Two bis-chelated metal complexes of nickel(II) and copper(II) with N,S Schiff bases in a cis configuration are presented and compared with similar species in the CSD having trans-configured ligands.
Keywords: crystal structure, dithiocarbazate ligand, nickel(II) complex, copper(II) complex, cis-trans configuration
Abstract
The structures are described of two bis-chelated metal complexes of nickel(II) and copper(II) with S-n-hexyl 3-(1-phenylethylidene)dithiocarbazate Schiff bases in a cis configuration, namely, bis[S-n-hexyl 3-(1-phenylethylidene)dithiocarbazato-κ2 N 3,S]nickel(II), [Ni(C15H21N2S2)2], and bis[S-n-hexyl 3-(1-phenylethylidene)dithiocarbazato-κ2 N 3,S]copper(II), [Cu(C15H21N2S2)2]. In both complexes, the metals have distorted square-planar geometries. A search in the Cambridge Structural Database [Groom et al. (2016 ▸). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179] for bis-chelated nickel(II) and copper(II) complexes with similar Schiff bases retrieved 55 and 36 hits for the two metals, respectively. An analysis of the geometrical parameters of complexes showing cis and trans configurations is reported and the values compared with those for the complexes described in this work.
Chemical context
Thiosemicarbazones, semicarbazones, hydrazide/hydrazones and dithiocarbazate Schiff bases and their complexes have been widely studied for their significant bioactivities and pharmacological properties (Beraldo et al. 2004 ▸; Altıntop et al., 2016 ▸). The presence of hard nitrogen and soft sulfur atoms enable these ligands to react with both transition and main-group metals (Arion, 2019 ▸) and transition-metal complexes derived from these N,S Schiff bases occupy a central role in the area of coordination chemistry. The nature of the long alkyl substituent chains, when present, may play a role in determining the liquid crystalline behavior of the complexes and thus their mesomorphic potential (Tomma et al., 2018 ▸; Lai et al., 1998 ▸).
Therefore, considering the above facts and in a continuation of our interest in this field (Zangrando et al., 2017 ▸), the present work reports a study on the synthesis and structural characterization of NiII and CuII complexes 1 and 2 with the Schiff base derived from S-n-hexyldithiocarbazate and acetophenone (HL). The single crystal X-ray structures of these distorted square-planar complexes of nickel and copper, NiL 2 and CuL 2, show cis configurations of the ligands. Since similar complexes can show both cis and trans configurations, we report herein a comparison with the geometry of structurally characterized complexes retrieved from the Cambridge Structural Database (Groom et al., 2016 ▸).
Structural commentary
Structure of complex 1
In the NiL 2 complex, the nickel atom is located on a crystallographic twofold axis and exhibits a distorted square-planar geometry. An ORTEP drawing of the complex is depicted in Fig. 1 ▸ and selected geometrical data are reported in Table 1 ▸. The two Schiff bases, in their deprotonated imino thiolate form, are coordinated through the β-nitrogen atom, N1, and the thiolate sulfur atom, S1, donors to the metal center in a cis-planar configuration. The Ni—S and Ni—N bond distances are 2.1600 (4) and 1.9295 (10) Å, respectively, with an S—Ni—N chelating angle of 85.68 (3)°.
Figure 1.
ORTEP view (50% probability ellipsoids) of the nickel(II) complex (1) with the labeling scheme for the asymmetric unit. (Primed atoms are related by the symmetry operation −x + 1, y, −z +  ).
).
Table 1. Selected geometric parameters (Å, °) for 1 .
| Ni1—N1 | 1.9295 (10) | Ni1—S1 | 2.1600 (4) |
| S1—Ni1—S1i | 93.12 (2) | N1—Ni1—S1i | 163.99 (3) |
| N1—Ni1—S1 | 85.68 (3) | N1—Ni1—N1i | 99.79 (6) |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
The square-planar geometry is tetrahedrally distorted and the dihedral angle formed by the mean planes through the two five-membered rings is 19.46 (5)°. The distortion from a planar arrangement is effected in order to circumvent steric clashes between the phenyl rings due to the cis configuration of the ligands.
Structure of complex 2
In CuL 2, the whole copper(II) complex is crystallographically independent although it exhibits pseudo twofold symmetry. An ORTEP view is shown in Fig. 2 ▸, and selected geometrical data are reported in Table 2 ▸. The arrangement of the ligands is similar to that of the nickel derivative, but a different conformation of the two alkyl chains leads to a lack of symmetry. Here the Cu—S and Cu—N bond distances are 2.2299 (9) and 2.2414 (9) Å, and 2.023 (3) and 2.020 (3) Å, respectively, while the chelating angles are similar at 85.43 (8) and 85.37 (8)°. The square-planar geometry shows a more significant tetrahedral distortion than is found in complex 1, having a dihedral angle between the two five-membered rings of 40.41 (12)°. It is worth noting that compared to similar ligands in their uncoordinated state (see for example Begum et al., 2015 ▸), a rotation about the C9—N2 by 180° is observed in the metal complexes in order to allow the N,S chelating behavior towards the metal.
Figure 2.
ORTEP view (50% probability ellipsoids) of the copper(II) complex (2).
Table 2. Selected geometric parameters (Å, °) for 2 .
| Cu1—N1 | 2.023 (3) | Cu1—S1 | 2.2299 (9) |
| Cu1—N3 | 2.020 (3) | Cu1—S3 | 2.2414 (9) |
| S1—Cu1—S3 | 98.53 (4) | N1—Cu1—S3 | 152.51 (8) |
| N1—Cu1—S1 | 85.43 (8) | N3—Cu1—S3 | 85.37 (8) |
| N3—Cu1—S1 | 149.66 (8) | N1—Cu1—N3 | 104.90 (11) |
The configuration assumed by the ligands in each complex leads the phenyl hydrogen atoms to sit above and below the metal centres with a separation of ∼2.6 Å, indicating the presence of M⋯H intramolecular interactions.
Supramolecular features
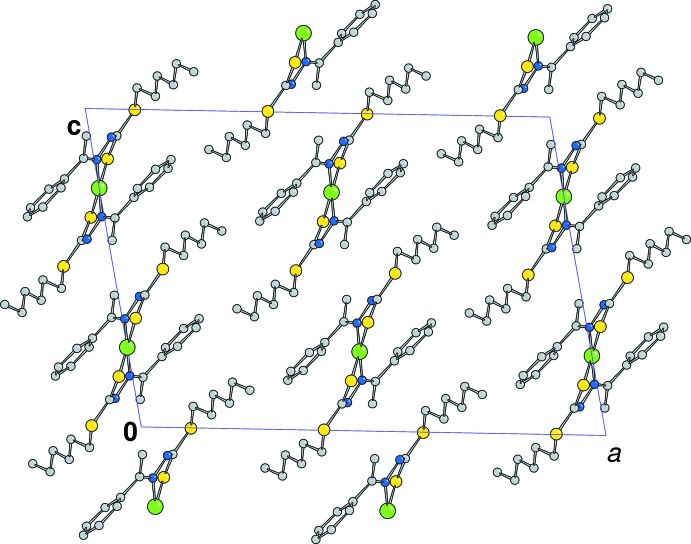
Figs. 3 ▸ and 4 ▸ display the crystal packing of the two complexes. The slightly shorter distance between the nickel ions in 1 (8.337 Å) compared to that of the copper atoms in 2 (8.518 Å) is likely the result of the different conformations of the alkyl chains. In both structures no significant π–π interactions involving phenyl rings are detected. C—H⋯π interactions are observed in 1 (Table 3 ▸) but no such interactions are observed in 2.
