Abstract
As intracerebral hemorrahge becomes more frequent as a result of an aging population with greater comorbidities, rapid identification and reversal of precipitators becomes increasingly paramount. The aformentioned population will ever more likely be on some form of anticoagulant therapy. Understanding the mechanisms of these agents and means by which to reverse them early on is critical in managing the acute intracerebral hemorrhage.
Keywords: anticoagulation, cerebral hemorrhage, hemorrhagic stroke, coagulopathy reversal
Introduction
Intracerebral haemorrhage (ICH) is a disease entity associated with high morbidity and mortality. It accounts for nearly 15% of all strokes.1 In the USA, the mortality rate of patients with ICH is nearly 34% confirming the increasing burden of the disease.2–4 Oral anticoagulation is a common cause of ICH and the use of oral anticoagulation is estimated to continually rise given increasing rate of atrial fibrillation detection.5 Coagulopathy-associated ICH results in poor functional outcomes given rapid haematoma expansion as early as 1 hour.1–3
This article will review the indications, efficacy and safety of vitamin K antagonists (VKAs) as well as direct-acting oral anticoagulants (DOACs) and outline the reversal of coagulopathy by these agents in ICH.
Comparison of efficacy and safety between DOACs and VKAs
Direct thrombin inhibitors and factor Xa inhibitors (FXa-Is) constitute the two classes of DOACs (table 1). Dabigatran (Pradaxa, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals) is a direct thrombin inhibitor, whereas rivaroxaban (Xarelto, Janssen Pharmaceuticals), apixaban (Eliquis, Bristol-Myers Squibb Company), edoxaban (Savaysa and Lixiana, Daiichi Sankyo) and betrixaban (Bevyxxa, Portola Pharmaceuticals) fall in the category of FXa-Is. DOACs do not require frequent monitoring of the international normalised ratio (INR) and have shorter half-lives with fewer drug interactions, making them more favourable for use than warfarin.6 Recent trials including ARISTOTLE (apixaban),7 8 RE-LY (dabigatran),9 ROCKET AF (rivaroxaban),10 ENGAGE AF-TIMI 48 (edoxaban)10 on stroke and systemic embolism have shown non-inferiority of DOACs when compared with warfarin. The rate of bleeding (including major haemorrhage, fatal haemorrhage, haemorrhagic stroke or ICH) is also lower for DOACs at 3% to 4% when compared with warfarin at 5% to 6%. Additionally, the rate of only ICH is lower for DOACs at 0.3% to 0.4% when compared with warfarin at 0.7% to 0.8%.7–11
Table 1.
Direct-acting oral anticoagulants (DOACs) and reversal
| DOAC | Brand name | Mechanism of action | Time to onset | t1/2 | Reversal |
| Dabigatran | Pradaxa | Direct thrombin inhibitor | 0.5–2 hour | 15 hours | Idarucizumab |
| Rivaroxaban | Xarelto | Factor Xa inhibitor | 2–4 hour | 6–12 hour | 3F- and 4F-PCC, andexanet alfa |
| Apixaban | Eliquis | 1–2 hour | |||
| Edoxaban | Savaysa, Lixiana | 1–2 hour | Andexanet alfa | ||
| Betrixaban | Bevyxxa | 3–4 hour | 24 hours |
The rate of ischaemic stroke in patients taking DOACs has been noted to be higher when compared with warfarin.12–14 This could be explained by inconsistent use of DOACs resulting in subtherapeutic levels given their short half-lives.15
The outcome of ICH while on DOACs remains a topic for research. CROMIS-2 (The Clinical Relevance of Microbleeds in Stroke Study) compared all-cause 90-day mortality, functional outcome, ICH volume and haematoma expansion between patients with ICH associated with VKA and ICH associated with DOAC. There were no significant differences between the two groups.16 Other studies have shown similar functional outcomes in patients with ICH receiving VKA and DOACs and also mortality benefit in patients on DOACs.17 18
DOACs are becoming the preferred agents for oral anticoagulation when compared with VKAs given their safety profile.19 There is limited data on the reversal protocol of DOACs. As their use will continue to rise, it is imperative to understand the management of DOAC related ICH.
Reversal of VKA-related coagulopathy
Pharmacology of VKAs
Warfarin interferes with production of vitamin K dependent clotting factors II, VII, IX, X by depleting vitamin K reserve.20 Warfarin is metabolised by cytochrome P450 enzyme, which can be inhibited or induced by a variety of drugs resulting in variable metabolism of warfarin.
