The dihydroquinoline unit is slightly twisted and the hexyl groups extend out on either side. In the crystal, C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds form chains of molecules extending along the b-axis direction, which are paired up by slipped π-stacking interactions. The ends of the hexyl groups from neighbouring chains are in contact but do not intercalate.
Keywords: crystal structure, dihydroquinoline, aliphatic chains, π-stacking, Hirshfeld surface analysis
Abstract
The asymmetric unit of the title compound, C22H31NO3, comprises of one molecule. The molecule is not planar, with the carboxylate ester group inclined by 33.47 (4)° to the heterocyclic ring. Individual molecules are linked by aromaticC—H⋯Ocarbonyl hydrogen bonds into chains running parallel to [001]. Slipped π–π stacking interactions between quinoline moieties link these chains into layers extending parallel to (100). Hirshfeld surface analysis, two-dimensional fingerprint plots and molecular electrostatic potential surfaces were used to quantify the intermolecular interactions present in the crystal, indicating that the most important contributions for the crystal packing are from H⋯H (72%), O⋯H/H⋯O (14.5%) and C⋯H/H⋯C (5.6%) interactions.
Chemical context
Quinoline derivatives represent an important class of heterocyclic compounds utilized as pharmaceuticals (Chu et al., 2019 ▸). They possess various biological properties such as antibacterial (Panda et al., 2015 ▸), anticancer (Tang et al., 2018 ▸), antitubercular (Xu et al., 2017 ▸), antiviral (Sekgota et al., 2017 ▸), anti-HCV (Cannalire et al., 2016 ▸), antimalarial (Hu et al., 2017 ▸), anti-Alzheimer’s (Bolognesi et al., 2007 ▸), antileishmanial (Palit et al., 2009 ▸) and anti-inflammatory (Pinz et al., 2016 ▸) activities.
In view of the biological importance of quinoline, and in a continuation of our research work devoted to the syntheses and crystal structures of quinoline derivatives (Bouzian et al., 2019a ▸,b ▸), we report herein on the molecular and crystal structures of hexyl 1-hexyl-2-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinoline-4-carboxylate, (I), which was prepared by reacting ethyl 6-chloro-2-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinoline-4-carboxylate with 1-bromohexane in the presence of a catalytic quantity of tetra-n-butylammonium bromide. Intermolecular interactions were quantified by Hirshfeld surface analysis.
Structural commentary
The molecule of (I) is shown in Fig. 1 ▸. It is non-planar, with the carboxyl ester group inclined by 33.47 (4)° to the heterocyclic ring (r.m.s. deviation of the ten atoms = 0.0174 Å). The hexyl chain attached to N1 is twisted out of this plane by 14.2 (2)° whereas the hexyl chain attached to O1 is twisted by 23.1 (2)° from this plane.
Figure 1.
The title molecule with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level.
Supramolecular features
In the crystal, C4—H4⋯O1 hydrogen bonds between the phenyl ring and the carbonyl group of an adjacent molecule lead to the formation of chains running parallel to [001] (Table 1 ▸, Fig. 2 ▸). These chains are connected in pairs along [010] through slipped π–π stacking interactions between inversion-related dihydroquinoline moieties [Cg1⋯Cg2i = 3.5472 (9) Å with a slippage of 0.957 Å; Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of the N1/C6/C1/C9/C8/C7 and C1–C6 rings; symmetry code: (i) 1 − x, −y, 1 − z] (Figs. 2 ▸, 3 ▸). This way, (100) layers with a width corresponding to the length of the a axis are formed. Unlike the packing features of similar molecules, the hexyl chains are not oriented in parallel. This is possibly a consequence of the π–π stacking interactions, which result in a ‘crossed’ orientation of neighbouring hexyl groups (Fig. 3 ▸).
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C4—H4⋯O1i | 0.960 (17) | 2.475 (17) | 3.3670 (19) | 154.7 (15) |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Figure 2.
The crystal packing viewed along [010], with C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and π–π stacking interactions indicated by black and orange dashed lines, respectively.
Figure 3.
The crystal packing viewed along [001], with π–π stacking interactions indicated by orange dashed lines.