Figure 3.
The crystal packing of the Ni complex viewed down the b axis (H atoms are not shown for clarity).
Figure 4.
The crystal packing of the Cu complex viewed down the b axis (H atoms are not shown for clarity).
Table 3. C—H⋯π interation (Å, °) in 1 .
Cg is the centroid of the C1–C6 ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C14—H14A⋯Cg ii | 0.99 | 2.75 | 3.5892 (18) | 143 |
Symmetry code: (ii) 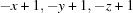 .
.
Database survey
Table 3 ▸ reports the mean values of the coordination bond lengths and angles of nickel(II) and copper(II) complexes bis-chelated by dithiocarbazate ligands, as retrieved from the CSD (version 5.40, update of August 2019; Groom et al., 2016 ▸). Whereas the number of trans-configured nickel complexes is higher than the number of cis complexes, for copper, the numbers of trans- and cis-planar complexes are almost equal. The Ni—N, Cu—N and Cu—S bond distances are comparable in the cis and trans isomers, while for the Ni–S bond distances, a slight shorter distance is observed for the cis isomers than for the trans isomers [2.157 (8) vs 2.174 (8) Å]. More significant is the dihedral angle between the five-membered rings of the chelating ligands, which has a value close to 0° in both the trans-configured Ni and Cu complexes, while in the cis-Ni complexes the angle does not exceed 31°, and in the cis-Cu complexes, the smallest value observed is 32.27°, indicating a propensity for copper(II) to assume a tetrahedral configuration. In fact, in some of the cis copper complexes in Table 4 ▸, the metal is present in effectively a tetrahedral geometry with a dihedral angle between the five-membered rings of ca 80° (Mondal et al., 2014 ▸; Santra et al., 2016 ▸; Tarafder et al., 2008 ▸). Another feature is a slight difference between the N—Ni—N and S—Ni—S angles in the cis complexes (100.39 and 92.30°, respectively), while the N—Cu—N and S—Cu—S angles are comparable (ca 106°) in the cis-Cu complexes.
Table 4. Coordination bond lengths and angles (Å, °) in the dithiocarbazate nickel and copper complexes with trans and cis configurations retrieved from the CSD.
α is the dihedral angle between the five-membered rings of the chelating ligands.
| trans-NiL 2 | cis-NiL 2 | trans-CuL 2 | cis-CuL 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of structures | 32 | 23 | 19 | 17 |
| M—N mean | 1.920 (13) | 1.924 (20) | 1.996 (37) | 2.013 (22) |
| M—N range | 1.878–1.952 | 1.851–1.995 | 1.923–2.043 | 1.986–2.066 |
| M—S mean | 2.174 (8) | 2.157 (8) | 2.244 (37) | 2.240 (17) |
| M—S range | 2.145–2.195 | 2.141–2.177 | 2.166–2.281 | 2.215–2.287 |
| N—M—N mean | 179.21 | 100.39 | 179.34 | 105.76 |
| S—M—S mean | 178.39 | 92.30 | 179.01 | 106.28 |
| α mean | 1.75 | 21.25 | 0.80 | 50.25 |
| α range | 0.00–19.41 | 10.24–30.10 | 0.00–10.93 | 32.27–81.61 |
Overall, it is difficult to assess what drives particular complexes to assume either a cis or a trans configuration upon crystallization and the most plausible reason may arise from crystal-packing requirements. Similar derivatives having thienylmethylene instead of the phenylethylidene fragments crystallize with a trans configuration (Begum et al., 2016 ▸).
Synthesis of the Schiff base ligand
Hydrazine hydrate (2.50 g, 0.05 mol, 99%) was added to an ethanolic solution (30 ml) of KOH (2.81 g, 0.05 mol) and the mixture was stirred at 273 K for 45 min. To this solution, carbon disulfide (3.81 g, 0.05 mol) was added dropwise under constant stirring for one h. Then 1-bromohexane (8.25 g, 0.05 mol) was added dropwise at 273 K under vigorous stirring for another hour. Finally, acetophenone (6.00 g, 0.05 mol) in ethanol (2.0 ml) was added and the mixture refluxed for 30 minutes. The hot mixture was filtered and then the filtrate cooled to 273 K to give a precipitate of the Schiff base product, which was recrystallized from ethanol at room temperature and dried in a vacuum desiccator over anhydrous CaCl2.
Synthesis of the Ni complex, 1
A solution of nickel(II) acetate tetrahydrate (0.06 g, 0.25 mmol, 7 mL methanol) was added to a solution of the ligand, (0.147 g, 0.5 mmol, 10 mL methanol). The resulting mixture was stirred at room temperature for five h. An olive green precipitate was formed, filtered off, washed with methanol and dried in vacuo over anhydrous CaCl2. Dark reddish brown single crystals of the compound, suitable for X-ray diffraction, were obtained by slow evaporation from a mixture of chloroform and toluene (5:1). Yield 85%. ESI-MS (FAB) calcd. m/z for C30H42N4S4Ni + H+: 644.1646 amu, found 645.1724 amu. M.p. 374 K.
Synthesis of the Cu complex, 2
The copper complex was prepared by a similar method to that used for nickel in the presence of Cu(CH3COO)2·H2O. Dark reddish brown single crystals of the compound, suitable for X-ray diffraction, were obtained by slow evaporation from a mixture of chloroform and acetonitrile (4:1). Yield 83%. ESI-MS (FAB) calcd. m/z for C30H42N4S4Cu + H+: 649.1588 amu, found 650.1665 amu. M.p. 418 K.
Refinement details
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 5 ▸. The hydrogen atoms were included as riding contributions with fixed isotropic displacement parameters in idealized positions [C—H = 0.95–0.99 Å; U iso(H) = 1.2 or 1.5U eq(C)]. The structure of 2 was refined as an inversion twin.
