Abstract
Introduction:
World Health Organization has declared COVID-19 a pandemic and a global health emergency. Thus, it is necessary to clearly characterize clinical manifestations and management of COVID-19 infection in children to provide accurate information for healthcare workers. Accordingly, the present study was designed to review articles published on clinical manifestations and characteristics of children and infants with COVID-19.
Methods:
In this systematic review, medical databases including Cochrane Library, Web of Science, Embase, Scopus, SID, Medline, WHO and LitCovid were searched using English and Persian keywords including COVID-19, Pediatrics, Newborn, Coronavirus 2019, 2019-nCoV, SARS-CoV-2. Finally, data of 14 related articles were included in the study.
Results:
A total of 2228 children, newborns and infants were studied. Clinical manifestation in children may be mild (72%), moderate (22%) or severe (6%), and the most common symptoms include dry cough (91%) and fever (96%). According to the included articles, two children had died, one of which was a 14-year-old boy and his exposure history and underlying disease were unclear, and the other was a male newborn with gestational age of 35 weeks and 5 days, birth weight of 2200, Apgar score of 8, 8 (1 min and 5 min) and his first symptom was increased heart rate. No differences were found between male and female children regarding infection with COVID-19.
Conclusion:
Most pediatrics were infected with COVID-19 due to family cluster or history of close contact. Infected children have relatively milder clinical symptoms compared to infected adults. We should pay special attention to early diagnosis and early treatment in children infected with COVID-19.
Key Words: COVID-19, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, Child, Infant, Infant, Newborn, Coronavirus
Introduction
In late December 2019, with the onset of a series of viral pneumonia and the detection of COVID-19, it spread rapidly throughout China and then the world (1-4). World Health Organization has declared COVID-19 a pandemic and a global health emergency (5-8). According to WHO reports, 196 countries and regions have been affected, 413,467 people have been infected worldwide and 18,433 have died up to March 25, 2020 (9). Iran is also one of the major countries involved with COVID-19 and according to official statistics, 23049 cases have been confirmed and 1812 people have died by March 23, 2020 (10). Coronaviruses are RNA viruses from the Coronaviridae family and Coronavirinae subfamily. The novel coronavirus that has spread worldwide after emerging in Wuhan is a beta-coronavirus (11-13). This virus has been labeled as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) as its phylogenetic features are similar to SARS-CoV (14, 15). Infection with COVID-19 can be mild or severe and infected patients have clinical manifestation such as cough, high fever, chest pain, lethargy, weakness, muscular pain and diarrhea (16-18). Many infected children and newborns with COVID-19 have been identified all over the word. Thus, it is necessary to clearly characterize clinical manifestations and management of COVID-19 infection in this age group in order to provide accurate information for neonatologists and pediatricians. Accordingly, the present study was designed to review articles published on clinical manifestations and characteristics of children and infants with COVID-19.
Methods
Study design
The present study is a systematic review that was prepared according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analysis (PRISMA) statement (19).