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD, version 5.40, update of August 2019; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) using 2-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinoline-4-carboxylic acid as the main skeleton revealed five structures similar to the title compound. They contain the oxoquinoline moiety with different substituents, viz. 2-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinoline-4-carboxylic acid monohydrate (EQAVAV; Filali Baba et al., 2016 ▸), ethyl 1H-3-hydroxy-2-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinoline-4-carboxylate (RAVJAA01; Paterna et al., 2013 ▸), ethyl 1-methyl-2-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinoline-4-carboxylate (SECCAH; Filali Baba et al., 2017a ▸), prop-2-yn-1-yl 2-oxo-1-(prop-2-yn-1-yl)-1,2-dihydroquinoline-4-carboxylate (XILYUP; Filali Baba et al., 2017b ▸) and ethyl 1-benzyl-3-hydroxy-2-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinoline-4-carboxylate (ZINHEL; Paterna et al., 2013 ▸). The layers present in EQAVAV are linked together by pairwise N—H⋯O interactions. In SECCAH, weak C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds link the molecules into zigzag chains along [100]. A single weak C—H⋯O intermolecular interaction links the molecules into [001] chains in XILYUP.
Hirshfeld surface analysis
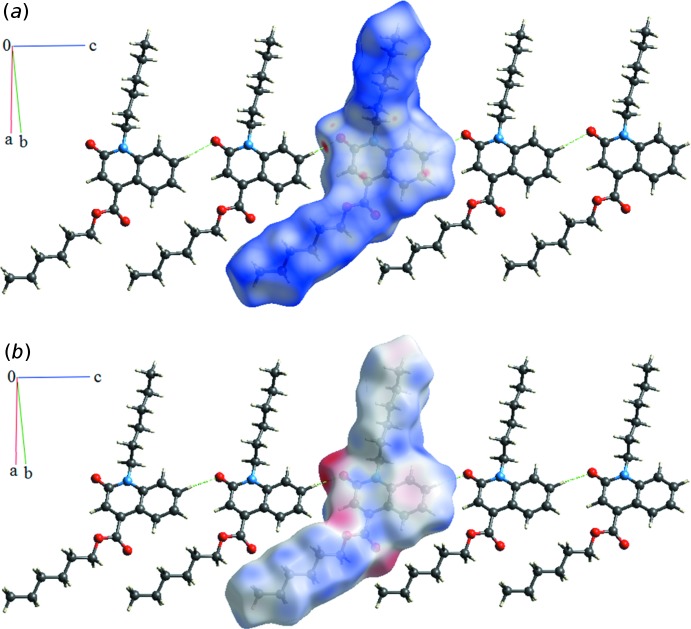
To investigate the intermolecular interactions, Hirshfeld surface analysis (Spackman & Jayatilaka, 2009 ▸) and two-dimensional fingerprint plots were generated for the molecule using CrystalExplorer17.5 (Turner et al., 2017 ▸). Hirshfeld surface analysis depicts intermolecular interactions by different colours, representing short or long contacts and further the relative strength of the interaction. The generated Hirshfeld surface mapped over dnorm is shown in Fig. 4 ▸ a. A view of the three-dimensional Hirshfeld surface of the title compound plotted over electrostatic potential, highlighting the C—H⋯O contacts, is given in Fig. 4 ▸ b. As revealed by the two-dimensional fingerprint plots (Fig. 5 ▸), the crystal packing is dominated by H⋯H contacts, representing van der Waals interactions (72% contribution to the overall surface), followed by O⋯H and C⋯H interactions, which contribute with 14.5% and 5.6%, respectively. The contributions of the C⋯C (5.4%), C⋯O (0.8%), C⋯N (0.7%) and N⋯H (0.6%) interactions are less significant.
Figure 4.
(a) The Hirshfeld surfaces of the title compound mapped over d norm, with a fixed colour scale of −0.1822 (red) to 1.3083 (blue) a.u., and (b) the Hirshfeld surface mapped over molecular electrostatic potential showing C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, with a fixed colour scale of −0.0733 (red) to 0.0381(blue) a.u..
Figure 5.
Two-dimensional fingerprint plots to the Hirshfeld surface with (a) a d norm view for (I) and delineated into relative contributions for (b) H⋯H, (c) O⋯H/H⋯H and (d) C⋯H/H⋯C interactions.