Table 5. Experimental details.
| 1 | 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | ||
| Chemical formula | [Ni(C15H21N2S2)2] | [Cu(C15H21N2S2)2] |
| M r | 645.62 | 650.45 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, C2/c | Monoclinic, C c |
| Temperature (K) | 173 | 173 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 23.9721 (5), 8.3967 (2), 16.6739 (3) | 22.7441 (7), 8.8636 (3), 17.0117 (6) |
| β (°) | 101.046 (1) | 109.158 (1) |
| V (Å3) | 3294.05 (12) | 3239.53 (19) |
| Z | 4 | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.87 | 0.96 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.38 × 0.30 × 0.07 | 0.23 × 0.10 × 0.03 |
| Data collection | ||
| Diffractometer | Rigaku R-AXIS RAPID | Rigaku R-AXIS RAPID |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (ABSCOR; Rigaku, 1995 ▸) | Multi-scan (ABSCOR; Rigaku, 1995 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.684, 0.941 | 0.772, 0.976 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 15965, 3768, 3589 | 7274, 7274, 6505 |
| R int | 0.025 | 0.025 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.649 | 0.649 |
| Refinement | ||
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.027, 0.081, 1.15 | 0.031, 0.074, 1.04 |
| No. of reflections | 3768 | 7274 |
| No. of parameters | 179 | 357 |
| No. of restraints | 0 | 2 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.32, −0.33 | 0.70, −0.22 |
| Absolute structure | – | Refined as an inversion twin. |
| Absolute structure parameter | – | 0.482 (10) |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, II, global. DOI: 10.1107/S205698902000506X/cq2035sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S205698902000506X/cq2035Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S205698902000506X/cq2035IIsup3.hkl
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
KB and SB are grateful to the Department of Chemistry, Shahjalal University of Science and Technology, for the provision of laboratory facilities. MCS acknowledges the Department of Applied Chemistry, Toyama University, for providing funds for the single-crystal X-ray analysis.
supplementary crystallographic information
Bis[S-n-hexyl 3-(1-phenylethylidene)dithiocarbazato-κ2N3,S]nickel(II) (I) . Crystal data
| [Ni(C15H21N2S2)2] | F(000) = 1368 |
| Mr = 645.62 | Dx = 1.302 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, C2/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71075 Å |
| a = 23.9721 (5) Å | Cell parameters from 4789 reflections |
| b = 8.3967 (2) Å | θ = 3.3–27.5° |
| c = 16.6739 (3) Å | µ = 0.87 mm−1 |
| β = 101.046 (1)° | T = 173 K |
| V = 3294.05 (12) Å3 | Prism, purple |
| Z = 4 | 0.38 × 0.30 × 0.07 mm |
Bis[S-n-hexyl 3-(1-phenylethylidene)dithiocarbazato-κ2N3,S]nickel(II) (I) . Data collection
| Rigaku R-AXIS RAPID diffractometer | 3589 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 10.000 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.025 |
| ω scans | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 3.3° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (ABSCOR; Rigaku, 1995) | h = −30→30 |
| Tmin = 0.684, Tmax = 0.941 | k = −10→10 |
| 15965 measured reflections | l = −21→21 |
| 3768 independent reflections |
Bis[S-n-hexyl 3-(1-phenylethylidene)dithiocarbazato-κ2N3,S]nickel(II) (I) . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.027 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.081 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.15 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0458P)2 + 1.5849P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3768 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.002 |
| 179 parameters | Δρmax = 0.32 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.33 e Å−3 |
Bis[S-n-hexyl 3-(1-phenylethylidene)dithiocarbazato-κ2N3,S]nickel(II) (I) . Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Bis[S-n-hexyl 3-(1-phenylethylidene)dithiocarbazato-κ2N3,S]nickel(II) (I) . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Ni1 | 0.5000 | 1.00787 (2) | 0.7500 | 0.02259 (8) | |
| S1 | 0.47077 (2) | 1.18475 (4) | 0.65741 (2) | 0.03381 (10) | |
| S2 | 0.39340 (2) | 1.11935 (4) | 0.50136 (2) | 0.03696 (11) | |
| N1 | 0.49459 (4) | 0.85983 (12) | 0.66033 (6) | 0.0216 (2) | |
| N2 | 0.45428 (5) | 0.89369 (13) | 0.58858 (6) | 0.0260 (2) | |
| C1 | 0.60886 (5) | 0.81446 (16) | 0.75593 (8) | 0.0270 (3) | |
| H1 | 0.6020 | 0.9207 | 0.7371 | 0.032* | |
| C2 | 0.65594 (6) | 0.78033 (19) | 0.81594 (8) | 0.0344 (3) | |
| H2 | 0.6814 | 0.8631 | 0.8376 | 0.041* | |
| C3 | 0.66588 (6) | 0.6262 (2) | 0.84440 (9) | 0.0379 (3) | |
| H3 | 0.6981 | 0.6034 | 0.8857 | 0.046* | |
| C4 | 0.62895 (7) | 0.50520 (18) | 0.81276 (10) | 0.0363 (3) | |
| H4 | 0.6354 | 0.3998 | 0.8331 | 0.044* | |
| C5 | 0.58238 (6) | 0.53742 (16) | 0.75130 (8) | 0.0283 (3) | |
| H5 | 0.5579 | 0.4534 | 0.7284 | 0.034* | |
| C6 | 0.57150 (5) | 0.69294 (15) | 0.72306 (7) | 0.0230 (2) | |
| C7 | 0.52256 (5) | 0.72868 (14) | 0.65686 (7) | 0.0220 (2) | |
| C8 | 0.50807 (6) | 0.61449 (16) | 0.58659 (8) | 0.0304 (3) | |
| H8A | 0.4700 | 0.5709 | 0.5851 | 0.046* | |
| H8B | 0.5358 | 0.5275 | 0.5935 | 0.046* | |
| H8C | 0.5090 | 0.6706 | 0.5353 | 0.046* | |
| C9 | 0.44213 (6) | 1.04365 (16) | 0.58425 (8) | 0.0269 (3) | |
| C10 | 0.38023 (7) | 0.9506 (2) | 0.43216 (8) | 0.0369 (3) | |
| H10A | 0.3617 | 0.9900 | 0.3776 | 0.044* | |
| H10B | 0.4173 | 0.9042 | 0.4267 | 0.044* | |
| C11 | 0.34357 (6) | 0.81914 (19) | 0.45734 (8) | 0.0347 (3) | |
| H11A | 0.3070 | 0.8649 | 0.4654 | 0.042* | |
| H11B | 0.3630 | 0.7733 | 0.5101 | 0.042* | |
| C12 | 0.33199 (7) | 0.6872 (2) | 0.39342 (9) | 0.0406 (3) | |
| H12A | 0.3093 | 0.7315 | 0.3425 | 0.049* | |
| H12B | 0.3687 | 0.6502 | 0.3811 | 0.049* | |
| C13 | 0.30051 (6) | 0.5448 (2) | 0.41990 (9) | 0.0359 (3) | |
| H13A | 0.3242 | 0.4961 | 0.4689 | 0.043* | |
| H13B | 0.2649 | 0.5824 | 0.4354 | 0.043* | |
| C14 | 0.28614 (7) | 0.4183 (2) | 0.35383 (10) | 0.0437 (4) | |
| H14A | 0.3219 | 0.3761 | 0.3408 | 0.052* | |
| H14B | 0.2645 | 0.4686 | 0.3037 | 0.052* | |
| C15 | 0.25158 (8) | 0.2802 (2) | 0.37790 (12) | 0.0532 (4) | |
