Abstract
To control and prevent the current COVID-19 pandemic, the development of novel vaccines is an emergent issue. In addition, we need to develop tools that can measure/monitor T-cell and B-cell responses to know how our immune system is responding to this deleterious virus. However, little information is currently available about the immune target epitopes of novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) to induce host immune responses. Through a comprehensive bioinformatic screening of potential epitopes derived from the SARS-CoV-2 sequences for HLAs commonly present in the Japanese population, we identified 2013 and 1399 possible peptide epitopes that are likely to have the high affinity (<0.5%- and 2%-rank, respectively) to HLA class I and II molecules, respectively, that may induce CD8+ and CD4+ T-cell responses. These epitopes distributed across the structural (spike, envelope, membrane, and nucleocapsid proteins) and the nonstructural proteins (proteins corresponding to six open reading frames); however, we found several regions where high-affinity epitopes were significantly enriched. By comparing the sequences of these predicted T cell epitopes to the other coronaviruses, we identified 781 HLA-class I and 418 HLA-class II epitopes that have high homologies to SARS-CoV. To further select commonly-available epitopes that would be applicable to larger populations, we calculated population coverages based on the allele frequencies of HLA molecules, and found 2 HLA-class I epitopes covering 83.8% of the Japanese population. The findings in the current study provide us valuable information to design widely-available vaccine epitopes against SARS-CoV-2 and also provide the useful information for monitoring T-cell responses.
Subject terms: Immunogenetics, High-throughput screening
Introduction
In December 2019, a cluster of several severe pneumonia cases of unknown etiology was found in the city of Wuhan in Hubei province of China. Shortly thereafter, a novel Betacoronavirus, SARS-CoV-2, was identified as a causative microbial agent to cause severe acute respiratory disease. The World Health Organization (WHO) declared the outbreak of a coronavirus disease of 2019 (COVID-19) as public health emergency of international concern and put in place a series of temporary recommendations on January 30. The current outbreak of COVID-19 has nearly 3 million confirmed cases worldwide with more than 200,000 deaths, as of April 27, 2020, according to the WHO. The genome sequences of the SARS-CoV-2 were reported to consist of ~30,000 nucleotides with high sequence similarities to Betacoronavirus, including severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV; 79%) and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV; 50%) [1–3]. The SARS-CoV-2 genome, like other coronaviruses, encodes for multiple structural and nonstructural proteins. The structural proteins include spike protein (S), envelope protein (E), membrane glycoprotein (M), nucleocapsid phosphoprotein (N), and the nonstructural proteins include open reading frame 1ab (ORF1ab), ORF3a, ORF6, ORF7a, ORF8, and ORF10. The previous studies have suggested that SARS-CoV-2 has putatively a similar cell entry mechanism and human cell receptor usage [4, 5].
Many researches are now underway to develop effective interventions for controlling and preventing the COVID-19 pandemic, including therapeutic drugs such as inhibitors of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase or the viral protease, and blockers of virus-cell membrane fusion as well as vaccines, and large scale clinical trials have just begun [6, 7]. For the vaccine design against SARS-CoV-2 and the evaluation of immunogenicity of candidate vaccines, it is important to predict epitopes of SARS-CoV-2 and detect their immune responses to SARS-CoV-2. However, little information is currently available on which parts of the SARS-CoV-2 sequence are important for our immune responses.
Therefore, in the current study, we comprehensively screened potential T cell epitopes from the SARS-CoV-2 sequence using bioinformatic tools, and also assessed the conservation of these epitopes across different coronavirus species, including SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV.
Methods
Coronavirus sequences
Full-length viral nucleotide sequences of SARS-CoV-2 (accession number MN908947 and MN996527-MN996531) [1, 2], SARS-CoV (accession number AY274119, AY278488 and AY390556), bat-derived SARS-like coronavirus (bat-SL-CoV) RaTG13 (accession number MN996532), and MERS-CoV (accession number JX869059) were downloaded from the NCBI GenBank.
Comparison of coronavirus sequences
Alignment of downloaded sequences was done with Genetyx software (version 8.0.0). The similarity among the sequences was visualized using SimPlot software (version 3.5.1) [8], with the consensus sequence of SARS-CoV-2 isolated from Wuhan-Hu-1 (MN908947) as the query.