Synthesis and crystallization
A mixture of 2-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinoline-4-carboxylic acid (0.5 g, 2.6 mmol), K2CO3 (0.73 g, 5.29 mmol), 1-bromohexane (0.66 g, 4 mmol) and tetra-n-butylammonium bromide as catalyst in DMF (25 ml) was stirred at room temperature for 48 h. The solution was filtered by suction, and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The residue was chromatographed on a silica-gel column using hexane and ethyl acetate (v/v, 95/5) as eluents to afford (I). Single crystals were obtained by slow evaporation of an ethanolic solution.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. All H atoms were located in difference-Fourier maps and were refined freely.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C22H31NO3 |
| M r | 357.48 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 150 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 17.6928 (7), 13.2512 (5), 8.5916 (3) |
| β (°) | 90.184 (2) |
| V (Å3) | 2014.30 (13) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Cu Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.61 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.25 × 0.17 × 0.10 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker D8 VENTURE PHOTON 100 CMOS |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Krause et al., 2015 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.82, 0.94 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 14697, 3924, 3044 |
| R int | 0.048 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.618 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.046, 0.105, 1.07 |
| No. of reflections | 3924 |
| No. of parameters | 359 |
| H-atom treatment | All H-atom parameters refined |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.19, −0.18 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989020004521/wm5550sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989020004521/wm5550Isup2.hkl
CCDC reference: 1994187
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C22H31NO3 | F(000) = 776 |
| Mr = 357.48 | Dx = 1.179 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54178 Å |
| a = 17.6928 (7) Å | Cell parameters from 9350 reflections |
| b = 13.2512 (5) Å | θ = 5.0–72.3° |
| c = 8.5916 (3) Å | µ = 0.61 mm−1 |
| β = 90.184 (2)° | T = 150 K |
| V = 2014.30 (13) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.25 × 0.17 × 0.10 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker D8 VENTURE PHOTON 100 CMOS diffractometer | 3924 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: INCOATEC IµS micro–focus source | 3044 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Mirror monochromator | Rint = 0.048 |
| Detector resolution: 10.4167 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 72.4°, θmin = 4.2° |
| ω scans | h = −21→21 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Krause et al., 2015) | k = −16→15 |
| Tmin = 0.82, Tmax = 0.94 | l = −9→10 |
| 14697 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: dual |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.046 | Hydrogen site location: difference Fourier map |
| wR(F2) = 0.105 | All H-atom parameters refined |
