Abstract
The role of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) in the successful resumption of oocyte meiosis and cumulus expansion has been well-documented. However, there remains very little information available on the influence of PGE2 on other processes that occur during oocyte maturation. In this study, we supplemented a maturation medium with PGE2 and monitored oocyte quality markers, glucose metabolism, mitochondrial status, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in the cumulus-oocyte complexes (COCs), using a well-established in vitro model of embryo production in cattle. We found that this increased availability of PGE2 during maturation led to an increase in the expression of genes associated with oocyte competence and improved the quality of blastocysts produced. Prostaglandin E2 also appeared to stimulate glucose uptake and lactate production in the COCs, both influencing the expression of enzymes involved in glycolysis and the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway. We found that PGE2 reduced intracellular reactive oxygen species levels, and simultaneously increased glutathione concentration and stimulated antioxidant gene expression in the oocyte. These results indicate that PGE2 has an important role in the protection of oocytes against oxidative stress. Mitochondrial membrane potential was also improved in PGE2-treated oocytes, and there was a reduction in the occurrence of apoptosis in the COCs. Promotion of an anti-apoptotic balance in transcription of genes involved in apoptosis was present in both oocytes and the cumulus cells. In summary, PGE2 could represent a novel autocrine/paracrine player in the mechanisms that can facilitate successful oocyte maturation and oocyte survival in the cow.
Keywords: Apoptosis, Cumulus cells, Embryo culture, Gene expression, In vitro fertilization (IVF), In vitro maturation (IVM), Mitochondria, Oocyte, Oxidative stress, Cow
Background
Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) belongs to a group of cell signalling molecules that mediate many important reproductive processes, including ovulation, implantation, maintenance of luteal function and establishment of pregnancy [1, 2]. This important derivative of arachidonic acid is produced by prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase S1 (PTGS1) or PTGS2 (previously identified as cyclooxygenase enzymes COX1 and COX2) [3, 4], specific terminal synthases: two membrane bound enzymes (PTGES and PTGES2), and one cytosolic isoform (PTGES3 or cPGES) [5–7]. Once produced, PGE2 acts in both an autocrine or paracrine manner by binding to specific G protein-coupled receptors that have different but coinciding tissue distributions [8, 9]. Four isoforms of PGE2 receptors have been identified: PTGER1, PTGER2, PTGER3 and PTGER4 (commonly referred to as EP1, EP2, EP3, and EP4). These are known to activate different intracellular signalling pathways [8, 9] and can have a very influential role on the success of reproductive processes.
In mammals, PGE2 is the most abundant type of prostaglandin [10] and is the main prostaglandin secreted following PTGS2 induction in mice cumulus-oocyte complexes (COCs) [11]. There is a 6-fold increase in PTGS2 expression in competent COCs in human cumulus cells [12], with PTGS2 dependent PGE2 production also found in bovine COCs [13, 14]. The role of PGE2 during early embryogenesis has been studied in several species, including humans [15], rhesus monkeys [16], mice [17, 18], and various domestic animals [19–24]. Prostaglandin E2 is also involved in ovulation cascade events, including the expansion of cumulus cells and the expression of proteases associated with follicle rupture [15, 16, 18]. In these processes, PGE2 indirectly mediates LH action or directly acts on the expression of ovulatory genes, including AREG, EREG, HAS2 and TNFAIP6 [15, 18].
The influence of PGE2 on oocyte maturation and subsequent developmental competence has been the subject of extensive research, with authors typically assigning PGE2 an essential role in the successful resumption of oocyte meiosis and cumulus expansion [11, 17, 25–27]. However, little is known about the effect of PGE2 on other processes that occur during oocyte maturation. The present study was designed to investigate the effect of supplementing a maturation medium with PGE2 on several aspects of oocyte maturation, in a well-established in vitro model of maturation, fertilization, and embryo culture in cattle. We tested the hypothesis that during IVM, PGE2 effects the expression of oocyte quality markers, glucose metabolism, mitochondrial status, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in the COCs. Oocyte quality markers included their maturation level, embryonic development and blastocyst morphological quality. We measured the role of PGE2 on overall glucose metabolism and expression of genes involved in glucose metabolism in cumulus cells, as well as mRNA abundance of oocyte quality markers in cumulus cells. Mitochondrial status was determined by analysing mitochondrial distribution and mitochondrial membrane potential in the bovine oocytes. We also explored oxidative stress by assessing intracellular GSH and ROS levels and mRNA expression of antioxidation-associated genes in the oocytes. Finally, we evaluated the effect of PGE2 supplementation during IVM on apoptosis of COCs and the expression of genes involved in apoptotic pathway.
Materials and methods
Chemicals and suppliers
Culture media for the in vitro production of bovine embryos were procured from Minitube (Minitüb, Tiefenbach, Germany). All reagents and supplements for the in vitro culture were purchased from Merck (Sigma-Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany) unless otherwise stated. Plastic dishes, four-well plates and tubes were acquired from Nunc (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA). All the chemicals for reverse transcription were obtained from Invitrogen (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA).
Oocyte collection
Ovaries were collected from non-pregnant Holstein cows with normal cycles at a local slaughterhouse (Warmia, Biskupiec, Poland) and transported to the laboratory in sterile PBS at 32 °C. Cumulus-oocyte complexes (COCs) were acquired by aspiration from subordinate ovarian follicles that were less than 5 mm in diameter. Following assessment under a stereo microscope (Discovery V20, Carl Zeiss, Poznan, Poland; SZX7, Olympus, Warsaw, Poland), only COCs consisting of oocytes with homogeneous ooplasm without dark spots and surrounded by at least three layers of compact cumulus cells were selected for the study. COCs were washed twice in wash medium (M199; #M5017) supplemented with 20 mM HEPES (#H3784), 25 mM sodium bicarbonate (#S4019), 0.4% bovine serum albumin (BSA; #A9418) and 40 μg/ml gentamicin (#G1272). They were then washed in maturation medium.
In vitro oocyte maturation
After washing, groups of 50 immature COCs were allowed to mature in four-well plates (#144444) containing 400 μl of maturation medium (TCM 199 Maturation Medium (19,990/0010)) supplemented with 0.02 IU/ml of pregnant mare’s serum gonadotropin (PMSG, #G4527), 0.01 IU/ml of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG, #C0684) and 5% foetal bovine serum (FBS, #12106C). They were overlaid with 400 μl of mineral oil (#M5310) and incubated at 38.5 °C in a 5% CO2 humidified air atmosphere for 24 h for IVM. For the analysis of PGE2 effects on oocyte maturation, maturation medium was supplemented with 10 μM PGE2 (#14010; Cayman Chemical, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA). The dose of PGE2 was based on previous bovine studies [26, 28]. Stock solution of PGE2 was dissolved in EtOH (#396420113; Avantor Performance Materials Poland, Gliwice, Poland) and stored at − 20 °C until use. On the day of the experiment, stock solution was further diluted by 1:100 in the maturation medium to reach the chosen concentration. The final concentration of EtOH (0.06%, v/v) in the medium was the same in all treatment groups. An additional group, containing the same volume of EtOH only, was included in each experiment as a control. Following maturation, a part of oocytes from each experimental group were completely denuded of cumulus cells by using hyaluronidase solution (H4272; Merck, Sigma-Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany). These denuded oocytes were used to test the effect of PGE2 on oocyte maturation. To assess maturation ratio at the end of the maturation time, the denuded oocytes were observed at × 400 magnification under an inverted phase contrast microscope (CKX41, Olympus, Warsaw, Poland). Mature (MII) oocytes were characterized by extrusion of the first polar body without germinal vesicle in the cytoplasm, whereas the oocytes that had a germinal vesicle or had no germinal vesicle with non-extrusion of the first polar body were defined as immature. The maturation rates were calculated based on the total number of cultured oocytes. The results of developmental rates were derived from two independent experiments.