| H15A | 0.2721 | 0.2320 | 0.4286 | 0.080* | |
| H15B | 0.2458 | 0.2002 | 0.3343 | 0.080* | |
| H15C | 0.2146 | 0.3195 | 0.3863 | 0.080* |
Bis[S-n-hexyl 3-(1-phenylethylidene)dithiocarbazato-κ2N3,S]nickel(II) (I) . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Ni1 | 0.02882 (14) | 0.01537 (12) | 0.02345 (13) | 0.000 | 0.00467 (9) | 0.000 |
| S1 | 0.0469 (2) | 0.01795 (16) | 0.03453 (18) | 0.00174 (13) | 0.00255 (15) | 0.00438 (12) |
| S2 | 0.0389 (2) | 0.03350 (19) | 0.03533 (19) | 0.00545 (14) | −0.00088 (15) | 0.01283 (14) |
| N1 | 0.0239 (5) | 0.0193 (5) | 0.0213 (5) | −0.0007 (4) | 0.0033 (4) | 0.0022 (4) |
| N2 | 0.0268 (5) | 0.0271 (5) | 0.0226 (5) | 0.0012 (4) | 0.0012 (4) | 0.0033 (4) |
| C1 | 0.0269 (6) | 0.0278 (6) | 0.0272 (6) | −0.0019 (5) | 0.0077 (5) | −0.0024 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0265 (6) | 0.0456 (8) | 0.0306 (6) | −0.0044 (6) | 0.0043 (5) | −0.0074 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0269 (7) | 0.0561 (9) | 0.0294 (6) | 0.0087 (6) | 0.0021 (5) | 0.0032 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0313 (7) | 0.0396 (8) | 0.0386 (8) | 0.0105 (5) | 0.0078 (6) | 0.0116 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0268 (6) | 0.0244 (6) | 0.0344 (7) | 0.0033 (5) | 0.0077 (5) | 0.0024 (5) |
| C6 | 0.0222 (6) | 0.0250 (6) | 0.0231 (5) | 0.0017 (4) | 0.0071 (4) | −0.0004 (5) |
| C7 | 0.0243 (6) | 0.0191 (5) | 0.0231 (5) | −0.0020 (4) | 0.0057 (4) | 0.0005 (4) |
| C8 | 0.0367 (7) | 0.0246 (6) | 0.0291 (6) | 0.0000 (5) | 0.0039 (5) | −0.0056 (5) |
| C9 | 0.0282 (6) | 0.0249 (6) | 0.0274 (6) | 0.0010 (5) | 0.0052 (5) | 0.0061 (5) |
| C10 | 0.0378 (8) | 0.0472 (8) | 0.0250 (6) | 0.0008 (7) | 0.0040 (5) | 0.0060 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0303 (7) | 0.0472 (8) | 0.0263 (6) | −0.0003 (6) | 0.0048 (5) | 0.0002 (6) |
| C12 | 0.0391 (8) | 0.0529 (9) | 0.0310 (7) | −0.0024 (7) | 0.0100 (6) | −0.0052 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0292 (7) | 0.0482 (8) | 0.0296 (7) | 0.0020 (6) | 0.0039 (5) | −0.0044 (6) |
| C14 | 0.0380 (8) | 0.0549 (10) | 0.0398 (8) | −0.0032 (7) | 0.0116 (6) | −0.0123 (7) |
| C15 | 0.0461 (10) | 0.0583 (11) | 0.0551 (10) | −0.0091 (8) | 0.0095 (8) | −0.0104 (9) |
Bis[S-n-hexyl 3-(1-phenylethylidene)dithiocarbazato-κ2N3,S]nickel(II) (I) . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Ni1—N1i | 1.9295 (10) | C7—C8 | 1.5023 (17) |
| Ni1—N1 | 1.9295 (10) | C8—H8A | 0.9800 |
| Ni1—S1i | 2.1600 (4) | C8—H8B | 0.9800 |
| Ni1—S1 | 2.1600 (4) | C8—H8C | 0.9800 |
| S1—C9 | 1.7443 (14) | C10—C11 | 1.519 (2) |
| S2—C9 | 1.7493 (13) | C10—H10A | 0.9900 |
| S2—C10 | 1.8163 (17) | C10—H10B | 0.9900 |
| N1—C7 | 1.2963 (16) | C11—C12 | 1.526 (2) |
| N1—N2 | 1.4151 (14) | C11—H11A | 0.9900 |
| N2—C9 | 1.2913 (17) | C11—H11B | 0.9900 |
| C1—C2 | 1.3872 (19) | C12—C13 | 1.524 (2) |
| C1—C6 | 1.3984 (17) | C12—H12A | 0.9900 |
| C1—H1 | 0.9500 | C12—H12B | 0.9900 |
| C2—C3 | 1.383 (2) | C13—C14 | 1.521 (2) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9500 | C13—H13A | 0.9900 |
| C3—C4 | 1.384 (2) | C13—H13B | 0.9900 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C14—C15 | 1.523 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.390 (2) | C14—H14A | 0.9900 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9500 | C14—H14B | 0.9900 |
| C5—C6 | 1.3956 (18) | C15—H15A | 0.9800 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C15—H15B | 0.9800 |
| C6—C7 | 1.4794 (17) | C15—H15C | 0.9800 |
| S1—Ni1—S1i | 93.12 (2) | N2—C9—S1 | 124.67 (10) |
| N1—Ni1—S1 | 85.68 (3) | N2—C9—S2 | 120.52 (11) |
| N1—Ni1—S1i | 163.99 (3) | S1—C9—S2 | 114.81 (8) |
| N1—Ni1—N1i | 99.79 (6) | C11—C10—S2 | 115.51 (10) |
| N1i—Ni1—S1i | 85.68 (3) | C11—C10—H10A | 108.4 |
| N1i—Ni1—S1 | 163.99 (3) | S2—C10—H10A | 108.4 |
| C9—S1—Ni1 | 93.62 (4) | C11—C10—H10B | 108.4 |
| C9—S2—C10 | 103.11 (7) | S2—C10—H10B | 108.4 |
| C7—N1—N2 | 114.09 (10) | H10A—C10—H10B | 107.5 |
| C7—N1—Ni1 | 128.55 (9) | C10—C11—C12 | 111.85 (12) |
| N2—N1—Ni1 | 117.34 (8) | C10—C11—H11A | 109.2 |
| C9—N2—N1 | 110.70 (10) | C12—C11—H11A | 109.2 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 120.22 (13) | C10—C11—H11B | 109.2 |
| C2—C1—H1 | 119.9 | C12—C11—H11B | 109.2 |
| C6—C1—H1 | 119.9 | H11A—C11—H11B | 107.9 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.23 (13) | C13—C12—C11 | 113.67 (12) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.9 | C13—C12—H12A | 108.8 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.9 | C11—C12—H12A | 108.8 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.03 (13) | C13—C12—H12B | 108.8 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.0 | C11—C12—H12B | 108.8 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.0 | H12A—C12—H12B | 107.7 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.20 (13) | C14—C13—C12 | 113.20 (13) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.9 | C14—C13—H13A | 108.9 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.9 | C12—C13—H13A | 108.9 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.18 (13) | C14—C13—H13B | 108.9 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.9 | C12—C13—H13B | 108.9 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.9 | H13A—C13—H13B | 107.8 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 119.09 (12) | C13—C14—C15 | 113.56 (14) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 120.78 (11) | C13—C14—H14A | 108.9 |
| C1—C6—C7 | 120.07 (11) | C15—C14—H14A | 108.9 |
| N1—C7—C6 | 118.82 (11) | C13—C14—H14B | 108.9 |
| N1—C7—C8 | 122.19 (11) | C15—C14—H14B | 108.9 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 118.96 (11) | H14A—C14—H14B | 107.7 |
| C7—C8—H8A | 109.5 | C14—C15—H15A | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—H8B | 109.5 | C14—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| H8A—C8—H8B | 109.5 | H15A—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—H8C | 109.5 | C14—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| H8A—C8—H8C | 109.5 | H15A—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| H8B—C8—H8C | 109.5 | H15B—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+1, y, −z+3/2.
