The title compounds, 5-(2H-1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-N-cyclohexylpenta-2,4-dienamide, (I), and 5-(2H-1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-1-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)penta-2,4-dien-1-one (II), are derivatives of piperine, which is known as a pungent component of pepper. Their geometrical parameters are similar to those of the three polymorphs of piperine, which indicate conjugation of electrons over the length of the molecules. The extended structure of (I) features N—H⋯O amide hydrogen bonds, which generate C(4) [010] chains. The crystal of (II) features aromatic π–π stacking, as for two of three known piperine polymorphs.
Keywords: crystal structure, organic crystal, piperine, hydrogen bond
Abstract
The title compounds, 5-(2H-1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-N-cyclohexylpenta-2,4-dienamide, C18H21NO3 (I), and 5-(2H-1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-1-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)penta-2,4-dien-1-one C16H17NO3 (II), are derivatives of piperine, which is known as a pungent component of pepper. Their geometrical parameters are similar to those of the three polymorphs of piperine, which indicate conjugation of electrons over the length of the molecules. The extended structure of (I) features N—H⋯O amide hydrogen bonds, which generate C(4) [010] chains. The crystal of (II) features aromatic π–π stacking, as for two of three known piperine polymorphs.
Chemical context
Piperine [(2E,4E)-1-[5-(1,3-benzodioxol-5yl)-1-oxo-2,4-pentadienyl]piperidine, C17H19NO3, is the major pungent ingredient of Piperaceae pepper (Piper nigrum). Piperine is an amide having a methylenedioxyphenyl grouping as a characteristic of its chemical structure (Fig. 1 ▸). Interestingly, when the amide group is in a near planar conformation, the conjugated state of the pentadiene chain of piperine has the property that electrons are easily donated and the stretching vibration of the amide carbonyl group is affected (Pfund et al., 2015 ▸). As part of our studies in this area, we have already reported a complex using the poorly water-soluble piperine (log P = 2.25) and the cyclic polysaccharide cyclodextrin (Szejtli, 1998 ▸; Ezawa et al., 2016 ▸). In addition, piperine has been evaluated for its inclusion mechanism and dissolution properties using various cyclodextrins (Ezawa et al., 2018 ▸, 2019 ▸). The synthesis of piperine derivatives was necessary to understand the inclusion mechanism of piperine and cyclodextrin and the detailed molecular behaviour of piperine.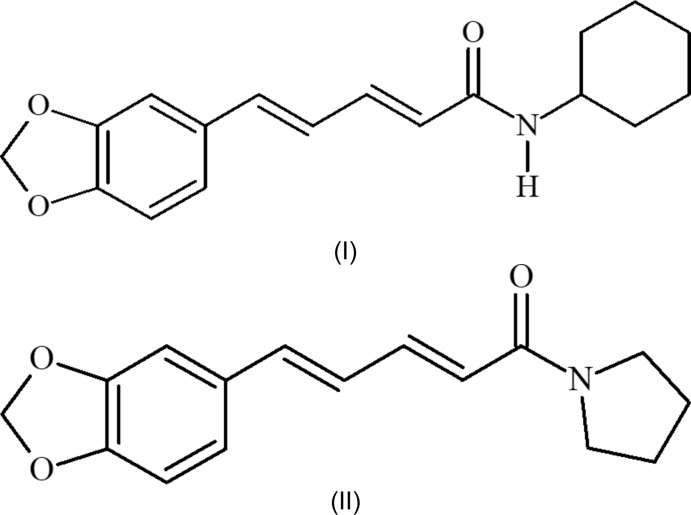
Figure 1.
The chemical structure of piperine.
Therefore, the aim of this study was to synthesize the title compounds (2E,4E)-5-(2H-1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-N-cyclohexylpenta-2,4-dienamide, C18H21NO3, (I), and (2E,4E)-5-(2H-1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-1-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)penta-2,4-dien-1-one, C16H17NO3, (II), from piperine and to determine their X-ray crystal structures. The log P of (I) is 3.36 and that of (II) is 2.36. Assessing the structural properties of the title compounds (crystal structure, geometry, intermolecular interactions, etc.) will help to evaluate the inclusion behaviour of piperine with cyclodextrin.
Structural commentary
Compound (I) (Fig. 2 ▸) crystallizes in the monoclinic space group P21/c with four molecules per unit cell. The C1–C6 cyclohexyl ring adopts a chair conformation with the exocyclic C5—N1 bond in an equatorial orientation. The C7–C12/O2/O3 fused-ring system is almost planar (r.m.s. deviation = 0.020 Å) and subtends a dihedral angle of 21.57 (4)° with the cyclohexyl ring. The bond distances and angles (amide, pentadiene and methylenedioxyphenyl moieties) of (I) are not significantly different from the equivalent data for the three polymorphs of piperine (Pfund et al., 2015 ▸) (Table 1 ▸).
Figure 2.
Displacement ellipsoid drawing at a 50% probability level of the asymmetric unit of (I).