In vitro embryo production
To assess embryo development of treated COCs, in vitro matured oocytes were fertilized. Pools of COCs from the control and PGE2-stimulated group were washed in fertilization medium (TL fertilization medium (19,990/0030) supplemented with 10 μg/ml of heparin (#08BK0110, WZF Polfa, Warsaw, Poland), 0.2 mM sodium pyruvate (#P3662) and 0.6% BSA). For IVF, frozen-thawed semen from the same bull was used throughout the experiment. After thawing, the semen was layered underneath capacitation medium (TL sperm capacitation medium (19,990/0020) supplemented with 0.1 mM sodium pyruvate, 0.6% BSA and 0.1 mg/ml gentamicin) and incubated for 1 h at 38.5 °C in a 5% CO2 and humidified air atmosphere to allow recovery of motile sperm using a swim-up procedure. After incubation, the upper two-thirds of the capacitation medium were recovered, centrifuged at 200×g for 10 min, the supernatant was removed, and the sperm pellet was diluted in an appropriate volume of fertilization medium to give a final concentration of 106 motile sperm/ml. Groups of 50 COCs were co-incubated with spermatozoa in four-well dishes containing 400 µl of fertilization medium under 400 µl of mineral oil for 18 h at 38.5 °C, in a 5% CO2 humidified air atmosphere. The day of in vitro insemination was considered Day 0. At 18 h postinsemination (hpi) embryos were separated from cumulus cells by vortexing, washed three times in wash medium and at 48 hpi the cleavage rates were assessed. Embryos were then cultured in four-well dishes containing 400 µl of culture medium (SOF; synthetic oviduct fluid medium (19,990/0040) supplemented with amino acids: 10 µl/ml BME (#B6766) and 20 µl/ml MEM (#M7145)), 3.3 mM sodium pyruvate and 5% FBS under 400 µl of mineral oil. Culture was carried out at 38.5 °C in an atmosphere of 5% CO2, 5% O2, 95% N2 with high humidity for 7 days. The number and morphological quality of blastocysts were then determined. Embryo quality was evaluated based on the International Embryo Transfer Society (IETS) Manual [29]. The quality of the blastocysts were scored as follows: grade A = excellent and good; grade B = fair and moderate; grade C = poor; and grade D = dead or degenerating [29]. Embryos classified as quality grade A-C were counted for blastocyst formation and blastocyst quality ratios. The rates of development to the blastocyst stage were calculated based on the total number of fertilized oocytes. The results of developmental rates were derived from twelve independent experiments.
RNA isolation and reverse transcription
For transcript level analysis, total RNA was extracted from oocytes and cumulus cells. Each experimental group used for total RNA isolation contained eight pools of 10 oocytes or all cumulus cells, separated from the respective oocytes. The oocytes and corresponding cumulus cells were suspended in the extraction buffer and were processed for RNA isolation according to the manufacturer’s instructions (#KIT0204; Arcturus PicoPure RNA Isolation Kit, Applied Biosystems, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA). DNase treatment was performed for the removal of genomic DNA contamination using the RNase-free DNase Set (#79254, Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). Samples were stored at − 80 °C until reverse transcription. Reverse transcription (RT) was carried out using oligo (dT)12–18 primers (#18418–012) by Super Script III reverse transcriptase (#18080–044), in a total volume of 20 μl, to prime the RT reaction and produce cDNA. The RT reaction was carried out at 65 °C for 5 min and then 42 °C for 60 min, followed by a denaturation step at 70 °C for 15 min. RNase H (#18021–071) was used to degrade the RNA strand of an RNA-DNA hybrid (37 °C for 20 min). Reverse transcription products were diluted fifteen times and were stored at − 20 °C until real-time PCR amplification.
Quantitative real-time PCR
Real-time PCR was conducted for the quantification of mRNA for the examined genes. The gene symbols, gene names, specific primer sequences and size of the amplified fragments of all transcripts are listed in Table 1. The results of mRNA abundance were normalized to the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH, an internal control) mRNA level and were expressed as arbitrary units. This housekeeping gene was chosen using NormFinder software, comparing three candidate genes: GAPDH, β-actin and H2A.1 [30]. The primers were designed using an online software package (http://bioinfo.ut.ee/primer3/). Real-time PCR was performed using an ABI Prism 7900 (Applied Biosystems, Thermo Fischer Scientific, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA) sequence detection system and Maxima® SYBR Green/ROX qPCR Master Mix (#K0222, Thermo Fischer Scientific, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA). The PCR samples were analyzed in 384-well plates. Each reaction well (10 μl) contained 3 μl of RT product, 5 μM each of forward and reverse primers and 5 μl SYBR Green PCR master mix. In each reaction, we used a quantity of cDNA equivalent to 0.2 oocyte or cumulus cells from each COC. Real-time PCR was performed under the following conditions: 95 °C for 10 min, followed by 40 cycles of 94 °C for 15 s and 60 °C for 60 s. Subsequently, in each case PCR melting curves were obtained to ensure single-product amplification. To exclude the possibility of genomic DNA contamination in the RNA samples, the reactions were also performed either with blank-only buffer samples or in the absence of the reverse transcriptase enzyme. The specificity of the PCR products for all the examined genes was confirmed by gel electrophoresis and sequencing. The efficiency range for the target and internal control amplifications was between 95 and 100%. For the relative quantification of the mRNA levels, the real-time PCR Miner algorithm was used [31].
Table 1.
Primers used for Real-time PCR
| Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Primer sequence (5′-3′) | Fragment size, bp | Gen Bank accession no. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTGS2 | prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase 2 |
TGGGTGTGAAAGGGAGGAAA AAGTGCTGGGCAAAGAATGC |
127 | NM_174445.2 |
| PTGES | microsomal prostaglandin E synthase 1 |
TGCTGGTCATCAAAATGTACG GCAGTTTCCCCAGGTATGC |
300 | NM_174443.2 |
| PTGES2 | microsomal prostaglandin E synthase 2 |
CCTCCTACAGAAAGGTGCC GTGATGATGTCTGCCAGGG |
133 | NM_001166554.1 |
| PTGES3 | cytosolic prostaglandin E synthase |
TGCAAAGTGGTACGATCGG TAACCTTGGCCATGACTGG |
253 | NM 001007806 |
| PTGER1 | prostaglandin E2 receptor 1 |
GAGTCCCTTGCTGGTGGTGGT CTGGTTCCACGAGGCGAGGC |
103 | NM_001192148.1 |
| PTGER2 | prostaglandin E2 receptor 2 |
GCTCCTTGCCTTTCACGATTTT CTCAGGATGGCAAAGACCCAA |
130 | NM_174588.2 |
| PTGER3 | prostaglandin E2 receptor 3 |
CATACTGGGGCTCTCGGCG TCATTATCAGCAACGGCGACCA |
200 | NM_181032.1 |
| PTGER4 | prostaglandin E2 receptor 4 |
CATCCCGCTTGTGGTGCGAG AGGGTTTTTGCCGATGACTGG |
76 | NM_174589.2 |
| CTSB | cathepsin B |
GGCTCACCCTCTCCAGTCCT TCACAACCGCCTTGTCTGAA |
136 | NM 174031.2 |
| CTSK | cathepsin K |
GAACCACTTGGGGGACATGA GGGAACGAGAAGCGGGTACT |
77 | NM 001034435.1 |
| CTSS | cathepsin S |
CCGCCGTCAGCATTCTTAGT CATGTGCCATTGCAGAGGAG |
99 | NM 001033615.1 |
| CTSZ | cathepsin Z |
GGGGAGGGAGAAGATGATGG CCACGGAGACGATGTGGTTT |
146 | NM 001077835.1 |
| GLUT1 | glucose transporter 1 |
GATCCACAGAGCGCAGCC TGTCAGCTTCTTGCTGGTGG |
90 | NM_174602.2 |
| GLUT4 | glucose transporter 4 |
ATTGTGGCCATCTTTGGCTTCGTG AACCCATGCCGATGATGAAGTTGC |
160 | NM_174604.1 |
| GFPT1 | glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate transaminase 1 |
AAACACAGTCGGCAGTTCCA TGGCTACACCAATCTCAGGC |
80 | NM_001109961.1 |
| GFPT2 | glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate transaminase 2 |
GAGATGTGCGGAATCTTTGCC ACCTGCTGAGTCATAGCCTCT |
120 | NM_001076883.1 |
| PFKP | phosphofructokinase |
TCAGAGAACCGTGCCTGGAAGAAA TGACCACAAGCTCCTTGATCTGCT |
112 | NM_001193220.1 |
| LDHA | lactate dehydrogenase A |
TCTGGATTCAGCTCGCTTCCGTTA TTCTTCAGGGAGACACCAGCAACA |
147 | NM_174099.2 |
| CAT | catalase |
CTGGGACCCAACTATCTCCA GATGCTCGGGAGCACTAAAG |
112 | NM_001035386.2 |
| GPX4 | glutathione peroxidase 4 |
GTGCTCGCTCCATGCACGA CCTGGCTCCTGCCTCCCA |
120 | NM_174770.4 |
| FAS | Fas cell surface death receptor |
AAAAACTGGGGCTGCCCTTA CTTTGTGGGGGATGGAACAA |
148 | NM_174662.2 |
| FASLG | Fas ligand |
ACTACCGCCACCACCTCTGA GGCCACCAGAACCATGAAAA |
85 | NM_001098859.1 |
| TNFα | tumor necrosis factor alpha |
CCGCATTGCAGTCTCCTACC TGGGTTCATACCAGGGCTTG |
110 | NM_173966.2 |
| TNFR1 | tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 |
CCACTGGTGCTTCCAGCTCT TTTCCTTGGGGACAGGGACT |
110 | NM_174674.2 |
| TNFR2 | tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 |
CCCCAGGACTCTGGCTCTTT CCAAGACAGGACCCATCAGG |
113 | NM_001040490.1 |
| BAX | BCL2 associated X, apoptosis regulator |
GTGCCCGAGTTGATCAGGAC CCATGTGGGTGTCCCAAAGT |
126 | NM_173894.1 |
| BCL2 | BCL2 apoptosis regulator |
GAGTTCGGAGGGGTCATGTG GCCTTCAGAGACAGCCAGGA |
203 | NM_001166486.1 |
| CASP8 | caspase 8 |
CTGAGAGAAGAGGCCCGTGA CCCGGCTTAGGAACTTGAGG |
173 | NM_001045970.2 |
| CASP3 | caspase 3 |
TGGTGCTGAGGATGACATGG GAGCCTGTGAGCGTGCTTTT |
163 | NM_001077840.1 |
| GAPDH | glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
CACCCTCAAGATTGTCAGCA GGTCATAAGTCCCTCCACGA |
103 | NM_001034034.2 |
PGE2 measurement
The concentration of PGE2 in maturation medium from the control group was established using the PGE2 ELISA kit (#ADI-901-001; Enzo Life Sciences Farmingdale, New York, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The standard curve for PGE2 ranged from 19.6 to 2500 pg/ml. The average intra- and inter-assay coefficients of variation were 10.7 and 12.8% respectively. The samples of six independent repeats were measured in duplicate. To determine PGE2 production, the measured concentration in media blanks was subtracted from the concentration in the control. Prostaglandin E2 production was expressed as pg/ml per COC.
