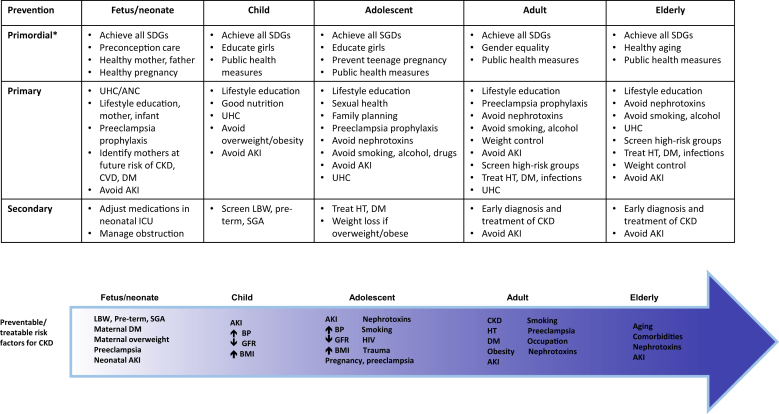
The authors regret an error in Figure 1. A preventable/treatable risk factor for chronic kidney disease in adult women is preeclampsia (incorrectly written as pregnancy in the figure).
The authors would like to apologize for any inconvenience caused.
Figure 1.
Illustration of the spectrum of strategies for chronic kidney disease (CKD) prevention across the life course. ∗Primordial prevention refers to strategies to optimize upstream factors that may lead to increased risk of CKD at an individual- or population-level. AKI, acute kidney injury; ANC, antenatal care; BMI, body mass index; BP, blood pressure; CVD, cardiovascular disease; DM, diabetes mellitus; GFR, glomerular filtration rate; HT, hypertension; ICU, intensive care unit; LBW, low birth weight; SDGs, Sustainable Development Goals37; SGA, small for gestational age at birth; UHC, Universal Health Coverage.