Abstract
The Drosophila obscura species group shows dramatic variation in karyotype, including transitions among sex chromosomes. Members of the affinis and pseudoobscura subgroups contain a neo-X chromosome (a fusion of the X with an autosome), and ancestral Y genes have become autosomal in species harboring the neo-X. Detailed analysis of species in the pseudoobscura subgroup revealed that ancestral Y genes became autosomal through a translocation to the small dot chromosome. Here, we show that the Y-dot translocation is restricted to the pseudoobscura subgroup, and translocation of ancestral Y genes in the affinis subgroup likely followed a different route. We find that most ancestral Y genes have translocated to unique autosomal or X-linked locations in different taxa of the affinis subgroup, and we propose a dynamic model of sex chromosome formation and turnover in the obscura species group. Our results suggest that Y genes can find unique paths to escape unfavorable genomic environments that form after sex chromosome–autosome fusions.
Keywords: Y chromosome, Drosophila, neo-sex chromosome, Y degeneration
Introduction
Sex chromosomes have formed independently many times from a pair of ordinary autosomes by acquiring a sex-determining gene (Bull 1983). In some species groups, such as many fish or reptiles, the proto-X and proto-Y keep recombining over most of their length and evolve little differentiation beyond the sex-determining gene (homomorphic sex chromosomes) (Kitano and Peichel 2012; Miura 2017). However, once the proto-sex chromosomes stop recombining over part or all of their length, they follow different evolutionary trajectories and differentiate genetically and morphologically (Charlesworth and Charlesworth 2000; Bachtrog 2013). Old Y chromosomes often are characterized by a loss of most of their original genes, an acquisition of male-specific genes, and an accumulation of repeats and heterochromatin. X chromosomes, in contrast, often evolve dosage compensation (Charlesworth and Charlesworth 2000).
Sex chromosome turnover can be frequent in some groups, especially if the X and Y show little differentiation (Vicoso 2019), but is thought to be rare for heteromorphic sex chromosomes (Bachtrog et al. 2014). The highly specialized gene content of old sex chromosomes (i.e., male-fertility genes on the Y) and chromosome-wide regulatory mechanisms (dosage compensation of the X, heterochromatin formation on the Y) is thought to make reversals of highly differentiated sex chromosomes into autosomes increasingly difficult (Bachtrog et al. 2014). Recent genomic studies, however, have uncovered turnover of heteromorphic sex chromosomes in multiple taxa. For example, the identity of the X chromosome was found to have changed multiple times across Diptera clades (Vicoso and Bachtrog 2015).
The evolutionary steps converting an autosome to a sex chromosome have been carefully studied at the molecular level in Drosophila using neo-sex chromosomes (Zhou and Bachtrog 2012, 2015). The fusion of autosomes to either or both of the ancestral sex chromosomes has repeatedly and independently created neo-sex chromosomes (i.e., an X-autosome fusion creates a neo-X, and a Y-autosome fusion creates a neo-Y). Neo-X chromosomes have evolved dosage compensation in multiple Drosophila species (Bone and Kuroda 1996; Marín et al. 1996; Ellison and Bachtrog 2013, 2019), whereas neo-Y chromosomes lose most of their genes, accumulate repetitive DNA, and become heterochromatic (Steinemann and Steinemann 1992; Zhou et al. 2013; Zhou and Bachtrog 2015; Mahajan et al. 2018).
Genomic comparisons, however, have also started to uncover examples in the reverse direction (that is, a sex chromosome reverting back to an autosome). In particular, the dot chromosome in Drosophila, a tiny autosome with strongly suppressed recombination, was ancestrally an X chromosome in flies (Vicoso and Bachtrog 2013). Indeed, multiple unusual features of this autosome can be better understood in light of its evolutionary history, such as the presence of a dosage-compensation machinery on the dot, or its peculiar expression patterns (Larsson et al. 2004; Riddle et al. 2009). Intriguingly, comparative analysis of Y-linked genes across Drosophila species also uncovered a Y to autosome reversion in members of the obscura species group (the affinis and pseudoobscura subgroups; see fig. 1).
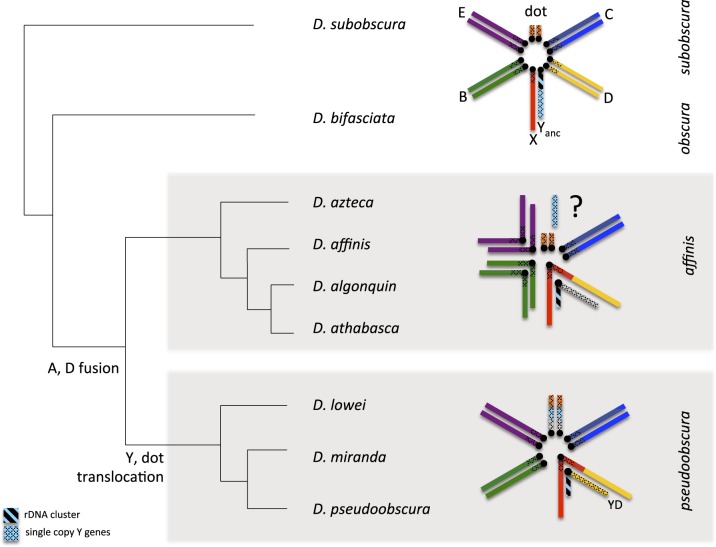
Fig. 1.
—Phylogenetic relationships and model of karyotype evolution of species in the obscura group (male karyotype). Only representative karyotypes that involve transitions of sex chromosomes are drawn (Drosophila subobscura, D. athabasca, D. pseudoobscura). The ancestral Y chromosome contains the repetitive rDNA cluster, and single-copy ancestral genes. Muller elements are color-coded; fragments of unknown origin are in gray.