Glucose metabolism
After 24 h of IVM, the maturation medium from the control and PGE2-treated group was recovered and stored at − 20 °C until measurements were taken of glucose and lactate concentrations. These levels were determined using an ABL 800 FLEX analyzer (Radiometer Medical, Copenhagen, Denmark). To determine glucose uptake, the measured glucose concentration was subtracted from the concentration of glucose in media blanks (medium cultured without COCs). To determine lactate production the measured concentration in media blanks was subtracted from the concentration of the studied factors in experimental media. The results of glucose metabolism were derived from six independent experiments. Glucose uptake and lactate production were expressed as mg/dl per COC and mmol/L per COC, respectively.
Mitochondrial staining
Mitochondrial distribution patterns were examined using MitoTracker™ Red CMXRos (#M7512; Invitrogen/Molecular Probes, Invitrogen (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA). After 24 h of IVM, denuded oocytes were incubated with 0.1 μM MitoTrackerR probe for 20 min at 37 °C in the dark. The oocytes were then washed three times in 0.1% PVA in PBS and placed at 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS for 15 min at 37 °C. After fixation, the oocytes were washed twice in PBS and observed under an LSM 800 Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope System (Carl Zeiss, Poznan, Poland), using appropriate fluorescence filters with excitation/emission at 579 nm/599 nm. The oocytes were categorized into one of three groups based on the pattern of mitochondrial distribution: (1) oocytes with homogeneous distribution, where mitochondria were evenly distributed throughout the cytoplasm, (2) oocytes with semi-peripheral distribution, where mitochondria were unequally dispersed in the cytoplasm, and (3) oocytes with peripheral distribution, where mitochondria were located underneath the oolemma. This experiment was repeated three times with 25 COCs per treatment group. The mitochondrial distribution patterns were expressed as a percentage of total COCs.
Tetraethylbenzimidazolylcarbocyanine iodide dye (JC-1; JC-1 Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Assay Kit, #ab113850, Abcam, Cambridge, UK) was used to assess the mitochondrial membrane potential of the oocytes. After 24 h of IVM, denuded oocytes were washed three times in 0.1% PVA in PBS and incubated with 4 μM JC-1 solution for 30 min in humidified air with 5% CO2 at 38.5 °C in the dark. Oocytes were then washed twice in PBS and immediately observed under an LSM 800 Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope System (Carl Zeiss, Poznan, Poland) using an appropriate fluorescence filter: the JC-1 monomer (low mitochondria polarization/low membrane potential) was detected with a green filter (excitation: 495 nm, emission: 529 nm), and JC-1 aggregates (high mitochondria polarization/high membrane potential) were detected with a red filter (excitation: 565 nm, emission: 590 nm). The fluorescent images obtained were analyzed using ZEN blue 2.5 Pro Software (Carl Zeiss, Poznan, Poland) to determine the intensity of fluorescence in each oocyte. This experiment was repeated three times with 25 COCs per treatment group. Mitochondrial membrane potential was expressed as the ratio of red fluorescence intensity to green fluorescence intensity in each experimental group.
Assessment of intracellular ROS and GSH levels
The intracellular ROS and GSH levels in the control and PGE2-treated oocytes were measured using 2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (DCHFDA, #D6883; Merck, Sigma-Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany) and ThiolTracker™ Violet Glutathione Detection Reagent (#T10095; Invitrogen/Molecular Probes, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA), respectively. After 24 h of IVM, denuded oocytes were incubated with 100 μM DCHFDA or 20 μM ThiolTracker™ Violet dye solution for 30 min at 37 °C in the dark. The oocytes were then washed three times in 0.1% PVA in D-PBS and placed at 4% paraformaldehyde in D-PBS for 30 min at room temperature (RT). After fixation, the oocytes were washed twice in D-PBS and observed under an Axio Observer Microscope System (Carl Zeiss, Poznan, Poland) using appropriate fluorescence filters with excitation/emission at 495 nm/529 nm and 404 nm/526 nm for DCHFDA and ThiolTracker™ Violet, respectively. The fluorescent images obtained were analyzed using ZEN blue 2.5 Pro Software (Carl Zeiss, Poznan, Poland) to determine the intensity of fluorescence in each oocyte. The data were calculated as an average fluorescence intensity ratio. This experiment was repeated three times with 25 COCs per treatment group.
Detection of apoptosis in COCs
Terminal-uridine nick-end labeling (TUNEL) was used to detect apoptotic cells in the COCs using an In Situ Cell Death Detection Kit, Fluorescein (#11684795910; Roche, Merck, Sigma-Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany). At the end of the maturation time, COCs were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS for 1 h at RT. The COCs were then permeabilized in 0.3% Triton X-100 (#T9284, Sigma-Aldrich, Germany) in 0.1% sodium citrate for 2 min on ice and washed twice in PBS. Before TUNEL labeling, positive control COCs were treated with 3000 U/ml DNase (#79254; Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) in the reaction buffer and incubated at RT for 10 min to induce DNA strand breaks. Following incubation, positive control and sample COCs were placed in 50 μl of TUNEL reaction mixture with the enzyme (terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase) and incubated at 37 °C for 1 h in the dark. At the same time, negative control COCs were incubated in TUNEL label solution without the enzyme. Following incubation, COCs were washed three times in PBS, then stained with 10 μg/ml DAPI (#D9564; Merck, Sigma-Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany) for 30 min at 30 °C in the dark. The COCs were observed under a confocal laser scanning microscope Olympus Fluoview FV10i (Olympus, Warsaw, Poland) using the DAPI filter to estimate the total number of nuclei and the FITC filter for assessment of TUNEL positive cells. The data was calculated as a percentage of FITC positive (apoptotic) cells within all detected DAPI positive cells. This experiment was repeated three times with 25 COCs per treatment group.
Statistical analysis
Maturation rates, cleavage rates, rates of development to blastocyst and blastocyst quality were analyzed by Fisher’s exact test. The differences in the transcript levels of PGE2 synthases and receptors were determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test. The effects of treatment with PGE2 on mRNA expressions, apoptosis, mitochondrial membrane potential, and glucose, lactate, GSH and ROS levels were examined by Student’s t-test for independent pairs. Two-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey multiple comparison test was used to determine differences in mitochondrial distribution. All analyses were performed using the statistical software GraphPad PRISM 8.0 (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, California, USA), and the results are presented as the means ± SEM. Differences were considered statistically significant at the 95% confidence level (P < 0.05).