Search process and search strategy
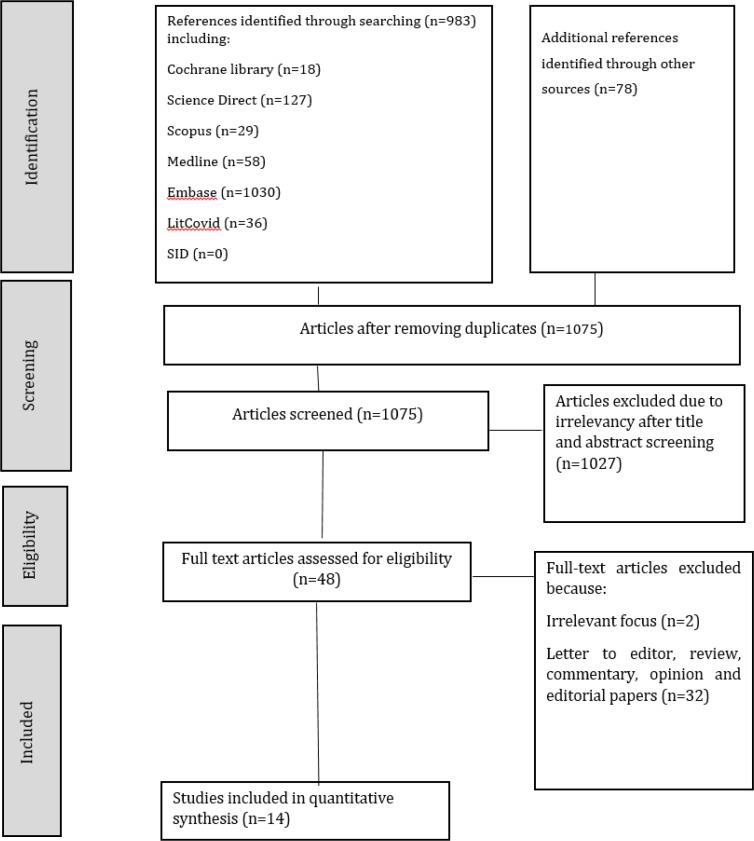
In this review article, a comprehensive search was conducted on medical databases including Cochrane Library, Web of Science, Science Direct, Embase, Scopus, SID, Medline, WHO and LitCovid using English and Persian keywords including COVID-19, children, newborn, child, neonate, infant, adolescent, Coronavirus 2019, 2019-nCoV, SARS-CoV-2 between 1 January and 30 March 2020 using Boolean Logics including AND, OR, NOT. We used this example syntax in searching databases: (COVID-19 OR 2019-nCoV OR Coronavirus 2019 OR SARS-CoV-2) AND (Children OR Child OR Newborn OR Infant OR Neonate OR Adolescents OR Pediatric). Initial search using these keywords yielded 983 articles that were assessed. After reviewing the titles and excluding duplicates, 60 relevant full-text articles remained. 46 of 60 articles were excluded due to lack of relevance to the purpose of the study or being a review article, letter to editor or commentary. Finally, 14 full-text articles were included. Moreover, we searched grey literature and used hand searching on references of articles that yielded 78 articles that were duplicates. Details of the search process are presented in figure 1.
Figure 1.
Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses (PRISMA) flowchart of the present study
Screening and inclusion criteria of articles
Inclusion criteria were: All articles published as case studies, case series, cohorts or observational studies from 1 December 2019 to 30 March 2020 using specific keywords in Persian or English that dealt with characteristics of COVID-19 infection in children. Exclusion criteria were: articles published as letter to editor, review, or commentary. In order to reduce bias, data were collected by two researchers separately (SP and LP) and any disagreement was resolved through discussion with a third author (MA). Most of the articles were performed in China and there were very few studies and reports on children from USA, Italy, France or South Korea, despite the high number of infected patients with COVID-19 in those countries. Among the included studies, 1 article was from Singapore, 1 from Japan and 12 articles were from China.
Quality assessment
We used the three statements of Joanna Briggs Institute critical appraisal tools in order to assess the three types of included studies (case series, case reports and retrospective cohort studies). The quality appraisal tool for case reports, case series and retrospective cohort studies have 8, 10 and 11 items, respectively. Therefore, the total score of quality assessment for articles using these checklists was 8, 10 and 11 respectively. Their answers were: yes, no, unclear or not applicable (20). The quality scores of the evaluated papers are presented in Table 1.
Table 1.