In particular, five genes (Ary, kl-2, kl-3, Ory, and Ppr-Y) that were ancestrally present on the Y chromosome of Drosophila were found to all be autosomal in several members of the affinis and pseudoobscura subgroups (Carvalho and Clark 2005; Koerich et al. 2008). Detailed follow-up investigation and genomic analysis showed that the ancestral Y genes are incorporated in the dot chromosome in one piece in both Drosophila pseudoobscura and its relative Drosophila miranda, suggesting a chromosomal fusion or translocation creating this reversion (Larracuente et al. 2010; Chang and Larracuente 2017; Mahajan et al. 2018). Interestingly, members of the affinis and pseudoobscura subgroups also share a neo-X chromosome (Patterson and Stone 1952; Buzzati-Traverso and Scossiroli 1955). In an ancestor of these lineages, a former autosome (termed Muller element D) fused to the ancestral X chromosome (Muller element A) ∼15 Ma, and the neo-X has evolved the typical properties of an X (Sturgill et al. 2007; Ellison and Bachtrog 2013) (fig. 1). The fate of its former homolog (the Muller D element in males not fused to the X) was less clear. In some Drosophila species (such as Drosophila americana), X-autosome fusions result in two Y chromosomes (with the unfused chromosome forming a neo-Y), whereas in others (such as Drosophila albomicans and Drosophila busckii), the autosomes fuse to both the ancestral X and Y. Males in the affinis and pseudoobscura subgroups have a single Y chromosome, so it was initially assumed that an unfused neo-Y either completely degenerated, or that the neo-Y became incorporated into the ancestral Y and lost the majority of its genes (Patterson and Stone 1952; Buzzati-Traverso and Scossiroli 1955).
The discovery of a fusion or translocation between the ancestral Y and the dot chromosome led to an alternative hypothesis about the evolution of the Y in that species group (Carvalho and Clark 2005). Namely, it was suggested that the ancestral Y and neo-Y did not fuse after the X-autosome fusion, but that putative problems in meiosis that require pairing of multiple sex chromosomes were avoided by the fusion of the ancestral Y with the dot chromosome, and the current Y is a degenerate remnant of the neo-Y of this clade. Support for this notion came from genomic analysis of gene content of the Y chromosome in D. pseudoobscura, which was found to be enriched for genes from Muller element D (as would be expected if this chromosome formed from the neo-Y) (Mahajan and Bachtrog 2017).
Recent work involving more species, however, hints toward an even more complicated evolutionary history of the sex chromosomes in this clade (Dupim et al. 2018). In particular, although PCR analysis of the five ancestral Y genes confirms their presence in both males and females in most species of the pseudoobscura and affinis clade, some of those genes were found to be Y-linked in two species of the affinis subgroup: Ary, kl-2, and Ory could only be PCR-amplified from males in Drosophila athabasca and Ary and kl-2 showed male-limited PCR-amplification in Drosophila algonquin (Dupim et al. 2018). This was interpreted as the “reappearance of Y-linkage” for some ancestral Y genes, or as the result of a Y duplication with a free copy of the Y chromosome remaining and one copy becoming incorporated into the dot chromosome followed by random inactivation of duplicate Y genes (Dupim et al. 2018). Here, we use genome analysis to reconstruct the evolutionary history of ancestral Y genes in the obscura group (fig. 1) by taking advantage of chromosome-level assemblies for nine different species (or semispecies). Contrary to current belief, our results suggest that the Y-dot fusion/translocation only happened in members of the pseudoobscura clade. Surprisingly, we find that ancestral Y genes independently moved away from the Y chromosome to different locations on the autosomes or the X in different species of the affinis subgroup. This suggests that Y-linkage of some ancestral Y genes in D. athabasca and D. algonquin is likely the ancestral configuration. We propose that the translocation of ancestral Y genes can best be understood as them escaping from the hostile genomic environment of a neo-Y chromosome, where they suffered the deleterious effects of genetic linkage to a large number of selective targets.
Materials and Methods
Seven of the Drosophila obscura group genome assemblies (D. athabasca Eastern-A [EA] and Eastern-B [EB], Drosophila lowei, D. miranda, D. pseudoobscura, Drosophila subobscura, and Drosophila bifasciata) used in our analyses are described in detail in Mahajan et al. (2018) and Bracewell et al. (2019, 2020) and are available through GenBank (accessions: GCA_008121225.1, GCA_008121215.1, GCA_008121275.1, GCA_009664405.1, GCA_008121235.1, GCA_004329205.1, and GCA_003369915.2). For Drosophila affinis, we used a newly generated PacBio-based genome assembly kindly provided by Rob Unckless. For Drosophila azteca, we downloaded the most recent version from GenBank (accession: GCA_005876895.1) and additional details can be found at NCBI Bioproject PRJNA475270. To assign D. azteca contigs/scaffolds to Muller elements, we used D-Genies (Cabanettes and Klopp 2018) to perform whole-genome alignments with our other chromosome-level genome assemblies. During genome alignments and BLAST searches (below), we flagged contig VCKU01000055.1 as chimeric as it is a composite of sequences that map uniquely to different pericentromeric regions on all chromosomes in other assemblies. After identifying the Muller F from all assemblies, we generated alignments and dot plots using MUMmer (Kurtz et al. 2004) with NUCmer -mum -c 200 and mummerplot with the -filter option.
To find ancestral Y genes, we used the annotation file (gtf) and dot (Muller F) assembly from Chang and Larracuente (2017) along with gffread (https://github.com/gpertea/gffread) to generate transcripts of ancestral-Y genes for use in blastn searches with obscura group genome assemblies (above). We retained the longest transcript for these five genes (see supplementary fasta file, Supplementary Material online). To further confirm our blastn results, we downloaded all Drosophila melanogaster translations (r6.30) from FlyBase (flybase.org) and used tblastn to again search all obscura group assemblies. All blastn and tblastn searches had colocalized hits, except for Ppr-Y, which was only found using blastn searches with the obscura group transcript. Results from blastn searches can be found in supplementary table 2, Supplementary Material online. Only hits with ≥80% sequence identify were kept. BLAST searches of D. azteca for kl-3, Ppr-Y, and Ory also returned high-scoring hits to contig VCKU01000055.1 which are not shown due to it likely being an assembly artifact.
To estimate sequencing coverage over genes, we generated whole-genome sequencing data (Illumina) for an individual female of D. azteca and D. affinis, and males and females of D. athabasca. We extracted DNA using a Qiagen DNeasy kit following manufacturer’s recommendations. DNA libraries were prepared using the Illumina TruSeq Nano Prep kit and sequenced on a Hiseq 4000 with 100-bp PE reads. We downloaded D. algonquin Illumina data that have previously been deposited with the SRA (accession SRR5768634). To estimate coverage over genes, we used as a reference the longest D. athabasaca (EB) transcript for each gene from MAKER annotations (Bracewell et al. 2019) along with the D. pseudobscura transcripts for kl-2, Ary, and Ory. We then used BWA MEM (Li and Durbin 2009) to map all paired-end Illumina reads as single-end reads to these transcripts. Samtools (Li et al. 2009) was used to manipulate files and coverage over each transcript (gene) was estimated from the bam files using bedtools genomecov and groupBy (Quinlan and Hall 2010). To estimate coverage for D. melanogaster, we downloaded Illumina data from Wei et al. (2018) (SRA accessions: SRX3492597 and SRX3492598) and used methods outlined above but mapped reads to the longest D. melanogaster transcript for each gene (release 6.31, FlyBase).