Results
Maturation rate, embryonic development and blastocyst morphological quality
The maturation rate of oocytes matured in the presence of PGE2 was not significantly different than those of control oocytes (61.36% vs. 74.51%, respectively; P = 0.061; Table 2). The cleavage rates assessed at 48 hpi were also similar in the control and PGE2-treated groups (81.55% vs. 82.35%, respectively; P > 0.1; Table 3). We found no difference in the proportion of oocytes reaching the blastocyst stage on Day 7 in the control compared to the PGE2-stimulated groups (26.94% vs. 31.25%, respectively; P > 0.1; Table 3). The analysis of the distribution of blastocyst quality showed that there were significantly more blastocysts given a grade of A or B in the PGE2-treated groups compared to the control (95.29% vs. 83.56%, respectively; P = 0.0006; Table 3).
Table 2.
The effect of PGE2 treatment of in vitro oocyte maturation medium on maturation of bovine oocytes
| Treatment | Total oocytes, n | Immature oocyte, n | Mature (MII) oocyte, n | Maturation rate, % | P value of maturation rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| control | 88 | 34 | 54 | 61.36 | 0.061 |
| PGE2 | 102 | 26 | 76 | 74.51 |
Proportion of mature oocytes relative to the total number of oocytes
P values determined by Fisher’s exact test
Table 3.
The effect of PGE2 treatment of in vitro oocyte maturation medium on the bovine embryo development and blastocyst morphological quality
| Treatment | Fertilized oocytes, n | Cleaved embryos, n (%) | Blastocyst on Day 7, n (%) | Qualities A and B, n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| control | 542 | 442 (81.55)a | 146 (26.94)a | 122 (83.56)a |
| PGE2 | 544 | 448 (82.35)a | 170 (31.25)a | 162 (95.29)b |
| P = 0.7527 | P = 0.1246 | P = 0.0006 |
Proportion of the cleaved embryos on Day 2 and blastocysts on Day 7 of embryo culture relative to the total number of fertilized oocytes
Proportion of qualities A and B of blastocysts relative to the total number of blastocysts
P values determined by Fisher’s exact test
a,b Different within each column
PGE2 synthesis and action in COCs
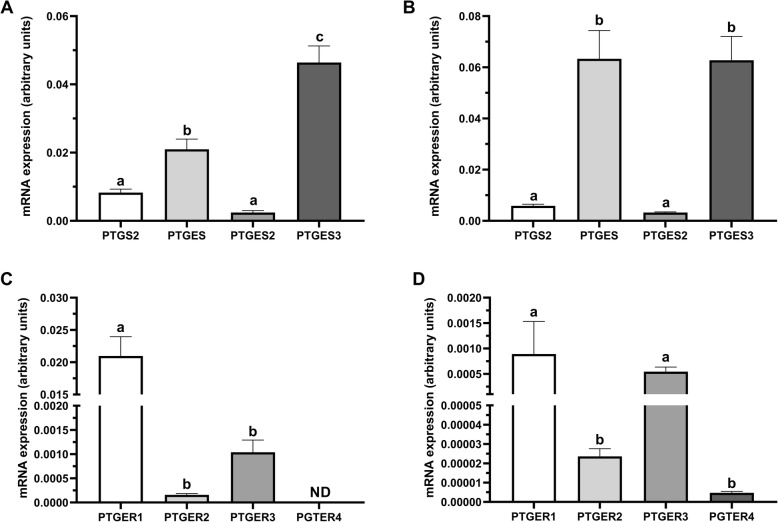
We found the highest mRNA level of PTGES3 in oocytes (P < 0.0001; Fig. 1a), and a significantly higher transcript abundance of PTGES compared to PTGS2 and PTGES2 (P < 0.05; Fig. 1a). Similarly, the transcript levels of PTGES and PTGES3 were significantly higher than those of PTGS2 and PTGES2 in cumulus cells (P < 0.0001; Fig. 1b). A high mRNA level of PTGER1 was also found in oocytes compared to PTGER2 and PTGER3 (P < 0.01; Fig. 1c). Transcripts for PTGER4 were not identified in the oocytes (Fig. 1c). In turn, the mRNA abundance of PTGER1 and PTGER3 was significantly higher than those of PTGER2 and PTGER4 in the cumulus cells (P < 0.05; Fig. 1d). Prostaglandin E2 was also detected in the maturation medium after 24 h incubation of non-treated oocytes. The concentration of PGE2 in maturation medium amounts to 7.60 ± 3.88 pg/ml per COC.
Fig. 1.
Transcription profiles of (a, b) PGE2 synthases: PTGS2, PTGES, PTGES2, PTGES3, and (c, d) PGE2 receptors: PTGER1, PTGER2, PTGER3, PTGER4 in bovine oocytes (a, c) and cumulus cells (b, d) after IVM. The values are presented as arbitrary units and are expressed as the means ± SEM of eight independent repeats (10 oocytes and all cumulus cells separated from the respective oocytes in each replicate). Different letters indicate significant differences (P < 0.05), as determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test
PGE2 effect on mRNA abundance of oocyte quality markers
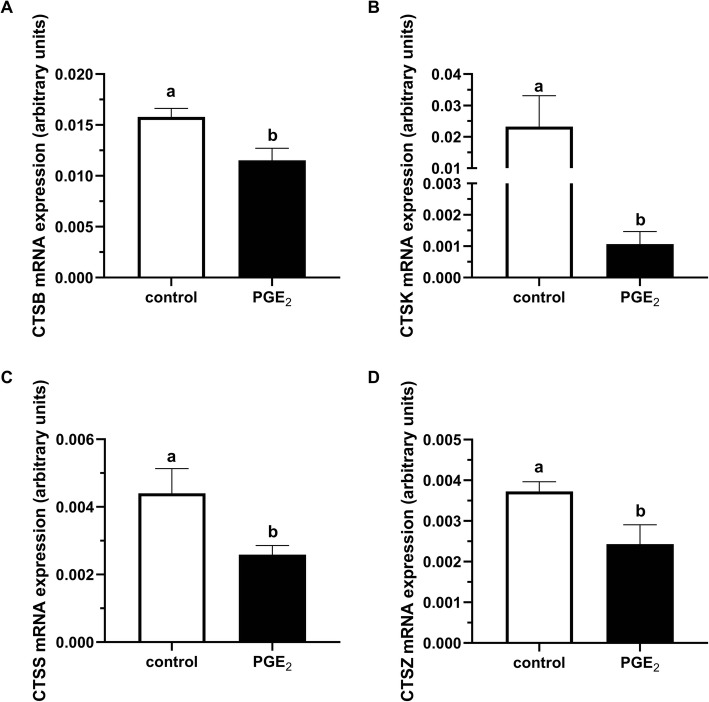
Prostaglandin E2 supplementation of the maturation medium significantly decreased the transcript level of CTSB, CTSK, CTSS, and CTSZ in the cumulus cells (P < 0.05; Fig. 2a-d, respectively).
Fig. 2.
The effect of PGE2 (10 μM) treatment of maturation medium on mRNA abundance of cathepsins: aCTSB, bCTSK, cCTSS, and dCTSZ in cumulus cells. The values are presented as arbitrary units and expressed as mean ± SEM of eight independent repeats (all cumulus cells separated from 10 respective oocytes in each replicate). Different letters indicate significant differences (P < 0.05), as determined by Student’s t-test
PGE2 effect on glucose metabolism in the COCs
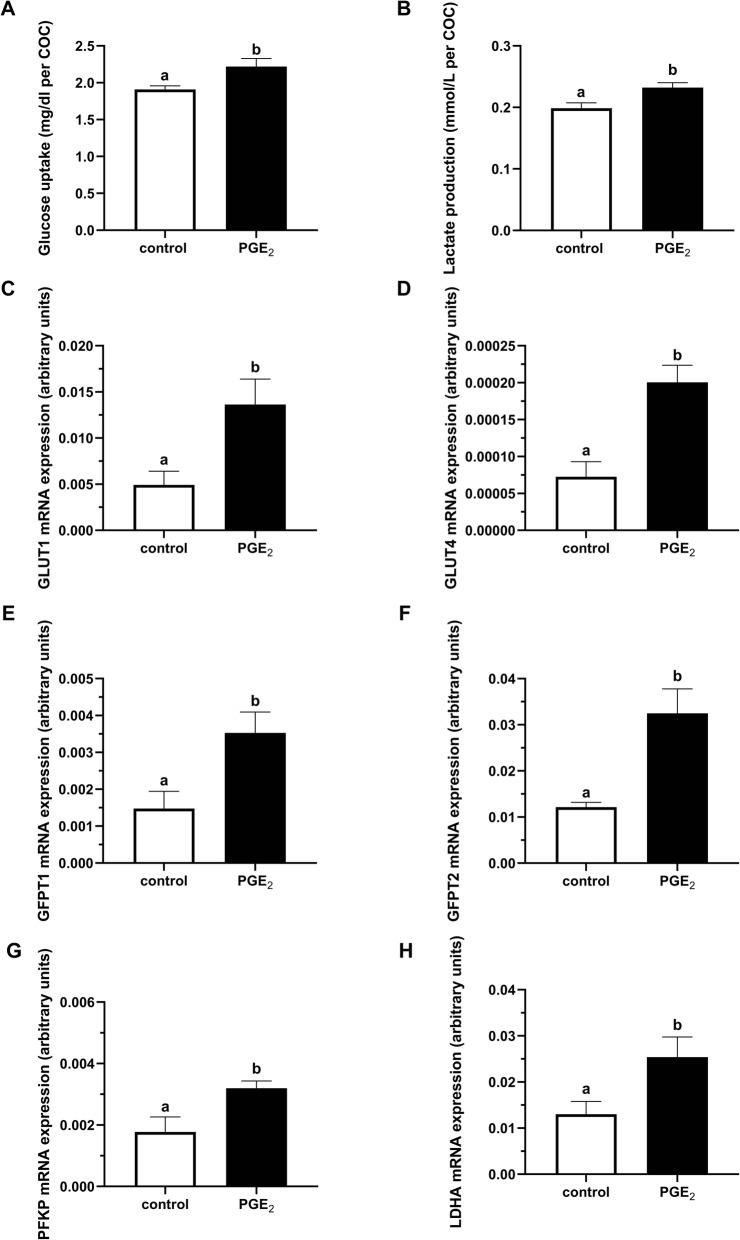
During the IVM, PGE2 stimulated glucose uptake and lactate production by bovine COCs (P < 0.05; Fig. 3a, b, respectively). Moreover, in the cumulus cells, we found that addition of PGE2 to maturation medium significantly increased mRNA abundance of genes coding glucose transporters (GLUT1 and GLUT4; P < 0.05; Fig. 3c, d, respectively), enzymes involved in hexosamine biosynthetic pathway (GFPT1 and GFPT2; P < 0.05; Fig. 3e, f, respectively), and enzymes regulating glycolysis (PFKP and LDHA; P < 0.05; Fig. 3g, h, respectively).