Characteristics of included studies
| Study | Gender/Age | No | Cause | Onset | UD | Severity of disease (%) | Clinical manifestations | ST | QS | Outcome | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dong et al. (2020) (4) China |
Boy (56.6%) Girl (44.4%)/ Median: 7 years |
2143 | Exposed to a COVID-19 case or lived in an epidemic area | 2 days (Range: 0-42 days) |
ND | Asymptomatic: 4.4 Mild: 50.9 moderate: 38.8 |
Fever, respiratory symptoms or digestive symptoms, fatigue | Cohort Study | 7 | Recovered:2142 Died: 1 |
|
| Ji et al. (2020) (23) China |
Two boys: 9 and 15 years-old | 2 | Travel history to COVID-19 center | 1-2 days | No | Mild: 100 | Fever, pharyngeal congestion, mild diarrhea | Case Series | 8 | Recovered: 2 |
|
| Yong Park et al. (2020) (28) Japan |
One 10 year-old girl | 1 | Contact with infected family member | 13 days | ND | Mild: 100 | Fever | Case report | 8 | Recovered: 1 |
|
| Zhu et al. (2020) (33) China |
Boy (80%) Girl (20%)/ One day-old newborn |
10 | Born from infected mother with COVID-19 and close contact after birth | 1-9 days | ND | Mild: 100 | Fever, shortness of breath, thrombocytopenia, rapid heart rate, vomiting | Case series | 8 | Recovered:9 Died: 1 |
|
| Li et al. (2020) (25) China |
One boy and one girl | 2 | Contact with infected family member | 3-10 days | ND | Mild :100 | Cough, runny nose | Case report | 8 | Not discharged yet: 2 |
|
| Liu et al. (2020) (26) China |
2 female/ 2 male: 2 & 11 month, 5 &9 years | 4 | Exposure history | ND | ND | Mild: 100 | Fever, Cough, Fatigue | Cohort | 9 | Recovered: 4 |
|
| Cui et al. (2020) (22) China |
A 55 days-old female infant | 1 | Exposure to her infected parents and family | 17 days | No | Severe:100 | Rhinorrhea, dry cough | Case report | 9 | Recovered: 1 |
|
| Wang et al. (2020) (31) China |
A 36 hours-old male | 1 | Born from infected mother with COVID-19 and close contact after birth | Immediately after birth | No | Mild: 100 | Vomiting | Case report | 8 | Recovered: 1 |
|
| Qiu et al. (2020) (12) China |
Female: 46%; Male: 64%/ Age: 1-16 years | 36 | Close contact with family members and history of exposure to the epidemic area | ND | ND | Mild: 47 Moderate: 53 |
Fever, dry Cough | Cohort Study | 9 | Recovered: 36 |
|
| Kam et al. (2020) (34) Singapore |
A 6 months-old boy | 1 | Close contact with family members | 23 days | No | Mild: 100 | Asymptomatic | Brief report | 8 | Not discharged yet: 1 |
|
| Zhou et al. (2020) (35) China | Female: 66.6% Male: 33.3%/ Median: 1-7 years |
6 | Unknown | 2-13 days | No | Mild: 33.3 Moderate: 50 Severe: 16.6 |
Fever, dry Cough, vomiting | Case report | 8 | Recovered: 6 |
|
| Jiehao et al. (2020)(36) China | Female: 70% Male: 30%/ Median: 6 years |
10 | Close contact with family members and exposure to the epidemic area | 2-10 days | ND | Mild: 40 Moderate: 60 |
Fever, dry Cough, sore throat, stuffy nose, sneezing | Case series | 8 | Recovered: 10 |
|
| Zhang et al. (2020) (37) China | Female: 70% Male:30%/ Median: 6 years |
10 | Born from infected mother with COVID-19 | Immediately after birth | No | Mild: 40 Moderate: 60 |
Fever, vomiting | Case series | 7 | Recovered: 10 |
|
| Tang et al. (2020) (38) China | A 10 year-old boy | 1 | Close contact with infected COVID-19 case | 17 days | ND | Mild: 100 | Asymptomatic | Case report | 7 | Recovered: 1 |
|
ND: Not Determined; UD: underlying disease; QS: Quality score; ST: study type.