Bis[S-n-hexyl 3-(1-phenylethylidene)dithiocarbazato-κ2N3,S]nickel(II) (I) . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg is the centroid of the C1–C6 ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C14—H14A···Cgii | 0.99 | 2.75 | 3.5892 (18) | 143 |
Symmetry code: (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1.
Bis[S-n-hexyl 3-(1-phenylethylidene)dithiocarbazato-κ2N3,S]copper(II) (II) . Crystal data
| [Cu(C15H21N2S2)2] | F(000) = 1372 |
| Mr = 650.45 | Dx = 1.334 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, Cc | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71075 Å |
| a = 22.7441 (7) Å | Cell parameters from 4858 reflections |
| b = 8.8636 (3) Å | θ = 3.3–27.4° |
| c = 17.0117 (6) Å | µ = 0.96 mm−1 |
| β = 109.158 (1)° | T = 173 K |
| V = 3239.53 (19) Å3 | Platelet, brown |
| Z = 4 | 0.23 × 0.10 × 0.03 mm |
Bis[S-n-hexyl 3-(1-phenylethylidene)dithiocarbazato-κ2N3,S]copper(II) (II) . Data collection
| Rigaku R-AXIS RAPID diffractometer | 6505 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 10.000 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.025 |
| ω scans | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 3.3° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (ABSCOR; Rigaku, 1995) | h = −29→29 |
| Tmin = 0.772, Tmax = 0.976 | k = −11→11 |
| 7274 measured reflections | l = −22→22 |
| 7274 independent reflections |
Bis[S-n-hexyl 3-(1-phenylethylidene)dithiocarbazato-κ2N3,S]copper(II) (II) . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.031 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.074 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0443P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.03 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 7274 reflections | Δρmax = 0.70 e Å−3 |
| 357 parameters | Δρmin = −0.22 e Å−3 |
| 2 restraints | Absolute structure: Refined as an inversion twin |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Absolute structure parameter: 0.482 (10) |
Bis[S-n-hexyl 3-(1-phenylethylidene)dithiocarbazato-κ2N3,S]copper(II) (II) . Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refined as a two-component inversion twin |
Bis[S-n-hexyl 3-(1-phenylethylidene)dithiocarbazato-κ2N3,S]copper(II) (II) . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cu1 | 0.76372 (2) | 0.47483 (4) | 0.64581 (2) | 0.02901 (10) | |
| S1 | 0.72319 (5) | 0.66910 (10) | 0.56233 (6) | 0.0427 (2) | |
| S2 | 0.65326 (5) | 0.65000 (14) | 0.38556 (6) | 0.0541 (3) | |
| S3 | 0.80973 (4) | 0.60386 (9) | 0.76328 (5) | 0.0377 (2) | |
| S4 | 0.87369 (5) | 0.46750 (11) | 0.92560 (6) | 0.0422 (2) | |
| N1 | 0.76458 (13) | 0.3684 (3) | 0.54100 (16) | 0.0298 (6) | |
| N2 | 0.72530 (14) | 0.4255 (4) | 0.46522 (18) | 0.0372 (7) | |
| N3 | 0.75419 (12) | 0.3083 (3) | 0.72177 (16) | 0.0283 (6) | |
| N4 | 0.79439 (13) | 0.3123 (3) | 0.80456 (16) | 0.0320 (6) | |
| C1 | 0.83534 (16) | 0.1791 (4) | 0.6128 (2) | 0.0328 (7) | |
| C2 | 0.83552 (19) | 0.0237 (4) | 0.6288 (3) | 0.0449 (9) | |
| H2 | 0.8092 | −0.0422 | 0.5884 | 0.054* | |
| C3 | 0.8741 (2) | −0.0326 (5) | 0.7033 (3) | 0.0593 (13) | |
| H3 | 0.8732 | −0.1374 | 0.7144 | 0.071* | |
| C4 | 0.9139 (2) | 0.0595 (6) | 0.7618 (3) | 0.0577 (12) | |
| H4 | 0.9401 | 0.0185 | 0.8129 | 0.069* | |
| C5 | 0.91577 (18) | 0.2123 (5) | 0.7460 (3) | 0.0498 (9) | |
| H5 | 0.9436 | 0.2763 | 0.7860 | 0.060* | |
| C6 | 0.87702 (16) | 0.2717 (4) | 0.6720 (2) | 0.0366 (8) | |
| H6 | 0.8787 | 0.3764 | 0.6611 | 0.044* | |
| C7 | 0.79159 (15) | 0.2419 (4) | 0.5351 (2) | 0.0339 (7) | |
| C8 | 0.7800 (2) | 0.1604 (5) | 0.4547 (2) | 0.0489 (10) | |
| H8A | 0.7354 | 0.1395 | 0.4299 | 0.073* | |
| H8B | 0.8031 | 0.0651 | 0.4648 | 0.073* | |
| H8C | 0.7938 | 0.2230 | 0.4166 | 0.073* | |
| C9 | 0.70540 (17) | 0.5602 (5) | 0.4723 (2) | 0.0389 (8) | |
| C10 | 0.6477 (2) | 0.5274 (5) | 0.2988 (3) | 0.0504 (10) | |
| H10A | 0.6293 | 0.5855 | 0.2468 | 0.061* | |
| H10B | 0.6904 | 0.4983 | 0.3016 | 0.061* | |
| C11 | 0.6101 (2) | 0.3855 (6) | 0.2931 (3) | 0.0636 (13) | |
| H11A | 0.5700 | 0.4110 | 0.3010 | 0.076* | |
| H11B | 0.6329 | 0.3158 | 0.3383 | 0.076* | |
| C12 | 0.5971 (2) | 0.3049 (5) | 0.2076 (3) | 0.0570 (11) | |
| H12A | 0.6346 | 0.3124 | 0.1906 | 0.068* | |
| H12B | 0.5892 | 0.1965 | 0.2143 | 0.068* | |
| C13 | 0.54203 (19) | 0.3702 (5) | 0.1394 (2) | 0.0470 (9) | |
| H13A | 0.5509 | 0.4772 | 0.1308 | 0.056* | |
| H13B | 0.5051 | 0.3677 | 0.1578 | 0.056* | |
| C14 | 0.5267 (2) | 0.2878 (5) | 0.0568 (3) | 0.0598 (11) | |
| H14A | 0.5221 | 0.1788 | 0.0661 | 0.072* | |
| H14B | 0.5618 | 0.2997 | 0.0350 | 0.072* | |
| C15 | 0.4673 (2) | 0.3451 (5) | −0.0081 (3) | 0.0626 (12) | |
| H15A | 0.4326 | 0.3366 | 0.0137 | 0.094* | |