T cell epitope prediction for SARS-CoV-2
Epitope prediction was carried out using the predicted proteins, including S, E, N, M, and ORFs (corresponding to accession numbers QHD43415-QHD43423, QHI42199) of the reference SARS-CoV-2_Wuhan-Hu-1 (accession number MN908947). To predict HLA-class I epitopes, we selected 7, 10, 8 of human leukocyte antigen-A (HLA-A), HLA-B, HLA-C alleles, respectively, which were reported to be present in more than 5% frequencies in the Japanese population (Supplementary Table 1) [9]. For HLA-class II epitope prediction, we selected 5 and 6 haplotypes of HLA-DPA1-DPB1 and HLA-DQA1-DQB1, respectively, and 7 alleles of HLA-DRB1 that are frequently observed in the Japanese populations (Supplementary Table 1) [9, 10].
Binding affinity to HLA class I molecules was calculated for all 9- and 10-mer peptides from SARS-CoV-2 proteins using NetMHCv4.0 and NetMHCpanv4.0 software [11, 12]. We selected the top 0.5%-ranked epitopes based on the prediction score as strongly binding epitopes. Binding affinity to HLA class II molecules was calculated for all 15-mer peptides from SARS-CoV-2 proteins using NetMHCIIpanv3.1 software [13]. We applied the threshold of top 2%-ranked epitopes based on the prediction score as strong binders.
Mutation analysis
To identify mutations of SARS-CoV-2, we used a total of 6421 SARS-CoV-2 sequences isolated in different areas, including 587 sequences from Asia, 1918 from North America, 3190 from Europe, and 726 from Oceania regions, which were deposited in the Global Initiative on Sharing Avian Influenza Data as of 18 April 2020. We first aligned each of these SARS-CoV-2 sequences to the reference sequence SARS-CoV-2_Wuhan-Hu-1 (accession number MN908947) using BLAT software [14]. After the alignment, we extracted nucleotide sequences corresponding to individual proteins of SARS-CoV-2, translated them to amino acid sequences, and then compared them to reference amino acid sequences of SARS-CoV-2_Wuhan-Hu-1 (accession numbers QHD43415-QHD43423, QHI42199).
Statistical analysis
Fisher’s exact test was used to analyze the enrichment of epitopes and differences of mutation rates of SARS-CoV-2 isolated from different areas. Statistical analysis was carried out using the R statistical environment version 3.6.1.
Results
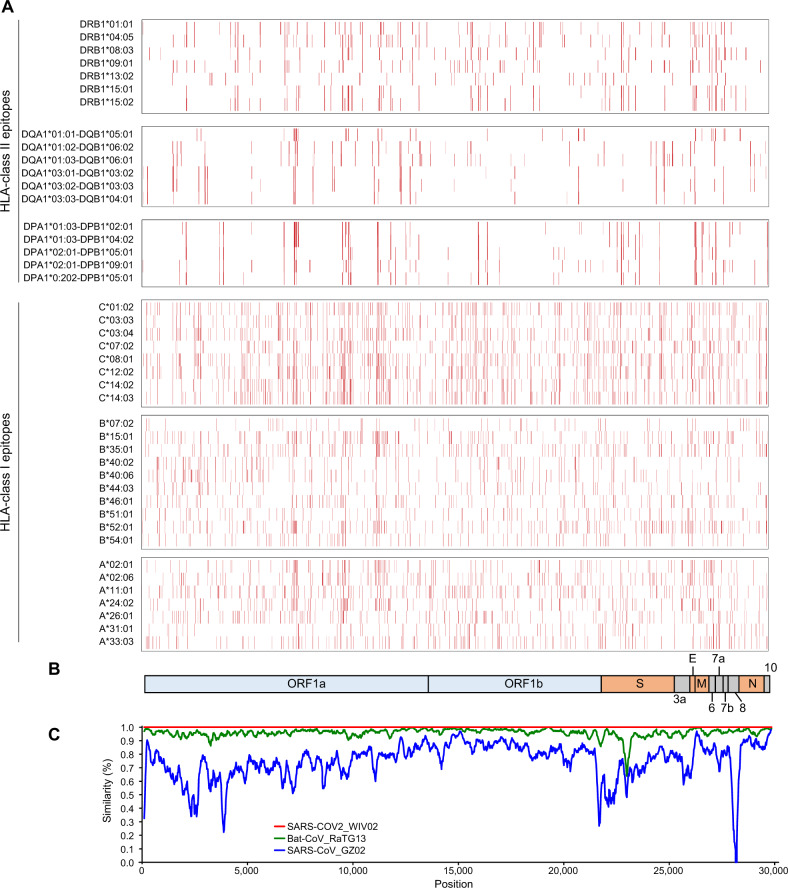
We first screened potential epitopes that are likely to be presented on certain HLA class I molecules, HLA-A, B, and C molecules, which are commonly observed (frequencies of more than 5%) in the Japanese population [9], using netMHC4.0 and netMHCpan4.0 algorithm [11, 12]. We selected the top 0.5%-ranked (high affinity) peptides derived from the SARS-CoV-2 protein sequences and obtained a total of 2013 unique predicted epitopes (Fig. 1, Table 1 and Supplementary Table 2). The predicted epitopes were significantly enriched in the M protein (P = 0.00062, odds ratio = 1.64), whereas less enriched in the N protein (P = 0.0074, odds ratio = 0.69). We then performed a screening of HLA-class II-candidate peptide epitopes that show the high affinity to HLA-DPA1, DPB1, DQA1, DQB1, and DRB1, which are common (frequencies of more than 5%) in the Japanese populations [9, 10], using netMHCIIpan3.1 algorithm [13]. We found a total of 1399 possible HLA-class II epitopes after selecting top 2%-ranked peptides (Fig. 1, Table 1 and Supplementary Table 3). The predicted HLA-class II epitopes were enriched in the M protein (P = 0.000051, odds ratio = 1.92), ORF3a (P = 0.0000016, odds ratio = 2.00), and ORF6 (P = 0.000000039, odds ratio = 4.22), whereas less enriched in the N protein (P = 0.00031, odds ratio = 0.53).