Data Extraction
We designed a data extraction form to record information, which included the name of the researchers, country, year of study, type of research, sample size, history of exposure, clinical manifestations, underlying diseases, outcome, and quality assessment score of included studies. We used descriptive statistics to summarize the etiological, demographic, and clinical characteristics of pediatric COVID-19 patients.
Results
Characteristics of included studies
After searching the selected databases using MesH-matching keywords, 983 articles were obtained; furthermore, searching in grey literature and hand searching of references yielded 78 articles. After removing duplicates, 760 articles remained, 712 of which were removed due to irrelevancy to subject. Finally, 48 full-text articles were assessed and 14 full-text articles were included (fig.1) (4, 21-33). The 14 included articles consisted of case studies, case series, correspondence, commentary and letter to editor, which were published about the clinical characteristics and management of children with COVID-19. The characteristics of the studies are presented in Table 1.
Analysis of the reports
A total of 2228 children, newborns and infants were studied. The age range of children was 1 day to 16 years and 70.32% were boys and 29.67% were girls, 740 children (32.1%) had confirmed test of COVID-19 and 1488 (67.9%) were suspicious to COVID-19 infection. Studies have shown that children of all ages are at risk of developing COVID-19, and there is no difference between children of different genders in this regard (4). The mean duration of infection with COVID-19 to diagnosis ranged from 1 to 42 days. Clinical manifestations of COVID-19 in children have been reported as asymptomatic (92%) or with symptoms such as fever (96%), dry cough (91%), fatigue (45%) with mild upper respiratory tract symptoms (66%), abdominal pain (23%), nausea and vomiting (12%) and diarrhea (7%). But the most common manifestation of COVID-19 was reported as fever and cough. According to the included studies, the clinical types of COVID-19 in children were categorized in three domains including: mild (Upper respiratory symptoms such as pharyngeal congestion, sore throat, and fever for a short duration or asymptomatic infection, positive RT-PCR test for SARS-CoV-2, no abnormal radiographic and septic presentation), moderate (Mild pneumonia, symptoms such as fever, cough, fatigue, headache, and myalgia, no complications and manifestations related to severe conditions) and severe (Mild or moderate clinical features, plus any manifestations that suggest disease progression: Rapid breathing (≥70 breaths per min for infants aged <1 year; ≥50 breaths per min for children aged >1 year), Hypoxia, loss of consciousness, depression, coma, convulsions, Dehydration, difficulty eating, gastrointestinal dysfunction, myocardial injury, elevated liver enzymes, coagulation dysfunction, rhabdomyolysis) (12). In the surveyed children, the severity of the disease was reported as mild (72%), moderate (22%) and severe (6%). Most of the children (78%) were asymptomatic and only 5% of asymptomatic children developed clinical symptoms such as dyspnea or hypoxia, and 0.6% developed acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) or multi-organ failure. Also, all articles stated that, based on existing knowledge, the childhood illness is much less severe than that of adults and its cause is unknown. In this regard, we assessed underlying diseases of children, but most of them did not have any underlying disease (42.8%) and some studies did not state if underlying illnesses were present or not (57%). Studies have also shown that lower respiratory tract involvement is rarely seen in children and most of them have upper respiratory tract involvement. Most of the reported cases had improved within 1 to 2 weeks and were discharged from the hospital (99.72%); however, some remained under treatment (0.13%) or had died (0.089%). According to articles, two children had died. One of them was a 14-year-old boy who lived in Hubei province, but no information was provided about his exposure history, underlying disease or comorbidity. The other case was a male newborn with gestational age of 35 weeks and 5 days, birth weight of 2200, and Apgar score of 8, 8 (1 min and 5 min) and his symptoms included increased heart rate (first symptom), refractory shock and gastric bleeding. Other complications included multiple organ failure and disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). This newborn’s mother was 30 years old and had undergone Cesarean section and her first symptom was fever, which began 3 days after delivery. Her umbilical cord, placenta and amniotic fluid were normal. No premature rupture of membranes or intrauterine fetal distress was reported. These finding indicate that the