Fig. 3.
The effect of PGE2 (10 μM) treatment of oocyte maturation medium on (a) glucose uptake and (b) lactate production by COCs, and on mRNA abundance of genes involved in glucose metabolism: cGLUT1, dGLUT4, eGFPT1, fGFPT2, gPFKP, and hLDHA in cumulus cells. Glucose uptake and lactate production are expressed as mean ± SEM of six independent experiments and presented as mg/dl per COC and mmol/L per COC, respectively. The values of mRNA expression are presented as arbitrary units and expressed as mean ± SEM of eight independent repeats (all cumulus cells separated from 10 respective oocytes in each replicate). Different letters indicate significant differences (P < 0.05), as determined by Student’s t-test
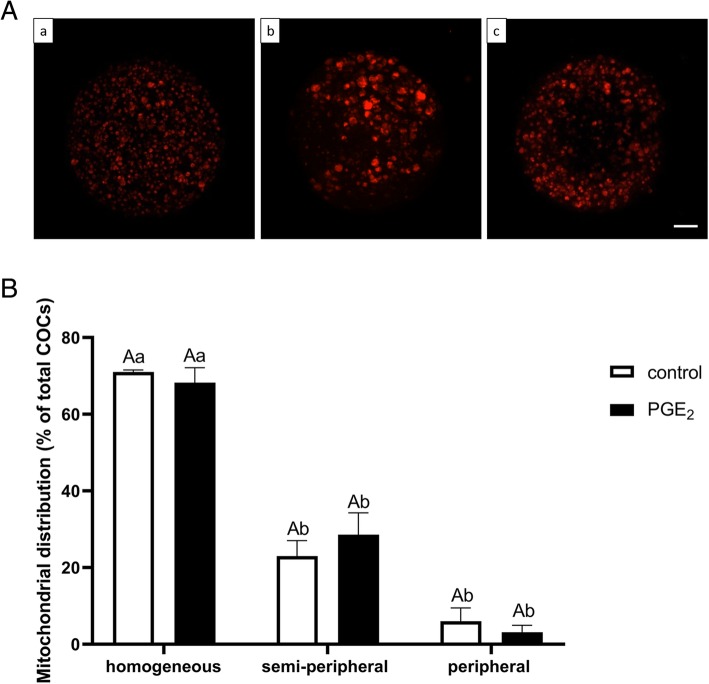
PGE2 effect on mitochondrial status in the oocytes
Figure 4A demonstrates representative fluorescent images of mitochondrial distribution in the bovine oocytes. In Fig. 5A, we present characteristic microphotographs of mitochondria with high and low polarization. The percentages of homogeneous, semi-peripheral and peripheral mitochondrial distribution were all similar in oocytes from the PGE2-treated group compared to the control oocytes (71.00% vs. 68.27, 23.00% vs. 28.6, 6.00% vs. 3.13%, respectively; P > 0.05; Fig. 4B). However, the ratio of red to green fluorescence intensity of JC-1 dye, which reflects the mitochondrial membrane potential of oocytes, was significantly increased in PGE2-treated oocytes compared with the control (P < 0.05; Fig. 5B).
Fig. 4.
The effect of PGE2 (10 μM) on mitochondrial distribution pattern in bovine oocytes after IVM. Panel (A) depicts representative fluorescent images of mitochondrial (a) homogeneous, (b) semi-peripheral, and (c) peripheral distribution in bovine oocytes after IVM. Bars = 25 μm. Panel (B) depicts quantitative analysis of PGE2 effect on mitochondrial distribution pattern. The values are presented as percentage of COCs and expressed as mean ± SEM of three independent repeats (25 COCs per treatment group). Capital letters indicate statistical significance (P > 0.05) between two treatments whilst different small letters indicate significant differences (P < 0.05) within each treatment, as determined by two-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey multiple comparison test
Fig. 5.
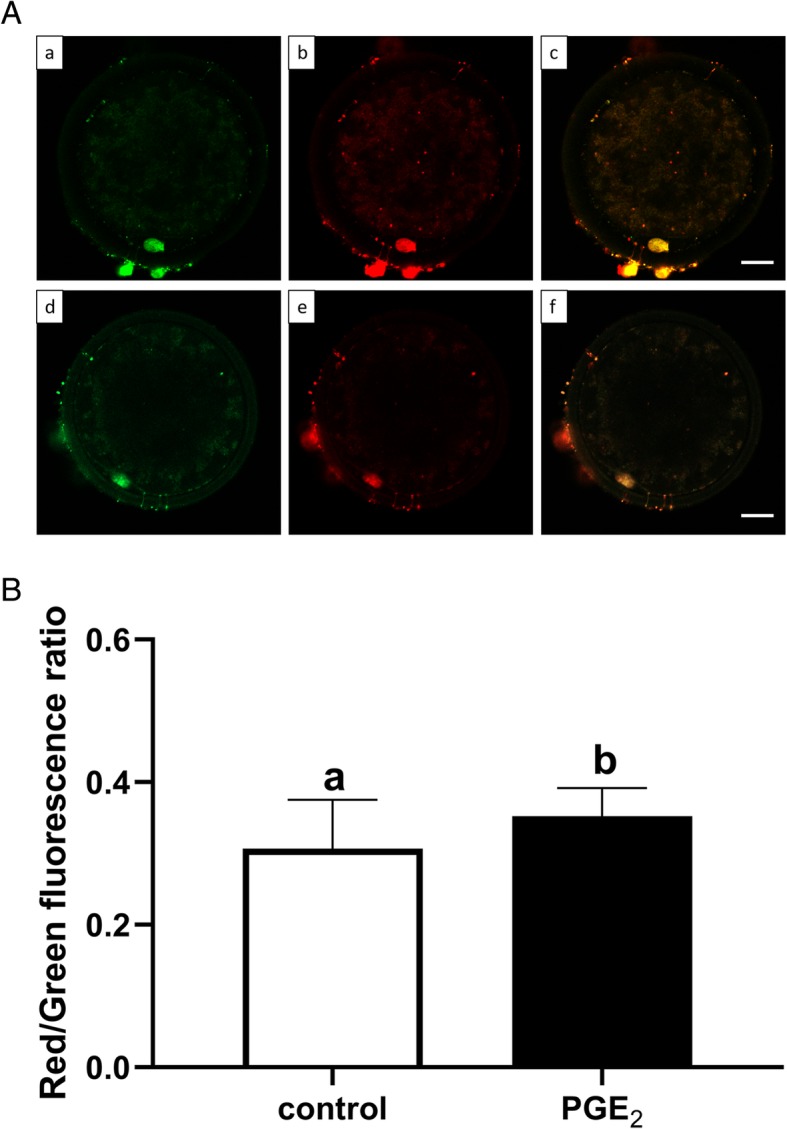
The effect of PGE2 (10 μM) on mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) in bovine oocytes after IVM. Panel (A) depicts representative fluorescent images of oocytes with high (a-c) or low (d-f) polarization of mitochondria as detected by the JC-1 dye (a, d – green; b, e – red; c, f – merge fluorescence). Bars = 25 μm. Panel (B) depicts quantitative analysis of PGE2 effect on mitochondrial membrane potential. The values are presented as the ratio of red fluorescence intensity to green fluorescence intensity and expressed as mean ± SEM of three independent repeats (25 COCs per treatment group). Different letters indicate significant differences (P < 0.05), as determined by Student’s t-test
PGE2 effect on oxidative stress in the oocytes
Figure 6A demonstrates representative fluorescent images of bovine oocytes, labelled for assessment of intracellular GSH and ROS levels, with GSH depicted by blue fluorescence and ROS by green fluorescence. Oocytes matured in the presence of PGE2 showed significantly higher intracellular level of GSH relative to control oocytes (P < 0.05; Fig. 6B). We also demonstrated a significantly greater decrease in intracellular ROS level in PGE2-stimulated oocytes compared to control oocytes (P < 0.05; Fig. 6C). Additionally, PGE2 treatment during IVM resulted in a significant increase in mRNA levels of antioxidation-associated genes in the oocyte (CAT and GPX4; P < 0.05; Fig. 6D, E, respectively).
