Abstract
Among Polyomaviridae family of viruses, Merkel Cell Polyomavirus (MCV) is the only human polyomavirus with convincing data supporting its classification as a direct causative agent of a human skin malignancy, Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Oncogenic transformation by MCV requires the integration of the viral genome into the human genome, truncation of the large T antigen (LT) to render the viral genome replication deficient and expression of small T antigen oncoprotein. The chromatin binding protein BRD4, was recently shown to transcriptionally regulate the expression of virus oncoproteins, thereby enhancing the tumorigenesis of virus-associated cancers, such as HPV associated cervical cancer. Previous work by Wang et al. revealed that BRD4 interacts with MCV full length LT during viral replication. In this study, we demonstrated that MCV truncated tumor LT antigen also interacts with BRD4 protein. We showed that the MCV tumor LT antigen and BRD4 protein complex co-localizes within the nucleus. Furthermore, we tested whether BRD4 protein transcriptionally regulates MCV Non Coding Control Region (NCCR), where we found that though full length LT and sT together, along with the BRD4 protein showed enhanced transcriptional activity whereas tumor truncated LT did not. These findings on the interactions of the MCV tumor truncated LT antigen with the BRD4 protein add to existing knowledge about interactions with LT and its role in tumorigenesis, and assist in efforts to more precisely define new therapy targets for this disease.
Keywords: Merkel Cell Polyomavirus, MCV, MCC, BRD4, Large T Antigen
Introduction
Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCV), the cause of a lethal skin cancer called Merkel cell carcinoma, is a unique member in the list of known human tumor viruses[1][2]. MCV is a small, non-enveloped virus with a circular double stranded 5 kb genome, divided into early and late regions by a noncoding control region (NCCR)[1]. The early region expresses a large T antigen (LT) and small T antigen protein (sT), which drive tumorigenesis in Merkel cells. MCV LT antigen is found in its full-length form in wild-type episomes of the virus, however in tumor cells, a truncated replication-incompetent form of the LT protein is expressed. Truncated LT antigen always, in every patient tumor thus far, conserves the N-terminal tumor-suppressor targeting domains, but loses the expression of the C-terminal ends responsible for viral replication functions. In 2012, Wang et al. uncovered the interaction between an epigenetic reader, the bromodomain protein 4 (BRD4) and the N-terminal end of the full-length LT oncoprotein[3]. Their studies showed that this interaction facilitates the localization of the complex to the MCV replication origin region where it regulates MCV replication, as tested using in vitro replication assays in HEK293T and C33A cells[3]. BRD4 is a BET family member that harbors two bromodomains and an ET (extra-terminal) domain[4]. It is a chromatin regulator involved in transcription programs in the development of several aggressive cancers and associates with a number of oncogenic viruses, including Human Papillomavirus (HPV)[4]. Recently McKinney et al. showed that BRD4 activates early HPV transcription in primary keratinocytes[5]. Furthermore, Dooley et al.found specific nuclear foci of BRD4, MED1 and H3K27ac at the sites of tandem HPV integration in cancer cells[6]. Evidence from their studies supports a BRD4 dependent super-enhancer like element in the viral genome regulating viral transcription[6].
Objective
In this study, we asked whether the truncated LT antigen, that retains the N-terminal but lacks the replication-important C-terminal, continues to interact with BRD4 protein. If yes, then what role would this interaction play in viral-mediated tumorigenesis? We further tested how this interaction may affect transcription through the MCV NCCR region, which houses the viral promoter/enhancer. The objective of our study was to validate this interaction (BRD4 and LT) and then investigate its implication in Merkel tumors.
