The molecule in the title crystal has the shape of the letter V with the dihedral angle between the phthalazin-1-one and mesityl residues being 83.26 (4)°. Molecules assemble into a linear, supramolecular tape by phthalazinone-C6-C—H⋯O(sulfoxide) and π(phthalazinone-N2C4)–π(phthalazinone-C6) stacking interactions.
Keywords: crystal structure, phthalazinone, Hirshfeld surface analysis
Abstract
The X-ray crystal structure of the title phthalazin-1-one derivative, C17H16N2O3S {systematic name: 2-[(2,4,6-trimethylbenzene)sulfonyl]-1,2-dihydrophthalazin-1-one}, features a tetrahedral sulfoxide-S atom, connected to phthalazin-1-one and mesityl residues. The dihedral angle [83.26 (4)°] between the organic substituents is consistent with the molecule having the shape of the letter V. In the crystal, phthalazinone-C6-C—H⋯O(sulfoxide) and π(phthalazinone-N2C4)–π(phthalazinone-C6) stacking [inter-centroid distance = 3.5474 (9) Å] contacts lead to a linear supramolecular tape along the a-axis direction; tapes assemble without directional interactions between them. The analysis of the calculated Hirshfeld surfaces confirm the importance of the C—H⋯O and π-stacking interactions but, also H⋯H and C—H⋯C contacts. The calculation of the interaction energies indicate the importance of dispersion terms with the greatest energies calculated for the C—H⋯O and π-stacking interactions.
Chemical context
Phthalazin-1(2H)-one derivatives are a group of diazaheterobicycles that are noteworthy for their interesting medicinal applications. Thus, this class of compound has been reported to possess a wide variety of biological properties such as anti-diabetic (Mylari et al., 1992 ▸), anti-cancer (Menear et al., 2008 ▸
), anti-inflammatory and analgesic (Pakulska et al., 2009 ▸), anti-histamine (Procopiou et al., 2011 ▸), anti-hypertensive and anti-thrombotic (Cherkez et al., 1986 ▸) activities. Some N-substituted phthalazinones have attracted attention as a result of their potential role as anti-asthmatic agents (Ukita et al., 1999 ▸), their ability to inhibit thromboxane A2 (TXA2) synthetase and to induce bronchodialation (Yamaguchi et al., 1993 ▸). At the present time, a number of phthalazin-1(2H)-one-based drugs are in use (Wu et al., 2012 ▸; Teran et al., 2019 ▸). A number of reaction pathways to the phthalazinone skeleton are known, notable among which include multi-step reactions involving cyclocondensation reactions of phthalic anhydrides, phthalimides, phthalaldehydic acid or 2-acylbenzoic acids with substituted hydrazines, in the presence of appropriate catalysts (Haider & Holzer, 2004 ▸). The conversion of phthalimides via Friedel–Crafts conditions or with organometallics to 2-keto benzoic acid hydrazides or 3,3-disubstituted indolinones, which are viable intermediates to substituted phthalazin-1(2H)-ones, have also been reported (Ismail et al., 1984 ▸; Chun et al., 2004 ▸) . Several other synthetic routes, involving various intermediates, have also been reported (Mylari et al., 1991 ▸; Yamaguchi et al., 1993 ▸; Acosta et al., 1995 ▸; Bele & Darabantu, 2003 ▸; Mahmoodi & Salehpour, 2003 ▸; Cockcroft et al., 2006 ▸; Del Olmo et al., 2006 ▸). In an earlier communication (Asegbeloyin et al., 2018 ▸), the dysprosium(III)-catalysed conversion of 2-{[2-(phenylsulfonyl)hydrazinylidene] methyl}benzoic acid to 2-(phenylsulfonyl)phthalazin-1-(2H)-one was described. In the present study, the title compound, 2-[(2,4,6-trimethylbenzene)sulfonyl]-1,2-dihydrophthalazin-1-one, (I), was obtained by the catalytic conversion of 2-{[2-(2,4,6-trimethylphenylsulfonyl)hydrazinylidene]methyl}benzoic acid. Herein, the crystal and molecular structures of (I) are described as is a detailed analysis of the molecular packing by an evaluation of the calculated Hirshfeld surfaces augmented by a computational chemistry study.