Fig. 1.
Summary of SARS-CoV-2-dreived T cell epitopes. a Distribution of SARS-CoV-2-dreived HLA-class I and II epitopes with the high binding affinity derived from the SARS-CoV-2 protein sequence (SARS-CoV-2_Wuhan-Hu-1) [1]. Red bars represent strong binding affinity epitopes with <0.5% rank and 2% rank, to HLA class I and class II, respectively, for each HLA molecule. b Genomic organization of SARS-CoV-2. ORF, open reading frame, S spike, E envelope, M membrane, N nucleocapsid proteins. c Similarity plot based on the full-length genome sequence of SARS-CoV-2. Genome sequences of SARS-CoV-2_WIV02 (accession number MN996527), SARS-CoV_GZ02 (AY390556), and Bat-CoV_RaTG13 (MN996532) were compared with SARS-CoV-2_Wuhan-Hu-1 (MN908947)
Table 1.
SARS-CoV-2-derived T cell epitopes predicted with high affinity to HLA molecules
| Protein | Length of protein (amino acids) | Number of epitopes | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HLA-class I epitopes (rank ≤ 0.5%) | HLA-class II epitopes (rank ≤ 2%) | ||||||||
| All | HLA-A | HLA-B | HLA-C | All | HLA-DP | HLA-DQ | HLA-DR | ||
| ORF1ab | 7096 | 1478 | 665 | 937 | 588 | 1002 | 268 | 377 | 572 |
| S | 1273 | 248 | 105 | 159 | 110 | 154 | 48 | 54 | 88 |
| ORF3a | 275 | 69 | 30 | 48 | 28 | 74 | 33 | 25 | 46 |
| E | 75 | 18 | 11 | 11 | 5 | 11 | 3 | 0 | 11 |
| M | 222 | 72 | 36 | 35 | 25 | 57 | 16 | 21 | 35 |
| ORF6 | 61 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 28 | 10 | 12 | 13 |
| ORF7a | 121 | 26 | 11 | 18 | 9 | 16 | 10 | 0 | 6 |
| ORF8 | 121 | 22 | 11 | 14 | 10 | 18 | 4 | 10 | 8 |
| N | 419 | 60 | 21 | 35 | 21 | 32 | 4 | 17 | 12 |
| ORF10 | 38 | 12 | 4 | 10 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 2013 | 898 | 1271 | 805 | 1399 | 403 | 516 | 791 | |
Since it is reported that SARS-CoV-2 has about 79% and 50% nucleotide sequence homology to SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, respectively [1–3], we compared the homology of predicted SARS-CoV-2 epitope sequences to 3 SARS-CoVs (BJ01, GZ02, and Tor2) and MERS-CoV to evaluate their cross-reactivities (Table 2 and Supplementary Tables 2 and 3). 781 (38.8%) of the 2013 HLA-class I epitopes are conserved in all the three SARS-CoV sequences. Among them, 633 (81.0%) are located in ORF1ab, and 58 (7.4%), 15 (1.9%), 28 (3.6%), and 33 (4.2%) peptides are located in S, E, M, and N proteins, respectively. 36 (1.8%) of the HLA-class I epitopes show 100% sequence identity to the MERS-CoV protein sequence, and among them, 33 and 3 are located in ORF1ab and S proteins, respectively. Thirty epitopes in ORF1ab are common to both SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV. Among the 1399 possible HLA-class II epitopes, 418 (29.9%) show 100% sequence identity to all the three SARS-CoVs; 362 (86.7%), 40 (11.0%), 4 (1.1%), 4 (1.1%), and 7 (1.9%) are located in ORF1ab, S, E, M, and N proteins, respectively. Ten (2.4%) epitopes, all of which are in ORF1ab, are also conserved in MERS-CoV.