Reversal
Vitamin K is available in oral, subcutaneous and intravenous preparations for patients with life threatening bleeding. Intravenous vitamin K is most efficacious among the three with a recommended dose of 10 mg intravenously.21 However, INR normalisation with vitamin K can take up to a day1–3 22 and therefore it is not sufficient alone in the management of ICH. It is usually given in combination with fresh frozen plasma (FFP) or prothrombin complex concentrate (PCC) (table 2).
Table 2.
Anticoagulant reversal agents and their pharmacokinetics
| Anticoagulant reversal | Brand name | Time to reverse coagulopathy | t1/2 | Terminal elimination t1/2 |
| Idarucizumab | Praxbind | Minutes | 47 m | 10 hours |
| Prothrombin complex concentrate | Kcentra | 40 min | factor dependent | factor dependent |
| Fresh frozen plasma | … | >24 hour | ||
| Andexanet alfa | Andexxa | Minutes | 1 hour | 5–7 hour |
FFP is the liquid portion derived from whole blood. It corrects coagulopathy by replacing plasma proteins to replete clotting factors. FFP reversal of INR can take up to 30 hours making it an ineffective treatment of early haematoma expansion.23–25 It requires high volumes and can worsen fluid balance in patients with heart failure resulting in pulmonary oedema as well as transfusion reactions.26
PCC is comprised of clotting factors II, IX and X at levels significantly higher than FFP. Activated PCC (aPCC) also contains factor VII in addition to II, IX and X. PCC results in rapid INR reversal and is not associated with complications such as fluid overload as seen with FPP.27 The INCH trial (International Normalised Ratio Normalisation in Coumadin-Associated Intracerebral Haemorrhage) compared 30 IU/kg dose of PCC to 20 mL/kg FFP in reversal of VKA associated ICH.25 PCC had a higher rate of INR reversal to <1.3 within 3 hours when compared with FFP (67% vs 9%; p=0.0003). The average time of INR reversal was 40 min in PCC group when compared with >24 hours for FFP and haematoma expansion was less for PCC group at 3 and 24 hours.28 The rate of thrombotic complications remains similar between PCC and FFP.29–32 PCC (more than US$5000 for 20 IU/kg dose in a 70 kg patient) is more expensive when compared with FFP (less than US$2000 per unit), however it is more cost-effective given its advantages over FFP as outlined above. aPCC (20 IU/kg) is also found to be more efficacious than FFP without significant increase in thrombotic complications.33 There are no studies comparing aPCC to PCC to date.
Reversal of DOAC-related coagulopathy
Pharmacology of DOACs
Dabigatran directly competes with thrombin, thus inhibiting production of fibrin. It has a half-life of approximately 15 hours and is primarily cleared by the kidneys.34 FXa-Is act by binding and inhibiting factor Xa with half-lives of 6 to 12 hours, except for betrixaban which is approximately 24 hours.35 They are also primarily cleared by the kidneys.36 Unfortunately, unlike warfarin, dabigatran has no modality, which accurately measures its anticoagulation effect. Currently, specific anti-Xa assays are available for the FXa-Is but they are not widely available, have a complex measurement system and are relatively expensive (over US$20 per test).37
Reversal
In vitro studies have demonstrated PCC efficacy in reversal of DOAC anticoagulation.38–41 Ex vivo studies have been done on small populations of healthy male volunteers that proved the efficacy of both three factor PCC and four factor PCC at 50 IU/kg. Both types of PCC decreased PT within 30 min.42–44 Multiple trials have been conducted in actively bleeding patients (table 3). The UPRATE trial (Unactivated Prothrombin Complex Concentrates for the Reversal of Anti-Factor Ten Inhibitors) showed that four factor PCC reliably reversed 84 patients with major bleeding on apixaban and rivaroxaban (70% with ICH, 15% with gastrointestinal bleed). The overall mortality was 32% at 30-day follow-up for both drugs.45–47
Table 3.