Structural commentary
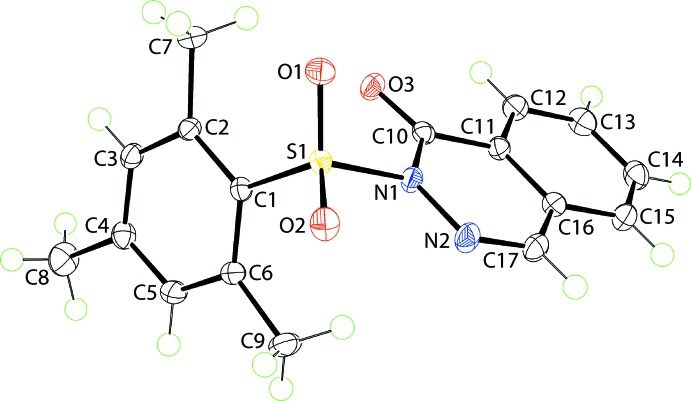
The molecule of (I), Fig. 1 ▸, may be conveniently described as a central SO2 residue with mesityl and phthalazin-1-one substituents. The geometry about the S1 atom is distorted tetrahedral with the range of angles subtended at S1 being a narrow 103.58 (6)° for N1—S1—C1, involving the singly-bonded N1 and C1 atoms, to a wide 118.39 (6)°, for O1—S1—O2, involving the doubly-bonded sulfoxide-O1, O2 atoms. The organic residues lie to the opposite side of the molecule to the SO2 residue, forming dihedral angles of 67.35 (4)° [phthalazin-1-one with r.m.s. deviation = 0.0105 Å] and 49.79 (6)° [mesityl]. The dihedral angle between the organic residues of 83.26 (4)° indicates a close to orthogonal relationship. The N2—N1—C10—O3 torsion angle of −179.88 (12)° indicates a co-planar arrangement for these atoms, which allows for the close approach of the N2 and O3 atoms, i.e. 2.6631 (15) Å, suggestive of a stabilizing contact (Nakanishi et al., 2007 ▸). Globally, the molecule has the shape of the letter V. Within the hetero-ring of the phthalazin-1-one substituent, the N1—N2 bond length is 1.3808 (15) Å and C10—N1 = 1.4003 (17) Å. In each of the C17=N2 [1.2911 (18) Å] and C10=O3 [1.2175 (15) Å] bonds, double-bond character is noted. The bond angles about the N1 atom are non-symmetric, with the endocyclic N2—N1—C10 angle of 126.97 (11) Å being significantly wider than the exocyclic N2—N1—S1 [113.93 (9) Å] and C10—N1—S1 [118.89 (8) Å] angles.
Figure 1.
The molecular structures of (I) showing the atom-labelling scheme and displacement ellipsoids at the 70% probability level.
Supramolecular features
The formation of a supramolecular tape sustained by phthalazinone-C6-C—H⋯O(sulfoxide) contacts, Table 1 ▸, and π(phthalazinone)–π(phthalazinone) stacking is the main feature of the molecular packing in the crystal of (I), Fig. 2 ▸(a). The π-stacking occurs between centrosymmetrically related phthalazinone rings, i.e. between the N2C4 and C6 i rings with an inter-centroid distance = 3.5474 (9) Å, angle of inclination = 1.17 (7)° for symmetry operation (i) 1 − x, 1 − y, 2 − z. As shown in Fig. 2 ▸(b), the tapes inter-digitate along the c-axis direction allowing for putative π-stacking between mesityl rings but, the inter-centroid separation is long at 4.1963 (8) Å. The assemblies shown in Fig. 2 ▸(b) stack along the a-axis direction, again without directional interactions between them, Fig. 2 ▸(c).
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C12—H12⋯O2i | 0.95 | 2.49 | 3.3395 (18) | 149 |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Figure 2.
Molecular packing in the crystal of (I): (a) supramolecular tape sustained by phthalazinone-C—H⋯O(sulfoxide) and π(phthalazinone)–π(phthalazinone) stacking interactions shown as orange and purple dashed lines, respectively, (b) a view of the unit-cell contents down the a axis showing the inter-digitation of tapes and (c) a view of the unit-cell contents down the c axis showing the stacking of assemblies of (b) along the a-axis direction.
Hirshfeld surface analysis
In order to probe the interactions between molecules of (I) in the crystal, the Hirshfeld surfaces and two-dimensional fingerprint plots were calculated with the program Crystal Explorer 17 (Turner et al., 2017 ▸) using established procedures described by Tan et al. (2019 ▸). In addition to the bright-red spots appearing near the sulfoxide-O2 and phthalazinone-H12 atoms on the Hirshfeld surface in Fig. 3 ▸(a),(b), the presence of diminutive red spots near methyl-C7 and benzene-H5 are indicative of intermolecular C—H⋯C contacts as C—H⋯π contacts are not preferred because of the V-shaped molecular geometry of (I). Also, the group of faint-red spots near alternate carbon atoms C10, C12, C14 and C16 of the phthalazinone-C6 ring on the d norm-mapped Hirshfeld surface in Fig. 3 ▸(b) is indicative of short intra-chain C⋯C contacts [Table 2 ▸ and Fig. 2 ▸(a)] and is consistent with the significant contribution from π–π stacking between centrosymmetrically related phthalazinone-N2C4 and C6 rings, encompassing connections between phthalazinone-C6 rings [3.6657 (9) Å with angle of inclination = 0.03 (7)°]. The involvement of the methyl-C8 atom in C—H⋯O [to provide links between the chains shown in Fig. 2 ▸(b)] and C—H⋯C contacts, Table 2 ▸, is highlighted in Fig. 3 ▸(c). The blue and red regions corresponding to positive and negative electrostatic potentials, respectively, on the Hirshfeld surface mapped over electrostatic potential shown in Fig. 4 ▸ represent the involvement of different atoms in the intermolecular interactions in the crystal.
Figure 3.
(a)–(c) Three views of Hirshfeld surface mapped over d norm for (I) in the range −0.128 to + 1.298 arbitrary units. The intermolecular C-H⋯O and short interatomic C⋯C contacts are represented with black dashed lines, and the short interatomic H⋯H, O⋯H/H⋯O and C⋯H/H⋯C contacts with sky-blue, yellow and red dashed lines, respectively.