We characterized gene expression of the five ancestral Y genes in D. athabasca by analyzing RNA-seq data from Bracewell et al. (2019). We first cleaned raw Illumina reads using SeqyClean (https://github.com/ibest/seqyclean) and then used the HISAT2 (Kim et al. 2015), Samtools (Li et al. 2009), and the StringTie pipeline (Pertea et al. 2015) to estimate FPKM (fragments per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads) for all expressed transcripts. To create de novo transcriptomes and identify ancestral Y gene transcripts from gene expression data from the subobscura subgroup, obscura subgroup, and affinis subgroup, we analyzed male-specific RNA-seq data for Drosophila guanche, D. obscura, and D. athabasca. For D. athabasca and D. obscura, we used testis-specific data, either from above, or downloaded from the SRA (accessions DRX049912 and DRX049913). For D. guanche, we downloaded data generated from whole adult males (accessions: ERX2096111, ERX2096112, and ERX2096113). Raw reads were cleaned using SeqyClean and we constructed de novo transcriptome assemblies using SPAdes version 3.14 (Bankevich et al. 2012) and default settings. We then identified ancestral Y transcripts from each assembly using blastn. Ancestral Y transcripts were aligned using MAFFT version 7 (Katoh and Standley 2013).
Plots of Muller F assemblies and locations of ancestral Y insertions were created using KaryoploteR (Gel and Serra 2017). Genes shown with D. melanogaster gene names are the result from tblastn searches (above) and only top hits with ≥50% sequence identity were plotted. To estimate repeat density in D. azteca, we used Repeatmasker version 4.0.7 (Smith et al. 2013–2015) with the -no_is and -nolow flags and the Repbase Drosophila repeat library (downloaded March 22, 2016, from www.girinst.org). The proportion of repeat-masked bases (Ns) in nonoverlapping windows along the masked genome was determined using bedtools nuc.
Results
Y-Dot Translocation Is Only Present in the pseudoobscura Subgroup
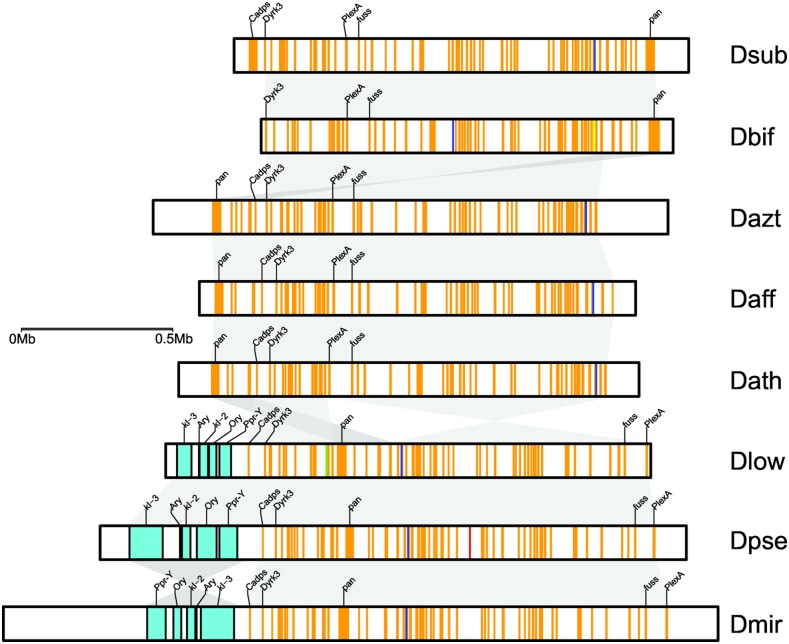
The pseudoobscura subgroup consists of five described species, and we recently completed chromosome-level genome sequences for three of them (Mahajan et al. 2018; Bracewell et al. 2019). For each of the three species (D. lowei, D. miranda, D. pseudoobscura), the dot chromosome was assembled in a single contig (fig. 2, table 1, and supplementary fig. 1, Supplementary Material online). Importantly, in each species, we detect the five ancestral Y genes assembled in a single genomic fragment, ranging from 180 to 357 kb. This fragment is in the same position at the end of each assembled chromosome (adjacent the genes Cadps and Dyrk3) although inverted in D. miranda relative to D. lowei and D. pseudoobscura (fig. 2 and supplementary fig. 2 and table 1, Supplementary Material online). Thus, our analysis supports that ancestral single-copy Y genes fused as a single segment to the dot chromosome in flies of the pseudoobscura subgroup and a lineage-specific inversion changed the linear order of the Y fragment in D. miranda (Larracuente et al. 2010; Chang and Larracuente 2017; Mahajan et al. 2018).
Fig. 2.
—Gene content of the dot chromosome in obscura group flies. Shown is the origin of dot genes (orange = Muller F; turquoise = ancestral Y; red = Muller A; green = Muller B; blue = Muller C; yellow = Muller D). Flies from the pseudoobscura subgroup all contain ancestral Y genes on the dot chromosome (turquoise), which are absent in other obscura group flies, including species from the affinis subgroup. The location of best BLAST hit is shown along with the inferred full-length coordinates for ancestral Y genes. Syntenic blocks (>100 kb) shown in gray. Select genes shown overtop each dot chromosome assembly (see supplementary fig. 1, Supplementary Material online, for all genes).
Table 1.
Genome Assemblies of the Dot Chromosome (Muller Element F)
| Species | Length (bp) | Contigs | Genes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dsub | 1,505,893 | 4 | 90 |
| Dbif | 1,364,133 | 1 | 90 |
| Daff | 1,445,299 | 1 | NA |
| Dath EB | 1,524,173 | 1 | 104 |
| Dath EA | 1,401,577 | 2 | 108 |
| Dlow | 1,606,711 | 1 | 108 |
| Dmir | 2,366,016 | 1 | 119 |
| Dpse | 1,941,385 | 1 | 101 |
| Dazt | 1,705,176 | 1 | NA |
Note.—NA: not available.