Results & Discussion
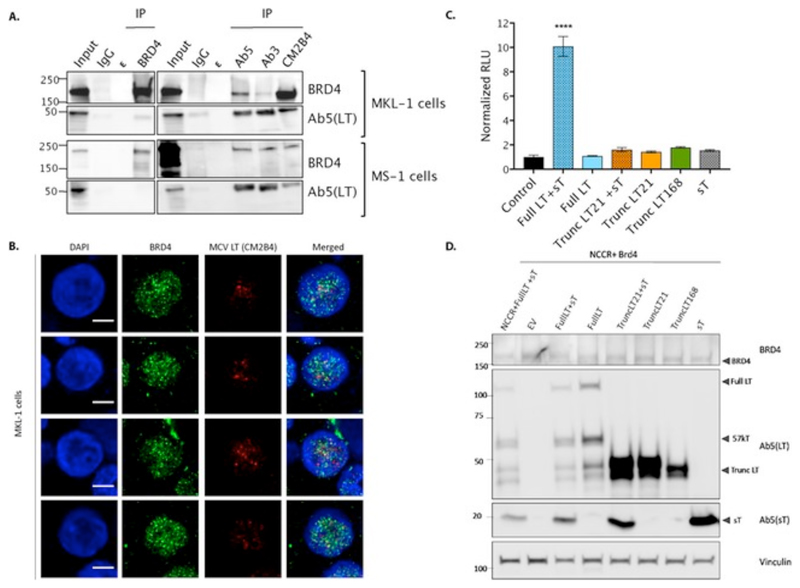
To test the interaction of truncated tumor LT antigen, we performed an immunoprecipitation (IP) assay in both MKL-1 and MS-1 cell lines[1][7][8]. These are both Merkel cell carcinoma cell lines that express truncated-LT and sT. The truncated-LTs from both MKL-1 and MS-1 are of different lengths corresponding to their respective truncation mutation and thus run at different sizes on a SDS-polyacrylamide[7]. We used three antibodies Ab3, Ab5 and CM2B4 to immunoprecipitate MCV LT, all three of which pulled down BRD4 (Fig. 1A). All the three antibodies used have different sensitivities and specificities besides binding different epitopes in MCV T antigen[9][10]. While Ab5 binds to the both LT and sT, Ab3 and CM2B4 are specific to LT and interact with its Exon 2 region[10][11]. IP using BRD4 antibody however, showed a very weak LT interaction. Wang et al. have previously shown that BRD4-LT interaction is facilitated through the N-terminal region (156-284 aa) of MCV LT, which is retained in the tumor antigens[3]. These assays corroborate the interaction, however in the tumor context, where truncated LT is endogenously expressed.
Figure 1. Truncated MCV LT antigen interacts with endogenous BRD4 protein in Merkel cell carcinoma cells.
(A) Nuclear proteins were isolated from MKL-1 and MS-1 cell lines and immunoprecipitated with polyclonal BRD4 antibody and 3 different antibodies against LT antigen i.e. Ab5, Ab3 and CM2B4. BRD4 protein was observed to be co-immunoprecipitated with LT targeting antibodies; however vice-versa was not seen. ε represents the empty lanes between the samples. Input is 2.7% (MKL-1) and 0.8% (MS-1) of total lysate.
(B) MKL-1 were immunostained for BRD4 and LT antigen (using CM2B4) and imaged using FV1000 at 60X magnification. The scale bar represents 5 microns. 4 cells imaged are shown here (of a total of 28 cells, in 3 experiments).
(C) Represents the Relative Luciferase activity in U2OS cells transfected with MCV NCCR region and BRD4 expressing plasmid along with different combinations of MCV T antigen. Two different truncated LT antigens (LT21 and LT168) were used to test increase in luciferase activity. Each column represents the mean value obtained from 3 independent experiments. Error bars represent SD. (2 technical replicates each time). One-way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey’s test showed Full LT+sT to be statistically significant in comparison to control and other conditions (p<0.0001).
(D) Corresponding western blot for the luciferase analysis confirms the expression of the different T antigen combinations.
To further validate this interaction we investigated whether MCV LT co-localizes with BRD4 in Merkel Cell Carcinoma cells. MKL-1 were immunostained with antibodies against MCV LT (CM2B4) and BRD4 protein (Fig. 1B). Since MCV positive MCC cell lines grow as suspension cells that clump together, before performing the immunofluorescence we treated them with 2 mM EDTA followed by gentle pipetting to break the clumps and get single cells that adhered to poly-L-Lysine coverslips. Immunofluoroscence analysis revealed that MCV LT antigen did co-localize with BRD4 protein in nucleus, although weakly at only an average 7.8 % with a correlation coefficient of 0.36 (coefficient range 4.4 to 11.9).
These results validate that BRD4 interacts with truncated (tumor) MCV LT antigen. Although, BRD4’s interaction with full-length MCV large T antigen aids in viral replication, we were unclear as to why BRD4 would interact with truncated LT in Merkel tumor cells.
To address this, we next studied the implication of this interaction with MCV transcription. We thereby performed luciferase reporter assays in U2OS cells by overexpressing the NCCR driving firefly luciferase in the presence of different plasmid combinations of viral T antigens and BRD4. We found that full length LT, along with sT antigen, significantly increased (p<0.0001) luciferase activity in the presence of BRD4, however the truncated LT antigens or sT alone did not (Fig. 1C). T antigen expression was validated by immunoblotting figure 1D.
Kwun et al and others[12][13][14][15][16], have previously shown that full-length LT drives viral replication by binding to the origin of replication. sT also contributes to viral replication by forming a complex with LT and stabilizing it[12][15][17].