Table 2. A summary of short interatomic contacts (Å) in (I)a .
| Contact | Distance | Symmetry operation |
|---|---|---|
| C10⋯C14 | 3.345 (2) | 1 − x, 1 − y, 2 − z |
| C12⋯C16 | 3.351 (2) | 1 − x, 1 − y, 2 − z |
| O1⋯H9C | 2.58 | 1 + x, y, z |
| O1⋯H14 | 2.61 | 1 − x, 1 − y, 2 − z |
| O3⋯H8A | 2.60 | −x, 1 − y, 1 − z |
| C5⋯H7C | 2.78 | 1 − x, 2 − y, 1 − z |
| C7⋯H5 | 2.61 | 1 + x, y, z |
| C10⋯H8A | 2.79 | −x, 1 − y, 1 − z |
| H12⋯H9A | 2.20 | x, −1 + y, z |
Notes: (a) The interatomic distances are calculated in Crystal Explorer 17 (Turner et al., 2017 ▸) whereby the X—H bond lengths are adjusted to their neutron values; (b) these interactions correspond to conventional hydrogen bonds.
Figure 4.
(a) and (b) Two views of the calculated electrostatic potential mapped onto the Hirshfeld surface within the isosurface range −0.093 to 0.040 atomic units. The red and blue regions represent negative and positive electrostatic potentials, respectively.
The overall two-dimensional fingerprint plots for (I) and those delineated into H⋯H, O⋯H/H⋯O, C⋯H/H⋯C and C⋯C contacts are illustrated in Fig. 5 ▸(a)–(e), respectively; the percentage contributions from the different interatomic contacts to the Hirshfeld surfaces are summarized in Table 3 ▸. A short interatomic H⋯H contact involving the phthalazinone-H12 and methyl-H9A atoms, Table 2 ▸, appears as a small peak at d e + d i ∼2.2 Å in the fingerprint plot delineated into H⋯H contacts, Fig. 5 ▸(b). In the fingerprint plot delineated into O⋯H/H⋯O contacts illustrated in Fig. 5 ▸(c), a pair of forceps-like tips at d e + d i ∼2.3 Å, indicate the intermolecular C—H⋯O interaction involving the phthalazinone-H12 and sulfoxide-O2 atoms, whereas the other interatomic O⋯H/H⋯O contacts are merged within the plot and appear as a pair of intense blue spikes at d e + d i ∼2.8 Å. Despite the observation that intermolecular C—H⋯π contacts are usually preferred by methyl groups, none are found involving those substituted at (C1–C6) benzene ring in the crystal due to the V-shaped geometry. Rather, the involvement of methyl-C7 and H5A atoms, and benzene-C5 and H7C atoms [to provide links between the chains shown in Fig. 2 ▸(b)] in C—H⋯C interactions, Table 2 ▸, are characterized as the pair of forceps-like flat tips about d e + d i ∼2.8 Å in the fingerprint plot delineated into C⋯H/H⋯C contacts, Fig. 5 ▸(d). The presence of π–π stacking interactions between symmetry-related phthalazinone-N2C4 and C6 rings is also evident as the arrow-shaped distribution of points around d e, d i ∼1.8 Å in the fingerprint plot delineated into C⋯C contacts, Fig. 5 ▸(e). The contribution from other interatomic contacts, summarized in Table 2 ▸, show a negligible effect on the calculated Hirshfeld surface of (I).
Figure 5.
(a) The overall two-dimensional fingerprint plots for (I), and those delineated into (b) H⋯H, (c) O⋯H/H⋯O, (d) C⋯H/H⋯C and (e) C⋯C contacts.
Table 3. Percentage contributions to intermolecular contacts on the Hirshfeld surface calculated for (I).
| Contact | Percentage contribution |
|---|---|
| H⋯H | 44.9 |
| O⋯H/H⋯O | 24.0 |
| C⋯H/H⋯C | 18.1 |
| C⋯C | 6.5 |
| N⋯H/H⋯ N | 4.0 |
| C⋯O/O⋯C | 1.1 |
| C⋯N/N⋯C | 0.7 |
| N⋯N | 0.4 |
| C⋯S/S⋯C | 0.2 |
Computational chemistry
The pairwise interaction energies between the molecules within the crystal of (I) were calculated by summing up four energy components, comprising electrostatic (E ele), polarization (E pol), dispersion (E dis) and exchange–repulsion (E rep) following Turner et al. (2017 ▸). The energies were obtained by using the wave function calculated at the B3LYP/6-31G(d,p) level of theory. The nature and strength of the intermolecular interactions in terms of their energies are quantitatively summarized in Table 4 ▸, where it is clear that the dispersive component makes the major contribution to the interaction energies in the crystal in the absence of conventional hydrogen bonding. It is revealed from the interaction energies listed in Table 4 ▸, that the π–π stacking interaction between phthalazinone-N2C4 and C6 rings and the short interatomic O1⋯H14 contact have the greatest energy. The short interatomic C5⋯H7C, O3⋯H8A and C10⋯H8A contacts also have significant interaction energies due to their participation in inversion-related contacts. Lower energies, compared to above interactions, are calculated for the H12⋯H9A, C7⋯H5 and O1⋯H9C contacts.