As expected, we find no ancestral Y genes on the dot chromosomes in obscura group species that lack the Muller A–D fusion (i.e., D. subobscura or D. bifasciata) and Cadps and/or Dyrk3 are located at the end of the dot chromosome (fig. 2 and table 1). De novo transcriptome assemblies from males generated from a subobscura subgroup species (D. guanche) and an obscura subgroup species (D. obscura) recovered several transcripts with clear sequence similarity to D. melanogaster Y transcripts (supplementary text files, Supplementary Material online), indicating that ancestral Y genes are present in these lineages and located on the Y chromosome. These results are consistent with the hypothesis that the formation of the neo-sex chromosomes causes problems in meiosis, thus driving the fusion or translocation of the ancestral Y chromosome and the dot. Surprisingly, however, we also could not find any ancestral Y genes on the dot chromosome in our high-quality assemblies of two semispecies of D. athabasca (EA and EB), or in a chromosome-level assembly of D. affinis or D. azteca (fig. 2 and table 1). The lack of ancestral Y genes on the dot is unexpected, as the Y-dot translocation is thought to be shared by members of the affinis and pseudoobscura subgroups (Dupim et al. 2018). Previous analyses showed that none of the ancestral Y genes were male-limited in D. affinis and most other species in this subgroup (Dupim et al. 2018). Y-linkage of Ary, kl-2, and Ory in some lineages of the affinis group was interpreted as these genes either gaining Y-linkage secondarily, or as a Y duplication in an ancestor of the affinis/pseudoobscura group followed by random gene inactivation of duplicate Y genes on either the free Y chromosome or the Y copy on the dot (Dupim et al. 2018).
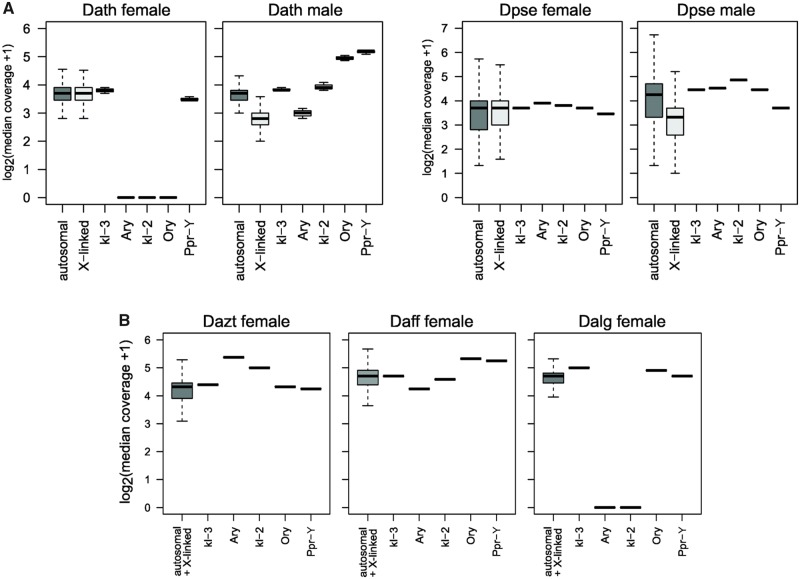
Consistent with the PCR results (Dupim et al. 2018), we find all five ancestral Y genes in female Illumina libraries from D. affinis and D. azteca (fig. 3). Likewise, we detect kl-3, Ory, and Ppr-Y in reads from a female D. algonquin library but not kl-2 or Ary. We find that kl-3 and Ppr-Y are present in female D. athabasca but not Ary, kl-2, and Ory (fig. 3). Each of the ancestral Y genes, however, is clearly present in reads from a male genomic library of D. athabasca, implying that copies of these genes are found on the male-limited Y chromosome. Genomic read coverage suggests that some of the ancestral Y genes may be present in multiple copies. For example, median read coverage in male and female D. athabasca supports one autosomal copy of kl-3, one Y-linked copy of Ary, whereas increased male read coverage suggests two Y-linked copies of kl-2, and multiple Y-linked copies (or parts of) for Ory and Ppr-Y (fig. 3). Likewise, read-coverage analysis supports multiple (possibly partial) copies of Ary and kl-2 in female D. azteca, and possibly multiple (partial) copies of Ory and Ppr-Y in female D. affinis (fig. 3). It is important to note, however, that detecting small changes in copy number (or gene fragments) using read coverage is challenging; when applying these methods to the reference strain of D. melanogaster, we consistently found lower than expected male coverage of ancestral Y genes (supplementary fig. 3, Supplementary Material online).
Fig. 3.
—Sex-linkage of ancestral Y genes in affinis group flies. (A) Shown is sequencing coverage of males and females for genes in Drosophila athabasca and D. pseudoobscura. (B) Shown is genomic coverage of genes for females in D. azteca, D. affinis, and D. algonquin. Outliers not shown for X-linked and autosomal genes.
Independent Incorporation of kl-3 and Ppr-Y on Muller B of D. athabasca
If not on the dot chromosome, where are ancestral Y genes found in affinis group flies? Consistent with our coverage analysis and PCR results (Dupim et al. 2018), we find kl-3 and Ppr-Y to be contained in both of our female assemblies of EA and EB D. athabasca, but not Ary, kl-2, and Ory. Surprisingly, however, both kl-3 and Ppr-Y are located on Muller B, in different chromosomal locations (fig. 4 and supplementary tables 1 and 2, Supplementary Material online). In particular, we find Ppr-Y on the short arm of Muller B (at ∼1.7 Mb), whereas kl-3 is located on the long arm (at ∼37.7 Mb) in the EB assembly, and their locations are conserved in the EA semispecies. Thus, unlike the Y- to dot translocation in the pseudoobscura subgroup, we find that kl-3 and Ppr-Y moved independently away from the Y chromosome to a different autosome in D. athabasca. We could not find Ary, kl-2, and Ory in our female assembly by BLAST (supplementary tables 1 and 2, Supplementary Material online), consistent with our Illumina read mapping and PCR results (Dupim et al. 2018).
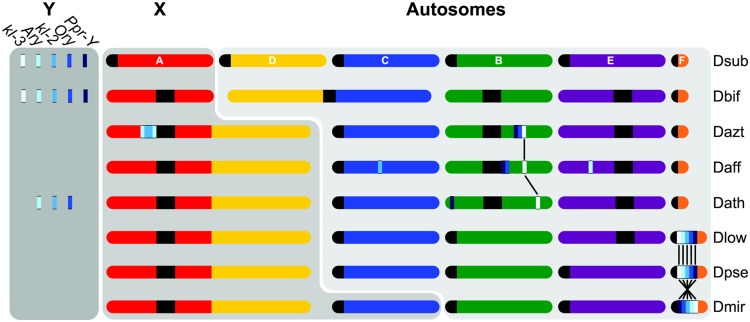
Fig. 4.