Table 1. Key geometrical parameters (Å) for the title compounds and piperine polymorphs.
| (I) | (II) | PIPINE10 | PIPINE12 | PIPINE13 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amide | C18—N1 (1.344) | C1—N1 (1.350) | C1—N1 (1.331) | C1—N1 (1.363) | C1—N1 (1.353) |
| C18—O1 (1.242) | C1—O1 (1.243) | C1—O1 (1.218) | C1—O1 (1.235) | C1—O1 (1.482) | |
| C14—C15 (1.346) | C4—C5 (1.345) | C4—C5 (1.312) | C4—C5 (1.330) | C4—C5 (1.347) | |
| Pentadiene | C15—C16 (1.444) | C3—C4 (1.441) | C3—C4 (1.437) | C3—C4 (1.440) | C3—C4 (1.442) |
| C16—C17 (1.342) | C2—C3 (1.341) | C2—C3 (1.311) | C2—C3 (1.332) | C2—C3 (1.341) | |
| C17—C18 (1.479) | C1—C2 (1.480) | C1—C2 (1.473) | C1—C2 (1.477) | C1—C2 (1.482) | |
| C8—C9 (1.390) | C6—C7 (1.397) | C6—C7 (1.387) | C6—C7 (1.399) | C6—C7 (1.403) | |
| C8—C13 (1.371) | C6—C12 (1.412) | C6—C12 (1.396) | C6—C12 (1.414) | C6—C12 (1.412) | |
| C9—C10 (1.374) | C7—C8 (1.403) | C7—C8 (1.393) | C7—C8 (1.395) | C7—C8 (1.393) | |
| Methylenedioxyphenyl | C10—C11 (1.402) | C8—C9 (1.369) | C8—C9 (1.343) | C8—C9 (1.360) | C8—C9 (1.371) |
| C11—C12 (1.399) | C9—C11 (1.385) | C9—C11 (1.357) | C9—C11 (1.377) | C9—C11 (1.381) | |
| C12—C13 (1.412) | C11—C12 (1.364) | C11—C12 (1.364) | C11—C12 (1.370) | C11—C12 (1.367) | |
| C8—O2 (1.371) | C9—O2 (1.378) | C9—O2 (1.373) | c9—O2 (1.383) | C9—O2 (1.378) | |
| C9—O3 (1.370) | C11—O3 (1.376) | C11—O3 (1.362) | C11—O3 (1.383) | C11—O3 (1.383) | |
| π-stacking close contacts | C9⋯C9 (3.268) | C8⋯C8 (3.110) | C9⋯C12 (3.327) | ||
| C9⋯C12 (3.322) | C8⋯C8 (3.303) | ||||
| C11⋯C12 (3.287) |
Compound (II) (Fig. 3 ▸), also known as piperilyn, crystallizes in the orthorhombic space group Pbca with eight molecules per unit cell. The C13–C16/N1 ring is well described as being twisted with C14 and C15 deviating from C13/N1/C16 by 0.205 (2) and −0.382 (2) Å, respectively. The C9/O2/C10/O3/C11 ring has a clear tendency towards an envelope conformation [deviation of C10 from the other four atoms = −0.216 (2) Å]. The dihedral angle between the C13–C16/N1 and C6–C12/O2/O3 rings (all atoms) is 12.29 (10)°. As with (I), the key bond-distance data for (II) are comparable to those of piperine (Table 1 ▸).
Figure 3.
Displacement ellipsoid drawing at a 50% probability level of the asymmetric unit of (II).
Thus, we may conclude that the title compounds show intramolecular resonance from the amide group to the ether O atoms of the methylenedioxyphenyl moiety, similar to piperine.
Supramolecular features
Piperine crystallizes in three polymorphs: form I [CCDC (Groom et al., 2016) refcode: PIPINE10] and form II (PIPINE12) in space group P21/n and form III (PIPINE13) in space group C2/c (Table 1 ▸) (Pfund et al., 2015 ▸). The packing for forms II and III features aromatic π–π stacking interactions, while that of form I does not.
The crystal structure of (I) does not feature π–π stacking interactions, which is similar to piperine form I. Compound (I) possesses an N—H grouping, which forms a classical N1—H⋯O1 hydrogen bond (Table 2 ▸) between the amide-bond sites, generating [010] C(4) chains (Fig. 4 ▸) with adjacent molecules related by simple translation. The unit-cell packing for (I) is illustrated in Fig. 5 ▸.
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (I) .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1⋯O1i | 0.874 (16) | 2.086 (16) | 2.9547 (12) | 172.8 (14) |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Figure 4.
A view along the c-axis direction of the crystal packing of (I). The N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds are drawn as dashed lines.
Figure 5.
The unit-cell packing for (I) viewed down [100] with hydrogen bonds drawn as dashed lines.
The structure of (II) does feature π–π stacking with the closest intermolecular contacts being C9⋯C9 = 3.268 (3), C9⋯C12 = 3.322 (3) and C11⋯C12 = 3.287 (3) Å (Fig. 6 ▸). The overall packing for (II) can be described as undulating sheets propagating in the (010) plane (Fig. 7 ▸).
Figure 6.
Fragment of the crystal of (II) showing close C⋯C contacts due to π–π stacking.
Figure 7.
The unit-cell packing for (II) viewed down [100].