Table 4. A summary of interaction energies (kJ mol−1) calculated for (I).
| Contact | R (Å) | E ele | E pol | E dis | E rep | E tot |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cg(N2C4)⋯Cg(C6)i + | ||||||
| Cg(C6)⋯Cg(C6)i + | 8.12 | −28.9 | −5.0 | −64.7 | 48.2 | −60.8 |
| O1⋯H14i | ||||||
| C5⋯H7C ii | 7.84 | −21.3 | −5.5 | −60.9 | 43.5 | −52.8 |
| O3 ⋯H8A iii + | ||||||
| C10 ⋯H8A iii | 7.54 | −10.7 | −2.0 | −56.8 | 32.6 | −42.1 |
| C12—H12⋯O2iv + | ||||||
| H12⋯H9A iv | 8.17 | −4.4 | −4.6 | −20.5 | 18.0 | −14.8 |
| O1⋯H9C v + | ||||||
| C7⋯H5v | 7.98 | −3.1 | −2.0 | −16.9 | 14.2 | −10.6 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 1 − x, 1 − y, 2 − z; (ii) 1 − x, 2 − y, 1 − z; (iii) − x, 1 − y, 1 − z; (iv) x, −1 + y, z; (v) 1 + x, y, z.
Fig. 6 ▸ illustrates the magnitudes of intermolecular energies represented graphically by energy frameworks to highlight the supramolecular architecture of the crystal through cylinders joining the centroids of molecular pairs using red, green and blue colour codes for the components E ele, E disp and E tot, respectively. The images emphasize the importance of dispersion interactions in the molecular packing.
Figure 6.
Perspective views of the energy frameworks calculated for (I), showing the (a) electrostatic force, (b) dispersion force and (c) total energy. The radii of the cylinders are proportional to the relative strength of the corresponding energies and were adjusted to the same scale factor of 50 with a cut-off value of 3 kJ mol−1 within 4 × 4 × 4 unit cells.
Database survey
There is only a single direct analogue to (I) in the crystallographic literature, namely 2-(phenylsulfonyl)phthalazin-1(2H)-one (Asegbeloyin et al., 2018 ▸), (II). A comparison of key geometric parameters for (I) and (II) is given in Table 5 ▸. The data in Table 5 ▸ confirm the closeness of the salient bond lengths, but also show significant differences in the torsion angles about the N1—S1 and C1—S1 bonds, i.e. by up to 18 and 8°, respectively. These conformational differences are highlighted in the overlay diagram of Fig. 7 ▸ and in the dihedral angles between the aromatic residues of 83.26 (4) and 78.12 (4)° for (I) and (II), respectively.
Table 5. A comparison of key geometric parameters (Å, °) for (I) and (II).
| (I) | (II) | |
|---|---|---|
| N1—N2 | 1.3808 (15) | 1.384 (2) |
| C10—O3 | 1.2175 (15 | 1.212 (3) |
| C10—N1 | 1.4003 (17) | 1.406 (2) |
| C17—N2 | 1.2911 (18) | 1.283 (2) |
| N2⋯O2 | 2.6631 (15) | 2.6394 (19) |
| N2—N1—S1—O1 | 120.33 (10) | 138.71 (12) |
| N2—N1—S1—O2 | −5.52 (11) | 9.59 (13) |
| N1—S1—C1—C2 | −111.55 (11) | −103.95 (16) |
| N1—S1—C1—C6 | 69.70 (11) | 76.49 (17) |
Figure 7.
An overlay diagram for (I) (red image) and (II) (blue). The molecules have been overlapped so the hetero-rings are coincident.
Synthesis and crystallization
2-{[2-(2,4,6-Trimethylphenylsulfonyl)hydrazinylidene]methyl}benzoic acid (III) was obtained by a method reported earlier (Asegbeloyin et al., 2018 ▸). Compound (I) was obtained from the following reaction. An ethanol solution (10 ml) of Dy(O2CCH3)3·4H2O (Wako Chemicals, Japan; 1 mmol, 411.692 mg) was added with constant stirring to an ethanol solution (20 ml) of (III) (1,039.2 mg, 3 mmol). The resulting mixture was refluxed for 3 h in an oil bath. The obtained colourless solution was concentrated to afford a colourless precipitate, which was filtered, dried under suction and further dried in vacuo over CaCl2. The precipitates were dissolved in ethanol, the resultant colourless solution was filtered and left at room temperature for 48 h to obtain colourless crystals of (I).
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 6 ▸. The carbon-bound H atoms were placed in calculated positions (C—H = 0.95–0.98 Å) and were included in the refinement in the riding-model approximation, with U iso(H) set to 1.2–1.5U eq(C).