—Schematic representation of location of ancestral Y genes in obscura group flies. Shown is the approximate genomic location of the five Yanc genes based on high-quality genome assemblies. The presence/absence of Yanc genes on the Y chromosome is inferred from genomic coverage patterns (fig. 3). Muller elements are color-coded as in figure 1 and identified in Drosophila subobscura. Vertical lines connect genes found in homologous positions. Note that Muller C is a neo-X chromosome in some D. athabasca (similar to D. miranda), but for simplicity is not shown.
Ancestral Y genes in D. melanogaster are expressed almost exclusively in testis (Gatti and Pimpinelli 1992). Testis expression patterns of ancestral Y genes have been conserved for pseudoobscura subgroup flies, where they moved as a single piece to the dot chromosome (Chang and Larracuente 2017; Mahajan et al. 2018). We used RNA-seq data from different male and female samples (male and female whole larvae, male and female adult and larvae heads; adult testis and ovaries) to investigate sex- and tissue-specific expression patterns of ancestral Y genes from both EA and EB D. athabasca. Consistent with these genes having important functions in Drosophila spermatogenesis, we find that they are all highly expressed in testis of D. athabasca (table 2). Thus, the genes that have stayed behind on the Y chromosome (Ary, kl-2, Ory) but also those that moved to an autosome (Ppr-Y, kl-3) have maintained their male-specific expression profile.
Table 2.
Gene Expression of Ancestral Y Genes from Different Tissues and Sexes of Two Drosophila athabasca Semispecies (Eastern-A and Eastern-B)
| kl-3 | Ary | kl-2 | Ory | Ppr-Y | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eastern-B | ||||||
| Male | Whole larvae | 0.8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.3 |
| Male | Larval heads | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Male | Testes | 67.2 | 0 | 11.3 | 39.54 | 73.8 |
| Male | Heads | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.7 |
| Female | Whole larvae | 0.4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Female | Larval heads | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Female | Ovaries | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8.3 |
| Female | Adult heads | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Eastern-A | ||||||
| Male | Whole larvae | 2.5 | 0 | 0.6 | 2.3 | 3.6 |
| Male | Larval heads | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.7 |
| Male | Testes | 81.3 | 10.2 | 12.1 | 44.5 | 292.2 |
| Male | Heads | 1.4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Female | Whole larvae | 0.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Female | Larval heads | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Female | Ovaries | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Female | Adult heads | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Note.—Values are in FPKM (fragments per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads). Values of FPKM > 1 are in bold.
To conclude, our analysis confirms that Ary, kl-2, and Ory are still present in the male genome of D. athabasca but not in females, that is, these genes are located on the Y chromosome in this species. This is consistent with the PCR results of Dupim et al. (2018). However, they assumed that the Y-dot translocation was shared by pseudoobscura/affinis flies and therefore interpreted their PCR screen of Ary, kl-2, and Ory being only present in males as them becoming Y-linked secondarily or as the Y having been duplicated with a free copy and one incorporated into the dot followed by random gene loss. We find no evidence of ancestral Y genes on the dot, indicating that the Y-dot translocation is unique to flies in the pseudoobscura subgroup (but also, see Discussion for an alternative model). We show that kl-3 and Ppr-Y independently became autosomal in D. athabasca, whereas Ary, kl-2, and Ory genes presumably never left the ancestral Y.
Independent Y Gene Gain in D. affinis and D. azteca
In most species in the affinis subgroup (of which D. athabasca is a member), ancestral Drosophila Y genes are present in both sexes (fig. 3) (Carvalho and Clark 2005; Dupim et al. 2018). This was interpreted as a single Y-dot translocation moving all ancestral Y genes to an autosome (Larracuente et al. 2010; Dupim et al. 2018), but a lack of Y genes on the dot of D. athabasca and D. affinis argues against this scenario, and our results from D. athabasca suggest that ancestral Y genes may have been moved independently to autosomal locations in different species. To test this hypothesis, we analyzed high-quality genomes from D. affinis, a sister species to D. athabasca from which it diverged <3 Ma (Beckenbach et al. 1993), and D. azteca (which diverged <6 Ma; Beckenbach et al. 1993), two species for which all ancestral Y genes were found in both sexes. Indeed, we find copies for each ancestral Y gene in the female assembly of both species, but at strikingly diverse genomic locations (fig. 4 and supplementary tables 1 and 2, Supplementary Material online).
In particular, four of the five ancestral Y genes are found on different chromosomal locations in the D. affinis genome: kl-2 is on Muller C (at 9.2 Mb), kl-3 is on Muller B (10.0 Mb), Ary is on Muller E (9.8 Mb), and Ory and Ppr-Y appear to have translocated together onto Muller B (15.6 Mb). Comparisons of flanking regions suggest that the translocation of kl-3 occurred in an ancestor of D. affinis/D. athabasca, as kl-3 is surrounded by the same genes in both species (fig. 5A). Ppr-Y, on the other hand, is found on nonhomologous positions between D. affinis/D. athabasca, suggesting that this gene moved independently to Muller B in the two species. The kl-2 translocation on Muller C in D. affinis appears to have only occurred in this species (fig. 5A).
Fig. 5.
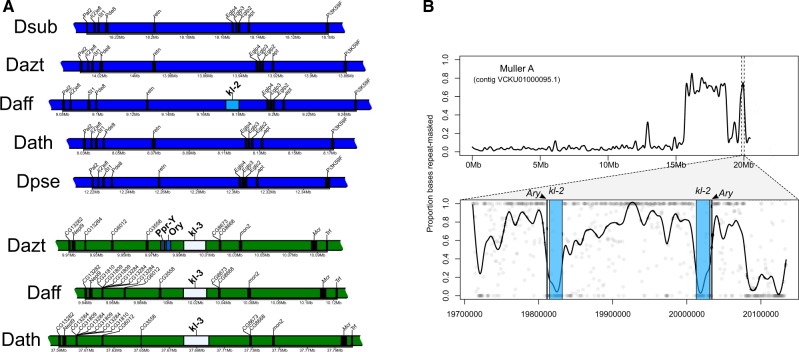
—Details of ancestral Y gene translocations. (A) Local alignments around kl-2 indicate that this gene translocated to a region on Muller C (blue) in Drosophila affinis. Local alignments of the translocation of kl-3 on Muller B (green) show it is in a homologous position in D. azteca, D. affinis, and D. athabasca. Ppr-Y and Ory appear absent from the region in D. affinis and D. athabasca. (B) Ary/kl-2 are duplicated on XL (Muller A) of D. azteca, resembling palindromes found on the human Y chromosome. Shown above is a LOESS smoother fit to the proportion of bases repeat-masked in 500-bp windows. Below highlights the genomic interval harboring Ary/kl-2. Dots show individual 500-bp window estimates with a LOESS smoother fit to the genomic interval.