Fig. 6.
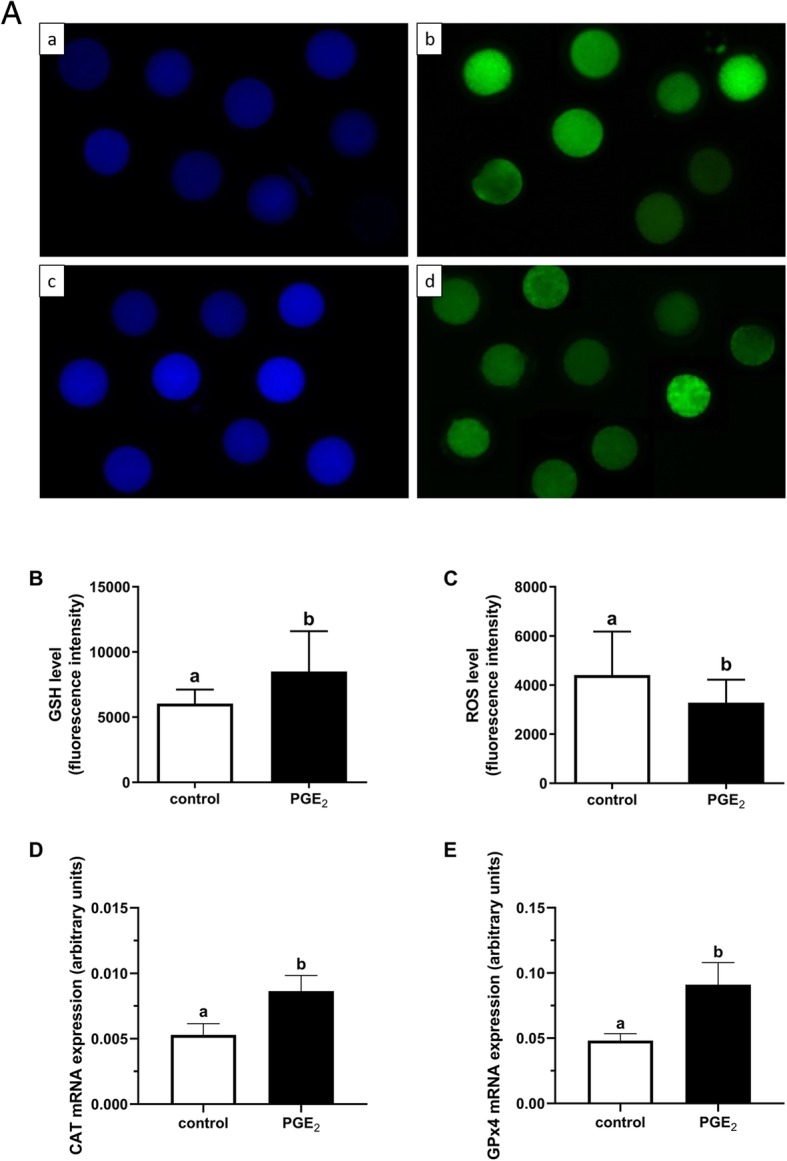
The effect of PGE2 (10 μM) on oxidative stress in bovine oocytes after IVM. Panel (A) depicts representative fluorescent images of intracellular GSH (a, c) and ROS (b, d) levels in the control (a, b) and PGE2-treated (c, d) oocytes. Bars = 50 μm. Panels (B) and (C) depict quantitative analysis of PGE2 effect on intracellular GSH and ROS levels, respectively. The values are presented as an average fluorescence intensity and expressed as mean ± SEM of three independent repeats (25 COCs per treatment group). Different letters indicate significant differences (P < 0.05), as determined by Student’s t-test. Panels (D) and (E) depict relative mRNA levels of the antioxidation-associated genes: CAT and GPX4, respectively, in the control and PGE2-treated oocytes. The values are presented as arbitrary units and expressed as mean ± SEM of eight independent repeats (10 oocytes in each replicate). Different letters indicate significant differences (P < 0.05), as determined by Student’s t-test
PGE2 effect on apoptosis in the COCs
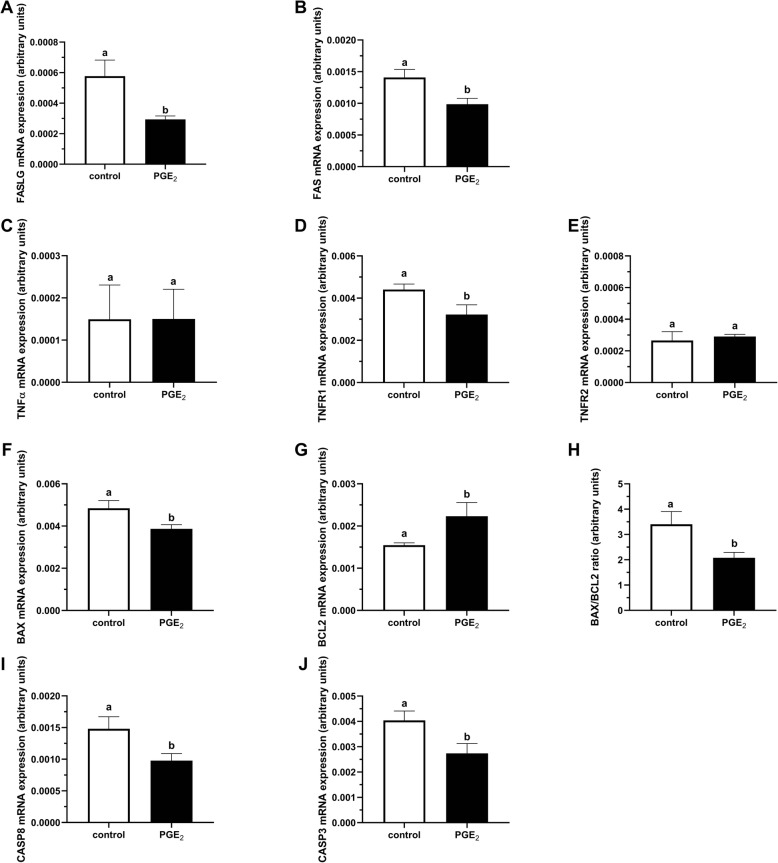
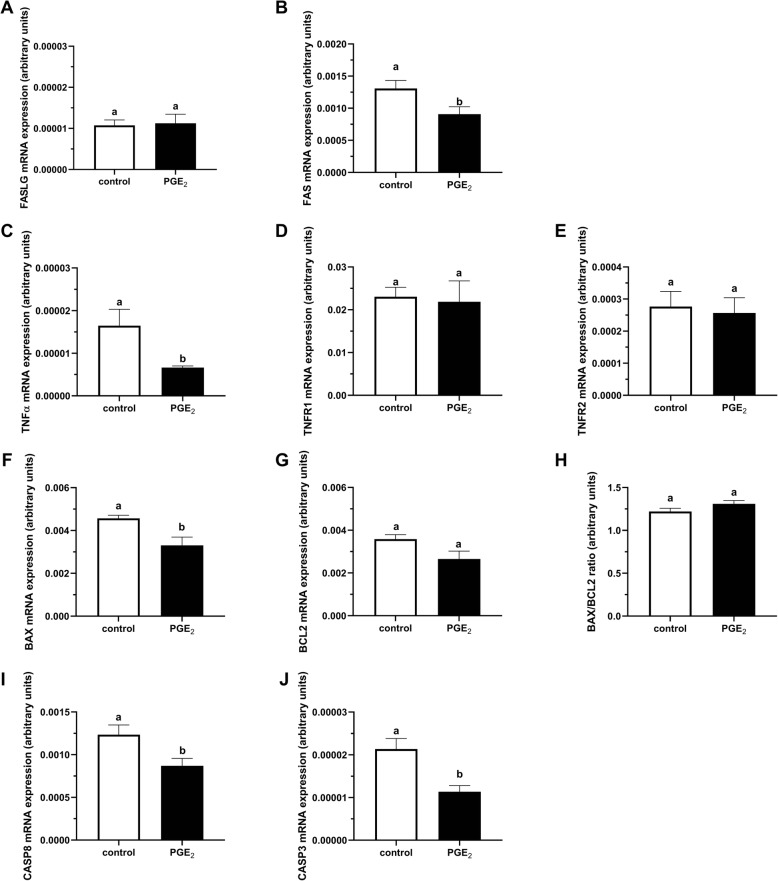
Figure 7A demonstrates representative fluorescent images of bovine COCs used for TUNEL labeling, with DNA fragmentation depicted by green fluorescence and total cells by blue fluorescence. The COCs matured in the presence of PGE2 showed a significantly reduced proportion of TUNEL positive apoptotic cumulus cells relative to control COCs (11.98% vs. 7.25%, respectively; P < 0.05; Fig. 7B). Moreover, in oocytes we found significantly lower mRNA abundance of genes coding for proteins linked to extrinsic apoptosis (FASLG, FAS, TNFR1; P < 0.05; Fig. 8a, b, d, respectively), intrinsic apoptosis (BAX; P < 0.05; Fig. 8f), and caspases (CASP8 and CASP3; P < 0.05; Fig. 8i, j, respectively) in the PGE2-treated group compared to control. We also found a higher mRNA level of antiapoptotic BCL2 and a lower BAX/BCL2 ratio in PGE2-stimulated oocytes compared to control oocytes (P < 0.05; Fig. 8g, h, respectively). In cumulus cells, we showed significantly lower mRNA abundance of genes coding for proteins associated with extrinsic apoptosis (FAS, TNFα; P < 0.05; Fig. 9b, c, respectively), mitochondrial apoptosis pathway (BAX; P < 0.05; Fig. 9f) and caspases (CASP8 and CASP3; P < 0.05; Fig. 9i, j, respectively) in the PGE2-treated group compared to control.
Fig. 7.
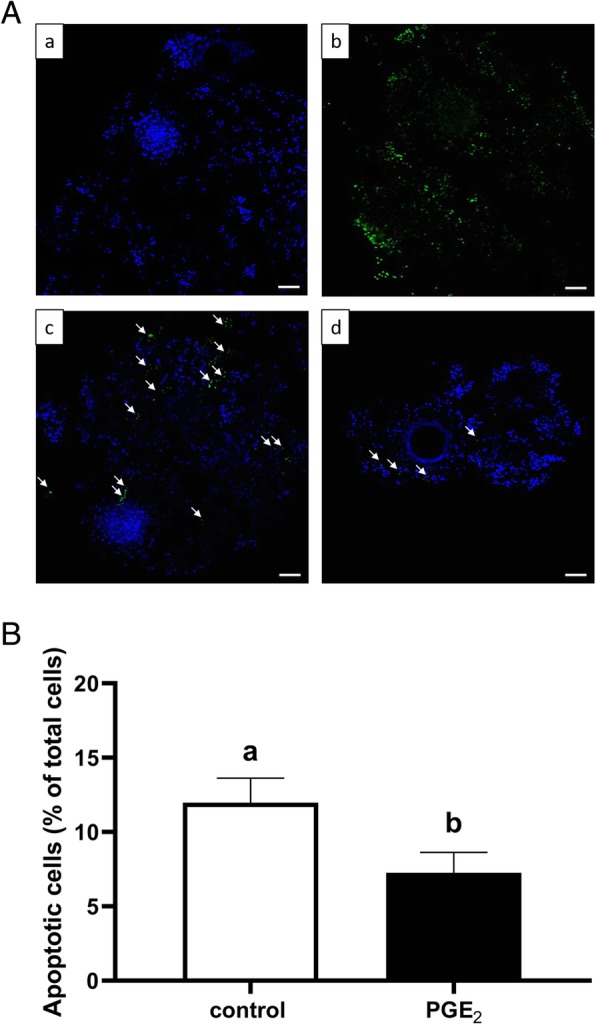
The effect of PGE2 (10 μM) treatment of oocyte maturation medium on apoptosis in COCs. Panel (A) depicts representative fluorescent images of bovine COCs used to TUNEL labeling: (a) negative control, (b) positive control, (c) control COCs, and (d) COCs matured in the presence of PGE2. White arrows indicate TUNEL stained apoptotic nuclei (green) in contrast to DAPI stained nuclei (blue). Bars = 100 μm. Panel (B) depicts quantitative analysis of PGE2 effect on apoptosis in COCs. The data are presented as a percentage of TUNEL positive apoptotic cells within all detected DAPI positive cells and expressed as mean ± SEM of three independent repeats (25 COCs per treatment group). Different letters indicate significant differences (P < 0.05), as determined by Student’s t-test