| S = 1.07 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.028P)2 + 0.8763P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3924 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 359 parameters | Δρmax = 0.19 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.18 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.38830 (7) | 0.40574 (9) | 0.54321 (12) | 0.0338 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.68998 (7) | 0.45106 (10) | 0.80686 (14) | 0.0384 (3) | |
| O3 | 0.66596 (7) | 0.37452 (8) | 0.57906 (13) | 0.0308 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.40867 (8) | 0.38809 (9) | 0.80434 (14) | 0.0254 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.53672 (9) | 0.37846 (11) | 0.90859 (17) | 0.0251 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.58415 (10) | 0.36524 (11) | 1.03887 (19) | 0.0281 (4) | |
| H2 | 0.6393 (11) | 0.3633 (14) | 1.024 (2) | 0.034 (5)* | |
| C3 | 0.55465 (10) | 0.35284 (12) | 1.18543 (19) | 0.0303 (4) | |
| H3 | 0.5872 (10) | 0.3427 (14) | 1.279 (2) | 0.039 (5)* | |
| C4 | 0.47679 (10) | 0.35250 (12) | 1.20670 (18) | 0.0298 (4) | |
| H4 | 0.4558 (10) | 0.3457 (14) | 1.309 (2) | 0.032 (5)* | |
| C5 | 0.42866 (10) | 0.36311 (12) | 1.08128 (18) | 0.0277 (4) | |
| H5 | 0.3734 (10) | 0.3620 (13) | 1.098 (2) | 0.031 (5)* | |
| C6 | 0.45761 (9) | 0.37626 (11) | 0.93073 (17) | 0.0246 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.43350 (10) | 0.39750 (11) | 0.65289 (17) | 0.0270 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.51480 (10) | 0.40045 (11) | 0.63199 (18) | 0.0269 (3) | |
| H8 | 0.5319 (10) | 0.4116 (14) | 0.529 (2) | 0.036 (5)* | |
| C9 | 0.56382 (9) | 0.39364 (11) | 0.75165 (17) | 0.0260 (3) | |
| C10 | 0.32666 (10) | 0.39452 (12) | 0.83043 (19) | 0.0285 (4) | |
| H10A | 0.3196 (10) | 0.4370 (13) | 0.927 (2) | 0.029 (4)* | |
| H10B | 0.3059 (10) | 0.4312 (14) | 0.736 (2) | 0.033 (5)* | |
| C11 | 0.28830 (10) | 0.29203 (12) | 0.8470 (2) | 0.0295 (4) | |
| H11A | 0.3155 (10) | 0.2489 (14) | 0.924 (2) | 0.027 (4)* | |
| H11B | 0.2890 (10) | 0.2551 (14) | 0.742 (2) | 0.035 (5)* | |
| C12 | 0.20666 (10) | 0.30564 (14) | 0.8979 (2) | 0.0351 (4) | |
| H12A | 0.2056 (11) | 0.3463 (15) | 1.001 (2) | 0.046 (6)* | |
| H12B | 0.1785 (11) | 0.3465 (16) | 0.818 (2) | 0.046 (6)* | |
| C13 | 0.16396 (11) | 0.20777 (15) | 0.9228 (2) | 0.0390 (4) | |
| H13A | 0.1920 (11) | 0.1658 (16) | 1.009 (2) | 0.049 (6)* | |
| H13B | 0.1668 (11) | 0.1653 (16) | 0.826 (2) | 0.045 (6)* | |
| C14 | 0.08281 (12) | 0.22432 (18) | 0.9724 (3) | 0.0485 (5) | |
| H14A | 0.0815 (13) | 0.2635 (19) | 1.075 (3) | 0.070 (7)* | |
| H14B | 0.0564 (13) | 0.2674 (19) | 0.896 (3) | 0.068 (7)* | |
| C15 | 0.03901 (15) | 0.1279 (2) | 0.9986 (4) | 0.0656 (7) | |
| H15A | 0.0625 (16) | 0.085 (2) | 1.085 (3) | 0.086 (9)* | |
| H15B | −0.0159 (16) | 0.1416 (19) | 1.031 (3) | 0.076 (8)* | |
| H15C | 0.0378 (15) | 0.089 (2) | 0.895 (3) | 0.086 (9)* | |
| C16 | 0.64634 (10) | 0.40936 (12) | 0.71935 (18) | 0.0280 (4) | |
| C17 | 0.74124 (10) | 0.40261 (14) | 0.5285 (2) | 0.0329 (4) | |
| H17A | 0.7783 (11) | 0.3728 (14) | 0.602 (2) | 0.036 (5)* | |
| H17B | 0.7456 (11) | 0.4763 (17) | 0.533 (2) | 0.044 (6)* | |
| C18 | 0.75172 (10) | 0.36435 (13) | 0.3648 (2) | 0.0325 (4) | |
| H18A | 0.7468 (11) | 0.2897 (16) | 0.365 (2) | 0.046 (6)* | |
| H18B | 0.7102 (11) | 0.3912 (14) | 0.299 (2) | 0.037 (5)* | |
| C19 | 0.82624 (11) | 0.39951 (15) | 0.2953 (2) | 0.0352 (4) | |
| H19A | 0.8683 (12) | 0.3685 (16) | 0.350 (2) | 0.050 (6)* | |