mortality rates in children are very low. Researchers stated that most of the children had been infected with COVID-19 through family cluster infection and close contact with infected people (98.69%); some were infected through travel to epidemic center of COVID-19 (0.089%) or due to an unknown origin (0.26%). In the studied children, for assessing COVID-19 infection, samples were taken from nasopharyngeal secretions in 2208 cases (99.10%), from blood in 2144 cases (96.22%), from stool in 3 cases (0.13%), from saliva in 1 case (0.044%), and from oropharyngeal stations in 19 cases (0.85%). It was notable that in the 3 cases that stool samples were assessed for COVID-19 infection, the result was positive 11-17 days (mean=15day) after symptom onset. So, one of the major concerns is the transmission of COVID-19 in children through fecal–oral route, because viral shedding has been found to take about 2-3 weeks after clinical manifestation of disease. Therefore, fecal–oral transmission should be considered in addition to droplets in transmission of COVID-19 in children and infants. Studies, including predictors of disease severity, have indicated that children with younger age, underlying diseases, and immunodeficiency diseases are at higher risk for severe infection. So, infants and preschool-aged children are at greater risk of developing severe forms of the disease compared to older children. Also, one of the most important methods of screening children with COVID-19 is using exposure history and clinical symptoms, and unlike adults, chest CT scan findings are not valid in children.
Discussion
The present study surveyed the published literature on the clinical characteristics of COVID-19 in infants and children. A literature review of studies demonstrated that children with COVID-19 can be completely asymptomatic or have mild to moderate symptoms that can result in not being diagnosed (undocumented). Findings of Ogimi et al. showed that younger age, especially in children younger than school age, underlying diseases and immunosuppressive diseases are predictors of disease severity (39). In one study, Li et al. indicated that about 86% of early infections with COVID-19 in patients in China were undiagnosed (40). Despite the low risk of infection transmission by undiagnosed cases, they are responsible for 79% of early infections (41). So, this raises concern about asymptomatic children that are taken care of by adults and elderly people, as they can be a source of COVID-19 transmission. According to studies, children make up 2% of COVID-19 cases in China, 1.2% in Italy and 5% in US (9, 42, 43). These statistics are in line with those of SARS epidemic, where only 6.9% of infected patients were children (41).
According to early reports, presence of comorbidities including diabetes, hypertension, chronic respiratory disease and cardiac disease is a risk factor for poor prognosis in the adult population. Studies showed that 67.2% of patients who died from COVID-19 had a comorbidity (44). In our review article, we presented clinical features of children and their comorbidities (if present), but until now, no article has been published on the correlation between comorbidities and disease outcome in children. Clinical manifestations of COVID-19 that have been reported in children and infants include fever, dry cough, fatigue, symptoms of upper respiratory tract infection such as runny nose, and gastrointestinal symptoms such as anorexia, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting. The most common symptoms that have been reported are fever and dry cough. Unlike adults, inferior respiratory tract involvement rarely occurs in children (17, 18, 22, 33). Study of literature indicated that children of all ages were susceptible to COVID-19, but were less likely than adults to develop symptoms (4, 20, 22).
The underlying cause of the lower incidence and milder manifestations of COVID-19 in children is obvious. Children, especially younger children, have been infected with numerous viral infections. It is possible that repetitive exposure to numerous viruses can boost the immune system against SARS-CoV-2 infection. Additionally, studies have shown that SARS-CoV-2 tends to attach to angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), which is premature in children and this may result in a low rate of infection with SARS-CoV-2 (41, 42).
It is very remarkable that various published articles reported high rates of lymphocytopenia. A study by Guan et al., which was performed on 1099 patients with COVID-19, showed that 82.3% of them had lymphocytopenia (45). While, in a study on 171 infected children, only 3.5% showed lymphocytopenia and in a study by Henry et al. only 3% of children had lymphocytopenia (46). So, further studies are needed to assess the role of lymphocytes and severity of COVID-19 in children.