Fig. 8.
The effect of PGE2 (10 μM) treatment of maturation medium on mRNA abundance of factors involved in apoptosis: aFASLG, bFAS, cTNFα, dTNFR1, eTNFR2, fBAX, gBCL2, hBAX/BCL2 ratio, iCASP8, and jCASP3 in oocytes. The values are presented as arbitrary units and expressed as mean ± SEM of eight independent repeats (10 oocytes in each replicate). Different letters indicate significant differences (P < 0.05), as determined by Student’s t-test
Fig. 9.
The effect of PGE2 (10 μM) treatment of maturation medium on mRNA abundance of factors involved in apoptosis: aFASLG, bFAS, cTNFα, dTNFR1, eTNFR2, fBAX, gBCL2, hBAX/BCL2 ratio, iCASP8, and jCASP3 in cumulus cells. The values are presented as arbitrary units and expressed as mean ± SEM of eight independent repeats (all cumulus cells separated from 10 oocytes in each replicate). Different letters indicate significant differences (P < 0.05), as determined by Student’s t-test
Discussion
PGE2 synthesis in bovine COCs after IVM
This study details the mRNA expression of enzymes involved in PGE2 synthesis and the PGE2 receptors present in bovine oocytes and cumulus cells. These account for the ability of the bovine COCs to produce and secrete PGE2 during IVM. Bovine COCs therefore appear to be both a source and a target of PGE2 action, and PGE2 may be involved in cellular signaling between the oocyte and cumulus cells during maturation. In earlier studies of bovine COCs, transcript coding for PTGS2 was detected in cumulus cells but not in the oocyte [13, 26]. However, Nuttinck et al. [14] and Marei et al. [27] examined the mRNA expression profile of PGE2 synthases in whole bovine COCs and found that expression of PTGES was significantly higher in mature than immature COCs. Moreover, the induction of PTGES expression coexisted with the induction of PTGS2 expression and PGE2 secretion by maturing COCs, suggesting the involvement of a PTGS2/PTGES pathway during the maturation process [14]. We found the highest expression of PTGES and PTGES3 in denuded oocytes and cumulus cells, which partially agrees with results obtained in whole COCs, where a significantly higher level of PTGES is found [14, 27]. Similar to earlier studies [27, 32], we showed that bovine COCs release PGE2 during IVM. In the expression of PGE2 receptors, only PTGER2 mRNA has previously been found in bovine oocytes, while mRNA expression of PTGER2, PTGER3 and PTGER4 were detectable in cumulus cells [26]. For the whole bovine COCs, PTGER2 and PTGER3 were found to be expressed, while very low levels of PTGER4 expression were detectable and PTGER1 was not detected [33]. However, in this study we found the mRNA level of PTGER1 to be the highest and no transcripts of PGTER4 in oocytes. The highest expression of PTGER1 and PTGER3 was found in cumulus cells. The present data, concerning cell specific expression of PGE2 synthases and PGE2 receptors in bovine COCs, confirm the inherence of a PGE2 autocrine/paracrine regulatory pathway during oocyte maturation.