In our experiments we included the entire NCCR region containing both, the origin of replication and the viral promoter, as opposed to only the viral origin region in other studies[12][15][17]. Hence, the reason for higher luciferase activity in the condition expressing BRD4 along with full length LT and sT could be explained by increased replication of the NCCR plasmid. Cheng et al.[10] and Borchert et al.[18] have not found any evidence for MCV tumor LT’s direct interaction with DNA. Hence, MCV truncated LT probably interacts with BRD4 to regulate BRD4’s DNA binding and gene regulation. One such important region may be the viral promoter itself. To further test the implications of this interaction, ChIP studies of BRD4 in MCC cell lines, specifically on the viral promoter and enhancer regions will be valuable.
Conclusions
We show that Merkel cell polyomavirus’s truncated (tumor) LT antigen, expressed in Merkel tumor cells, also interacts with BRD4, in the absence of virus replication in Merkel tumors.
Limitations
We were limited by the antibodies we had to detect MCV large T and BRD4. BRD4 is a large protein and doing western blotting and immunoprecipitations with the same antibody was challenging. Also we used only 2 MCC cell lines (MKL1 and MS-1) both of which grow in suspension as large clumps. For the Immunofluoresence experiments we had to treat these clumps with EDTA to disperse them as single cells and then attach them to slides for staining purposes.
Conjectures
While we showed that the truncated tumor T interacting with BRD4 was unable to increase viral transcription, nonetheless we used a luciferase reporter assay. It is still likely that truncated LT’s interaction with BRD4 is important for its transcription regulation function and further studies could test this via ChIP-PCR analysis and other direct investigations.
Methods
Cell Culture
MKL-1 and MS-1 cells were grown in RPMI media (Gibco #31800022) and U2OS cells were grown in McCoy’s 5Amedia (Himedia #AT179) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Gibco #16000-044), 1% GlutaMax (Gibco #35050-061), 1% penstrep (Gibco #15140-122) at 37°C in humidified air incubator containing 5% CO2.
Dual Gene Reporter Assay
U2OS cells were seeded in 6-well plate. After 24 h of seeding, cells were cotransfected with pGL4 NCCR (containing Firefly luciferase gene), pRL.TK (containing Renilla luciferase gene) and plasmids expressing MCV LT and BRD4 proteins using PEI transfection protocol (as described below). After 48 h of post-transfection, Dual-Luciferase reporter assay was performed using manufacturer’s protocol (Promega #E1901). Experiments were repeated independently 3 times with 2 technical repeats each time. The graphs were drawn using GraphPad Prism and statistical significance was calculated using one way ANOVA.
Transfection
Cells were seeded in an appropriate dish (6-well dish for Luciferase assay) with 50–60% confluency. After 24 h of seeding, media was changed and solution A containing PBS and DNA was prepared. After that solution B containing 1 part of 10 mM PEI (Polyethyleneimine) mixed with 5 parts of incubation for 5 min at room temperature. Transfection mixture was added dropwise to the desired plate. Cells were harvested after 48 h of transfection for further analysis. For 6-well plate- Solution A was = 2 mg of DNA + 36 ml of PBS and Solution B = 43.2 ml of PEI-PBS solution.
Immunoblot Analysis
Transfected cells were lysed in passive lysis buffer from Dual-luciferase kit (#E1901). Lysates were then electrophoresed in 8% and 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gels, transferred to Polyvinylidine fluoride (PVDF) Membrane (Bio-Rad- #1620177) and reacted with Ab5 (1:2000) and BRD4 (Bethyl Laboratories #A301-985A100) (1:2000) overnight at 4°C followed by 1 h incubation at room temperature with anti-mouse antibody (1:5000) Ab5 antibody and Anti- rabbit antibody (1:5000). Detection of peroxidase activity was performed by western lightening plus-ECL reagent (GE Healthcare #RPN2236) and images analyzed in ImageQuant LAS4000. Ab3 and Ab5 were kind gifts of Dr. James Decaprio, Dana Farber Cancer Institute, Boston.
Protein Quantitation
Protein concentration was quantified using Bicinchoninic assay (BCA) in accordance with the manufacturer’s protocol (Pierce BCA Protein assay kit, Thermo Fisher #23225).