| H19B | 0.8308 (11) | 0.4748 (17) | 0.311 (2) | 0.049 (6)* | |
| C20 | 0.83340 (11) | 0.37729 (15) | 0.1223 (2) | 0.0385 (4) | |
| H20A | 0.8297 (12) | 0.3045 (18) | 0.106 (2) | 0.052 (6)* | |
| H20B | 0.7894 (12) | 0.4082 (16) | 0.068 (2) | 0.047 (6)* | |
| C21 | 0.90568 (12) | 0.41679 (18) | 0.0503 (2) | 0.0440 (5) | |
| H21A | 0.9504 (13) | 0.3819 (17) | 0.102 (3) | 0.059 (7)* | |
| H21B | 0.9100 (14) | 0.490 (2) | 0.075 (3) | 0.069 (7)* | |
| C22 | 0.90816 (15) | 0.4025 (2) | −0.1249 (3) | 0.0579 (6) | |
| H22A | 0.9029 (15) | 0.332 (2) | −0.154 (3) | 0.080 (9)* | |
| H22B | 0.8651 (16) | 0.439 (2) | −0.178 (3) | 0.077 (8)* | |
| H22C | 0.9566 (14) | 0.4306 (19) | −0.170 (3) | 0.069 (7)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0371 (7) | 0.0385 (7) | 0.0258 (6) | −0.0021 (5) | −0.0026 (5) | 0.0022 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0351 (7) | 0.0463 (7) | 0.0337 (6) | −0.0085 (6) | 0.0025 (5) | −0.0066 (5) |
| O3 | 0.0322 (7) | 0.0304 (6) | 0.0301 (6) | −0.0038 (5) | 0.0069 (5) | −0.0041 (5) |
| N1 | 0.0296 (8) | 0.0219 (6) | 0.0248 (7) | −0.0008 (5) | 0.0015 (5) | −0.0004 (5) |
| C1 | 0.0335 (9) | 0.0164 (7) | 0.0253 (8) | −0.0021 (6) | 0.0003 (6) | −0.0015 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0324 (10) | 0.0213 (7) | 0.0307 (8) | −0.0010 (7) | −0.0018 (7) | −0.0003 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0402 (10) | 0.0247 (8) | 0.0260 (8) | −0.0032 (7) | −0.0036 (7) | 0.0005 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0443 (11) | 0.0228 (8) | 0.0223 (8) | −0.0037 (7) | 0.0036 (7) | −0.0014 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0352 (10) | 0.0221 (7) | 0.0259 (8) | −0.0025 (7) | 0.0037 (7) | −0.0018 (6) |
| C6 | 0.0344 (9) | 0.0166 (7) | 0.0230 (7) | −0.0006 (6) | 0.0006 (6) | −0.0009 (5) |
| C7 | 0.0363 (10) | 0.0198 (7) | 0.0249 (8) | −0.0010 (6) | 0.0004 (7) | 0.0009 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0346 (9) | 0.0223 (8) | 0.0240 (8) | −0.0023 (6) | 0.0044 (7) | 0.0001 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0336 (9) | 0.0177 (7) | 0.0267 (8) | −0.0012 (6) | 0.0033 (7) | −0.0027 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0293 (9) | 0.0266 (8) | 0.0297 (8) | 0.0024 (7) | 0.0027 (7) | 0.0014 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0302 (9) | 0.0276 (8) | 0.0308 (8) | −0.0008 (7) | 0.0016 (7) | 0.0002 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0316 (10) | 0.0358 (9) | 0.0380 (10) | 0.0001 (7) | 0.0033 (8) | 0.0040 (8) |
| C13 | 0.0340 (10) | 0.0405 (10) | 0.0426 (10) | −0.0039 (8) | 0.0017 (8) | 0.0051 (8) |
| C14 | 0.0342 (11) | 0.0584 (13) | 0.0530 (13) | −0.0058 (10) | 0.0038 (10) | 0.0092 (10) |
| C15 | 0.0428 (14) | 0.0811 (18) | 0.0730 (18) | −0.0203 (13) | 0.0015 (13) | 0.0178 (15) |
| C16 | 0.0335 (9) | 0.0224 (7) | 0.0282 (8) | −0.0006 (7) | 0.0025 (7) | −0.0001 (6) |
| C17 | 0.0296 (10) | 0.0343 (10) | 0.0347 (9) | −0.0024 (7) | 0.0053 (7) | −0.0017 (7) |
| C18 | 0.0326 (10) | 0.0319 (9) | 0.0332 (9) | −0.0029 (7) | 0.0027 (8) | −0.0019 (7) |
| C19 | 0.0304 (10) | 0.0415 (10) | 0.0336 (9) | −0.0011 (8) | 0.0037 (8) | −0.0016 (7) |
| C20 | 0.0372 (11) | 0.0432 (11) | 0.0350 (10) | −0.0033 (8) | 0.0038 (8) | −0.0031 (8) |
| C21 | 0.0374 (12) | 0.0568 (13) | 0.0379 (10) | −0.0043 (10) | 0.0080 (9) | −0.0041 (9) |
