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2012;131(3):993–1002 doi 10.1007/s10549-011-1812-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Yaghjyan L, Colditz G, Eliassen H, Rosner B, Gasparova A, Tamimi RM. Interactions of alcohol and postmenopausal hormone use in regards to mammographic breast density. Cancer Causes Control 2018;29(8):751–8 doi 10.1007/s10552-018-1053-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Azam S, Sjolander A, Eriksson M, Gabrielson M, Czene K, Hall P. Determinants of Mammographic Density Change. JNCI Cancer Spectr 2019;3(1):pkz004 doi 10.1093/jncics/pkz004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hjerkind KV, Ellingjord-Dale M, Johansson ALV, Aase HS, Hoff SR, Hofvind S, et al. Volumetric Mammographic Density, Age-Related Decline, and Breast Cancer Risk Factors in a National Breast Cancer Screening Program. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2018;27(9):1065–74 doi 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-18-0151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Pierce JP, Patterson RE, Senger CM, Flatt SW, Caan BJ, Natarajan L, et al. Lifetime cigarette smoking and breast cancer prognosis in the After Breast Cancer Pooling Project. J Natl Cancer Inst 2014;106(1):djt359 doi 10.1093/jnci/djt359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Xue F, Willett WC, Rosner BA, Hankinson SE, Michels KB. Cigarette smoking and the incidence of breast cancer. Arch Intern Med 2011;171(2):125–33 doi 10.1001/archinternmed.2010.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Gaudet MM, Carter BD, Brinton LA, Falk RT, Gram IT, Luo J, et al. Pooled analysis of active cigarette smoking and invasive breast cancer risk in 14 cohort studies. Int J Epidemiol 2017;46(3):881–93 doi 10.1093/ije/dyw288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kapoor D, Jones TH. Smoking and hormones in health and endocrine disorders. Eur J Endocrinol 2005;152(4):491–9 doi 10.1530/eje.1.01867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Butler LM, Gold EB, Conroy SM, Crandall CJ, Greendale GA, Oestreicher N, et al. Active, but not passive cigarette smoking was inversely associated with mammographic density. Cancer Causes Control 2010;21(2):301–11 doi 10.1007/s10552-009-9462-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Vachon CM, Kuni CC, Anderson K, Anderson VE, Sellers TA. Association of mammographically defined percent breast density with epidemiologic risk factors for breast cancer (United States). Cancer Causes Control 2000;11(7):653–62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Roubidoux MA, Kaur JS, Griffith KA, Stillwater B, Novotny P, Sloan J. Relationship of mammographic parenchymal patterns to breast cancer risk factors and smoking in Alaska Native women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2003;12(10):1081–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Gapstur SM, Lopez P, Colangelo LA, Wolfman J, Van Horn L, Hendrick RE. Associations of breast cancer risk factors with breast density in Hispanic women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2003;12(10):1074–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Yaghjyan L, Mahoney MC, Succop P, Wones R, Buckholz J, Pinney SM. Relationship between breast cancer risk factors and mammographic breast density in the Fernald Community Cohort. Br J Cancer 2012;106(5):996–1003 doi 10.1038/bjc.2012.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lindstrom S, Thompson DJ, Paterson AD, Li J, Gierach GL, Scott C, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies multiple loci associated with both mammographic density and breast cancer risk. Nat Commun 2014;5:5303 doi 10.1038/ncomms6303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Nazari SS, Mukherjee P. An overview of mammographic density and its association with breast cancer. Breast Cancer 2018;25(3):259–67 doi 10.1007/s12282-018-0857-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Banda Y, Kvale MN, Hoffmann TJ, Hesselson SE, Ranatunga D, Tang H, et al. Characterizing Race/Ethnicity and Genetic Ancestry for 100,000 Subjects in the Genetic Epidemiology Research on Adult Health and Aging (GERA) Cohort. Genetics 2015;200(4):1285–95 doi 10.1534/genetics.115.178616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kvale MN, Hesselson S, Hoffmann TJ, Cao Y, Chan D, Connell S, et al. Genotyping Informatics and Quality Control for 100,000 Subjects in the Genetic Epidemiology Research on Adult Health and Aging (GERA) Cohort. Genetics 2015;200(4):1051–60 doi 10.1534/genetics.115.178905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Habel LA, Lipson JA, Achacoso N, Rothstein JH, Yaffe MJ, Liang RY, et al. Case-control study of mammographic density and breast cancer risk using processed digital mammograms. Breast Cancer Res 2016;18(1):53 doi 10.1186/s13058-016-0715-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Alexeeff SE, Odo NU, McBride R, McGuire V, Achacoso N, Rothstein JH, et al. Reproductive Factors and Mammographic Density: Associations Among 24,840 Women and Comparison of Studies Using Digitized Film-Screen Mammography and Full-Field Digital Mammography. Am J Epidemiol 2019;188(6):1144–54 doi 10.1093/aje/kwz033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Byng JW, Boyd NF, Fishell E, Jong RA, Yaffe MJ. The quantitative analysis of mammographic densities. Phys Med Biol 1994;39(10):1629–38 doi 10.1088/0031-9155/39/10/008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Craig CL, Marshall AL, Sjostrom M, Bauman AE, Booth ML, Ainsworth BE, et al. International physical activity questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2003;35(8):1381–95 doi 10.1249/01.MSS.0000078924.61453.FB. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.McCormack VA, Burton A, dos-Santos-Silva I, Hipwell JH, Dickens C, Salem D, et al. International Consortium on Mammographic Density: Methodology and population diversity captured across 22 countries. Cancer Epidemiol 2016;40:141–51 doi 10.1016/j.canep.2015.11.