Various studies have also found that most children have been infected with COVID-19 due to family cluster transmission or close contact with the infected patient (20, 23). The study found that viral-shedding occurs more than 4 weeks after the onset of the disease, raising major concerns about fecal-oral transmission of COVID-19 in children. Fecal-oral transmission is especially very important in children who have not yet received toilet training, which is very important for infants and preschool aged children. Therefore, parents need to be well educated in this regard(47).
A study by Dong et al. showed that gender had no effect on the incidence or severity of COVID-19(4). In addition, vertical intrauterine transmission from pregnant mothers to newborns has not been reported yet. According to studies, samples taken from cord blood and placenta of pregnant women with positive COVID-19 had negative results and one study reported that 30 newborns of COVID-19 infected mothers had negative test results. Also, it should be noted that most of these neonates, were born via Caesarean section (40, 48, 49).
According to the findings of Liu et al., paying attention to clinical symptoms and history of exposure to COVID-19 have high diagnostic value in children, while chest CT scan is not able to accurately detect the severity of the disease in children(28). In conclusion, the results of this study indicate that paying attention to children's health is crucial during the COVID-19 pandemic and that effective training should be given to parents.
Limitations
One of the important limitations of our study was that we could not use Chinese databases and journals. Also, we could not study the full-text of some of the Chinese articles and we had to just rely on English-language summaries.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank all those who contributed to this study.
Authors’ contributions
Latif Panahi: Study design, data collection, writing draft of study.
Marzieh Amiri: Study design, data collection, writing draft of study.
Somaye Pouy: Study design, data collection, writing manuscript, supervision of study.
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest.
Funding support
No funding was provided for this study.
References
- 1.Chen Z-M, Fu J-F, Shu Q, Chen Y-H, Hua C-Z, Li F-B, et al. Diagnosis and treatment recommendations for pediatric respiratory infection caused by the 2019 novel coronavirus. World Journal of Pediatrics. 2020:1–7. doi: 10.1007/s12519-020-00345-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Yu A, Wang Z, Ren W, Wu Z, Hu Z, Li L, et al. Epidemic analysis of COVID-19 in China after Wuhan was restricted. 2020:1–19. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chen N, Zhou M, Dong X, Qu J, Gong F, Han Y, et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study. The Lancet. 2020;395(10223):507–713. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Dong Y, Mo X, Hu Y, Qi X, Jiang F, Jiang Z, et al. Epidemiological characteristics of 2143 pediatric patients with 2019 coronavirus disease in China. Pediatrics. 2020 [Google Scholar]
- 5.MacIntyre CR. Global spread of COVID-19 and pandemic potential. Global Biosecurity. 2020;1(3) [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yee J, Unger L, Zadravecz F, Cariello P, Seibert A, Johnson MA, et al. Novel coronavirus 2019 (COVID‐19): Emergence and implications for emergency care. Journal of the American College of Emergency Physicians Open. 2020:1–7. doi: 10.1002/emp2.12034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cucinotta D, Vanelli M. WHO Declares COVID-19 a Pandemic. Acta bio-medica: Atenei Parmensis. 2020;91(1):157–160. doi: 10.23750/abm.v91i1.9397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sohrabi C, Alsafi Z, O’Neill N, Khan M, Kerwan A, Al-Jabir A, et al. World Health Organization declares global emergency: A review of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19) International Journal of Surgery. 2020;76:71–76. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2020.02.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Jung H, Kim J, Jeong S. Factors affected with post-traumatic stress in nurses involved in direct care for Middle East respiratory syndrome patients. Health and Social Welfare Review. 2016;26(4):488–507. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Epidemiology NCoC- Daily Situation Report on Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in Iran. Archives of Academic Emergency Medicine. 2020;8(1):e24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cui J, Li F, Shi Z-L. Origin and evolution of pathogenic coronaviruses. Nature reviews Microbiology. 