Table 6. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C17H16N2O3S |
| M r | 328.38 |
| Crystal system, space group | Triclinic, P

|
| Temperature (K) | 100 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 7.9782 (4), 8.1711 (5), 12.6661 (7) |
| α, β, γ (°) | 92.214 (2), 93.423 (1), 114.274 (1) |
| V (Å3) | 749.55 (7) |
| Z | 2 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.23 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.38 × 0.12 × 0.08 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker APEXII CCD |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.924, 1.000 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 11665, 5913, 4625 |
| R int | 0.027 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.804 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.048, 0.122, 1.02 |
| No. of reflections | 5913 |
| No. of parameters | 211 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.59, −0.39 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989020005101/lh5956sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989020005101/lh5956Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989020005101/lh5956Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1996401
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Professor Masahiro Yamashita of the Department of Chemistry, Tohoku University, for the X-ray intensity data.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C17H16N2O3S | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 328.38 | F(000) = 344 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.455 Mg m−3 |
| a = 7.9782 (4) Å | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| b = 8.1711 (5) Å | Cell parameters from 5241 reflections |
| c = 12.6661 (7) Å | θ = 2.7–34.7° |
| α = 92.214 (2)° | µ = 0.23 mm−1 |
| β = 93.423 (1)° | T = 100 K |
| γ = 114.274 (1)° | Prism, colourless |
| V = 749.55 (7) Å3 | 0.38 × 0.12 × 0.08 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 4625 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.027 |
| ω scans | θmax = 34.9°, θmin = 1.6° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −12→12 |
| Tmin = 0.924, Tmax = 1.000 | k = −13→7 |
| 11665 measured reflections | l = −19→19 |
| 5913 independent reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.048 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.122 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.02 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0579P)2 + 0.3671P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 5913 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 211 parameters | Δρmax = 0.59 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.39 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.52952 (4) | 0.91549 (4) | 0.73039 (2) | 0.00972 (8) | |
| O1 | 0.70758 (13) | 0.91524 (14) | 0.72487 (8) | 0.01414 (19) | |
| O2 | 0.51875 (14) | 1.07825 (13) | 0.76724 (7) | 0.01422 (19) | |
| O3 | 0.45530 (14) | 0.53580 (14) | 0.72961 (7) | 0.01357 (19) | |
| N1 | 0.42015 (15) | 0.76225 (15) | 0.82277 (8) | 0.0107 (2) | |
| N2 | 0.36966 (17) | 0.83676 (16) | 0.90820 (9) | 0.0138 (2) | |
| C1 | 0.38648 (17) | 0.82486 (17) | 0.61201 (9) | 0.0097 (2) | |
| C2 | 0.44783 (17) | 0.75451 (17) | 0.52613 (10) | 0.0103 (2) | |
| C3 | 0.32852 (18) | 0.69064 (18) | 0.43396 (10) | 0.0116 (2) | |
| H3 | 0.367189 | 0.643377 | 0.375142 | 0.014* | |
| C4 | 0.15518 (18) | 0.69371 (18) | 0.42516 (10) | 0.0126 (2) | |
| C5 | 0.09886 (18) | 0.76139 (19) | 0.51177 (10) | 0.0133 (2) | |
| H5 | −0.020289 | 0.761710 | 0.506665 | 0.016* | |
| C6 | 0.21077 (18) | 0.82878 (18) | 0.60579 (10) | 0.0116 (2) | |
| C7 | 0.63166 (18) | 0.7437 (2) | 0.52408 (11) | 0.0141 (2) | |
| H7A | 0.636640 | 0.683730 | 0.456594 | 0.021* | |
| H7B | 0.647194 | 0.675014 | 0.582699 | 0.021* | |
| H7C | 0.730720 | 0.865470 | 0.531622 | 0.021* | |
| C8 | 0.0315 (2) | 0.6274 (2) | 0.32396 (11) | 0.0190 (3) | |
| H8A | −0.094563 | 0.608096 | 0.337969 | 0.028* | |
| H8B | 0.032099 | 0.513741 | 0.296720 | 0.028* | |
| H8C | 0.076289 | 0.717057 | 0.271317 | 0.028* | |
| C9 | 0.1341 (2) | 0.9043 (2) | 0.69211 (11) | 0.0190 (3) | |
| H9A | 0.184991 | 1.035634 | 0.691039 | 0.028* | |
| H9B | 0.168371 | 0.871735 | 0.761207 | 0.028* | |