| H15B | 0.4584 | 0.2845 | −0.0589 | 0.094* | |
| H15C | 0.4728 | 0.4509 | −0.0209 | 0.094* | |
| C16 | 0.67196 (15) | 0.1824 (4) | 0.6188 (2) | 0.0299 (7) | |
| C17 | 0.65939 (18) | 0.0441 (4) | 0.5760 (2) | 0.0390 (8) | |
| H17 | 0.6801 | −0.0451 | 0.6016 | 0.047* | |
| C18 | 0.6168 (2) | 0.0384 (4) | 0.4966 (3) | 0.0469 (10) | |
| H18 | 0.6090 | −0.0543 | 0.4670 | 0.056* | |
| C19 | 0.58533 (18) | 0.1674 (5) | 0.4601 (2) | 0.0453 (9) | |
| H19 | 0.5562 | 0.1628 | 0.4053 | 0.054* | |
| C20 | 0.59591 (16) | 0.3024 (4) | 0.5024 (2) | 0.0395 (8) | |
| H20 | 0.5736 | 0.3902 | 0.4773 | 0.047* | |
| C21 | 0.63895 (15) | 0.3099 (4) | 0.5813 (2) | 0.0316 (7) | |
| H21 | 0.6461 | 0.4033 | 0.6104 | 0.038* | |
| C22 | 0.71886 (15) | 0.1898 (4) | 0.7031 (2) | 0.0299 (7) | |
| C23 | 0.72371 (19) | 0.0637 (4) | 0.7638 (2) | 0.0434 (9) | |
| H23A | 0.7662 | 0.0234 | 0.7822 | 0.065* | |
| H23B | 0.6944 | −0.0165 | 0.7368 | 0.065* | |
| H23C | 0.7137 | 0.1019 | 0.8120 | 0.065* | |
| C24 | 0.82018 (17) | 0.4433 (4) | 0.8252 (2) | 0.0338 (8) | |
| C25 | 0.87310 (19) | 0.2823 (4) | 0.9736 (2) | 0.0451 (9) | |
| H25A | 0.8390 | 0.2782 | 0.9978 | 0.054* | |
| H25B | 0.8659 | 0.2022 | 0.9309 | 0.054* | |
| C26 | 0.93557 (19) | 0.2566 (5) | 1.0418 (2) | 0.0471 (9) | |
| H26A | 0.9364 | 0.1523 | 1.0630 | 0.057* | |
| H26B | 0.9691 | 0.2650 | 1.0167 | 0.057* | |
| C27 | 0.94983 (18) | 0.3651 (5) | 1.1151 (2) | 0.0408 (8) | |
| H27A | 0.9467 | 0.4700 | 1.0941 | 0.049* | |
| H27B | 0.9183 | 0.3519 | 1.1432 | 0.049* | |
| C28 | 1.01432 (18) | 0.3406 (5) | 1.1781 (2) | 0.0501 (10) | |
| H28A | 1.0200 | 0.2315 | 1.1909 | 0.060* | |
| H28B | 1.0458 | 0.3709 | 1.1524 | 0.060* | |
| C29 | 1.02664 (18) | 0.4269 (5) | 1.2592 (2) | 0.0477 (9) | |
| H29A | 1.0719 | 0.4248 | 1.2901 | 0.057* | |
| H29B | 1.0143 | 0.5335 | 1.2462 | 0.057* | |
| C30 | 0.99290 (19) | 0.3655 (5) | 1.3133 (2) | 0.0534 (10) | |
| H30A | 0.9480 | 0.3716 | 1.2842 | 0.080* | |
| H30B | 1.0036 | 0.4245 | 1.3648 | 0.080* | |
| H30C | 1.0048 | 0.2600 | 1.3266 | 0.080* |
Bis[S-n-hexyl 3-(1-phenylethylidene)dithiocarbazato-κ2N3,S]copper(II) (II) . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cu1 | 0.03446 (19) | 0.02179 (16) | 0.03268 (19) | −0.00067 (18) | 0.01359 (15) | −0.00063 (18) |
| S1 | 0.0537 (6) | 0.0254 (4) | 0.0478 (5) | 0.0061 (4) | 0.0151 (4) | 0.0052 (4) |
| S2 | 0.0525 (6) | 0.0622 (7) | 0.0448 (5) | 0.0179 (5) | 0.0124 (4) | 0.0183 (5) |
| S3 | 0.0465 (5) | 0.0260 (4) | 0.0391 (5) | −0.0078 (4) | 0.0120 (4) | −0.0041 (3) |
| S4 | 0.0466 (5) | 0.0408 (5) | 0.0335 (5) | −0.0107 (4) | 0.0054 (4) | −0.0032 (4) |
| N1 | 0.0329 (13) | 0.0283 (13) | 0.0301 (13) | 0.0021 (11) | 0.0129 (11) | 0.0022 (11) |
| N2 | 0.0380 (16) | 0.0435 (17) | 0.0314 (14) | 0.0007 (14) | 0.0129 (12) | 0.0036 (13) |
| N3 | 0.0305 (14) | 0.0255 (13) | 0.0300 (13) | −0.0037 (11) | 0.0115 (11) | −0.0044 (11) |
| N4 | 0.0349 (14) | 0.0304 (14) | 0.0312 (14) | −0.0054 (12) | 0.0115 (11) | −0.0032 (11) |
| C1 | 0.0354 (18) | 0.0269 (16) | 0.0435 (19) | 0.0024 (14) | 0.0227 (15) | 0.0011 (15) |
| C2 | 0.051 (2) | 0.0243 (16) | 0.066 (3) | 0.0055 (16) | 0.027 (2) | 0.0049 (18) |
| C3 | 0.064 (3) | 0.039 (2) | 0.085 (3) | 0.012 (2) | 0.039 (3) | 0.020 (2) |
| C4 | 0.052 (2) | 0.062 (3) | 0.062 (3) | 0.025 (2) | 0.024 (2) | 0.025 (2) |
| C5 | 0.038 (2) | 0.060 (2) | 0.051 (2) | 0.0027 (19) | 0.0147 (17) | 0.001 (2) |
| C6 | 0.0342 (17) | 0.0313 (16) | 0.049 (2) | 0.0042 (15) | 0.0195 (15) | 0.0038 (16) |
| C7 | 0.0374 (17) | 0.0298 (16) | 0.0390 (18) | −0.0010 (15) | 0.0189 (14) | −0.0029 (14) |
| C8 | 0.059 (2) | 0.045 (2) | 0.044 (2) | 0.0051 (19) | 0.0178 (19) | −0.0100 (18) |
| C9 | 0.0375 (19) | 0.0437 (19) | 0.0378 (19) | 0.0053 (17) | 0.0155 (16) | 0.0115 (17) |
| C10 | 0.041 (2) | 0.067 (3) | 0.043 (2) | 0.0022 (19) | 0.0135 (17) | 0.0181 (19) |
| C11 | 0.053 (2) | 0.082 (3) | 0.053 (3) | −0.010 (2) | 0.014 (2) | 0.027 (2) |
| C12 | 0.056 (3) | 0.049 (2) | 0.067 (3) | −0.002 (2) | 0.022 (2) | 0.013 (2) |
| C13 | 0.046 (2) | 0.049 (2) | 0.053 (2) | −0.0027 (19) | 0.0261 (18) | 0.0005 (19) |
| C14 | 0.069 (3) | 0.047 (2) | 0.072 (3) | −0.002 (2) | 0.034 (2) | −0.008 (2) |
| C15 | 0.078 (3) | 0.055 (3) | 0.055 (3) | −0.009 (2) | 0.024 (2) | −0.014 (2) |
| C16 | 0.0310 (16) | 0.0278 (15) | 0.0340 (16) | −0.0067 (13) | 0.0149 (13) | −0.0032 (13) |
| C17 | 0.045 (2) | 0.0290 (18) | 0.044 (2) | −0.0014 (16) | 0.0158 (16) | −0.0034 (16) |
| C18 | 0.052 (2) | 0.041 (2) | 0.046 (2) | −0.0160 (19) | 0.0134 (18) | −0.0131 (18) |
| C19 | 0.043 (2) | 0.053 (2) | 0.0363 (19) | −0.0130 (18) | 0.0079 (16) | −0.0038 (17) |
| C20 | 0.0335 (17) | 0.043 (2) | 0.0417 (19) | −0.0036 (16) | 0.0125 (15) | 0.0017 (17) |
| C21 | 0.0328 (16) | 0.0302 (16) | 0.0348 (17) | −0.0050 (14) | 0.0150 (13) | −0.0046 (14) |