Likewise, ancestral Y genes in D. azteca are located in different regions of the female genome assembly (fig. 4). Ppr-Y, kl-3, and Ory are found next to each other on Muller B (10.0 Mb), suggesting that they moved in one piece, and comparisons of flanking genes suggest that kl-3 is located on a homologous position in D. affinis and D. athabasca (fig. 5A). Comparisons of this region in the D. pseudoobscura and D. subobscura genomes show that this Y gene translocation occurred at an affinis subgroup-specific inversion breakpoint (i.e., breakpoint relative to the subobscura/pseudoobscura subgroups), which limits our understanding of the size of the translocation. Our findings suggests that kl-3 moved to Muller B in an ancestor of the affinis subgroup, and this initial translocation may have also included Ppr-Y and Ory, which were lost in the lineage leading to D. athabasca. An additional inversion may have moved Ppr-Y and Ory close to the pericentromere in D. affinis (but note that the long arm of Muller B appears completely syntenic between D. affinis and D. azteca, arguing against simple inversions; supplementary fig. 4, Supplementary Material online). Ppr-Y and Ory could also have moved secondarily onto the long arm of Muller B in D. azteca and independently in D. affinis, and Ppr-Y moved independently onto the short arm of Muller B in D. athabasca. Under either scenario, our results support a dynamic evolutionary history of ancestral Y gene movement in flies of the affinis subgroup. In D. azteca, we find that Ary and kl-2 moved together to Muller A (the ancestral X chromosome), and both appear to be duplicated next to each other in opposite directions, with ∼180 kb of sequence in between them (fig. 5B). This insertion appears close to, or in, the pericentromere as the region has high repeat density and shows sequence similarity with pericentromeric regions in D. athabasca and D. affinis (fig. 5B). The sequence in between the Ary/kl-2 duplication is almost entirely composed of repeats (75.1% repeat masked), and may thus be derived from the Y chromosome. The overall arrangement of Ary and kl-2 resembles the palindrome structure of multicopy genes on the human Y chromosome (Rozen et al. 2003; Skaletsky et al. 2003), but it is unclear if this arrangement arose before or after these genes moved onto Muller A.
In summary, the absence of the Y-dot fusion, and a lack of conservation of location for most ancestral Y genes in the affinis subgroup indicates that genes moved away independently from the Y in this clade. Y genes in D. melanogaster can be gigantic, due to huge introns (Gatti and Pimpinelli 1992) and require unique gene expression programs (Fingerhut et al. 2019). Multiple independent translocations of ancestral Y genes suggest that the Y chromosome may have been smaller in obscura subgroup flies compared with D. melanogaster, which is consistent with karyotypic findings (Chang and Larracuente 2017).
Discussion
The obscura species group of Drosophila provides a fascinating clade to study karyotype evolution (Bracewell et al. 2019), and it contains multiple sex chromosome transitions. Neo-sex chromosomes formed independently in different clades, including the fusion of the ancestral X with Muller D roughly 15 Ma, but also more recent fusions of Muller C with the Y chromosome in D. miranda and in some semispecies of D. athabasca, which allows us to reconstruct the events transforming an autosome into differentiated sex chromosomes. Intriguingly, however, we also observe the independent incorporation of ancestral Y genes in different species of affinis and pseudoobscura subgroup flies.
The ancestral Y of Drosophila contains both single-copy genes and the multicopy rDNA cluster (Hennig et al. 1975; Roy et al. 2005; Larracuente et al. 2010). FISH studies have shown that the rDNA cluster is present on both the X and the Y chromosome in multiple species of obscura flies, including members from the obscura, affinis, and pseudoobscura subgroups (Larracuente et al. 2010). This suggests that this is the ancestral configuration of the rDNA cluster, and its location on the Y was maintained even in species where single-copy Y genes translocated to the dot (pseudoobscura subgroup) or other chromosomes (affinis subgroup).
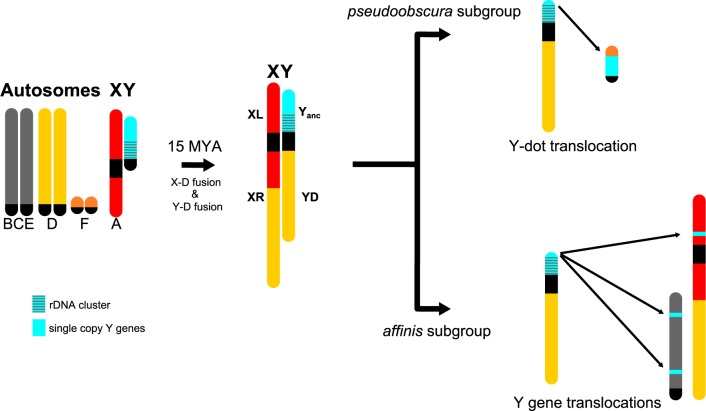
Although we cannot reconstruct the early events of sex chromosome evolution in the obscura group with certainty, we propose the following model that accounts for the genomic location of ancestral and newly formed sex-linked genes (fig. 6). In an ancestor of the affinis/pseudoobscura subgroups, the ancestral X fused to Muller D, and formed the second arm of the X chromosome found in all species belonging to these two subgroups. Such a fusion leaves the unfused Muller D, and the ancestral Y chromosome, and their fate has been less clear. Given Y-linkage of rDNA genes in species from all groups in obscura flies, this suggests that the rDNA cluster was ancestrally on the Y, and all species have incorporated at least part of the ancestral Y into their current Y (Larracuente et al. 2010). Additionally, some species in the affinis subgroup (D. athabasca, D. algonquin) have maintained ancestral single-copy Y genes on their current Y (see above; Dupim et al. 2018). Furthermore, an overabundance of Muller D genes was found on the current Y chromosome of D. pseudoobscura and D. miranda (Carvalho and Clark 2005; Mahajan and Bachtrog 2017; Mahajan et al. 2018), suggesting that Muller D (or part of it) also became incorporated into the Y of pseudoobscura subgroup flies. Thus, the simplest explanation for the current gene content of the Y in species with the X–D fusion is that Muller D also fused to the ancestral Y. Indeed, it is possible that the Y–D fusion actually preceded the X–D fusion, mimicking the current Y-autosome fusions found in D. miranda and D. athabasca, which would leave males with two unlinked X chromosomes. The fusion between either the X or the Y chromosome and Muller D would generate a trivalent in males (i.e., an X–D fusion creates two Y chromosomes in males, whereas a Y–D fusion would create two X’s in males that need to pair with one Y) and create problems in meiosis, resulting in higher rates of aneuploidy. This could rapidly select for a second fusion of Muller D with the unfused sex chromosome, as was experimentally demonstrated in a hybrid population of D. albomicans (a species that contains both a X-autosome and a Y-autosome fusions) and its sister species D. nasuta that lacks neo-sex chromosomes (Yu et al. 1999). If Muller D fused with both the ancestral X and Y, this should alleviate problems associated with segregating a trivalent. Ancestral Y genes then secondarily translocated to autosomal or X-linked locations, either as a single unit to the dot chromosome in an ancestor of the pseudoobscura subgroup, or individually to different chromosomal locations in species of the affinis subgroup (fig. 6). However, other more complicated scenarios are possible, including the Y-dot translocation happening in an ancestor of affinis/pseudoobscura flies, followed by a loss of all ancestral Y genes from the dot in affinis group species (see supplementary fig. 5, Supplementary Material online).