Immunoprecipitation assay
For immunoprecipitation assays, cells were pelleted and resuspended in Buffer A (10 mM HEPES (pH 7.9), 10 mM KCl, 0.1 mM EDTA, 0.1 mM EGTA, and 1 mM dithiothreitol (DTT) supplemented with protease inhibitors (Complete Roche Applied Science, #5892953001). The resuspended cells were incubated on ice for 10 min, and NP-40 was added to a final concentration of 0.6%. After vortexing and centrifugation at 5,000 rpm for 5 min, the nuclear pellet was resuspended in ice-cold EBC buffer (50 mM Tris pH 8, 150 mM NaCl, 0.5 mM EDTA, β-mercaptoethanol-1:10,000, 0.5% NP-40) supplemented with protease inhibitors) for left for 20 min on ice followed by centrifugation at 14,000 rpm for 10 min. Nuclear proteins were then mixed with 20 µl of protein G Dynabeads(Invitrogen #10004D) (washed thrice with EBC buffer beforehand) along with either 1 µg BRD4 antibody (Bethyl Laboratories #A301-985A100) and 1 µg CM2B4 (Santa Cruz #sc-136172), Ab3 and Ab5 (against MCV T antigens) followed by rotation overnight at 4°C. After overnight incubation, the bound proteins were eluted using laemli sample buffer followed by heating at 99°C for 5 min. These samples were then immunoblotted on 4–12% gradient gel (Biorad #4561094).
Immunofluoroscence Assay
For Immunofluoroscence staining, MKL-1 cells were brought to single cell suspension by treating them with 2 mM EDTA for 10 min with gentle pipetting in between. The EDTA containing cell suspension was then diluted in a 1:5 ratio with RPMI + 10% FBS media (1 ml of EDTA contacting cell suspension + 5 ml of RPMI + 10% FBS media). The cells were then adhered on poly-L-Lysine (0.1 mg/ml, diluted in borate buffer) coated coverslips for 2 h, washed once with 1X PBS and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 min at room temperature. Further they were permeabilized with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) containing 0.5% TritonX-100 for 10 min at room temperature. After permeabilization, cells were blocked with 10% donkey serum for 1 h at room temperature and stained with BRD4 rabbit polyclonal antibody (1:500 dilution, Bethyl Laboratories) and CM2B4 mouse monoclonal Antibody (1:100 dilution, Santa Cruz) overnight at 4°C. Cells were then washed thrice with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) with 0.5% TritonX-100 in the interval of 5 min and then stained with secondary antibodies (Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated anti-rabbit (Invitrogen, A21206), 1:500 dilution and Alexa Fluor 647-conjugated anti-mouse (Invitrogen, A31571), 1:100 dilution) for 1 h at room temperature. Stained cells were mounted in aqueous medium containing DAPI (VectorLaboratories #H-1200) and analyzed and imaged using FV1000 confocal microscope (Olympus) at 60X. Colocalization analysis was done on images of MKL1 cells stained with both BRD4 and MCV LT antibodies using the JaCoP plugin in ImageJ software.
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge and thank Dr. James Decaprio for his generous gifts of antibodies Ab3 and Ab5. We are also grateful to the Central Imaging and Flow Cytometry Facility, Sequencing facility, NCB Kitchen, stores and other facilities and administration at the National Centre for Biological Sciences (NCBS). Authors declare no conflict of interest. RA would also like to thank Zaina and Karan for their love, strength and support.
Funding Statement
This work was supported by the Wellcome Trust/DBT India Alliance (Early Career Award IA/E/14/1/501773 to Dr. Reety Arora.) and Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, Government of India fellowship (to Miss. Arushi Vats).
Footnotes
Conict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethics Statement
Not Applicable.
No fraudulence is committed in performing these experiments or during processing of the data. We understand that in the case of fraudulence, the study can be retracted by ScienceMatters.