Summary of trials for anticoagulant reversal and haemorrhage treatment
| Trial | Anticoagulant | Anticoagulant reversal | Primary endpoint | Results |
| INCH25 | VKA | PCC, FFP | Percentage of patients with INR <1.3 within 3 hours of treatment | PCC (vs FFP) had a higher rate of INR reversal |
| UPRATE42–44 | Rivaroxaban, apixaban | 4F-PCC | Haemostasis rate | 4F-PCC reverses apixaban and rivaroxaban associated bleeding |
| REVERSE-AD43 | Dabigatran | Idarucizumab | Percentage reversal at 4 hours | Idarucizumab reverses the effect of dabigatran for most patients (93%) within minutes |
| ANNEXA-444 | Rivaroxaban, apixaban | Andexanet alfa | Change in anti-Xa activity at 12 hours | 80% of those with DOAC associated ICH achieved excellent or good haemostasis 12 hours after andexanet alfa |
| SPOTLIGHT and STOP-IT46 | … | rFVIIa | Parenchymal ICH volume expansion on head CT at 24 hours | rFVIIa does not improve radiographic findings |
DOAC, direct-acting oral anticoagulant; FFP, fresh frozen plasma; ICH, intracerebral haemorrhage; INR, international normalised ratio; PCC, prothrombin complex concentrate; VKA, vitamin K antagonist.
There are anticoagulant reversal agents specific for different DOACs (tables 1 and 2). Idarucizumab is a monoclonal antibody that binds dabigatran. REVERSE-AD trial (Reversal Effects of Idarucizumab on Active Dabigatran) enrolled patients with active bleeding and patients that need reversal of anticoagulation prior to a procedure. Unfortunately, the study was was not designed for patients with ICH. Therefore it lacked objective measurement of clinical haemostasis in ICH.46 Nevertheless, idarucizumab was shown to reverse the effect of dabigatran for approximately 93% of patients within minutes.48
Recently, the Food and Drug Administration approved andexanet alfa, the second DOAC specific reversal agent. It is an elegant reversal agent for FXa-Is. It is a recombinant FXa that binds FXa-I. The ANNEXA-4 trial (Andexanet Alfa, a Novel Antidote to the Anticoagulation Effects of FXA Inhibitors) had 168 patients with ICH.47 Haemostatic efficacy was measured via serial CT scans. Of those with ICH, 80% achieved excellent or good haemostasis 12 hours after infusion. Excellent haemostasis was defined as haematoma growth <20% and good as <35% at 12 hours. The study has limitations, it excluded patients with ICH with Glasgow Coma Scale <7 and ICH with volume >60 mL.47
On recombinant activated coagulation factor VII
There is a growing interest in recombinant activated factor VII (rFVIIa) in all forms of active bleeding associated with coagulopathy. It was recently compared with placebo in patients with ICH and a spot sign on CT angiography. The study analysed 69 patients pooled from the SPOTLIGHT (‘Spot Sign’ Selection of Intracerebral Haemorrhage to Guide Haemostatic Therapy) and STOP-IT (The Spot Sign for Predicting and Treating ICH Growth Study) trials. These trials were closely coordinated between the investigators in Canada (SPOTLIGHT) and the USA (STOP-IT). Patients were given rFVIIa within 3 hours of stroke onset. The primary outcome was parenchymal ICH volume expansion and the secondary outcome was total haemorrhage volume expansion on head CT at 24 hours. The drug did not improve radiographic findings or outcomes compared with placebo. Baseline media ICH volumes were 19.6 (9.6 to 39.2) mL in the rFVIIa group and 20.4 (8.6 to 32.6) mL in the placebo.49 This further adds to the growing evidence against rFVIIa as a reversal agent.
Conclusion
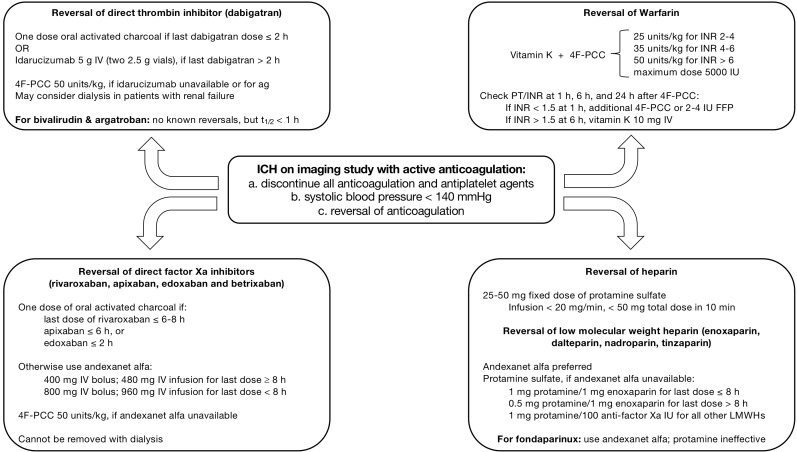
Anticoagulation associated with ICH remains under investigated. Ironically, an indication for anticoagulation is prevention of stroke. Though studies are showing DOACs lower the risk of bleeding associated complications compared with VKAs, there is paucity of strong data for the reversal of coagulopathy in ICH. Larger and more robust clinical trials targeting ICH are needed. Reversal agents need direct comparison against four factor PCC. Based on the current literature and standard of care, we developed a suggested algorithm for coagulopathy reversal in ICH (figure 1).