| C22 | 0.0516 (15) | 0.0812 (18) | 0.0410 (12) | −0.0106 (13) | 0.0126 (11) | −0.0032 (12) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C7 | 1.2388 (19) | C12—H12A | 1.04 (2) |
| O2—C16 | 1.2096 (19) | C12—H12B | 1.01 (2) |
| O3—C16 | 1.3376 (19) | C13—C14 | 1.515 (3) |
| O3—C17 | 1.451 (2) | C13—H13A | 1.05 (2) |
| N1—C7 | 1.380 (2) | C13—H13B | 1.00 (2) |
| N1—C6 | 1.395 (2) | C14—C15 | 1.511 (3) |
| N1—C10 | 1.471 (2) | C14—H14A | 1.02 (3) |
| C1—C2 | 1.408 (2) | C14—H14B | 0.98 (3) |
| C1—C6 | 1.413 (2) | C15—H15A | 1.02 (3) |
| C1—C9 | 1.447 (2) | C15—H15B | 1.03 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.374 (2) | C15—H15C | 1.02 (3) |
| C2—H2 | 0.985 (19) | C17—C18 | 1.507 (2) |
| C3—C4 | 1.390 (2) | C17—H17A | 0.992 (19) |
| C3—H3 | 0.998 (19) | C17—H17B | 0.98 (2) |
| C4—C5 | 1.378 (2) | C18—C19 | 1.522 (2) |
| C4—H4 | 0.956 (18) | C18—H18A | 0.99 (2) |
| C5—C6 | 1.404 (2) | C18—H18B | 0.99 (2) |
| C5—H5 | 0.988 (18) | C19—C20 | 1.521 (2) |
| C7—C8 | 1.451 (2) | C19—H19A | 0.97 (2) |
| C8—C9 | 1.346 (2) | C19—H19B | 1.01 (2) |
| C8—H8 | 0.945 (19) | C20—C21 | 1.515 (3) |
| C9—C16 | 1.502 (2) | C20—H20A | 0.98 (2) |
| C10—C11 | 1.525 (2) | C20—H20B | 0.99 (2) |
| C10—H10A | 1.011 (18) | C21—C22 | 1.518 (3) |
| C10—H10B | 1.015 (18) | C21—H21A | 1.02 (2) |
| C11—C12 | 1.521 (2) | C21—H21B | 1.00 (3) |
| C11—H11A | 0.997 (17) | C22—H22A | 0.97 (3) |
| C11—H11B | 1.022 (18) | C22—H22B | 1.01 (3) |
| C12—C13 | 1.516 (3) | C22—H22C | 1.01 (3) |
| C16—O3—C17 | 115.00 (13) | C12—C13—H13B | 109.7 (12) |
| C7—N1—C6 | 123.04 (14) | H13A—C13—H13B | 105.0 (16) |
| C7—N1—C10 | 117.09 (13) | C15—C14—C13 | 114.0 (2) |
| C6—N1—C10 | 119.84 (13) | C15—C14—H14A | 106.8 (14) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 118.59 (14) | C13—C14—H14A | 109.8 (14) |
| C2—C1—C9 | 124.05 (15) | C15—C14—H14B | 110.3 (14) |
| C6—C1—C9 | 117.37 (14) | C13—C14—H14B | 110.2 (14) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 121.07 (16) | H14A—C14—H14B | 105 (2) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.7 (11) | C14—C15—H15A | 111.5 (16) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.3 (11) | C14—C15—H15B | 112.2 (15) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.01 (16) | H15A—C15—H15B | 106 (2) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 122.4 (11) | C14—C15—H15C | 107.7 (16) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 117.5 (11) | H15A—C15—H15C | 111 (2) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 120.45 (16) | H15B—C15—H15C | 108 (2) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 118.9 (11) | O2—C16—O3 | 123.42 (15) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.6 (11) | O2—C16—C9 | 124.59 (15) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.45 (16) | O3—C16—C9 | 111.96 (13) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.7 (10) | O3—C17—C18 | 108.01 (14) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.9 (10) | O3—C17—H17A | 108.2 (11) |
| N1—C6—C5 | 120.25 (15) | C18—C17—H17A | 112.2 (11) |
| N1—C6—C1 | 120.34 (14) | O3—C17—H17B | 108.5 (12) |
| C5—C6—C1 | 119.41 (14) | C18—C17—H17B | 111.1 (11) |
| O1—C7—N1 | 121.22 (15) | H17A—C17—H17B | 108.8 (16) |
| O1—C7—C8 | 122.79 (15) | C17—C18—C19 | 111.86 (15) |
| N1—C7—C8 | 115.96 (14) | C17—C18—H18A | 108.8 (11) |
| C9—C8—C7 | 122.71 (15) | C19—C18—H18A | 112.4 (12) |
| C9—C8—H8 | 121.0 (11) | C17—C18—H18B | 108.6 (11) |