Synthesis and crystallization
Piperine was purchased from Fujifilm Wako Pure Chemical Co., Ltd. The synthesis of piperine derivatives was performed using a previously reported procedure (Takao et al., 2015 ▸). After dissolving piperine in ethanol, hydrolysis was performed by stirring for 20 h in the presence of KOH. After evaporating the solvent under vacuum, the resulting reaction mixture was suspended in water and acidified with 4 M HCl to pH < 1. The resultant pale-brown precipitate was collected by filtration, washed with cold water and recrystallized from methanol solution to give piperic acid. The piperic acid (1.0 mmol) was dissolved in CH2Cl2 (5 ml) and oxalyl chloride (10 mmol) was added and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 3 h. The solvent and excess oxalyl chloride were then evaporated under reduced pressure.
To prepare (I), the crude acid chloride generated was dissolved in CH2Cl2 (2 ml) and cyclohexylamine (1.2 mmol) and Et3N (8 mmol) were added, and the mixture was stirred at 273 K for 5 h. Ice-cold water was added to the mixture, followed by extraction with chloroform (5 ml). The organic layer was dried over Na2SO4 and the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by silica-gel column chromatography (eluent hexane:etyl acetate 1:1 v/v) to give (I) in the form of a yellow powder. Light-yellow needles of (I) were recrystallized from ethyl acetate solution.
Compound (II) was prepared by the same procedure with pyrrolidine (1.2 mmol) replacing the cyclohexylamine to give (II) in the form of a white powder. Colourless needles of (II) were recrystallized from ethyl acetate solution.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3 ▸. Hydrogen atoms for carbon atom were included in their calculated positions and refined as riding atoms with U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C). The hydrogen atom attached to N1 in (I) was located in a difference-Fourier map and its position freely refined with U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(N).
Table 3. Experimental details.
| (I) | (II) | |
|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | ||
| Chemical formula | C18H21NO3 | C16H17NO3 |
| M r | 299.36 | 271.30 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c | Orthorhombic, P b c a |
| Temperature (K) | 90 | 90 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 11.4982 (7), 5.0086 (3), 26.7240 (16) | 11.8747 (10), 7.2485 (6), 30.392 (2) |
| α, β, γ (°) | 90, 97.683 (2), 90 | 90, 90, 90 |
| V (Å3) | 1525.22 (16) | 2616.0 (4) |
| Z | 4 | 8 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.09 | 0.10 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.58 × 0.07 × 0.07 | 0.28 × 0.06 × 0.06 |
| Data collection | ||
| Diffractometer | Bruker D8 goniometer | Bruker D8 goniometer |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2018 ▸) | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2018 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.580, 0.747 | 0.666, 0.746 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 27741, 4862, 4204 | 41504, 3506, 2193 |
| R int | 0.066 | 0.128 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.725 | 0.685 |
| Refinement | ||
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.049, 0.121, 1.07 | 0.050, 0.143, 1.05 |
| No. of reflections | 4862 | 3506 |
| No. of parameters | 202 | 182 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.42, −0.26 | 0.28, −0.26 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, II, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989020004648/hb7897sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989020004648/hb7897Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989020004648/hb7897IIsup3.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989020004648/hb7897Isup4.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989020004648/hb7897IIsup5.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
supplementary crystallographic information
5-(2H-1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)-N-cyclohexylpenta-2,4-dienamide (I) . Crystal data
| C18H21NO3 | F(000) = 640 |
| Mr = 299.36 | Dx = 1.304 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 11.4982 (7) Å | Cell parameters from 9948 reflections |
| b = 5.0086 (3) Å | θ = 2.5–33.5° |
| c = 26.7240 (16) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| β = 97.683 (2)° | T = 90 K |