Figure 1.
Algorithm for the reversal of specific anticoagulants, including direct thrombin inhibitors, direct factor Xa inhibitors, warfarin and heparin. FFP, fresh frozen plasma; 4F-PCC, four factor prothrombin complex concentrate;ICH, intracerebral haemorrhage; INR, internationalnormalised ratio; IU, international unit; IV, intravenous; LMWH, low-molecular weight heparin; PCC, prothrombin complex concentrate.
Footnotes
Twitter: @neuro_md
Contributors: AS and NS contributed to drafting, revising and finalising the manuscript. JC revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content and prepared tables. MB, LG and MS revised critically for important intellectual content. WY revised critically for important intellectual content and finalised the manuscript.
Funding: The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests: None declared.
Patient consent for publication: Not required.
Provenance and peer review: Commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
References
- 1. Li Q, Zhang G, Xiong X, et al. . Black hole sign: novel imaging marker that predicts hematoma growth in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 2016;47:1777–81. 10.1161/STROKEAHA.116.013186 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Davis SM, Broderick J, Hennerici M, et al. . Hematoma growth is a determinant of mortality and poor outcome after intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurology 2006;66:1175–81. 10.1212/01.wnl.0000208408.98482.99 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Butcher KS, Jeerakathil T, Hill M, et al. . The intracerebral hemorrhage acutely decreasing arterial pressure trial. Stroke 2013;44:620–6. 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.000188 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Feigin VL, Lawes CMM, Bennett DA, et al. . Stroke epidemiology: a review of population-based studies of incidence, prevalence, and case-fatality in the late 20th century. Lancet Neurol 2003;2:43–53. 10.1016/S1474-4422(03)00266-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Huttner HB, Schellinger PD, Hartmann M, et al. . Hematoma growth and outcome in treated neurocritical care patients with intracerebral hemorrhage related to oral anticoagulant therapy: comparison of acute treatment strategies using vitamin K, fresh frozen plasma, and prothrombin complex concentrates. Stroke 2006;37:1465–70. 10.1161/01.STR.0000221786.81354.d6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Le Roux P, Pollack CV, Milan M, et al. . Race against the clock: overcoming challenges in the management of anticoagulant-associated intracerebral hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 2014;121:1–20. 10.3171/2014.8.paradigm [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Miller CS, Grandi SM, Shimony A, et al. . Meta-Analysis of efficacy and safety of new oral anticoagulants (dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban) versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol 2012;110:453–60. 10.1016/j.amjcard.2012.03.049 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Granger CB, Alexander JH, McMurray JJV, et al. . Apixaban versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 2011;365:981–92. 10.1056/NEJMoa1107039 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Connolly SJ, Ezekowitz MD, Yusuf S, et al. . Dabigatran versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 2009;361:1139–51. 10.1056/NEJMoa0905561 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Patel MR, Mahaffey KW, Garg J, et al. . Rivaroxaban versus warfarin in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 2011;365:883–91. 10.1056/NEJMoa1009638 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Giugliano RP, Ruff CT, Braunwald E, et al. . Edoxaban versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 2013;369:2093–104. 10.1056/NEJMoa1310907 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Shpak M, Ramakrishnan A, Nadasdy Z, et al. . Higher incidence of ischemic stroke in patients taking novel oral anticoagulants. Stroke 2018;49:2851–6. 10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.022636 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Coleman CI, Peacock WF, Bunz TJ, et al. . Effectiveness and safety of apixaban, dabigatran, and rivaroxaban versus warfarin in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation and previous stroke or transient ischemic attack. Stroke 2017;48:2142–9. 10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.017474 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Kohsaka S, Katada J, Saito K, et al. . Safety and effectiveness of apixaban in comparison to warfarin in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation: a propensity-matched analysis from Japanese administrative claims data. Curr Med Res Opin 2018;34:1627–34. 