Table 2.
SARS-CoV-2-derived T cell epitopes common to SARS-CoV or MERS-CoV
| Protein | Length of protein (amino acids) | Number of common epitopes to SARS-CoV or MERS-CoV | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HLA-class I epitopes | HLA-class II epitopes | ||||||
| SARS-CoV | MERS-CoV | SARS- and MERS-CoVs | SARS-CoV | MERS-CoV | SARS- and MERS-CoVs | ||
| ORF1ab | 7096 | 633 | 33 | 30 | 362 | 10 | 9 |
| S | 1273 | 58 | 3 | 0 | 40 | 0 | 0 |
| ORF3a | 275 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| E | 75 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| M | 222 | 28 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| ORF6 | 61 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| ORF7a | 121 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| ORF8 | 121 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| N | 419 | 33 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 |
| ORF10 | 38 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 781 | 36 | 30 | 418 | 10 | 9 | |
T cell epitopes, which are likely to be presented commonly on multiple HLA molecules, could cover a larger proportion of individuals/patients. Therefore, we estimated population coverages of SARS-CoV-2-derived, HLA-class I- and II-presented epitopes with high binding affinity on the basis of the allele/haplotype frequencies of HLA (Table 3 and Supplementary Tables 4, 5 and 6). Two epitopes in ORF1ab, ORF1ab2168-2176, and ORF1ab4089-4098, that were predicted to have strong affinity to HLA-A*24:02, HLA-A*02:01, and HLA-A*02:06 showed the highest coverage of 83.8% of the Japanese population. ORF1ab2168-2176 was also predicted as an epitope binding to four HLA-C molecules, including HLA-C*01:02, HLA-C*08:01, HLA-C*12:02, and HLA-C*14:02, which cover 76.5% of the Japanese. Two epitopes in S protein, S268-277, and S448-457, covered more than 70% of Japanese. HLA-oligomers with these peptides are also useful for monitoring the CD8+ T-cell responses in the patients and silently-infected individuals.
Table 3.