| V = 1525.22 (16) Å3 | Needle, light-yellow |
| Z = 4 | 0.58 × 0.07 × 0.07 mm |
5-(2H-1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)-N-cyclohexylpenta-2,4-dienamide (I) . Data collection
| Bruker D8 goniometer diffractometer | 4862 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: microfocus X-ray tube | 4204 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Multilayered conforacal mirror monochromator | Rint = 0.066 |
| Detector resolution: 7.391 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 31.0°, θmin = 2.2° |
| ω scans | h = −16→16 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2018) | k = −7→7 |
| Tmin = 0.580, Tmax = 0.747 | l = −38→38 |
| 27741 measured reflections |
5-(2H-1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)-N-cyclohexylpenta-2,4-dienamide (I) . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: dual |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.049 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.121 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0455P)2 + 0.7464P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.07 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 4862 reflections | Δρmax = 0.42 e Å−3 |
| 202 parameters | Δρmin = −0.26 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints |
5-(2H-1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)-N-cyclohexylpenta-2,4-dienamide (I) . Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
5-(2H-1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)-N-cyclohexylpenta-2,4-dienamide (I) . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.96864 (7) | 0.23821 (16) | 0.65434 (3) | 0.01577 (17) | |
| O2 | 0.26072 (7) | 0.95788 (18) | 0.47532 (3) | 0.01982 (18) | |
| O3 | 0.09239 (7) | 0.7586 (2) | 0.49784 (4) | 0.0246 (2) | |
| N1 | 1.02983 (8) | 0.66732 (19) | 0.66764 (4) | 0.01464 (18) | |
| H1 | 1.0072 (13) | 0.834 (3) | 0.6656 (6) | 0.018* | |
| C1 | 1.35763 (10) | 0.7868 (2) | 0.69502 (4) | 0.0179 (2) | |
| H1A | 1.387593 | 0.633931 | 0.677037 | 0.021* | |
| H1AB | 1.404140 | 0.946479 | 0.688562 | 0.021* | |
| C2 | 1.37316 (10) | 0.7289 (2) | 0.75164 (4) | 0.0177 (2) | |
| H2A | 1.456652 | 0.689410 | 0.763536 | 0.021* | |
| H2AB | 1.350298 | 0.887869 | 0.770054 | 0.021* | |
| C3 | 1.29754 (11) | 0.4914 (2) | 0.76259 (4) | 0.0184 (2) | |
| H3A | 1.306633 | 0.458942 | 0.799445 | 0.022* | |
| H3AB | 1.324548 | 0.329830 | 0.746168 | 0.022* | |
| C4 | 1.16802 (10) | 0.5412 (2) | 0.74321 (4) | 0.0174 (2) | |
| H4A | 1.121475 | 0.381401 | 0.749567 | 0.021* | |
| H4AB | 1.139004 | 0.693282 | 0.761708 | 0.021* | |
| C5 | 1.15165 (9) | 0.6024 (2) | 0.68667 (4) | 0.01204 (19) | |
| H5 | 1.174757 | 0.440743 | 0.668389 | 0.014* | |
| C6 | 1.22876 (10) | 0.8346 (2) | 0.67461 (4) | 0.0156 (2) | |
| H6A | 1.201602 | 1.000303 | 0.689604 | 0.019* | |
| H6AB | 1.220984 | 0.859459 | 0.637563 | 0.019* | |
| C7 | 0.13448 (10) | 0.9561 (2) | 0.46564 (4) | 0.0178 (2) | |
| H00F | 0.103160 | 1.134167 | 0.472821 | 0.021* | |
| H00G | 0.108313 | 0.912274 | 0.429779 | 0.021* | |
| C8 | 0.29070 (10) | 0.7663 (2) | 0.51139 (4) | 0.0146 (2) | |
| C9 | 0.19016 (9) | 0.6451 (2) | 0.52444 (4) | 0.0157 (2) | |
| C10 | 0.19552 (10) | 0.4395 (2) | 0.55871 (4) | 0.0172 (2) | |
| H10 | 0.126694 | 0.356487 | 0.567425 | 0.021* | |
| C11 | 0.30804 (10) | 0.3586 (2) | 0.58014 (4) | 0.0154 (2) | |
| H11 | 0.315407 | 0.213891 | 0.603318 | 0.018* | |
| C12 | 0.40980 (9) | 0.4841 (2) | 0.56850 (4) | 0.0135 (2) | |
| C13 | 0.40115 (9) | 0.6936 (2) | 0.53284 (4) | 0.0142 (2) | |
| H13 | 0.469038 | 0.780458 | 0.524074 | 0.017* | |
| C14 | 0.52399 (9) | 0.3949 (2) | 0.59388 (4) | 0.0151 (2) | |
| H14 | 0.528504 | 0.219194 | 0.607404 | 0.018* | |
| C15 | 0.62312 (9) | 0.5413 (2) | 0.59963 (4) | 0.0153 (2) | |
| H15 | 0.618873 | 0.720765 | 0.588024 | 0.018* | |
| C16 | 0.73553 (9) | 0.4407 (2) | 0.62246 (4) | 0.0144 (2) | |
| H16 | 0.741526 | 0.256496 | 0.630909 | 0.017* | |
| C17 | 0.83199 (9) | 0.5927 (2) | 0.63240 (4) | 0.0147 (2) | |
| H17 | 0.825437 | 0.779183 | 0.626212 | 0.018* | |
| C18 | 0.94810 (9) | 0.4819 (2) | 0.65259 (4) | 0.01252 (19) |
5-(2H-1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)-N-cyclohexylpenta-2,4-dienamide (I) . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0151 (4) | 0.0087 (3) | 0.0230 (4) | 0.0010 (3) | 0.0008 (3) | 0.0012 (3) |
| O2 | 0.0130 (4) | 0.0226 (4) | 0.0237 (4) | 0.0022 (3) | 0.0019 (3) | 0.0074 (3) |