References
- 1.Becker Jürgen C, Stang Andreas, Decaprio James A, Cerroni Lorenzo, Lebbé Celeste, Veness Michael, Nghiem Paul. Merkel cell carcinoma. Nature Reviews Disease Primers. 2017;3 doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2017.77. 17077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Moore Patrick S, Chang Yuan. Why do viruses cause cancer? Highlights of the rst century of human tumour virology. Nature Reviews Cancer. 2010;10:878–889. doi: 10.1038/nrc2961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wang Xin, Li Jing, Schowalter Rachel M, Jiao Jing, Buck Christopher B, You Jianxin. Bromodomain Protein Brd4 Plays a Key Role in Merkel Cell Polyomavirus DNA Replication. PLOS Pathogens. 2012;8:e1003021. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Filippakopoulos Panagis, Knapp Stefan. Targeting bromodomains: epigenetic readers of lysine acetylation. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. 2014;13:337–356. doi: 10.1038/nrd4286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.McKinney Caleb C, Kim Min Jung, Chen Dan, McBride Alison A. Brd4 Activates Early Viral Transcription upon Human Papillomavirus 18 Infection of Primary Keratinocytes. mBio. 2016;7:e01644–16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01644-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dooley Katharine E, Warburton Alix, McBride Alison A. Tandemly Integrated HPV16 Can Form a Brd4-Dependent Super-Enhancer-Like Element That Drives Transcription of Viral Oncogenes. mBio. 2016;7:e01446–16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01446-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Guastaerro Anna, Feng Huichen, Thant Mamie, 兛, Shuda Masahiro. Characterization of an early passage Merkel cell polyomavirus-positive Merkel cell carcinoma cell line, MS-1, and its growth in NOD scid gamma mice. Journal of Virological Methods. 2013;187:6–14. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2012.10.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Rosen St, Gould Ve, Salwen Hr, 兛, Kies Ms. Establishment and characterization of a neuroendocrine skin carcinoma cell line. Laboratory Investigation: Journal of Technical Methods and Pathology. 1987;56 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Moshiri Ata S, Doumani Ryan, Yelistratova Lola, 兛, Nghiem Paul. Polyomavirus-Negative Merkel Cell Carcinoma: A More Aggressive Subtype Based on Analysis of 282 Cases Using Multimodal Tumor Virus Detection. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 2017;137:819–827. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2016.10.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cheng Jingwei, Park Donglim Esther, Berrios Christian, White Elizabeth A, Arora Reety, Yoon Rosa, Branigan Timothy, Xiao Tengfei, Westerling Thomas, Federation Alexander, Zeid Rhamy, et al. Merkel cell polyomavirus recruits MYCL to the EP400 complex to promote oncogenesis. PLOS Pathogens. 2017;13:e1006668. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Shuda Masahiro, Arora Reety, Kwun Hyun Jin, Feng Huichen, Sarid Ronit, Fernández-gueras María-teresa, Tolstov Yanis, Gjoerup Ole, Mansukhani Mahesh M, Swerdlow Steven H, Chaudhary Preet M., et al. Human Merkel cell polyomavirus infection I. MCV T antigen expression in Merkel cell carcinoma, lymphoid tissues and lymphoid tumors. International Journal of Cancer. 2009;125:1243–1249. doi: 10.1002/ijc.24510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kwun Hyun Jin, Guastaerro Anna, Shuda Masahiro, Meinke Gretchen, Bohm Andrew, Moore Patrick S, Chang Yuan. The Minimum Replication Origin of Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Has a Unique Large T-Antigen Loading Architecture and Requires Small T-Antigen Expression for Optimal Replication. Journal of Virology. 2009;83:12118–12128. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01336-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Liu Wei, Yang Ruifeng, Payne Aimee S, 兛, You Jianxin. Identifying the Target Cells and Mechanisms of Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Infection. Cell Host & Microbe. 2016;19:775–787. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2016.04.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Tsang Sabrina H, Wang Ranran, Nakamaru-Ogiso Eiko, Knight Simon AB, Buck Christopher B, You Jianxin. The Oncogenic Small Tumor Antigen of Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Is an Iron-Sulfur Cluster Protein That Enhances Viral DNA Replication. Journal of Virology. 2015;90:1544–1556. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02121-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Feng Huichen, Kwun Hyun Jin, Liu Xi, Gjoerup Ole, Stolz Donna B, Chang Yuan, Moore Patrick S. Cellular and Viral Factors Regulating Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Replication. PLOS One. 2011;6:e22468. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Neumann Friederike, Borchert Sophie, Schmidt Claudia, Reimer Rudolph, Hohenberg Heinrich, Fischer Nicole, Grundhoff Adam. Replication, Gene Expression and Particle Production by a Consensus Merkel Cell Polyomavirus (MCPyV) Genome. PLOS One. 2011;6:e29112. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kwun Hyun Jin, Shuda Masahiro, Feng Huichen, 兛, Chang Yuan. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Small T Antigen Controls Viral Replication and Oncoprotein Expression by Targeting the Cellular Ubiquitin Ligase SCFFbw7. Cell Host & Microbe. 2013;14:125–135. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2013.06.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Borchert Sophie, Czech-Sioli Manja, Neumann Friederike, Schmidt Claudia, Wimmer Peter, Dobner Thomas, Grundhoff Adam, Fischer Nicole. High-Anity Rb Binding, p53 Inhibition, Subcellular Localization, and Transformation by Wild-Type or Tumor-Derived Shortened Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Large T Antigens. Journal of Virology. 2014;88:3144–3160. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02916-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]