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Cox C Delta Method. Encyclopedia of Biostatistics. Chichester, England: John Wiley & Sons; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Brockwell SE, Gordon IR. A comparison of statistical methods for meta-analysis. Stat Med 2001;20(6):825–40 doi 10.1002/sim.650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Huedo-Medina TB, Sanchez-Meca J, Marin-Martinez F, Botella J. Assessing heterogeneity in meta-analysis: Q statistic or I2 index? Psychol Methods 2006;11(2):193–206 doi 10.1037/1082-989X.11.2.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Preacher KJ, Hayes AF. Asymptotic and resampling strategies for assessing and comparing indirect effects in multiple mediator models. Behav Res Methods 2008;40(3):879–91 doi 10.3758/brm.40.3.879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Hayes AF, Preacher KJ. Statistical mediation analysis with a multicategorical independent variable. Br J Math Stat Psychol 2014;67(3):451–70 doi 10.1111/bmsp.12028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Jeffreys M, Warren R, Gunnell D, McCarron P, Smith GD. Life course breast cancer risk factors and adult breast density (United Kingdom). Cancer Causes Control 2004;15(9):947–55 doi 10.1007/s10522-004-2473-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Modugno F, Ngo DL, Allen GO, Kuller LH, Ness RB, Vogel VG, et al. Breast cancer risk factors and mammographic breast density in women over age 70. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2006;97(2):157–66 doi 10.1007/s10549-005-9105-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Bremnes Y, Ursin G, Bjurstam N, Gram IT. Different measures of smoking exposure and mammographic density in postmenopausal Norwegian women: a cross-sectional study. Breast Cancer Res 2007;9(5):R73 doi 10.1186/bcr1782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Jacobsen KK, Lynge E, Vejborg I, Tjonneland A, von Euler-Chelpin M, Andersen ZJ. Cigarette smoking and mammographic density in the Danish Diet, Cancer and Health cohort. Cancer Causes Control 2016;27(2):271–80 doi 10.1007/s10552-015-0704-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Elmore JG, Carney PA, Abraham LA, Barlow WE, Egger JR, Fosse JS, et al. The association between obesity and screening mammography accuracy. Arch Intern Med 2004;164(10):1140–7 doi 10.1001/archinte.164.10.1140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Monteiro R, Soares R, Guerreiro S, Pestana D, Calhau C, Azevedo I. Red wine increases adipose tissue aromatase expression and regulates body weight and adipocyte size. Nutrition 2009;25(6):699–705 doi 10.1016/j.nut.2009.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Fan S, Meng Q, Gao B, Grossman J, Yadegari M, Goldberg ID, et al. Alcohol stimulates estrogen receptor signaling in human breast cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 2000;60(20):5635–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Tansavatdi K, McClain B, Herrington DM. The effects of smoking on estradiol metabolism. Minerva Ginecol 2004;56(1):105–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Boyd NF, Stone J, Martin LJ, Jong R, Fishell E, Yaffe M, et al. The association of breast mitogens with mammographic densities. Br J Cancer 2002;87(8):876–82 doi 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Cooke PS, Naaz A. Role of estrogens in adipocyte development and function. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2004;229(11):1127–35 doi 10.1177/153537020422901107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Newell-Fugate AE. The role of sex steroids in white adipose tissue adipocyte function. Reproduction 2017;153(4):R133–R49 doi 10.1530/REP-16-0417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Boyd N, Martin L, Stone J, Little L, Minkin S, Yaffe M. A longitudinal study of the effects of menopause on mammographic features. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2002;11(10 Pt 1):1048–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Boyd NF, Connelly P, Byng J, Yaffe M, Draper H, Little L, et al. Plasma lipids, lipoproteins, and mammographic densities. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 1995;4(7):727–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Szkup M, Jurczak A, Karakiewicz B, Kotwas A, Kopec J, Grochans E. Influence of cigarette smoking on hormone and lipid metabolism in women in late reproductive stage. Clin Interv Aging 2018;13:109–15 doi 10.2147/CIA.S140487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Sung J, Song YM, Stone J, Lee K, Kim SY. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol, obesity, and mammographic density in Korean women: the Healthy Twin study. J Epidemiol 2011;21(1):52–60 doi 10.2188/jea.je20100078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Lucht SA, Eliassen AH, Bertrand KA, Ahern TP, Borgquist S, Rosner B, et al. Circulating lipids, mammographic density, and risk of breast cancer in the Nurses’ Health Study and Nurses’ Health Study II. Cancer Causes Control 2019;30(9):943–53 doi 10.1007/s10552-019-01201-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Dallongeville J, Marecaux N, Ducimetiere P, Ferrieres J, Arveiler D, Bingham A, et al. Influence of alcohol consumption and various beverages on waist girth and waist-to-hip ratio in a sample of French men and women. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1998;22(12):1178–83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Reichman ME, Judd JT, Longcope C, Schatzkin A, Clevidence BA, Nair PP, et al. Effects of alcohol consumption on plasma and urinary hormone concentrations in premenopausal women. J Natl Cancer Inst 1993;85(9):722–7 doi 10.1093/jnci/85.9.722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Wanders JO, Bakker MF, Veldhuis WB, Peeters PH, van Gils CH. The effect of weight change on changes in breast density measures over menopause in a breast cancer screening cohort. Breast Cancer Res 2015;17:74 doi 10.1186/s13058-015-0583-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Plurphanswat N, Rodu B. The association of smoking and demographic characteristics on body mass index and obesity among adults in the U.S., 1999–2012. BMC Obes 2014;1:18 doi 10.1186/s40608-014-0018-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Key TJ, Appleby PN, Reeves GK, Roddam A, Dorgan JF, Longcope C, et al. Body mass index, serum sex hormones, and breast cancer risk in postmenopausal women. J Natl Cancer Inst 2003;95(16):1218–26 doi 10.1093/jnci/djg022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