| O3 | 0.0116 (4) | 0.0333 (5) | 0.0284 (5) | 0.0015 (4) | 0.0014 (3) | 0.0109 (4) |
| N1 | 0.0124 (4) | 0.0082 (4) | 0.0228 (5) | 0.0014 (3) | 0.0006 (3) | 0.0001 (3) |
| C1 | 0.0146 (5) | 0.0186 (5) | 0.0199 (5) | −0.0044 (4) | 0.0007 (4) | 0.0004 (4) |
| C2 | 0.0181 (5) | 0.0134 (5) | 0.0201 (5) | 0.0006 (4) | −0.0034 (4) | −0.0003 (4) |
| C3 | 0.0222 (5) | 0.0137 (5) | 0.0181 (5) | 0.0006 (4) | −0.0016 (4) | 0.0024 (4) |
| C4 | 0.0191 (5) | 0.0176 (5) | 0.0160 (5) | −0.0002 (4) | 0.0037 (4) | 0.0016 (4) |
| C5 | 0.0112 (4) | 0.0089 (4) | 0.0158 (5) | 0.0010 (3) | 0.0012 (3) | 0.0004 (3) |
| C6 | 0.0160 (5) | 0.0119 (5) | 0.0181 (5) | −0.0033 (4) | −0.0007 (4) | 0.0031 (4) |
| C7 | 0.0140 (5) | 0.0196 (5) | 0.0195 (5) | 0.0029 (4) | 0.0010 (4) | 0.0003 (4) |
| C8 | 0.0149 (5) | 0.0148 (5) | 0.0144 (5) | 0.0007 (4) | 0.0035 (4) | −0.0001 (4) |
| C9 | 0.0106 (4) | 0.0198 (5) | 0.0167 (5) | 0.0007 (4) | 0.0020 (4) | −0.0022 (4) |
| C10 | 0.0128 (5) | 0.0208 (5) | 0.0183 (5) | −0.0038 (4) | 0.0035 (4) | −0.0010 (4) |
| C11 | 0.0148 (5) | 0.0160 (5) | 0.0156 (5) | −0.0028 (4) | 0.0031 (4) | 0.0003 (4) |
| C12 | 0.0121 (4) | 0.0134 (5) | 0.0153 (5) | −0.0005 (4) | 0.0030 (3) | −0.0015 (4) |
| C13 | 0.0117 (4) | 0.0145 (5) | 0.0169 (5) | −0.0008 (4) | 0.0037 (4) | 0.0006 (4) |
| C14 | 0.0137 (5) | 0.0148 (5) | 0.0169 (5) | 0.0016 (4) | 0.0030 (4) | 0.0016 (4) |
| C15 | 0.0138 (5) | 0.0138 (5) | 0.0183 (5) | 0.0025 (4) | 0.0027 (4) | 0.0006 (4) |
| C16 | 0.0144 (5) | 0.0129 (5) | 0.0162 (5) | 0.0023 (4) | 0.0029 (4) | 0.0011 (4) |
| C17 | 0.0138 (5) | 0.0110 (4) | 0.0194 (5) | 0.0030 (4) | 0.0023 (4) | 0.0020 (4) |
| C18 | 0.0127 (4) | 0.0108 (4) | 0.0143 (5) | 0.0006 (4) | 0.0027 (3) | 0.0010 (3) |
5-(2H-1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)-N-cyclohexylpenta-2,4-dienamide (I) . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C18 | 1.2429 (13) | C6—H6A | 0.9900 |
| O2—C8 | 1.3710 (14) | C6—H6AB | 0.9900 |
| O2—C7 | 1.4400 (14) | C7—H00F | 0.9900 |
| O3—C9 | 1.3705 (14) | C7—H00G | 0.9900 |
| O3—C7 | 1.4372 (15) | C8—C13 | 1.3710 (15) |
| N1—C18 | 1.3440 (14) | C8—C9 | 1.3909 (15) |
| N1—C5 | 1.4614 (13) | C9—C10 | 1.3741 (16) |
| N1—H1 | 0.874 (16) | C10—C11 | 1.4028 (15) |
| C1—C2 | 1.5275 (16) | C10—H10 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C6 | 1.5279 (16) | C11—C12 | 1.3991 (15) |
| C1—H1A | 0.9900 | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| C1—H1AB | 0.9900 | C12—C13 | 1.4120 (15) |
| C2—C3 | 1.5246 (17) | C12—C14 | 1.4648 (15) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9900 | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| C2—H2AB | 0.9900 | C14—C15 | 1.3468 (15) |
| C3—C4 | 1.5305 (16) | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| C3—H3A | 0.9900 | C15—C16 | 1.4442 (15) |
| C3—H3AB | 0.9900 | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| C4—C5 | 1.5284 (15) | C16—C17 | 1.3423 (15) |
| C4—H4A | 0.9900 | C16—H16 | 0.9500 |
| C4—H4AB | 0.9900 | C17—C18 | 1.4793 (15) |
| C5—C6 | 1.5228 (15) | C17—H17 | 0.9500 |
| C5—H5 | 1.0000 | ||
| C8—O2—C7 | 105.94 (9) | H6A—C6—H6AB | 107.9 |
| C9—O3—C7 | 106.11 (9) | O3—C7—O2 | 107.98 (9) |
| C18—N1—C5 | 123.36 (9) | O3—C7—H00F | 110.1 |
| C18—N1—H1 | 116.8 (10) | O2—C7—H00F | 110.1 |
| C5—N1—H1 | 119.9 (10) | O3—C7—H00G | 110.1 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 111.27 (9) | O2—C7—H00G | 110.1 |
| C2—C1—H1A | 109.4 | H00F—C7—H00G | 108.4 |
| C6—C1—H1A | 109.4 | C13—C8—O2 | 127.72 (10) |
| C2—C1—H1AB | 109.4 | C13—C8—C9 | 122.25 (10) |
| C6—C1—H1AB | 109.4 | O2—C8—C9 | 110.03 (10) |
| H1A—C1—H1AB | 108.0 | O3—C9—C10 | 128.10 (10) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 110.13 (9) | O3—C9—C8 | 109.91 (10) |
| C3—C2—H2A | 109.6 | C10—C9—C8 | 121.98 (10) |
| C1—C2—H2A | 109.6 | C9—C10—C11 | 116.43 (10) |
| C3—C2—H2AB | 109.6 | C9—C10—H10 | 121.8 |
| C1—C2—H2AB | 109.6 | C11—C10—H10 | 121.8 |
| H2A—C2—H2AB | 108.1 | C12—C11—C10 | 122.19 (11) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 111.23 (9) | C12—C11—H11 | 118.9 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 109.4 | C10—C11—H11 | 118.9 |
| C4—C3—H3A | 109.4 | C11—C12—C13 | 119.88 (10) |
| C2—C3—H3AB | 109.4 | C11—C12—C14 | 118.98 (10) |
| C4—C3—H3AB | 109.4 | C13—C12—C14 | 121.13 (10) |
| H3A—C3—H3AB | 108.0 | C8—C13—C12 | 117.22 (10) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 110.66 (9) | C8—C13—H13 | 121.4 |
