A 50-year-old man was admitted for acute motor aphasia, he was treated with fibrinolysis by stroke in the left brain media artery territory. Before admission, he had fever and dyspnea for 5 days. He presented hypoxemic bilateral interstitial pneumonia highly suggestive for COVID 19 infection, although 3 samples (two nasopharyngeal and one bronchial exudates) for PCR were negative. The blood test revealed lymphocytopenia and an increase in LDH, AST, ALT, C-reactive protein and d-dimer.
Getting worse that requires invasive mechanical ventilation, so that treatment with azithromycin, hydroxychloroquine, lopinavir/ritonavir was initiated.
Ten days after the respiratory symptoms the IgM and IgG rapid detection test for SARS-Cov 2 was performed, being positive for both (Fig. 1 ).
Figure 1.
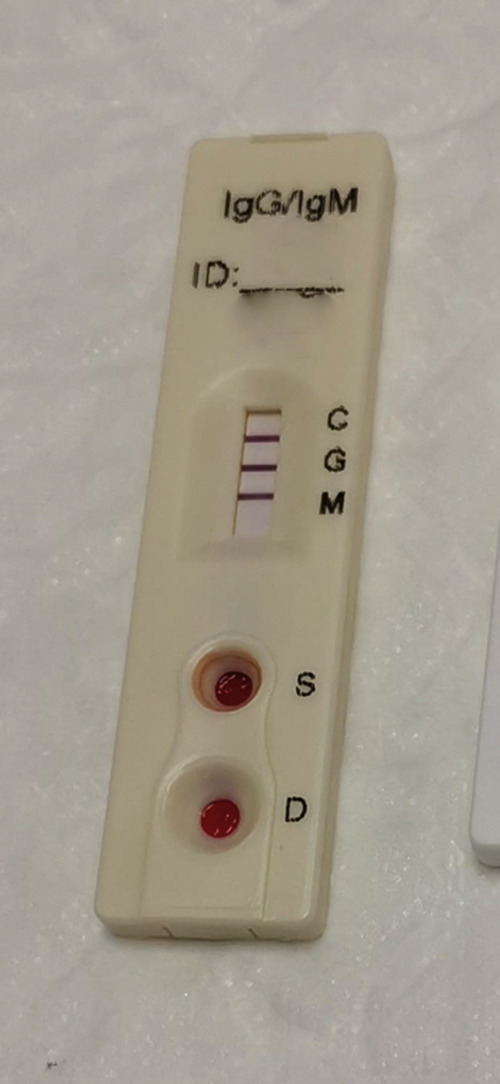
Rapid inmunoglobulin test.
Clinical and radiological improvement were demonstrated after adding pronation and the administration of tocilizumab.
Immunoglobulin detection by immunochromatography can confirm coronavirus infection when PCR is negative when have passed at least 6–10 days since the onset of symptoms.