| C7—C8—H8 | 116.2 (11) | C19—C18—H18B | 107.9 (11) |
| C8—C9—C1 | 120.44 (15) | H18A—C18—H18B | 107.1 (15) |
| C8—C9—C16 | 118.29 (14) | C20—C19—C18 | 113.51 (15) |
| C1—C9—C16 | 121.13 (14) | C20—C19—H19A | 109.0 (12) |
| N1—C10—C11 | 113.70 (13) | C18—C19—H19A | 110.2 (12) |
| N1—C10—H10A | 106.4 (10) | C20—C19—H19B | 108.3 (11) |
| C11—C10—H10A | 111.3 (10) | C18—C19—H19B | 108.6 (12) |
| N1—C10—H10B | 105.1 (10) | H19A—C19—H19B | 107.0 (17) |
| C11—C10—H10B | 110.0 (10) | C21—C20—C19 | 113.87 (16) |
| H10A—C10—H10B | 110.2 (14) | C21—C20—H20A | 109.8 (13) |
| C12—C11—C10 | 110.15 (14) | C19—C20—H20A | 109.0 (12) |
| C12—C11—H11A | 109.5 (10) | C21—C20—H20B | 109.1 (12) |
| C10—C11—H11A | 111.0 (10) | C19—C20—H20B | 108.0 (12) |
| C12—C11—H11B | 108.9 (10) | H20A—C20—H20B | 106.7 (17) |
| C10—C11—H11B | 109.7 (11) | C20—C21—C22 | 112.87 (18) |
| H11A—C11—H11B | 107.6 (14) | C20—C21—H21A | 108.7 (13) |
| C13—C12—C11 | 114.40 (15) | C22—C21—H21A | 110.7 (13) |
| C13—C12—H12A | 108.3 (11) | C20—C21—H21B | 108.2 (14) |
| C11—C12—H12A | 109.1 (11) | C22—C21—H21B | 109.4 (14) |
| C13—C12—H12B | 108.1 (12) | H21A—C21—H21B | 106.7 (19) |
| C11—C12—H12B | 109.7 (12) | C21—C22—H22A | 112.0 (16) |
| H12A—C12—H12B | 107.0 (16) | C21—C22—H22B | 111.1 (15) |
| C14—C13—C12 | 112.89 (17) | H22A—C22—H22B | 106 (2) |
| C14—C13—H13A | 109.1 (11) | C21—C22—H22C | 111.1 (14) |
| C12—C13—H13A | 108.5 (11) | H22A—C22—H22C | 110 (2) |
| C14—C13—H13B | 111.3 (12) | H22B—C22—H22C | 107 (2) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −1.6 (2) | C7—C8—C9—C16 | −173.12 (13) |
| C9—C1—C2—C3 | 178.89 (14) | C2—C1—C9—C8 | 176.52 (15) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.5 (2) | C6—C1—C9—C8 | −3.0 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.9 (2) | C2—C1—C9—C16 | −7.8 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −1.2 (2) | C6—C1—C9—C16 | 172.65 (13) |
| C7—N1—C6—C5 | −177.49 (14) | C7—N1—C10—C11 | 99.07 (16) |
| C10—N1—C6—C5 | 4.7 (2) | C6—N1—C10—C11 | −82.96 (17) |
| C7—N1—C6—C1 | 3.2 (2) | N1—C10—C11—C12 | 171.38 (14) |
| C10—N1—C6—C1 | −174.68 (13) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −178.17 (15) |
| C4—C5—C6—N1 | −179.30 (14) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −179.66 (16) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.1 (2) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | −179.8 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6—N1 | −179.37 (13) | C17—O3—C16—O2 | −8.3 (2) |
| C9—C1—C6—N1 | 0.2 (2) | C17—O3—C16—C9 | 169.68 (13) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 1.3 (2) | C8—C9—C16—O2 | 143.61 (17) |
| C9—C1—C6—C5 | −179.14 (13) | C1—C9—C16—O2 | −32.2 (2) |
| C6—N1—C7—O1 | 178.45 (14) | C8—C9—C16—O3 | −34.38 (19) |
| C10—N1—C7—O1 | −3.6 (2) | C1—C9—C16—O3 | 149.83 (14) |
| C6—N1—C7—C8 | −3.5 (2) | C16—O3—C17—C18 | −175.71 (14) |
| C10—N1—C7—C8 | 174.39 (13) | O3—C17—C18—C19 | 174.17 (14) |
| O1—C7—C8—C9 | 178.56 (15) | C17—C18—C19—C20 | −170.54 (17) |
| N1—C7—C8—C9 | 0.6 (2) | C18—C19—C20—C21 | 177.03 (17) |
| C7—C8—C9—C1 | 2.7 (2) | C19—C20—C21—C22 | −174.6 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C4—H4···O1i | 0.960 (17) | 2.475 (17) | 3.3670 (19) | 154.7 (15) |
Symmetry code: (i) x, y, z+1.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by National Science Foundation grant 1228232. Tulane University grant .
