Figure 3: TIMP-GLIA tolerance induction in mice with delayed-type hypersensitivity to gliadin.
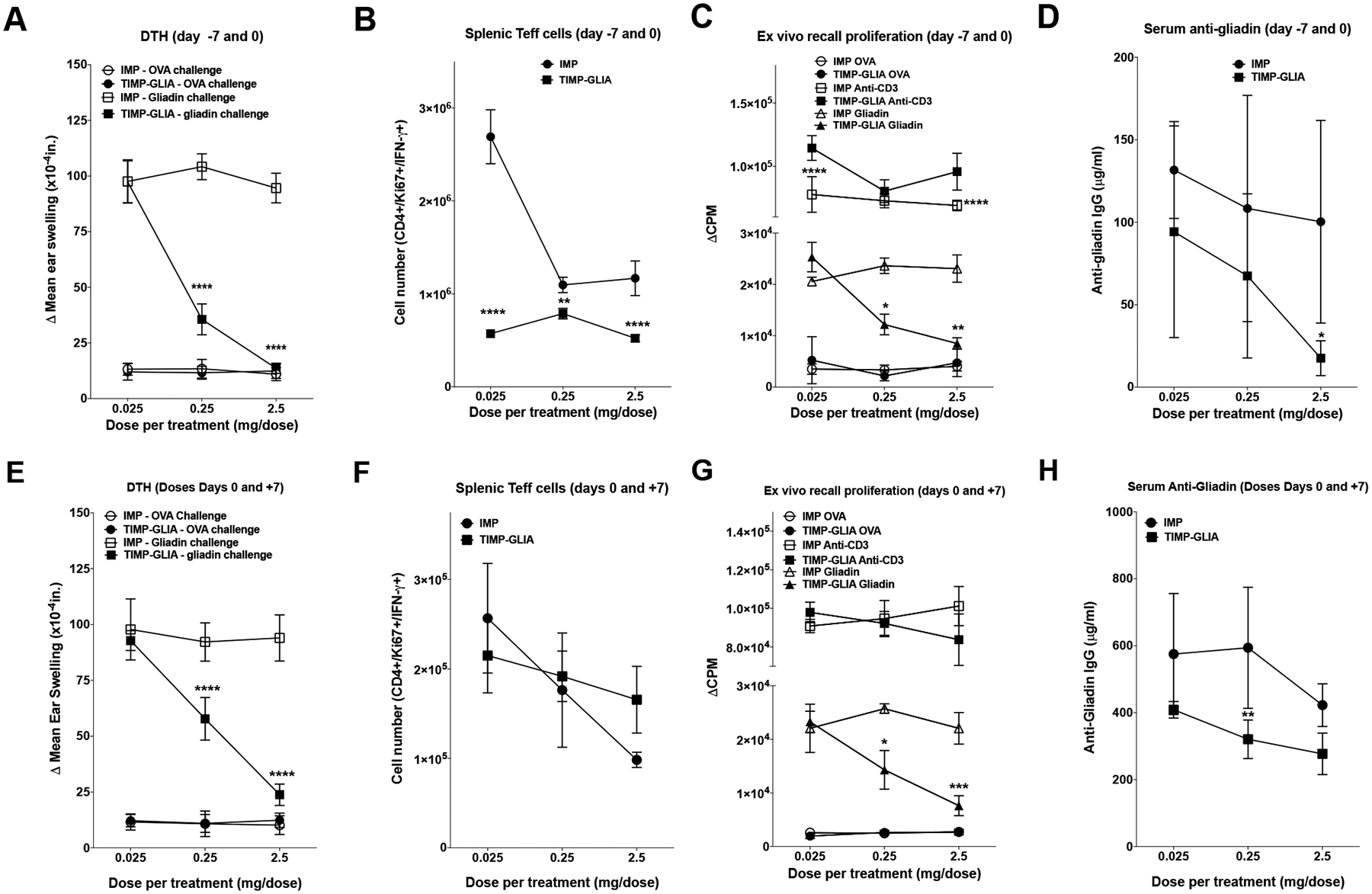
A-H) C57BL/6 female mice (n=5) were treated with TIMP-GLIA, or unloaded control particles (IMP), either on days −7 and 0 (A-D), or days 0 and 7 (E-H). Mice were primed with gliadin in CFA on day 0. A, E) On day 14 post priming, mice were injected with gliadin or ovalbumin (OVA) into the ear pinna for DTH analysis (Δ mean ear thickness after 24h +/− SEM; x10−4in). B, F) The numbers of live, CD3+/CD4+/Ki67+/IFNG+ splenic effector T cells were determined (Teffs; mean +/− SEM; flow cytometry). C, G) To assess proliferation, spleen cells were stimulated with anti-CD3, OVA, or gliadin (mean counts per minute +/− SEM; 3H-TdR incorporation). D, H) Serum anti-gliadin IgG antibody levels were analyzed, testing serial dilutions (mean concentration +/− SEM; ELISA). Statistical analyses were performed using one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparison test (A-H; *p≤0.05, **p≤0.01, ***p≤0.001, ****p≤0.0001).