2019;17(3):181–192. doi: 10.1038/s41579-018-0118-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Zhou D, Zhang P, Bao C, Zhang Y, Zhu N. Emerging Understanding of Etiology and Epidemiology of the Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) infection in Wuhan, China. 2020:2020020283. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chen Y, Liu Q, Guo D. Emerging coronaviruses: genome structure, replication, and pathogenesis. Journal of medical virology. 2020;92(4):418–423. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, Li X, Yang B, Song J, et al. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. New England Journal of Medicine. 2020;382:727–733. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hui DS, I Azhar E, Madani TA, Ntoumi F, Kock R, Dar O, et al. The continuing 2019-nCoV epidemic threat of novel coronaviruses to global health—The latest 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan, China. International Journal of Infectious Diseases. 2020;91:264–266. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.01.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lipsitch M, Swerdlow DL, Finelli L. Defining the epidemiology of Covid-19—studies needed. New England Journal of Medicine. 2020;382:1194–1196. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp2002125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Zhou F, Yu T, Du R, Fan G, Liu Y, Liu Z, et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. The Lancet. 2020;395(10229):1054–1062. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA. 2020;323(13):1239–1242. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.2648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Heymann DL, Shindo N. COVID-19: what is next for public health? The Lancet. 2020 doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30374-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Peiris JS, Yuen KY, Osterhaus AD, Stöhr K. The severe acute respiratory syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine. 2003;349(25):2431–2441. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra032498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Cai J, Xu J, Lin D, Xu L, Qu Z, Zhang Y, et al. A Case Series of children with 2019 novel coronavirus infection: clinical and epidemiological features. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2020:ciaa198. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Cui Y, Tian M, Huang D, Wang X, Huang Y, Fan L, et al. A 55-Day-Old Female Infant infected with COVID 19: presenting with pneumonia, liver injury, and heart damage. The Journal of infectious diseases. 2020:jiaa113. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ji L-N, Chao S, Wang Y-J, Li X-J, Mu X-D, Lin M-G, et al. Clinical features of pediatric patients with COVID-19: a report of two family cluster cases. World Journal of Pediatrics. 2020:1–4. doi: 10.1007/s12519-020-00356-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kam K-q, Yung CF, Cui L, Tzer Pin Lin R, Mak TM, Maiwald M, et al. A Well Infant with Coronavirus Disease 2019 with High Viral Load. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2020:ciaa201. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Li Y, Guo F, Cao Y, Li L, Guo Y. Insight into COVID‐2019 for pediatricians. Pediatric Pulmonology. . 2020:1–4. doi: 10.1002/ppul.24734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Liu H, Liu F, Li J, Zhang T, Wang D, Lan W. Clinical and CT imaging features of the COVID-19 pneumonia: Focus on pregnant women and children. Journal of infection. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.03.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Liu W, Zhang Q, Chen J, Xiang R, Song H, Shu S, et al. Detection of Covid-19 in children in early January 2020 in Wuhan, China. New England Journal of Medicine. 2020;382:1370–1371. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2003717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Park JY, Han MS, Park KU, Kim JY, Choi EH. First pediatric case of coronavirus disease 2019 in Korea. Journal of Korean Medical Science. 2020;35(11):e124. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Qiu H, Wu J, Hong L, Luo Y, Song Q, Chen D. Clinical and epidemiological features of 36 children with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Zhejiang, China: an observational cohort study. The Lancet Infectious Diseases. . 2020:1–8. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30198-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Tang A, Tong Z, Wang H, Dai Y, Li K, Liu J, et al. Detection of Novel Coronavirus by RT-PCR in Stool Specimen from Asymptomatic Child, China. Emerging infectious diseases. 2020;26(6) doi: 10.3201/eid2606.200301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Wang S, Guo L, Chen L, Liu W, Cao Y, Zhang J, et al. A case report of neonatal COVID-19 infection in China. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2020 doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Zhang L, Jiang Y, Wei M, Cheng B, Zhou X, Li J, et al. Analysis of the pregnancy outcomes in pregnant women with COVID-19 in Hubei Province. Zhonghua fu chan ke za zhi. 2020;55:E009–E. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112141-20200218-00111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zhu H, Wang L, Fang C, Peng S, Zhang L, Chang G, et al. Clinical analysis of 10 neonates born to mothers with 2019-nCoV pneumonia. Translational pediatrics. 2020;9(1):51–60. doi: 10.21037/tp.2020.02.06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Zhang Jj, Dong X, Cao YY, Yuan Yd, Yang Yb, Yan Yq, et al. Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected by SARS‐CoV‐2 in Wuhan, China. Allergy. 2020;00:1–12. doi: 10.1111/all.14238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Jin J-M, Bai P, He W, Wu F, Liu X-F, Han D-M, et al. Gender differences in patients with COVID-19: Focus on severity and mortality. medRxiv. 2020:02.23.20026864. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.00152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Li J-PO, Lam DSC, Chen Y, Ting DSW. Novel Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): The importance of recognising possible early ocular manifestation and using protective eyewear. BMJ. 2020;104:297–298. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2020-315994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Zhou F, Yu T, Du R, Fan G, Liu Y, Liu Z, et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. 2020;395(10229):1054–1062. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Chan JF-W, Yuan S, Kok K-H, To KK-W, Chu H, Yang J, et al. A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: a study of a family cluster. The Lancet. 2020;395(10223):514–523. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30154-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Ogimi C, Englund JA, Bradford MC, Qin X, Boeckh M, Waghmare A. Characteristics and outcomes of coronavirus infection in children: the role of viral factors and an immunocompromised state. Journal of the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society. 2019;8(1):21–28. doi: 10.1093/jpids/pix093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Liu W, Tao Z-W, Lei W, Ming-Li Y, Kui L, Ling Z, et al. Analysis of factors associated with disease outcomes in hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus disease. Chinese Medical Journal. 2020 doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Huang L, rong Liu H. Emotional responses and coping strategies of nurses and nursing college students during COVID-19 outbreak. medRxiv. 2020 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Liu Z, Han B, Jiang R, Huang Y, Ma C, Wen J, et al. Mental Health Status of Doctors and Nurses During COVID-19 Epidemic in China. Available at SSRN. 2020:3551329. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Li Z, Ge J, Yang M, Feng J, Qiao M, Jiang R, et al. Vicarious traumatization in the general public, members, and non-members of medical teams aiding in COVID-19 control. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.03.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Maunder RG, Lancee WJ, Balderson KE, Bennett JP, Borgundvaag B, Evans S, et al. Long-term psychological and occupational effects of providing hospital healthcare during SARS outbreak. Emerging infectious diseases. 2006;12(12):1924. doi: 10.3201/eid1212.060584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.France NEM, Byers D, Kearney B, Myatt SU. Creating a Healing Environment: Nurse-to-Nurse Caring in the Critical Care Unit. Int J Hum Caring. (1):44–48. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. The Lancet. 2020;395(10223):497–506. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Xing Y-H, Ni W, Wu Q, Li W-J, Li G-J, Wang W-D, et al. Prolonged Viral Shedding in Feces of Pediatric Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019. Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and Infection. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2020.03.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Jin J-M, Bai P, He W, Liu S, Wu F, Liu X-F, et al. Higher severity and mortality in male patients with COVID-19 independent of age and susceptibility. medRxiv. 2020 [Google Scholar]
- 49.Kim Y. Nurses' experiences of care for patients with Middle East respiratory syndrome-coronavirus in South Korea. American journal of infection control. 2018;46(7):781–787. doi: 10.1016/j.ajic.2018.01.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]