| C22 | 0.0339 (17) | 0.0264 (15) | 0.0333 (16) | −0.0009 (13) | 0.0163 (13) | −0.0024 (13) |
| C23 | 0.051 (2) | 0.0363 (18) | 0.042 (2) | −0.0107 (18) | 0.0138 (17) | 0.0035 (17) |
| C24 | 0.0337 (18) | 0.0371 (19) | 0.0301 (17) | −0.0023 (15) | 0.0098 (14) | −0.0044 (15) |
| C25 | 0.055 (2) | 0.0394 (19) | 0.0387 (19) | −0.0092 (18) | 0.0131 (17) | −0.0028 (16) |
| C26 | 0.054 (2) | 0.048 (2) | 0.0388 (19) | 0.0107 (19) | 0.0141 (17) | −0.0030 (18) |
| C27 | 0.044 (2) | 0.041 (2) | 0.0378 (18) | 0.0061 (17) | 0.0138 (16) | −0.0044 (16) |
| C28 | 0.042 (2) | 0.061 (3) | 0.044 (2) | 0.0095 (19) | 0.0111 (17) | −0.0032 (19) |
| C29 | 0.039 (2) | 0.050 (2) | 0.046 (2) | −0.0037 (18) | 0.0040 (16) | −0.0035 (19) |
| C30 | 0.047 (2) | 0.065 (3) | 0.045 (2) | −0.010 (2) | 0.0096 (17) | −0.008 (2) |
Bis[S-n-hexyl 3-(1-phenylethylidene)dithiocarbazato-κ2N3,S]copper(II) (II) . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Cu1—N1 | 2.023 (3) | C13—H13A | 0.9900 |
| Cu1—N3 | 2.020 (3) | C13—H13B | 0.9900 |
| Cu1—S1 | 2.2299 (9) | C14—C15 | 1.524 (7) |
| Cu1—S3 | 2.2414 (9) | C14—H14A | 0.9900 |
| S1—C9 | 1.742 (4) | C14—H14B | 0.9900 |
| S2—C9 | 1.752 (4) | C15—H15A | 0.9800 |
| S2—C10 | 1.804 (5) | C15—H15B | 0.9800 |
| S3—C24 | 1.740 (4) | C15—H15C | 0.9800 |
| S4—C24 | 1.755 (4) | C16—C21 | 1.391 (5) |
| S4—C25 | 1.835 (4) | C16—C17 | 1.406 (5) |
| N1—C7 | 1.298 (4) | C16—C22 | 1.481 (4) |
| N1—N2 | 1.400 (4) | C17—C18 | 1.381 (5) |
| N2—C9 | 1.296 (5) | C17—H17 | 0.9500 |
| N3—C22 | 1.297 (4) | C18—C19 | 1.383 (6) |
| N3—N4 | 1.406 (4) | C18—H18 | 0.9500 |
| N4—C24 | 1.296 (5) | C19—C20 | 1.376 (5) |
| C1—C6 | 1.399 (5) | C19—H19 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C2 | 1.404 (5) | C20—C21 | 1.380 (5) |
| C1—C7 | 1.478 (5) | C20—H20 | 0.9500 |
| C2—C3 | 1.377 (7) | C21—H21 | 0.9500 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9500 | C22—C23 | 1.501 (5) |
| C3—C4 | 1.373 (7) | C23—H23A | 0.9800 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C23—H23B | 0.9800 |
| C4—C5 | 1.384 (7) | C23—H23C | 0.9800 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9500 | C25—C26 | 1.528 (5) |
| C5—C6 | 1.383 (5) | C25—H25A | 0.9900 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C25—H25B | 0.9900 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9500 | C26—C27 | 1.523 (5) |
| C7—C8 | 1.491 (5) | C26—H26A | 0.9900 |
| C8—H8A | 0.9800 | C26—H26B | 0.9900 |
| C8—H8B | 0.9800 | C27—C28 | 1.522 (5) |
| C8—H8C | 0.9800 | C27—H27A | 0.9900 |
| C10—C11 | 1.506 (6) | C27—H27B | 0.9900 |
| C10—H10A | 0.9900 | C28—C29 | 1.521 (6) |
| C10—H10B | 0.9900 | C28—H28A | 0.9900 |
| C11—C12 | 1.559 (7) | C28—H28B | 0.9900 |
| C11—H11A | 0.9900 | C29—C30 | 1.481 (6) |
| C11—H11B | 0.9900 | C29—H29A | 0.9900 |
| C12—C13 | 1.515 (6) | C29—H29B | 0.9900 |
| C12—H12A | 0.9900 | C30—H30A | 0.9800 |
| C12—H12B | 0.9900 | C30—H30B | 0.9800 |
| C13—C14 | 1.519 (6) | C30—H30C | 0.9800 |
| S1—Cu1—S3 | 98.53 (4) | C13—C14—H14B | 109.0 |
| N1—Cu1—S1 | 85.43 (8) | C15—C14—H14B | 109.0 |
| N3—Cu1—S1 | 149.66 (8) | H14A—C14—H14B | 107.8 |
| N1—Cu1—S3 | 152.51 (8) | C14—C15—H15A | 109.5 |
| N3—Cu1—S3 | 85.37 (8) | C14—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| N1—Cu1—N3 | 104.90 (11) | H15A—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C9—S1—Cu1 | 93.45 (13) | C14—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C9—S2—C10 | 105.16 (19) | H15A—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C24—S3—Cu1 | 93.07 (12) | H15B—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C24—S4—C25 | 102.70 (18) | C21—C16—C17 | 118.9 (3) |
| C7—N1—N2 | 114.6 (3) | C21—C16—C22 | 121.1 (3) |
| C7—N1—Cu1 | 127.8 (2) | C17—C16—C22 | 120.0 (3) |
| N2—N1—Cu1 | 117.1 (2) | C18—C17—C16 | 119.8 (3) |
| C9—N2—N1 | 112.6 (3) | C18—C17—H17 | 120.1 |
| C22—N3—N4 | 114.4 (3) | C16—C17—H17 | 120.1 |
| C22—N3—Cu1 | 128.5 (2) | C17—C18—C19 | 120.2 (3) |
| N4—N3—Cu1 | 116.84 (18) | C17—C18—H18 | 119.9 |
| C24—N4—N3 | 112.5 (3) | C19—C18—H18 | 119.9 |
| C6—C1—C2 | 118.6 (3) | C20—C19—C18 | 120.5 (3) |
| C6—C1—C7 | 121.4 (3) | C20—C19—H19 | 119.7 |