References
- Bolognesi, M. L., Cavalli, A., Valgimigli, L., Bartolini, M., Rosini, M., Andrisano, V., Recanatini, M. & Melchiorre, C. (2007). J. Med. Chem. 50, 6446–6449. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bouzian, Y., Faizi, M. S. H., Mague, J. T., Otmani, B. E., Dege, N., Karrouchi, K. & Essassi, E. M. (2019a). Acta Cryst. E75, 980–983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bouzian, Y., Karrouchi, K., Anouar, E. H., Bouhfid, R., Arshad, S. & Essassi, E. M. (2019b). Acta Cryst. E75, 912–916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Brandenburg, K. & Putz, H. (2012). DIAMOND, Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Bruker (2016). APEX3 and SAINT. Bruker AXS, Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Cannalire, R., Barreca, M. L., Manfroni, G. & Cecchetti, V. (2016). J. Med. Chem. 59, 16–41. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Chu, X. M., Wang, C., Liu, W., Liang, L. L., Gong, K. K., Zhao, C. Y. & Sun, K. L. (2019). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 161, 101–117. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Filali Baba, Y., Kandri Rodi, Y., Hayani, S., Jasinski, J. P., Kaur, M. & Essassi, E. M. (2017a). IUCrData, 2, x170917.
- Filali Baba, Y., Kandri Rodi, Y., Jasinski, J. P., Kaur, M., Ouzidan, Y. & Essassi, E. M. (2017b). IUCrData, 2, x171072.
- Filali Baba, Y., Mague, J. T., Kandri Rodi, Y., Ouzidan, Y., Essassi, E. M. & Zouihri, H. (2016). IUCrData, 1, x160997.
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y. Q., Gao, C., Zhang, S., Xu, L., Xu, Z., Feng, L. S., Wu, X. & Zhao, F. (2017). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 139, 22–47. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Krause, L., Herbst-Irmer, R., Sheldrick, G. M. & Stalke, D. (2015). J. Appl. Cryst. 48, 3–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Palit, P., Paira, P., Hazra, A., Banerjee, S., Gupta, A. D., Dastidar, S. G. & Mondal, N. B. (2009). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 44, 845–853. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Panda, S. S., Liaqat, S., Girgis, A. S., Samir, A., Hall, C. D. & Katritzky, A. R. (2015). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 25, 3816–3821. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Paterna, R., André, V., Duarte, M. T., Veiros, L. F., Candeias, N. R. & Gois, P. M. P. (2013). Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 6280–6290.
- Pinz, M., Reis, A. S., Duarte, V., da Rocha, M. J., Goldani, B. S., Alves, D., Savegnago, L., Luchese, C. & Wilhelm, E. A. (2016). Eur. J. Pharmacol. 780, 122–128. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sekgota, K. C., Majumder, S., Isaacs, M., Mnkandhla, D., Hoppe, H. C., Khanye, S. D., Kriel, F. H., Coates, J. & Kaye, P. T. (2017). Bioorg. Chem. 75, 310–316. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spackman, M. A. & Jayatilaka, D. (2009). CrystEngComm, 11, 19–32.
- Tang, Q. D., Duan, Y. L., Xiong, H. H., Chen, T., Xiao, Z., Wang, L. X., Xiao, Y. Y., Huang, S. M., Xiong, Y., Zhu, W., Gong, P. & Zheng, P. (2018). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 158, 201–213. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Turner, M. J., MacKinnon, J. J., Wolff, S. K., Grimwood, D. J., Spackman, P. R., Jayatilaka, D. & Spackman, M. A. (2017). CrystalExplorer17.5. University of Western Australia. http://hirshfeldsurface.net.
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
- Xu, Z., Gao, C., Ren, Q. C., Song, X. F., Feng, L. S. & Lv, Z. S. (2017). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 139, 429–440. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989020004521/wm5550sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989020004521/wm5550Isup2.hkl
CCDC reference: 1994187
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report