SARS-CoV-2-derived HLA-class I epitopes with high coverage of Japanese population based on HLA-A frequency
| Protein | Position in protein | Peptide length | Peptide sequence | Population coveragea | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HLA-A | HLA-B | HLA-C | |||||||
| ORF1ab | 2168 | 9 | YMPYFFTLL | 83.8% | A*02:01, A*02:06, A*24:02 | 0.0% | – | 76.5% | C*01:02, C*08:01, C*12:02, C*14:02 |
| ORF1ab | 4089 | 10 | FTYASALWEI | 83.8% | A*02:01, A*02:06, A*24:02 | 22.0% | B*52:01 | 22.2% | C*12:02 |
| ORF1ab | 3653 | 10 | VYMPASWVMR | 75.7% | A*24:02, A*31:01, A*33:03 | 0.0% | – | 0.0% | – |
| S | 448 | 10 | NYNYLYRLFR | 75.7% | A*24:02, A*31:01, A*33:03 | 0.0% | – | 0.0% | – |
| ORF1ab | 3654 | 10 | YMPASWVMRI | 75.1% | A*02:01, A*24:02 | 14.1% | B*51:01 | 0.0% | – |
| ORF1ab | 1674 | 10 | CYLATALLTL | 75.1% | A*02:01, A*24:02 | 0.0% | – | 0.0% | – |
| ORF1ab | 6418 | 10 | LYLDAYNMMI | 75.1% | A*02:01, A*24:02 | 0.0% | – | 0.0% | – |
| S | 268 | 10 | GYLQPRTFLL | 75.1% | A*02:01, A*24:02 | 0.0% | – | 0.0% | – |
| ORF3a | 106 | 10 | LYLYALVYFL | 75.1% | A*02:01, A*24:02 | 0.0% | – | 0.0% | – |
| ORF1ab | 3605 | 10 | FLYENAFLPF | 72.3% | A*02:06, A*24:02 | 24.3% | B*15:01, B*46:01 | 74.7% | C*03:04, C*07:02, C*08:01, C*12:02, C*14:03 |
| ORF1ab | 3126 | 10 | IQWMVMFTPL | 72.3% | A*02:06, A*24:02 | 33.4% | – | 0.0% | – |
aCalculated based on the allele frequency of HLA (Supplementary Table 1)
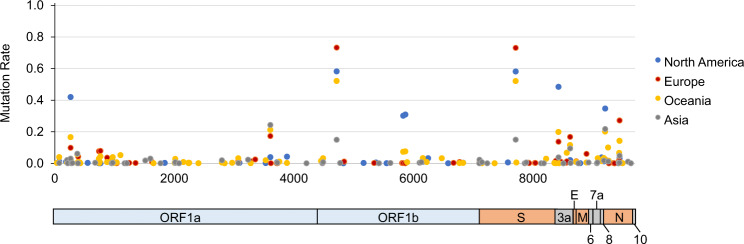
All replicating viruses, including coronavirus, accumulate some mutations that persist due to natural selection, and these mutations contribute to an escape from immune responses. Thus, we finally investigated mutation rates in 6421 SARS-CoV-2 genome sequences isolated from patients/individuals in four different regions, including Asia, North America, Europe, and Oceania, and identified a total of 156 amino acid mutations, which were observed at more than 0.5% frequencies (Fig. 2, Table 4 and Supplementary Table 7). ORF1ab P4715L and S D614G, which were previously reported [15, 16], were commonly found in all the four regions, although the frequencies of ORF1ab 4715L and S 614G types were significantly lower in Asian countries than other countries (15.4% vs. 52.6–73.7%; P = 3.81 × 10−125). ORF1ab P5828L and ORF1ab Y5865C were predominant in only North America (30.6% vs. others 0–7.8%; P = 3.26 × 10−237 and 31.4% vs. 0–8.1%; 5.54 × 10−246, respectively). N P13L was frequently observed in only Oceania (10.5% vs. others 0.13–1.7%; P = 4.41 × 10−64) and N R203K/G204R were observed at higher frequencies in Oceania and Europe compared with the other regions (14.7–27.6% vs. 3.6–5.3%; P = 2.56 × 10−105). We found no mutation in the epitope sequences described above.
Fig. 2.
Distribution of mutation rates of SARS-CoV-2. A total of 6421 SARS-CoV-2 sequences isolated from four different regions; 587 viruses from an Asian region, 1918 from a North American region, 3190 from European countries, and 726 from an Oceanian region, were compared with the reference protein sequence of SARS-CoV-2_Wuhan-Hu-1 [1]. 156 amino acid mutations, which were observed at more than 0.5% frequencies in at least one region, were plotted
Table 4.