| C5—C4—H4A | 109.5 | C12—C13—H13 | 121.4 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 109.5 | C15—C14—C12 | 125.40 (10) |
| C5—C4—H4AB | 109.5 | C15—C14—H14 | 117.3 |
| C3—C4—H4AB | 109.5 | C12—C14—H14 | 117.3 |
| H4A—C4—H4AB | 108.1 | C14—C15—C16 | 123.65 (11) |
| N1—C5—C6 | 108.34 (9) | C14—C15—H15 | 118.2 |
| N1—C5—C4 | 111.98 (9) | C16—C15—H15 | 118.2 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 111.37 (9) | C17—C16—C15 | 123.70 (10) |
| N1—C5—H5 | 108.3 | C17—C16—H16 | 118.1 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 108.3 | C15—C16—H16 | 118.1 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 108.3 | C16—C17—C18 | 122.76 (10) |
| C5—C6—C1 | 111.66 (9) | C16—C17—H17 | 118.6 |
| C5—C6—H6A | 109.3 | C18—C17—H17 | 118.6 |
| C1—C6—H6A | 109.3 | O1—C18—N1 | 123.06 (10) |
| C5—C6—H6AB | 109.3 | O1—C18—C17 | 122.66 (10) |
| C1—C6—H6AB | 109.3 | N1—C18—C17 | 114.26 (9) |
5-(2H-1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)-N-cyclohexylpenta-2,4-dienamide (I) . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1···O1i | 0.874 (16) | 2.086 (16) | 2.9547 (12) | 172.8 (14) |
Symmetry code: (i) x, y+1, z.
5-(2H-1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)-1-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)penta-2,4-dien-1-one (II) . Crystal data
| C16H17NO3 | Dx = 1.378 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 271.30 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Orthorhombic, Pbca | Cell parameters from 3874 reflections |
| a = 11.8747 (10) Å | θ = 2.7–25.8° |
| b = 7.2485 (6) Å | µ = 0.10 mm−1 |
| c = 30.392 (2) Å | T = 90 K |
| V = 2616.0 (4) Å3 | Needle, colorless |
| Z = 8 | 0.28 × 0.06 × 0.06 mm |
| F(000) = 1152 |
5-(2H-1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)-1-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)penta-2,4-dien-1-one (II) . Data collection
| Bruker D8 goniometer diffractometer | 3506 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: microfocus X-ray tube | 2193 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Multilayered conforacal mirror monochromator | Rint = 0.128 |
| Detector resolution: 7.391 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 29.1°, θmin = 2.7° |
| ω scans | h = −16→16 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2018) | k = −9→9 |
| Tmin = 0.666, Tmax = 0.746 | l = −41→41 |
| 41504 measured reflections |
5-(2H-1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)-1-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)penta-2,4-dien-1-one (II) . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.050 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0492P)2 + 1.9223P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.143 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| S = 1.05 | Δρmax = 0.28 e Å−3 |
| 3506 reflections | Δρmin = −0.26 e Å−3 |
| 182 parameters | Extinction correction: SHELXL-2018/3 (Sheldrick 2015b), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction coefficient: 0.0038 (6) |
5-(2H-1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)-1-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)penta-2,4-dien-1-one (II) . Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
5-(2H-1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)-1-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)penta-2,4-dien-1-one (II) . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.90586 (12) | 0.3421 (2) | 0.67241 (5) | 0.0219 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.77314 (12) | 0.9757 (2) | 0.35830 (4) | 0.0239 (4) | |
| O3 | 0.62806 (12) | 0.8589 (2) | 0.40118 (5) | 0.0238 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.72232 (13) | 0.3304 (2) | 0.69173 (5) | 0.0178 (4) | |
| C1 | 0.80525 (16) | 0.3650 (3) | 0.66249 (6) | 0.0179 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.77084 (17) | 0.4355 (3) | 0.61881 (6) | 0.0200 (4) | |
| H2 | 0.693195 | 0.435608 | 0.611273 | 0.024* | |
| C3 | 0.84580 (17) | 0.4994 (3) | 0.58954 (6) | 0.0195 (4) | |
| H3 | 0.923497 | 0.493700 | 0.596862 | 0.023* | |
| C4 | 0.81458 (18) | 0.5762 (3) | 0.54755 (6) | 0.0202 (4) | |
| H4 | 0.737486 | 0.571321 | 0.539278 | 0.024* | |
| C5 | 0.88758 (17) | 0.6543 (3) | 0.51932 (6) | 0.0204 (4) | |
| H5 | 0.964674 | 0.654787 | 0.527665 | 0.024* | |