| H9C | −0.000599 | 0.854423 | 0.680026 | 0.028* | |
| C10 | 0.40551 (17) | 0.58589 (17) | 0.80886 (10) | 0.0099 (2) | |
| C11 | 0.32443 (17) | 0.47264 (18) | 0.89581 (10) | 0.0106 (2) | |
| C12 | 0.30524 (18) | 0.29500 (18) | 0.89276 (10) | 0.0132 (2) | |
| H12 | 0.343082 | 0.246095 | 0.834285 | 0.016* | |
| C13 | 0.23047 (19) | 0.19062 (19) | 0.97587 (11) | 0.0153 (3) | |
| H13 | 0.216814 | 0.069423 | 0.974185 | 0.018* | |
| C14 | 0.17479 (19) | 0.2621 (2) | 1.06236 (11) | 0.0160 (3) | |
| H14 | 0.123129 | 0.189023 | 1.118763 | 0.019* | |
| C15 | 0.19460 (19) | 0.4382 (2) | 1.06607 (11) | 0.0154 (3) | |
| H15 | 0.157015 | 0.486375 | 1.124986 | 0.018* | |
| C16 | 0.27053 (18) | 0.54625 (18) | 0.98247 (10) | 0.0118 (2) | |
| C17 | 0.2996 (2) | 0.73194 (19) | 0.98264 (10) | 0.0145 (2) | |
| H17 | 0.264466 | 0.781298 | 1.042086 | 0.017* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.00989 (13) | 0.01011 (14) | 0.00894 (13) | 0.00401 (11) | 0.00008 (10) | 0.00083 (10) |
| O1 | 0.0094 (4) | 0.0174 (5) | 0.0147 (4) | 0.0047 (4) | 0.0002 (3) | 0.0018 (4) |
| O2 | 0.0193 (5) | 0.0103 (4) | 0.0128 (4) | 0.0061 (4) | 0.0007 (4) | −0.0004 (3) |
| O3 | 0.0168 (5) | 0.0153 (5) | 0.0105 (4) | 0.0083 (4) | 0.0033 (3) | 0.0004 (3) |
| N1 | 0.0139 (5) | 0.0110 (5) | 0.0083 (4) | 0.0060 (4) | 0.0022 (4) | 0.0010 (4) |
| N2 | 0.0203 (6) | 0.0139 (5) | 0.0094 (4) | 0.0093 (5) | 0.0019 (4) | −0.0013 (4) |
| C1 | 0.0105 (5) | 0.0107 (5) | 0.0082 (5) | 0.0046 (4) | 0.0002 (4) | 0.0007 (4) |
| C2 | 0.0109 (5) | 0.0109 (5) | 0.0106 (5) | 0.0054 (4) | 0.0030 (4) | 0.0023 (4) |
| C3 | 0.0139 (5) | 0.0121 (6) | 0.0094 (5) | 0.0059 (5) | 0.0025 (4) | 0.0006 (4) |
| C4 | 0.0121 (5) | 0.0128 (6) | 0.0113 (5) | 0.0035 (5) | −0.0001 (4) | 0.0009 (4) |
| C5 | 0.0107 (5) | 0.0176 (6) | 0.0130 (5) | 0.0073 (5) | 0.0002 (4) | 0.0008 (5) |
| C6 | 0.0115 (5) | 0.0143 (6) | 0.0107 (5) | 0.0071 (5) | 0.0010 (4) | 0.0005 (4) |
| C7 | 0.0118 (5) | 0.0181 (6) | 0.0151 (5) | 0.0086 (5) | 0.0035 (5) | 0.0016 (5) |
| C8 | 0.0167 (6) | 0.0226 (7) | 0.0134 (6) | 0.0050 (6) | −0.0036 (5) | −0.0036 (5) |
| C9 | 0.0186 (6) | 0.0309 (8) | 0.0138 (6) | 0.0172 (6) | 0.0002 (5) | −0.0043 (5) |
| C10 | 0.0091 (5) | 0.0112 (5) | 0.0094 (5) | 0.0045 (4) | −0.0012 (4) | −0.0005 (4) |
| C11 | 0.0100 (5) | 0.0122 (6) | 0.0094 (5) | 0.0044 (4) | 0.0004 (4) | 0.0010 (4) |
| C12 | 0.0140 (6) | 0.0125 (6) | 0.0132 (5) | 0.0059 (5) | 0.0001 (4) | −0.0003 (4) |
| C13 | 0.0143 (6) | 0.0119 (6) | 0.0185 (6) | 0.0041 (5) | 0.0009 (5) | 0.0038 (5) |
| C14 | 0.0135 (6) | 0.0188 (7) | 0.0149 (6) | 0.0052 (5) | 0.0024 (5) | 0.0069 (5) |
| C15 | 0.0148 (6) | 0.0207 (7) | 0.0116 (5) | 0.0079 (5) | 0.0031 (5) | 0.0020 (5) |
| C16 | 0.0114 (5) | 0.0137 (6) | 0.0108 (5) | 0.0060 (5) | 0.0003 (4) | 0.0006 (4) |
| C17 | 0.0195 (6) | 0.0167 (6) | 0.0103 (5) | 0.0104 (5) | 0.0025 (5) | −0.0008 (4) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—O1 | 1.4273 (10) | C7—H7C | 0.9800 |
| S1—O2 | 1.4300 (10) | C8—H8A | 0.9800 |
| S1—N1 | 1.7422 (11) | C8—H8B | 0.9800 |
| S1—C1 | 1.7646 (12) | C8—H8C | 0.9800 |
| O3—C10 | 1.2175 (15) | C9—H9A | 0.9800 |
| N1—N2 | 1.3808 (15) | C9—H9B | 0.9800 |
| N1—C10 | 1.4003 (17) | C9—H9C | 0.9800 |
| N2—C17 | 1.2911 (18) | C10—C11 | 1.4694 (18) |
| C1—C6 | 1.4130 (18) | C11—C12 | 1.3943 (19) |
| C1—C2 | 1.4142 (17) | C11—C16 | 1.4034 (18) |
| C2—C3 | 1.3975 (18) | C12—C13 | 1.3847 (19) |
| C2—C7 | 1.5066 (18) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| C3—C4 | 1.3913 (19) | C13—C14 | 1.400 (2) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| C4—C5 | 1.3883 (18) | C14—C15 | 1.380 (2) |
| C4—C8 | 1.5055 (19) | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| C5—C6 | 1.3917 (18) | C15—C16 | 1.4059 (19) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| C6—C9 | 1.5125 (18) | C16—C17 | 1.438 (2) |
| C7—H7A | 0.9800 | C17—H17 | 0.9500 |
| C7—H7B | 0.9800 | ||
| O1—S1—O2 | 118.39 (6) | C4—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| O1—S1—N1 | 106.22 (6) | H8A—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| O2—S1—N1 | 104.37 (6) | C4—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| O1—S1—C1 | 112.48 (6) | H8A—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| O2—S1—C1 | 110.28 (6) | H8B—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| N1—S1—C1 | 103.58 (6) | C6—C9—H9A | 109.5 |