Mutations frequently (≥10%) observed in SARS-CoV-2 isolated from four different regions
| Protein | Position in protein | Reference amino acida | Mutant amino acid | Mutation frequency | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asia (N = 587) | North America (N = 1918) | Europe (N = 3190) | Oceania (N = 726) | ||||
| ORF1ab | 265 | T | I | 0.0346 | 0.424 | 0.104 | 0.171 |
| ORF1ab | 3606 | L | F | 0.248 | 0.0438 | 0.178 | 0.17 |
| ORF1ab | 4715 | P | L | 0.154 | 0.587 | 0.737 | 0.526 |
| ORF1ab | 5828 | P | L | 0 | 0.306 | 0.00599 | 0.0783 |
| ORF1ab | 5865 | Y | C | 0 | 0.314 | 0.00530 | 0.0805 |
| S | 614 | D | G | 0.155 | 0.586 | 0.736 | 0.526 |
| ORF3a | 57 | Q | H | 0.0426 | 0.489 | 0.142 | 0.204 |
| ORF3a | 251 | G | V | 0.0991 | 0.0256 | 0.172 | 0.121 |
| ORF8 | 84 | L | S | 0.222 | 0.351 | 0.0295 | 0.206 |
| N | 13 | P | L | 0.0171 | 0.00313 | 0.00126 | 0.105 |
| N | 203 | R | K | 0.0532 | 0.0365 | 0.276 | 0.148 |
| N | 204 | G | R | 0.0532 | 0.0355 | 0.276 | 0.147 |
aProtein sequence based on the reference SARS-CoV-2_Wuhan-Hu-1 sequence (GenBank accession number MN908947)
Discussion
To control the current COVID-19 pandemic and prevent the second pandemic in the near future, the development of new drugs and vaccines, and the establishment of tools investigating the immune responses in patients or silently-infected individuals are urgent issues. Especially, effective vaccination or immunotherapy could play a significant role in suppressing the spread of the virus. Since antibodies recognize cell surface proteins, the targets of antibody-based vaccine were limited. Upon viral infection, the viral proteins express in the infected cells and are processed into small peptides by proteasomes. These peptides are then presented by HLA molecules on the surface of the infected cells and recognized by T cells through their T cell receptors. Thus, the potential T cell epitopes can be derived from any of the viral structural and nonstructural proteins. In this study, using the bioinformatics tools, we comprehensively screened potential SARS-CoV-2-derived, HLA-class I- and II-presented epitopes for 43 HLA alleles that are common in the Japanese population, and identified 2013 and 1399 epitopes, respectively. 781 HLA-class I and 418 HLA-class II epitopes are considered to be common between SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV (Table 2). We found that four epitopes, S1060-1068, S1220-1229, N222-230, and N315-324 of SARS-CoV-2, have exactly same sequences reported as immunogenic SARS-CoV-derived epitopes for HLA-A*02:01, that correspond to S1042-1050, S1203-1211, N223-231, and N317-325 of SARS-CoV, respectively [17, 18]. Interestingly, SARS-CoV-2-derived S1060-1068 epitope is also predicted as high affinity epitopes for HLA-A*02:06 (belonging to the same HLA-A*02 family), HLA-B*52:01, and HLA-C*12:02. In the Japanese population, HLA-A*24:02 is the most common HLA-A molecule with the allelic frequency of 37.8% (implying that 61.3% of the Japanese have at least one HLA-A*24:02 allele), followed by 12.3% and 9.6% of HLA-A*02:01 and HLA-A*02:06, respectively. Two epitopes in ORF1ab, ORF1ab2168-2176, and ORF1ab4089-4098, latter of which is conserved in SARS-CoV, were predicted to have the strong affinity to HLA-A*24:02 as well as HLA-A*02:01 and HLA-A*02:06. Based on their allele frequency, these epitopes could cover 83.8% of the Japanese individuals. Since no mutation was identified in these epitope sequences we identified, these potential candidate epitopes could lead to the contribution to development of rationally designed epitope-based peptide vaccines against SARS-CoV-2. If these epitopes are immunogenic, we are able to use HLA-oligomer with each of these peptides for monitoring T-cell responses in patients and silently-infected individuals. In addition, several reports have suggested that a subset of patients with severe COVID-19 might have a cytokine release syndrome [19, 20]. These HLA-oligomers might be useful to predict and monitor acute T-cell responses in COVID-19 patients who cause these life-threatning symptoms.
In conclusion, through bioinformatic screening, we identified a large number of potential T cell epitopes, some of which could cover other coronavirus spices, including SARS-CoV. These peptides can possibly cover a large proportion of the Japanese population. Although further experimental proof to evaluate immunogenicity of the predicted peptides is required, we hope our findings in the current study could contribute to designing vaccines (DNA or RNA vaccine, inactivated viral vaccines, or peptides vaccines) and evaluating these vaccines, and also to immune monitoring of SARS-CoV2-infected patients.
Supplementary information
Acknowledgements
The super-computing resource was provided by Human Genome Center, the Institute of Medical Science, the University of Tokyo (http://sc.hgc.jp/shirokane.html).