| C6 | 0.85964 (17) | 0.7386 (3) | 0.47701 (6) | 0.0189 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.94619 (18) | 0.8085 (3) | 0.45072 (7) | 0.0233 (5) | |
| H7 | 1.021461 | 0.801352 | 0.461170 | 0.028* | |
| C8 | 0.92613 (18) | 0.8889 (3) | 0.40946 (7) | 0.0238 (5) | |
| H8 | 0.985763 | 0.934891 | 0.391755 | 0.029* | |
| C9 | 0.81622 (17) | 0.8975 (3) | 0.39603 (6) | 0.0197 (4) | |
| C10 | 0.65583 (18) | 0.9250 (3) | 0.35806 (7) | 0.0243 (5) | |
| H10A | 0.608744 | 1.033210 | 0.350559 | 0.029* | |
| H10B | 0.642106 | 0.827357 | 0.335911 | 0.029* | |
| C11 | 0.72958 (17) | 0.8288 (3) | 0.42176 (6) | 0.0192 (4) | |
| C12 | 0.74749 (17) | 0.7485 (3) | 0.46174 (6) | 0.0194 (4) | |
| H12 | 0.686800 | 0.701056 | 0.478668 | 0.023* | |
| C13 | 0.74989 (17) | 0.2759 (3) | 0.73696 (6) | 0.0191 (4) | |
| H13A | 0.803365 | 0.364049 | 0.750477 | 0.023* | |
| H13B | 0.783182 | 0.150743 | 0.737737 | 0.023* | |
| C14 | 0.63666 (17) | 0.2799 (3) | 0.76059 (7) | 0.0214 (4) | |
| H14A | 0.633146 | 0.183869 | 0.783722 | 0.026* | |
| H14B | 0.622901 | 0.401963 | 0.774158 | 0.026* | |
| C15 | 0.55179 (17) | 0.2411 (3) | 0.72417 (7) | 0.0229 (5) | |
| H15A | 0.476464 | 0.289608 | 0.731974 | 0.028* | |
| H15B | 0.545712 | 0.107030 | 0.718398 | 0.028* | |
| C16 | 0.59994 (16) | 0.3421 (3) | 0.68437 (7) | 0.0202 (4) | |
| H16A | 0.578131 | 0.280454 | 0.656583 | 0.024* | |
| H16B | 0.574336 | 0.472052 | 0.683550 | 0.024* |
5-(2H-1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)-1-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)penta-2,4-dien-1-one (II) . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0160 (7) | 0.0250 (8) | 0.0247 (7) | 0.0012 (6) | −0.0006 (6) | 0.0005 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0236 (8) | 0.0286 (8) | 0.0195 (7) | −0.0012 (6) | −0.0007 (6) | 0.0050 (6) |
| O3 | 0.0196 (8) | 0.0307 (8) | 0.0209 (7) | 0.0019 (6) | −0.0009 (6) | 0.0048 (6) |
| N1 | 0.0134 (8) | 0.0218 (9) | 0.0181 (8) | −0.0001 (7) | −0.0008 (6) | 0.0024 (7) |
| C1 | 0.0177 (10) | 0.0158 (9) | 0.0204 (10) | −0.0005 (8) | −0.0011 (8) | −0.0021 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0186 (10) | 0.0206 (10) | 0.0208 (10) | 0.0005 (8) | −0.0025 (8) | −0.0014 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0199 (10) | 0.0194 (10) | 0.0191 (10) | 0.0002 (8) | −0.0009 (8) | −0.0017 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0201 (10) | 0.0201 (10) | 0.0203 (10) | 0.0012 (8) | −0.0022 (8) | −0.0017 (8) |
| C5 | 0.0181 (10) | 0.0214 (10) | 0.0216 (10) | 0.0014 (8) | −0.0003 (8) | −0.0002 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0187 (10) | 0.0197 (10) | 0.0184 (10) | 0.0013 (8) | 0.0002 (8) | −0.0022 (8) |
| C7 | 0.0185 (10) | 0.0283 (11) | 0.0230 (10) | −0.0001 (9) | 0.0006 (8) | 0.0003 (9) |
| C8 | 0.0214 (11) | 0.0265 (11) | 0.0236 (10) | −0.0015 (9) | 0.0048 (8) | 0.0028 (9) |
| C9 | 0.0232 (11) | 0.0204 (10) | 0.0156 (9) | −0.0011 (8) | 0.0008 (8) | 0.0006 (8) |
| C10 | 0.0218 (11) | 0.0308 (12) | 0.0204 (10) | 0.0001 (9) | −0.0006 (8) | 0.0026 (9) |
| C11 | 0.0180 (10) | 0.0197 (10) | 0.0200 (10) | 0.0009 (8) | −0.0011 (8) | −0.0004 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0182 (10) | 0.0202 (10) | 0.0197 (9) | −0.0001 (8) | 0.0025 (8) | −0.0001 (8) |
| C13 | 0.0198 (10) | 0.0196 (10) | 0.0180 (9) | 0.0017 (8) | −0.0007 (8) | 0.0008 (8) |
| C14 | 0.0206 (10) | 0.0218 (10) | 0.0218 (10) | 0.0007 (9) | 0.0021 (8) | 0.0008 (8) |
| C15 | 0.0171 (10) | 0.0266 (11) | 0.0251 (10) | −0.0011 (9) | 0.0018 (8) | −0.0016 (9) |
| C16 | 0.0144 (9) | 0.0241 (11) | 0.0221 (10) | 0.0011 (8) | −0.0007 (8) | 0.0000 (8) |
5-(2H-1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)-1-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)penta-2,4-dien-1-one (II) . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C1 | 1.243 (2) | C7—H7 | 0.9500 |
| O2—C9 | 1.377 (2) | C8—C9 | 1.369 (3) |
| O2—C10 | 1.441 (2) | C8—H8 | 0.9500 |
| O3—C11 | 1.376 (2) | C9—C11 | 1.385 (3) |
| O3—C10 | 1.434 (2) | C10—H10A | 0.9900 |
| N1—C1 | 1.350 (2) | C10—H10B | 0.9900 |
| N1—C13 | 1.467 (2) | C11—C12 | 1.364 (3) |
| N1—C16 | 1.473 (2) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C2 | 1.480 (3) | C13—C14 | 1.525 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.341 (3) | C13—H13A | 0.9900 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9500 | C13—H13B | 0.9900 |
| C3—C4 | 1.441 (3) | C14—C15 | 1.523 (3) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C14—H14A | 0.9900 |