Fig. 6.
—Model of sex chromosome evolution in the obscura group. In an ancestor of the affinis and pseudoobscura subgroups, the ancestral X (Muller A) and Muller D fused ∼15 Ma. We hypothesize that the ancestral Y, which carries the rDNA cluster and single-copy Yanc genes, also fused to Muller D, which would explain Y-linkage of the rDNA cluster in all species, and Y-linkage of Yanc genes in several species. In the pseudoobscura subgroup, single-copy Yanc genes translocated in one fragment to the dot chromosome, leaving behind (fragments of) Yanc genes on the Y chromosome. In the affinis group, Yanc genes moved independently to different autosomal and X-linked locations in different clades/species.
What might drive the relocation of ancestral Y genes? Becoming linked to a gene-rich chromosome will present a novel challenge for genes with important functions in spermatogenesis that have managed to survive for millions of years on a nonrecombining Y chromosome. In particular, evolutionary models to explain the degeneration of a Y are based on interference among selected mutations on a nonrecombining chromosome (Charlesworth 1978; Rice 1987). Theory and computer simulations have shown that the magnitude of selection interference, and thus the rate of degeneration, depends on the number of functional genes present on the Y chromosome (Bachtrog 2008). Gene loss is highest on a gene rich Y chromosome, but declines rapidly as active genes are lost (Bachtrog 2008). Although old, degenerate Y chromosomes may provide safe havens for important male-specific genes, and ancestral Y genes will suffer the deleterious effects of genetic linkage to more selective targets when fused to an autosome containing thousands of functional genes. Their translocation may thus be driven to avoid mutation accumulation and degeneration on the neo-Y where purifying selection is highly impaired. This resembles the fate of a Y gene (kl-5) in the testacea group species of Drosophila that duplicated to the dot chromosome (Dyer et al. 2011). The dot, like the Y chromosome, lacks recombination but contains about seven times more genes. It was shown that slightly deleterious mutations have accumulated in the dot-linked copy of kl-5 faster than in the Y-linked copy (Dyer et al. 2011), consistent with the copy on the dot suffering the deleterious effects of genetic linkage to more selective targets compared with the Y chromosome.
Thus, our findings suggest a turbulent history of Y genes in the obscura group. After being protected from the accumulation of deleterious mutations on the gene-poor ancestral Y for millions of years, linkage to Muller D would have caused massive selective interference and degeneration of these genes. Y genes in the pseudoobscura subgroup escaped to a suboptimal genomic environment on the dot chromosome, whereas ancestral Y genes in the affinis subgroup began to duplicate or translocate to other autosomal locations. Therefore, a highly degenerate Y chromosome may not be as inhospitable as commonly assumed and may instead be a safe haven for male-beneficial genes.
A noticeable commonality between several of the ancestral Y gene translocations is that their autosomal copies are often found near heterochromatin. Ancestral Y genes fused to the heterochromatic dot chromosome in the pseudoobscura subgroup, Ary/kl-2 are adjacent the pericentromere on Muller A in D. azteca, and Ory/Ppr-Y are near the pericentromere on Muller B in D. affinis (fig. 4). In addition, we found fragments of Y-linked genes in the pericentromeres of several other species and a small fragment of Ory even exists in a unique repetitive location on the end of the dot in D. affinis (supplementary table 2, Supplementary Material online). This suggests that ancestral Y genes may have an affinity for heterochromatin, and nonallelic homologous recombination between the repeat-rich Y chromosome and repetitive autosomal regions could facilitate movement of ancestral Y genes. Additionally, heterochromatin may be a preferential location for ancestral Y genes, as their regulatory machinery has evolved in a heterochromatic environment on the ancestral Y.
Acknowledgments
We thank Rob Unckless for providing the D. affinis assembly. This work was supported by National Institutes of Health grants (NIH grants nos. R01GM076007, R01GM101255, and R01GM093182) to D.B.
Supplementary Material
Data deposition: All sequence data generated for this study have been deposited at the NCBI SRA under the NCBI BioProject accession PRJNA589338.