10.1080/03007995.2018.1478282 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Robert-Ebadi H, Righini M. Anticoagulation in the elderly. Pharmaceuticals 2010;3:3543–69. 10.3390/ph3123543 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Wilson D, Seiffge DJ, Traenka C, et al. . Outcome of intracerebral hemorrhage associated with different oral anticoagulants. Neurology 2017;88:1693–700. 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003886 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Tsivgoulis G, Lioutas V-A, Varelas P, et al. . Direct oral anticoagulant- vs vitamin K antagonist-related nontraumatic intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurology 2017;89:1142–51. 10.1212/WNL.0000000000004362 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Kurogi R, Nishimura K, Nakai M, et al. . Comparing intracerebral hemorrhages associated with direct oral anticoagulants or warfarin. Neurology 2018;90:e1143–9. 10.1212/WNL.0000000000005207 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Whitlon DS, Sadowski JA, Suttie JW. Mechanism of coumarin action: significance of vitamin K epoxide reductase inhibition. Biochemistry 1978;17:1371–7. 10.1021/bi00601a003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Feeney JM, Santone E, DiFiori M, et al. . Compared to warfarin, direct oral anticoagulants are associated with lower mortality in patients with blunt traumatic intracranial hemorrhage: a TQIP study. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 2016;81:843–8. 10.1097/TA.0000000000001245 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Patriquin C, Crowther M. Treatment of warfarin-associated coagulopathy with vitamin K. Expert Rev Hematol 2011;4:657–67. 10.1586/ehm.11.59 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Lubetsky A, Hoffman R, Zimlichman R, et al. . Efficacy and safety of a prothrombin complex concentrate (Octaplex) for rapid reversal of oral anticoagulation. Thromb Res 2004;113:371–8. 10.1016/j.thromres.2004.04.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Chapman SA, Irwin ED, Beal AL, et al. . Prothrombin complex concentrate versus standard therapies for Inr reversal in trauma patients receiving warfarin. Ann Pharmacother 2011;45:869–75. 10.1345/aph.1P605 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Lee SB, Manno EM, Layton KF, et al. . Progression of warfarin-associated intracerebral hemorrhage after INR normalization with FFP. Neurology 2006;67:1272–4. 10.1212/01.wnl.0000238104.75563.2f [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Menzin J, White LA, Friedman M, et al. . Factors associated with failure to correct the International normalised ratio following fresh frozen plasma administration among patients treated for warfarin-related major bleeding. An analysis of electronic health records. Thromb Haemost 2012;107:662–72. 10.1160/TH11-09-0646 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Hickey M, Gatien M, Taljaard M, et al. . Outcomes of urgent warfarin reversal with frozen plasma versus prothrombin complex concentrate in the emergency department. Circulation 2013;128:360–4. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.001875 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Frontera JA, Gordon E, Zach V, et al. . Reversal of coagulopathy using prothrombin complex concentrates is associated with improved outcome compared to fresh frozen plasma in warfarin-associated intracranial hemorrhage. Neurocrit Care 2014;21:397–406. 10.1007/s12028-014-9972-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Steiner T, Poli S, Griebe M, et al. . Fresh frozen plasma versus prothrombin complex concentrate in patients with intracranial haemorrhage related to vitamin K antagonists (inch): a randomised trial. Lancet Neurol 2016;15:566–73. 10.1016/S1474-4422(16)00110-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Woo CH, Patel N, Conell C, et al. . Rapid warfarin reversal in the setting of intracranial hemorrhage: a comparison of plasma, recombinant activated factor VII, and prothrombin complex concentrate. World Neurosurg 2014;81:110–5. 10.1016/j.wneu.2012.12.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Sarode R, Milling TJ, Refaai MA, et al. . Efficacy and safety of a 4-factor prothrombin complex concentrate in patients on vitamin K antagonists presenting with major bleeding: a randomized, plasma-controlled, phase IIIB study. Circulation 2013;128:1234–43. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.002283 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Parry-Jones AR, Di Napoli M, Goldstein JN, et al. . Reversal strategies for vitamin K antagonists in acute intracerebral hemorrhage. Ann Neurol 2015;78:54–62. 10.1002/ana.24416 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Majeed A, Meijer K, Larrazabal R, et al. . Mortality in vitamin K antagonist-related intracerebral bleeding treated with plasma or 4-factor prothrombin complex concentrate. Thromb Haemost 2014;111:233–9. 