| C2—C1—C7 | 120.0 (3) | C18—C19—H19 | 119.7 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 119.6 (4) | C19—C20—C21 | 119.9 (3) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.2 | C19—C20—H20 | 120.1 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.2 | C21—C20—H20 | 120.1 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 121.4 (4) | C20—C21—C16 | 120.7 (3) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.3 | C20—C21—H21 | 119.7 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.3 | C16—C21—H21 | 119.7 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.8 (4) | N3—C22—C16 | 117.7 (3) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.1 | N3—C22—C23 | 122.3 (3) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.1 | C16—C22—C23 | 120.0 (3) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 119.9 (4) | C22—C23—H23A | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.1 | C22—C23—H23B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.1 | H23A—C23—H23B | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 120.7 (3) | C22—C23—H23C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.6 | H23A—C23—H23C | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—H6 | 119.6 | H23B—C23—H23C | 109.5 |
| N1—C7—C1 | 116.9 (3) | N4—C24—S3 | 127.5 (3) |
| N1—C7—C8 | 122.9 (3) | N4—C24—S4 | 118.7 (3) |
| C1—C7—C8 | 120.2 (3) | S3—C24—S4 | 113.7 (2) |
| C7—C8—H8A | 109.5 | C26—C25—S4 | 109.3 (3) |
| C7—C8—H8B | 109.5 | C26—C25—H25A | 109.8 |
| H8A—C8—H8B | 109.5 | S4—C25—H25A | 109.8 |
| C7—C8—H8C | 109.5 | C26—C25—H25B | 109.8 |
| H8A—C8—H8C | 109.5 | S4—C25—H25B | 109.8 |
| H8B—C8—H8C | 109.5 | H25A—C25—H25B | 108.3 |
| N2—C9—S1 | 127.2 (3) | C27—C26—C25 | 115.0 (3) |
| N2—C9—S2 | 120.1 (3) | C27—C26—H26A | 108.5 |
| S1—C9—S2 | 112.7 (2) | C25—C26—H26A | 108.5 |
| C11—C10—S2 | 116.2 (3) | C27—C26—H26B | 108.5 |
| C11—C10—H10A | 108.2 | C25—C26—H26B | 108.5 |
| S2—C10—H10A | 108.2 | H26A—C26—H26B | 107.5 |
| C11—C10—H10B | 108.2 | C28—C27—C26 | 112.6 (3) |
| S2—C10—H10B | 108.2 | C28—C27—H27A | 109.1 |
| H10A—C10—H10B | 107.4 | C26—C27—H27A | 109.1 |
| C10—C11—C12 | 111.9 (4) | C28—C27—H27B | 109.1 |
| C10—C11—H11A | 109.2 | C26—C27—H27B | 109.1 |
| C12—C11—H11A | 109.2 | H27A—C27—H27B | 107.8 |
| C10—C11—H11B | 109.2 | C29—C28—C27 | 114.5 (3) |
| C12—C11—H11B | 109.2 | C29—C28—H28A | 108.6 |
| H11A—C11—H11B | 107.9 | C27—C28—H28A | 108.6 |
| C13—C12—C11 | 113.3 (4) | C29—C28—H28B | 108.6 |
| C13—C12—H12A | 108.9 | C27—C28—H28B | 108.6 |
| C11—C12—H12A | 108.9 | H28A—C28—H28B | 107.6 |
| C13—C12—H12B | 108.9 | C30—C29—C28 | 113.6 (4) |
| C11—C12—H12B | 108.9 | C30—C29—H29A | 108.8 |
| H12A—C12—H12B | 107.7 | C28—C29—H29A | 108.8 |
| C12—C13—C14 | 113.9 (4) | C30—C29—H29B | 108.8 |
| C12—C13—H13A | 108.8 | C28—C29—H29B | 108.8 |
| C14—C13—H13A | 108.8 | H29A—C29—H29B | 107.7 |
| C12—C13—H13B | 108.8 | C29—C30—H30A | 109.5 |
| C14—C13—H13B | 108.8 | C29—C30—H30B | 109.5 |
| H13A—C13—H13B | 107.7 | H30A—C30—H30B | 109.5 |
| C13—C14—C15 | 112.9 (4) | C29—C30—H30C | 109.5 |
| C13—C14—H14A | 109.0 | H30A—C30—H30C | 109.5 |
| C15—C14—H14A | 109.0 | H30B—C30—H30C | 109.5 |
References
- Altıntop, M. D., Temel, H. E., Sever, B., Akalın Çiftçi, G. & Kaplancıklı, Z. A. (2016). Molecules, 21, 1598.
- Altomare, A., Cascarano, G., Giacovazzo, C., Guagliardi, A., Burla, M. C., Polidori, G. & Camalli, M. (1994). J. Appl. Cryst. 27, 435.
- Arion, V. B. (2019). Coord. Chem. Rev. 387, 348–397.
- Begum, M. S., Howlader, M. B. H., Miyatake, R., Zangrando, E. & Sheikh, M. C. (2015). Acta Cryst. E71, o199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Begum, M. S., Zangrando, E., Howlader, M. B. H., Sheikh, M. C., Miyatake, R., Hossain, M. M., Alam, M. M. & Hasnat, M. A. (2016). Polyhedron, 105, 56–61.
- Beraldo, H. & Gambino, D. (2004). Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 4, 31–39. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Lai, C. K., Tsai, C. & Pang, Y. (1998). J. Mater. Chem. 8, 1355–1360.
- Mondal, G., Bera, P., Santra, A., Jana, S., Mandal, T. N., Mondal, A., Seok, S. I. & Bera, P. (2014). New J. Chem. 38, 4774–4782.
- Rigaku (1995). ABSCOR. Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Rigaku (2010). RAPID-AUTO and CrystalStructure. Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Santra, A., Mondal, G., Acharjya, M., Bera, P., Panja, A., Mandal, T. K., Mitra, P. & Bera, P. (2016). Polyhedron, 113, 5–15.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Tarafder, M. T. H., Islam, M. T., Islam, M. A. A. A. A., Chantrapromma, S. & Fun, H.-K. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, m416–m417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Tomma, H. J., Ghali, S. T. & Al-Dujaili, H. A. (2018). Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 664, 85–94.
- Zangrando, E., Begum, M. S., Sheikh, M. C., Miyatake, R., Hossain, M. M., Alam, M. M., Hasnat, M. A., Halim, M. A., Ahmed, S., Rahman, M. N. & Ghosh, A. (2017). Arabian J. Chem 10, 172–184.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, II, global. DOI: 10.1107/S205698902000506X/cq2035sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S205698902000506X/cq2035Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S205698902000506X/cq2035IIsup3.hkl
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report