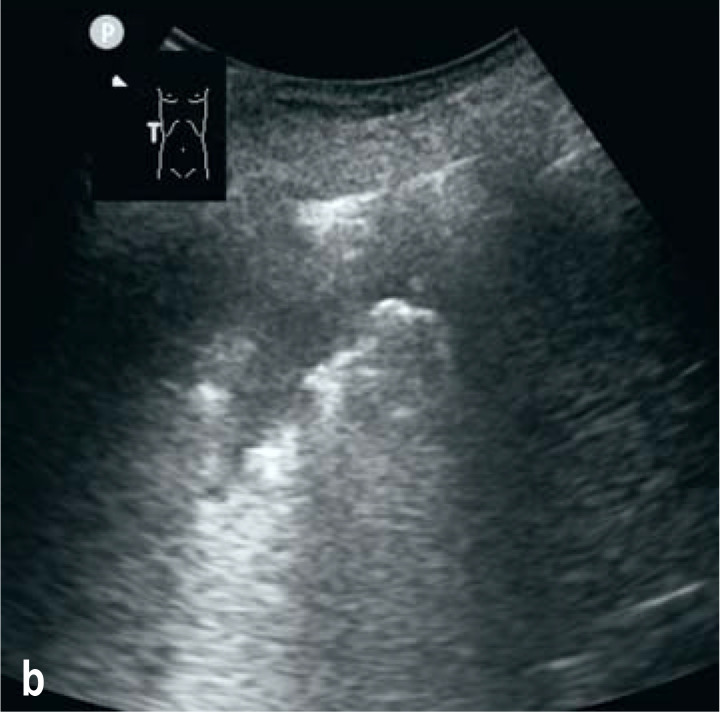
A 76-year-old otherwise healthy man was delivered by ambulance to the emergency room with a 4-day history of fever (up to 39°C), a dry cough, and diarrhea. The main clinical findings were tachypnea and respiratory insufficiency (SpO2 93%, 15 L oxygen with reservoir mask). Laboratory tests detected elevated concentrations of C-reactive protein (86 mg/L) and lactate dehydrogenase (431 U/L); the procalcitonin level was normal. Pulmonary sonography at the bedside revealed areas of jagged fragmentary pleural line with partially confluent B lines, particularly in the upper anterior portion of the left lung; lung sliding was present (Figure a). In adjacent lung areas the sonographic findings were normal. A consolidation with liver-like echo texture and air bronchogram was visualized in the right costophrenic angle (Figure b). A pleural effusion was also seen. This pattern on pulmonary sonography is currently considered indicative of COVID-19 viral pneumonia. Computed tomography confirmed the morphological findings, with ground-glass opacities concentrated in the left upper lobe and a consolidation in the right lower lobe. Despite intensive treatment the patient developed severe acute respiratory distress syndrome and multiorgan failure. He died on day 14 after admission.
Figure a:
Areas of jagged fragmentary pleural line with partially confluent B lines, in the upper anterior portion of the left lung (red arrows). Lung sliding is present.
Figure b:
A consolidation with liver-like echo texture and air bronchogram in the right costophrenic angle.
Footnotes
Conflict of interest statement:
The author declares that no conflict of interest exists.
Translated from the original German by David Roseveare.
Cite this as: Schmid, M: Lung ultrasound findings in COVID-19 pneumonia.