Compliance with ethical standards
Conflict of interest
KK is a scientific advisor of Cancer Precision Medicine, Inc. YN is a stockholder and a scientific advisor of OncoTherapy Science, Inc. This study is unrelated to the activity in these companies.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
The online version of this article (10.1038/s10038-020-0771-5) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
References
- 1.Wu F, Zhao S, Yu B, Chen YM, Wang W, Song ZG, et al. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature. 2020;579:265–9. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2008-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Zhou P, Yang XL, Wang XG, Hu B, Zhang L, Zhang W, et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature. 2020;579:270–3. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lu R, Zhao X, Li J, Niu P, Yang B, Wu H, et al. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet. 2020;395:565–74. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30251-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Letko M, Marzi A, Munster V. Functional assessment of cell entry and receptor usage for SARS-CoV-2 and other lineage B betacoronaviruses. Nat Microbiol. 2020;5:562–9. doi: 10.1038/s41564-020-0688-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hoffmann M, Kleine-Weber H, Schroeder S, Kruger N, Herrler T, Erichsen S, et al. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell. 2020;181:271–80. e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Tu YF, Chien CS, Yarmishyn AA, Lin YY, Luo YH, Lin YT, et al. A review of SARS-CoV-2 and the ogoing clinical trials. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:E2657. doi: 10.3390/ijms21072657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sanders JM, Monogue ML, Jodlowski TZ, Cutrell JB. Pharmacologic treatments for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A review. JAMA. In press 2020. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 8.Lole KS, Bollinger RC, Paranjape RS, Gadkari D, Kulkarni SS, Novak NG, et al. Full-length human immunodeficiency virus type 1 genomes from subtype C-infected seroconverters in India, with evidence of intersubtype recombination. J Virol. 1999;73:152–60. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.1.152-160.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hirata J, Hosomichi K, Sakaue S, Kanai M, Nakaoka H, Ishigaki K, et al. Genetic and phenotypic landscape of the major histocompatibilty complex region in the Japanese population. Nat Genet. 2019;51:470–80. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0336-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Begovich AB, Moonsamy PV, Mack SJ, Barcellos LF, Steiner LL, Grams S, et al. Genetic variability and linkage disequilibrium within the HLA-DP region: analysis of 15 different populations. Tissue Antigens. 2001;57:424–39. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-0039.2001.057005424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Andreatta M, Nielsen M. Gapped sequence alignment using artificial neural networks: application to the MHC class I system. Bioinformatics. 2016;32:511–7. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Jurtz V, Paul S, Andreatta M, Marcatili P, Peters B, Nielsen M. NetMHCpan-4.0: improved peptide-MHC class I interaction predictions integrating eluted ligand and peptide binding affinity data. J Immunol. 2017;199:3360–8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Andreatta M, Karosiene E, Rasmussen M, Stryhn A, Buus S, Nielsen M. Accurate pan-specific prediction of peptide-MHC class II binding affinity with improved binding core identification. Immunogenetics. 2015;67:641–50. doi: 10.1007/s00251-015-0873-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kent WJ. BLAT–the BLAST-like alignment tool. Genome Res. 2002;12:656–64. doi: 10.1101/gr.229202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Pachetti M, Marini B, Benedetti F, Giudici F, Mauro E, Storici P, et al. Emerging SARS-CoV-2 mutation hot spots include a novel RNA-dependent-RNA polymerase variant. J Transl Med. 2020;18:179. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02344-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Phan T. Genetic diversity and evolution of SARS-CoV-2. Infect Genet Evol. 2020;81:104260. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2020.104260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Tsao YP, Lin JY, Jan JT, Leng CH, Chu CC, Yang YC, et al. HLA-A*0201 T-cell epitopes in severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronavirus nucleocapsid and spike proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;344:63–71. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.03.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Cheung YK, Cheng SC, Sin FW, Chan KT, Xie Y. Induction of T-cell response by a DNA vaccine encoding a novel HLA-A*0201 severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus epitope. Vaccine. 2007;25:6070–7. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2007.05.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mehta P, McAuley DF, Brown M, Sanchez E, Tattersall RS, Manson JJ, et al. COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression. Lancet. 2020;395:1033–4. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hirano T, Murakami M. COVID-19: A new virus, but a familiar receptor and cytokine release syndrome. Immunity. In press 2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.