| C4—C5 | 1.345 (3) | C14—H14B | 0.9900 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9500 | C15—C16 | 1.525 (3) |
| C5—C6 | 1.462 (3) | C15—H15A | 0.9900 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C15—H15B | 0.9900 |
| C6—C7 | 1.397 (3) | C16—H16A | 0.9900 |
| C6—C12 | 1.412 (3) | C16—H16B | 0.9900 |
| C7—C8 | 1.403 (3) | ||
| C9—O2—C10 | 104.98 (15) | O2—C10—H10A | 110.2 |
| C11—O3—C10 | 105.50 (15) | O3—C10—H10B | 110.2 |
| C1—N1—C13 | 120.26 (16) | O2—C10—H10B | 110.2 |
| C1—N1—C16 | 127.52 (16) | H10A—C10—H10B | 108.5 |
| C13—N1—C16 | 112.21 (15) | C12—C11—O3 | 127.55 (19) |
| O1—C1—N1 | 121.10 (18) | C12—C11—C9 | 122.74 (19) |
| O1—C1—C2 | 121.93 (18) | O3—C11—C9 | 109.69 (17) |
| N1—C1—C2 | 116.95 (17) | C11—C12—C6 | 117.50 (19) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 122.08 (19) | C11—C12—H12 | 121.3 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.0 | C6—C12—H12 | 121.3 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.0 | N1—C13—C14 | 103.86 (16) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 123.4 (2) | N1—C13—H13A | 111.0 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 118.3 | C14—C13—H13A | 111.0 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 118.3 | N1—C13—H13B | 111.0 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 124.2 (2) | C14—C13—H13B | 111.0 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 117.9 | H13A—C13—H13B | 109.0 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 117.9 | C15—C14—C13 | 103.75 (16) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 126.23 (19) | C15—C14—H14A | 111.0 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 116.9 | C13—C14—H14A | 111.0 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 116.9 | C15—C14—H14B | 111.0 |
| C7—C6—C12 | 119.16 (18) | C13—C14—H14B | 111.0 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 119.19 (18) | H14A—C14—H14B | 109.0 |
| C12—C6—C5 | 121.64 (18) | C14—C15—C16 | 103.87 (16) |
| C6—C7—C8 | 122.5 (2) | C14—C15—H15A | 111.0 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 118.8 | C16—C15—H15A | 111.0 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 118.8 | C14—C15—H15B | 111.0 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 116.59 (19) | C16—C15—H15B | 111.0 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 121.7 | H15A—C15—H15B | 109.0 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 121.7 | N1—C16—C15 | 102.81 (16) |
| C8—C9—O2 | 128.41 (18) | N1—C16—H16A | 111.2 |
| C8—C9—C11 | 121.54 (19) | C15—C16—H16A | 111.2 |
| O2—C9—C11 | 110.01 (18) | N1—C16—H16B | 111.2 |
| O3—C10—O2 | 107.62 (16) | C15—C16—H16B | 111.2 |
| O3—C10—H10A | 110.2 | H16A—C16—H16B | 109.1 |
Funding Statement
This work was funded by Josai University grant .
References
- Bruker (2018). APEX3, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Ezawa, T., Inoue, Y., Murata, I., Takao, K., Sugita, Y. & Kanamoto, I. (2018). AAPS PharmSciTech, 19, 923–933. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Ezawa, T., Inoue, Y., Murata, I., Takao, K., Sugita, Y. & Kanamoto, I. (2019). Int. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 1–14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Ezawa, T., Inoue, Y., Tunvichien, S., Suzuki, R. & Kanamoto, I. (2016). Int. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 1–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Hübschle, C. B., Sheldrick, G. M. & Dittrich, B. (2011). J. Appl. Cryst. 44, 1281–1284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Pfund, L. Y., Chamberlin, B. L. & Matzger, A. J. (2015). Cryst. Growth Des. 15, 2047–2051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Szejtli, J. (1998). Chem. Rev. 98, 1743–1754. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Takao, K., Miyashiro, T. & Sugita, Y. (2015). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 63, 326–333. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, II, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989020004648/hb7897sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989020004648/hb7897Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989020004648/hb7897IIsup3.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989020004648/hb7897Isup4.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989020004648/hb7897IIsup5.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report