| N2—N1—C10 | 126.97 (11) | C6—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| N2—N1—S1 | 113.93 (9) | H9A—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| C10—N1—S1 | 118.89 (8) | C6—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C17—N2—N1 | 116.47 (12) | H9A—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—C2 | 121.56 (11) | H9B—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—S1 | 117.50 (9) | O3—C10—N1 | 120.86 (12) |
| C2—C1—S1 | 120.94 (10) | O3—C10—C11 | 124.94 (12) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 117.37 (12) | N1—C10—C11 | 114.19 (11) |
| C3—C2—C7 | 116.62 (11) | C12—C11—C16 | 120.62 (12) |
| C1—C2—C7 | 126.01 (11) | C12—C11—C10 | 120.00 (11) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 122.42 (12) | C16—C11—C10 | 119.36 (12) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 118.8 | C13—C12—C11 | 119.31 (12) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 118.8 | C13—C12—H12 | 120.3 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 118.48 (12) | C11—C12—H12 | 120.3 |
| C5—C4—C8 | 120.39 (12) | C12—C13—C14 | 120.60 (13) |
| C3—C4—C8 | 121.12 (12) | C12—C13—H13 | 119.7 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 122.33 (12) | C14—C13—H13 | 119.7 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 118.8 | C15—C14—C13 | 120.31 (13) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 118.8 | C15—C14—H14 | 119.8 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 117.83 (11) | C13—C14—H14 | 119.8 |
| C5—C6—C9 | 116.57 (12) | C14—C15—C16 | 119.85 (13) |
| C1—C6—C9 | 125.58 (12) | C14—C15—H15 | 120.1 |
| C2—C7—H7A | 109.5 | C16—C15—H15 | 120.1 |
| C2—C7—H7B | 109.5 | C11—C16—C15 | 119.30 (13) |
| H7A—C7—H7B | 109.5 | C11—C16—C17 | 117.99 (12) |
| C2—C7—H7C | 109.5 | C15—C16—C17 | 122.69 (12) |
| H7A—C7—H7C | 109.5 | N2—C17—C16 | 125.01 (12) |
| H7B—C7—H7C | 109.5 | N2—C17—H17 | 117.5 |
| C4—C8—H8A | 109.5 | C16—C17—H17 | 117.5 |
| O1—S1—N1—N2 | 120.33 (10) | C2—C1—C6—C5 | −0.2 (2) |
| O2—S1—N1—N2 | −5.52 (11) | S1—C1—C6—C5 | 178.53 (10) |
| C1—S1—N1—N2 | −120.99 (10) | C2—C1—C6—C9 | −178.71 (14) |
| O1—S1—N1—C10 | −54.70 (11) | S1—C1—C6—C9 | 0.02 (19) |
| O2—S1—N1—C10 | 179.45 (10) | N2—N1—C10—O3 | −179.88 (12) |
| C1—S1—N1—C10 | 63.98 (11) | S1—N1—C10—O3 | −5.57 (17) |
| C10—N1—N2—C17 | −0.8 (2) | N2—N1—C10—C11 | 0.98 (18) |
| S1—N1—N2—C17 | −175.38 (10) | S1—N1—C10—C11 | 175.29 (9) |
| O1—S1—C1—C6 | −176.04 (10) | O3—C10—C11—C12 | 2.1 (2) |
| O2—S1—C1—C6 | −41.49 (12) | N1—C10—C11—C12 | −178.79 (11) |
| N1—S1—C1—C6 | 69.70 (11) | O3—C10—C11—C16 | −179.23 (12) |
| O1—S1—C1—C2 | 2.71 (13) | N1—C10—C11—C16 | −0.13 (17) |
| O2—S1—C1—C2 | 137.26 (11) | C16—C11—C12—C13 | 0.6 (2) |
| N1—S1—C1—C2 | −111.55 (11) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 179.29 (12) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.74 (19) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −0.1 (2) |
| S1—C1—C2—C3 | −177.95 (10) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | −0.3 (2) |
| C6—C1—C2—C7 | 179.99 (13) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 0.2 (2) |
| S1—C1—C2—C7 | 1.30 (19) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | −0.75 (19) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.3 (2) | C10—C11—C16—C15 | −179.40 (12) |
| C7—C2—C3—C4 | −179.65 (12) | C12—C11—C16—C17 | 177.93 (12) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.6 (2) | C10—C11—C16—C17 | −0.72 (18) |
| C2—C3—C4—C8 | 178.73 (13) | C14—C15—C16—C11 | 0.3 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 1.2 (2) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | −178.29 (13) |
| C8—C4—C5—C6 | −178.16 (13) | N1—N2—C17—C16 | −0.2 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.8 (2) | C11—C16—C17—N2 | 0.9 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C9 | 177.86 (14) | C15—C16—C17—N2 | 179.58 (14) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C12—H12···O2i | 0.95 | 2.49 | 3.3395 (18) | 149 |
Symmetry code: (i) x, y−1, z.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by Sunway University Sdn Bhd grant STR-RCTR-RCCM-001-2019.