10.1160/TH13-07-0536 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Yin EB, Tan B, Nguyen T, et al. . Safety and effectiveness of factor VIII inhibitor bypassing activity (FEIBA) and fresh frozen plasma in oral anticoagulant-associated intracranial hemorrhage: a retrospective analysis. Neurocrit Care 2017;27:51–9. 10.1007/s12028-017-0383-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Stangier J. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the oral direct thrombin inhibitor dabigatran etexilate. Clin Pharmacokinet 2008;47:285–95. 10.2165/00003088-200847050-00001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Gelosa P, Castiglioni L, Tenconi M, et al. . Pharmacokinetic drug interactions of the non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants (NOACs). Pharmacol Res 2018;135:60–79. 10.1016/j.phrs.2018.07.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Mahan CE, Fanikos J. New antithrombotics: the impact on global health care. Thromb Res 2011;127:518–24. 10.1016/j.thromres.2011.03.022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Crowther M, Crowther MA. Antidotes for novel oral anticoagulants: current status and future potential. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2015;35:1736–45. 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.303402 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Perzborn E, Heitmeier S, Laux V, et al. . Reversal of rivaroxaban-induced anticoagulation with prothrombin complex concentrate, activated prothrombin complex concentrate and recombinant activated factor VII in vitro. Thromb Res 2014;133:671–81. 10.1016/j.thromres.2014.01.017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Escolar G, Fernandez-Gallego V, Arellano-Rodrigo E, et al. . Reversal of apixaban induced alterations in hemostasis by different coagulation factor concentrates: significance of studies in vitro with circulating human blood. PLoS One 2013;8:e78696 10.1371/journal.pone.0078696 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Zahir H, Brown KS, Vandell AG, et al. . Edoxaban effects on bleeding following punch biopsy and reversal by a 4-factor prothrombin complex concentrate. Circulation 2015;131:82–90. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.013445 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Fukuda T, Honda Y, Kamisato C, et al. . Reversal of anticoagulant effects of edoxaban, an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor, with haemostatic agents. Thromb Haemost 2012;107:253–9. 10.1160/TH11-09-0668 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Eerenberg ES, Kamphuisen PW, Sijpkens MK, et al. . Reversal of rivaroxaban and dabigatran by prothrombin complex concentrate: a randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover study in healthy subjects. Circulation 2011;124:1573–9. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.029017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Marlu R, Hodaj E, Paris A, et al. . Effect of non-specific reversal agents on anticoagulant activity of dabigatran and rivaroxaban: a randomised crossover ex vivo study in healthy volunteers. Thromb Haemost 2012;108:217–24. 10.1160/TH12-03-0179 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Levi M, Moore KT, Castillejos CF, et al. . Comparison of three-factor and four-factor prothrombin complex concentrates regarding reversal of the anticoagulant effects of rivaroxaban in healthy volunteers. J Thromb Haemost 2014;12:1428–36. 10.1111/jth.12599 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Majeed A, Ågren A, Holmström M, et al. . Management of rivaroxaban- or apixaban-associated major bleeding with prothrombin complex concentrates: a cohort study. Blood 2017;130:1706–12. 10.1182/blood-2017-05-782060 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Pollack CV, Reilly PA, van Ryn J, et al. . Idarucizumab for Dabigatran Reversal - Full Cohort Analysis. N Engl J Med 2017;377:431–41. 10.1056/NEJMoa1707278 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Connolly SJ, Milling TJ, Eikelboom JW, et al. . Andexanet alfa for acute major bleeding associated with factor Xa inhibitors. N Engl J Med 2016;375:1131–41. 10.1056/NEJMoa1607887 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Pollack CV, Reilly PA, Eikelboom J, et al. . Idarucizumab for dabigatran reversal. N Engl J Med 2015;373:511–20. 10.1056/NEJMoa1502000 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Gladstone DJ, Aviv RI, Demchuk AM, et al. . Effect of recombinant activated coagulation factor VII on hemorrhage expansion among patients with spot Sign–Positive acute intracerebral hemorrhage: the spotlight and STOP-IT randomized clinical trials. JAMA Neurol 2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]