Literature Cited
- Bachtrog D. 2008. The temporal dynamics of processes underlying Y chromosome degeneration. Genetics 179:1513–1525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachtrog D. 2013. Y-chromosome evolution: emerging insights into processes of Y-chromosome degeneration. Nat Rev Genet. 14:113–124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachtrog D, et al. 2014. Sex determination: why so many ways of doing it? PLoS Biol. 12:e1001899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bankevich A, et al. 2012. SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol. 19:455–477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckenbach AT, Wei YW, Liu H.. 1993. Relationships in the Drosophila obscura species group, inferred from mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase II sequences. Mol Biol Evol. 10:619–634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone JR, Kuroda MI.. 1996. Dosage compensation regulatory proteins and the evolution of sex chromosomes in Drosophila. Genetics 144:705–713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bracewell R, Chatla K, Nalley MJ, Bachtrog D.. 2019. Dynamic turnover of centromeres drives karyotype evolution in Drosophila. Elife 8:923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bracewell R, Tran A, Chatla K, Bachtrog D.. 2020. Chromosome-level assembly of Drosophila bifasciata reveals important karyotypic transition of the X chromosome. G3 (Bethesda) 10(3):891–897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull JJ. 1983. Evolution of sex determining mechanisms. Menlo Park: Benjamin/Cummings. [Google Scholar]
- Buzzati-Traverso AA, Scossiroli RE.. 1955. The obscura group of the genus Drosophila. Adv Genet. 7:47–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabanettes F, Klopp C.. 2018. D-GENIES: dot plot large genomes in an interactive, efficient and simple way. PeerJ 6:e4958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho AB, Clark AG.. 2005. Y chromosome of D. pseudoobscura is not homologous to the ancestral Drosophila Y. Science 307:108–110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C-H, Larracuente AM.. 2017. Genomic changes following the reversal of a Y chromosome to an autosome in Drosophila pseudoobscura. Evolution 71:1285–1296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlesworth B. 1978. Model for evolution of Y chromosomes and dosage compensation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 75:5618–5622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlesworth B, Charlesworth D.. 2000. The degeneration of Y chromosomes. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 355:1563–1572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupim EG, et al. 2018. An investigation of Y chromosome incorporations in 400 species of Drosophila and related genera. PLoS Genet. 14:e1007770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyer KA, White BE, Bray MJ, Piqué DG, Betancourt AJ.. 2011. Molecular evolution of a Y chromosome to autosome gene duplication in Drosophila. Mol Biol Evol. 28:1293–1306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison C, Bachtrog D.. 2019. Contingency in the convergent evolution of a regulatory network: dosage compensation in Drosophila. PLoS Biol. 17:e3000094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison CE, Bachtrog D.. 2013. Dosage compensation via transposable element mediated rewiring of a regulatory network. Science 342:846–850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fingerhut JM, Moran JV, Yamashita YM.. 2019. Satellite DNA-containing gigantic introns in a unique gene expression program during Drosophila spermatogenesis. PLoS Genet. 15:e1008028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatti M, Pimpinelli S.. 1992. Functional elements in Drosophila melanogaster heterochromatin. Annu Rev Genet. 26:239–275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gel B, Serra E.. 2017. karyoploteR: an R/Bioconductor package to plot customizable genomes displaying arbitrary data. Bioinformatics 33:3088–3090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennig W, Link B, Leoncini O.. 1975. The location of the nucleolus organizer regions in Drosophila hydei. Chromosoma 51:57–63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh K, Standley DM.. 2013. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Mol Biol Evol. 30:772–780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim D, Langmead B, Salzberg SL.. 2015. HISAT: a fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat Methods. 12:357–360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitano J, Peichel CL.. 2012. Turnover of sex chromosomes and speciation in fishes. Environ Biol Fishes. 94:549–558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerich LB, Wang X, Clark AG, Carvalho AB.. 2008. Low conservation of gene content in the Drosophila Y chromosome. Nature 456:949–951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz S, et al. 2004. Versatile and open software for comparing large genomes. Genome Biol. 5:R12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larracuente AM, Noor MAF, Clark AG.. 2010. Translocation of Y-linked genes to the dot chromosome in Drosophila pseudoobscura. Mol Biol Evol. 27:1612–1620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson J, Svensson MJ, Stenberg P, Mäkitalo M.. 2004. Painting of fourth in genus Drosophila suggests autosome-specific gene regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 101:9728–9733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H, Durbin R.. 2009. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 25:1754–1760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H, et al. 2009. The sequence alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25:2078–2079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahajan S, Bachtrog D.. 2017. Convergent evolution of Y chromosome gene content in flies. Nat Commun. 8:785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahajan S, Wei K-C, Nalley MJ, Gibilisco L, Bachtrog D.. 2018. De novo assembly of a young Drosophila Y chromosome using single-molecule sequencing and chromatin conformation capture. PLoS Biol. 16:e2006348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marín I, Franke A, Bashaw GJ, Baker BS.. 1996. The dosage compensation system of Drosophila is co-opted by newly evolved X chromosomes. Nature 383:160–163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura I. 2017. Sex determination and sex chromosomes in Amphibia. Sex Dev. 11:298–306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson JT, Stone WS.. 1952. Evolution in the genus Drosophila. New York: The Macmillan Company. [Google Scholar]
- Pertea M, et al. 2015. StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat Biotechnol. 33:290–295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan AR, Hall IM.. 2010. BEDTools: a flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics 26:841–842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice WR. 1987. Genetic hitchhiking and the evolution of reduced genetic activity of the Y sex chromosome. Genetics 116:161–167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddle NC, Shaffer CD, Elgin S.. 2009. A lot about a little dot – lessons learned from Drosophila melanogaster chromosome 4. Biochem Cell Biol. 87:229–241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy V, et al. 2005. Evolution of the chromosomal location of rDNA genes in two Drosophila species subgroups: ananassae and melanogaster. Heredity 94:388–395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozen S, et al. 2003. Abundant gene conversion between arms of palindromes in human and ape Y chromosomes. Nature 423:873–876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skaletsky H, et al. 2003. The male-specific region of the human Y chromosome is a mosaic of discrete sequence classes. Nature 423:825–837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A, Hubley R, Green P.. 2013. –2015. RepeatMasker Open-4.0. Available from: httpwww.repeatmasker.org.
- Steinemann M, Steinemann S.. 1992. Degenerating Y chromosome of Drosophila miranda: a trap for retrotransposons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 89:7591–7595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgill D, Zhang Y, Parisi M, Oliver B.. 2007. Demasculinization of X chromosomes in the Drosophila genus. Nature 450:238–241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vicoso B. 2019. Molecular and evolutionary dynamics of animal sex-chromosome turnover. Nat Ecol Evol. 3(12):1632–1641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vicoso B, Bachtrog D.. 2013. Reversal of an ancient sex chromosome to an autosome in Drosophila. Nature 499:332–335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vicoso B, Bachtrog D.. 2015. Numerous transitions of sex chromosomes in Diptera. PLoS Biol. 13:e1002078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei K-C, et al. 2018. Variable rates of simple satellite gains across the Drosophila phylogeny. Mol Biol Evol. 35:925–941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu YC, Lin FJ, Chang HY.. 1999. Stepwise chromosome evolution in Drosophila albomicans. Heredity 83 (Pt 1):39–45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Q, Bachtrog D.. 2012. Sex-specific adaptation drives early sex chromosome evolution in Drosophila. Science 337:341–345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Q, Bachtrog D.. 2015. Ancestral chromatin configuration constrains chromatin evolution on differentiating sex chromosomes in Drosophila. PLoS Genet. 11:e1005331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Q, et al. 2013. The epigenome of evolving Drosophila neo-sex chromosomes: dosage compensation and heterochromatin formation. PLoS Biol. 11:e1001711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.