References
- Acosta, A., de la Cruz, P., De Miguel, P., Diez-Barra, E., de la Hoz, A., Langa, F., Loupy, A., Majdoub, M., Martin, N., Sanchez, C. & Seoane, C. (1995). Tetrahedron Lett. 36, 2165–2168.
- Asegbeloyin, J. N., Izuogu, D. C., Oyeka, E. E., Okpareke, O. C. & Ibezim, A. (2018). J. Mol. Struct. 1175, 219–229.
- Bele, C. & Darabantu, M. (2003). Heterocycl. Commun. 9, 641–646.
- Brandenburg, K. (2006). DIAMOND. Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Bruker (2002). APEX2 and SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Cherkez, S., Herzig, J. & Yellin, H. (1986). J. Med. Chem. 29, 947–959. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Chun, T. G., Kim, K. S., Lee, S., Jeong, T. S., Lee, H. Y., Kim, Y. H. & Lee, W. S. (2004). Synth. Commun. 34, 1301–1308.
- Cockcroft, X. L., Dillon, K. J., Dixon, L., Drzewiecki, J., Kerrigan, F., Loh, V. M. Jr, Martin, N. M. B., Meneara, K. A. & Smith, G. C. M. (2006). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 16, 1040–1044. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Del Olmo, E., Barboza, B., Ybarra, M. I., Lopez-Perez, J. L., Carron, R., Sevilla, M. A., Bosellid, C. & San Feliciano, A. (2006). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 16, 2786–2790. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Haider, N. & Holzer, W. (2004). Science Synth. 16, 315–372.
- Ismail, M. F., El-Bassiouny, F. A. & Younes, H. A. (1984). Tetrahedron 40, 983–2984.
- Mahmoodi, N. O. & Salehpour, M. J. (2003). Heterocycl. Chem. 40, 875–878.
- Menear, K. A., Adcock, C., Boulter, R., Cockcroft, X., Copsey, L., Cranston, A., Dillon, K. J., Drzewiecki, J., Garman, S., Gomez, S., Javaid, H., Kerrigan, F., Knights, C., Lau, A., Loh, V. M. Jr, Matthews, I. T. W., Moore, S., O’Connor, M. J., Smith, G. C. M. & Martin, N. M. B. (2008). J. Med. Chem. 51, 6581–6591. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Mylari, B. L., Beyer, T. A., Scott, P. J., Aldinger, C. E., Dee, M. F., Siegel, T. W. & Zembrowski, W. J. (1992). J. Med. Chem. 35, 457–465. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Mylari, B. L., Larson, E. R., Beyer, T. A., Zembrowski, W. J., Aldinger, C. E., Dee, M. F., Siegel, T. W. & Singleton, D. H. (1991). J. Med. Chem. 34, 108–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, W., Nakamoto, T., Hayashi, S., Sasamori, T. & Tokitoh, N. (2007). Chem. Eur. J 13, 255–268. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Pakulska, W., Malinowski, Z., Szczesniak, A. K., Czarnecka, E. & Epsztajn, J. (2009). Arch. Pharm. Chem. Life Sci 342, 41–47. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Procopiou, P. A., Browning, C., Buckley, J. M., Clark, K. L., Fechner, L., Gore, P. M., Hancock, A. P., Hodgson, S. T., Holmes, D. S., Kranz, M., Looker, B. E., Morriss, K. M. L., Parton, D. L., Russell, L. J., Slack, R. J., Sollis, S. L., Vile, S. & Watts, C. J. (2011). J. Med. Chem. 54, 2183–2195. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS. University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Tan, S. L., Jotani, M. M. & Tiekink, E. R. T. (2019). Acta Cryst. E75, 308–318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Teran, C., Besada, P., Vila, N. & Costa-Lago, M. C. (2019). Eur. J. Med. Chem 161, 468–478. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Turner, M. J., Mckinnon, J. J., Wolff, S. K., Grimwood, D. J., Spackman, P. R., Jayatilaka, D. & Spackman, M. A. (2017). Crystal Explorer 17. The University of Western Australia.
- Ukita, T., Sugahara, M., Terakawa, Y., Kuroda, T., Wada, K., Nakata, A., Ohmachi, Y., Kikkawa, H., Ikezawa, K. & Naito, K. (1999). J. Med. Chem. 42, 1088-1099. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
- Wu, X.-F., Neumann, H., Neumann, S. & Beller, M. (2012). Chem. Eur. J. 18, 8596-8599. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, M., Kamei, K., Koga, T., Akima, M., Kuroki, T. & Ohi, N. (1993). J. Med. Chem. 36, 4052–4060. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989020005101/lh5956sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989020005101/lh5956Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989020005101/lh5956Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1996401
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report