PGE2 influence on oocyte developmental competence
In human cumulus cells, higher PTGS2 expression is reported in competent COCs, from which oocytes develop into better quality embryos [12]. Addition of PGE2 to the fertilization medium also increases the cleavage rate as well as bovine oocytes with low cleavage rates produce less PGE2 than oocytes with high cleavage rates [32]. This suggests that PGE2 could be involved in the acquisition of oocyte developmental competence. We demonstrated that in bovine cumulus cells, PGE2 supplementation of maturation medium reduces the expression of CTSB, CTSK, CTSS and CTSZ. A higher expression of these enzymes is associated with developmental incompetence of bovine oocytes and thus this expression could serve as oocyte quality markers [34]. In turn, PGE2 added to the oocyte maturation medium had no effect on the number of matured oocytes, cleaved embryos or gained blastocysts. This supports previous studies that suggest the presence of PGE2 during IVM and IVF does not influence the proportion of cleaved embryos and blastocysts on Day 8 of culture [28]. Inhibition of PTGS2 during IVM, resulting in a reduced maturation rate at 22 h of IVM and decreased embryo output rates on Day 6 of culture, had no more effect on both rates at a further time point of IVM or on Day 7 of culture [26, 27]. Moreover, the addition of PGE2 to maturation medium with inhibited PTGS2 activity abrogated oocyte maturation and early embryonic developmental defects [26, 27]. The authors suggested that these adverse effects of PTGS2 inhibition during IVM are due to a delay in nuclear maturation and in the kinetics of early embryonic development [26, 27]. However, our study demonstrated that, although addition of PGE2 during IVM had no effect on the normal embryonic development rates, it enhanced the number of better-quality blastocysts. This suggests that PGE2 has a role in increasing the quality of the bovine oocytes.
PGE2 action on glucose metabolism
The terminal differentiation of the COCs, leading to the resumption of meiosis and cumulus expansion, includes processes that require substantial energy from several substrates [35, 36]. Previous studies have suggested that glucose metabolism has a positive effect on oocyte maturation and subsequent blastocyst development [36]. Additionally, the dynamics of the glucose metabolism can be used as a predictive marker of oocyte quality [37]. The lower glucose metabolism in oocytes from pre-pubertal cows in comparison to adult cows [37], as well as the expression of genes coding for GLUT1 in bovine blastocysts produced in vitro compared with in vivo obtained embryos [38], could account for its relevance of the developmental competence of bovine oocytes and embryos. In our study, addition of PGE2 to the oocyte maturation medium increased mRNA expression of GLUT1 and GLUT4. Oocyte capacity for glucose uptake and metabolism is limited and thus cumulus cells provide the intermediates of glucose metabolism, including pyruvate or lactate, to the oocyte [39, 40]. We found that PGE2 increased glucose uptake and lactate production by bovine COCs and simultaneously stimulated expression of genes encoding glycolytic enzymes (PFKP and LDHA). During IVM of bovine oocytes, the linear correlation between glucose utilization and lactate production suggests that COCs preferentially consume glucose via glycolysis [41]. The presence of pyruvate or lactate plus NAD in the maturation medium enhances the maturity level of denuded oocytes, suggesting that the oocytes use them as substrates for energy production [39]. In the present study, we demonstrated that addition of PGE2 to the maturation medium stimulated the expression of genes encoding GFPT1 and GFPT2 in the cumulus cells. These are the rate-limiting enzymes in the hexosamine pathway, in which glucose is converted to glucosamine, a substrate for hyaluronic acid, a major component of the cumulus extracellular matrix [42–44]. It has been shown that a quarter of glucose used by bovine COCs in the later period of IVM is not metabolized through glycolysis [45]. However, addition of glucosamine to IVM medium leads to a decrease in glucose depletion and reduces the requirement of glucose for synthesis of matrix components [41], demonstrating a shift from glucose metabolism to the hexosamine pathway [40]. Therefore, the results of our study suggest that PGE2 increased glucose uptake and stimulated lactate production in bovine COCs, simultaneously affecting the expression of glycolytic enzymes. This indicates a role for PGE2 in directing glucose metabolism down the glycolytic pathway. In addition, PGE2 influence on the expression of enzymes involved in the hexosamine pathway, together with evidence of the role of PGE2 on cumulus expansion [27, 33], suggests it has a role in directing COCs glucose consumption towards the end of IVM to generate extracellular matrix.
PGE2 action on oxidative stress and mitochondrial status
During ovarian follicle and oocyte development, ROS have important biological roles in the stimulation of meiotic resumption, extrusion of the first polar body, and in promoting the follicular wall rupture to allow the release of oocytes during ovulation [46–48]. However, high levels of ROS and low levels of antioxidants in follicular fluid in women are associated with a reduced pregnancy outcome after intracytoplasmic sperm injection [49, 50]. An increased level of ROS during IVM also causes disturbances in chromosomal distribution, alterations in microtubules on MII spindles, and aneuploidy in mice oocytes. This suggests that oxidative stress can induce chromosomal errors and effect oocyte developmental potential [51, 52]. A higher intrafollicular level of DNA damage biomarker was found in women with high rates of degenerated oocytes, suggesting again the association between oxidative stress and oocyte quality [53]. The authors also demonstrated a lower rate of matured mice oocytes after ROS treatment [53]. Moreover, bovine embryos cultured in atmospheric oxygen tension show higher ROS concentrations, lower blastocyst rates, lower total blastomere numbers, and differences in the expression of DNA-dependent transcription factors related to multiple pathways important for early embryo development [54]. This indicates that the oxidative stress may cause developmental failures and disturb embryo viability. In our study, we found that the addition of PGE2 to IVM medium reduced intracellular ROS level, simultaneously increasing GSH concentration and stimulating mRNA expression of antioxidant genes CAT and GPX4 in the oocyte. One of the main roles of GSH is the maintenance of the redox status in cells, thereby protecting them from oxidative injuries [55, 56]. Optimal cumulus expansion during IVM of bovine oocytes is dependent on intracellular GSH content [57], while high GSH level during IVM improves the efficiency of embryo development [58]. Thus, our study suggests that PGE2 treatment during IVM of bovine oocytes ensures an adequate GSH accumulation for subsequent embryo development. Imbalance between ROS and antioxidants leads to irreversible damage of mitochondrial DNA and alteration of lipids and proteins of the inner membrane, resulting in mitochondrial dysfunction and finally in cell death [59]. In the present study, we found that the mitochondrial membrane potential of oocytes was improved by addition of PGE2 to the maturation medium. Since oxidative injury can induce the release of apoptogenic factors from the mitochondria, leading to the apoptosis of the cell [60], our data imply that PGE2 may protect bovine COCs from both oxidative stress and apoptosis during IVM.
PGE2 action on apoptosis
Apoptosis of embryonic cells is a physiological process that occurs during embryo development and can be an indicator of embryo quality. The negative relationship between embryonic cell number and incidence of the TUNEL reaction is documented in both murine [61] and bovine [62, 63] embryos. This suggests that apoptosis may have an important role in appropriate embryo development, since blastocysts containing higher numbers of cells develop to form better quality embryos [64]. The degree of apoptosis in bovine cumulus cells is also negatively correlated with oocyte developmental capacity [65]. In cows, DNA damage detected by TUNEL labeling is also observed in morphologically fragmented oocytes and embryos [63, 66]. Results from the present study show that the presence of PGE2 during oocyte maturation reduced the number of TUNEL-positive apoptotic nuclei in bovine COCs. Similarly, supplementation of IVM and IVF medium with PGE2 reduces the apoptotic activity in blastocysts [28]. Apoptosis in blastocysts is also increased by PTGS2 inhibition during the IVM/IVF period, whereas addition of PGE2 overrides this effect, suggesting a role for PGE2 in the enhancement of embryonic cell survival during preimplantation development [28]. The incidence of apoptosis is regulated by numerous genes that are involved in either the extrinsic or intrinsic/mitochondrial pathways. Both apoptotic pathways stimulate the CASPs activity, leading to the execution of the apoptotic program [67, 68]. Thus, we examined through which pathway PGE2 could exert its prosurvival effect during IVM. The presence of PGE2 inhibits the expression of genes coding for proteins related to extrinsic apoptosis, including FASLG, FAS, TNFR1 in oocytes and FAS, TNFα in cumulus. CASP8 and CASP3 are also affected in both oocytes and cumulus cells. In terms of the mitochondrial pathway, PGE2 increases antiapoptotic BCL2 expression, decreases proapoptotic BAX expression, and reduces BAX/BCL2 ratio in oocytes. It also inhibits mRNA expression of BAX in cumulus cells. The treatment of IVM and IVF medium with PGE2 has been found to increase the ratio of BCL2/BAX mRNA expression in bovine embryos [28]. Furthermore, inhibition of PTGS2 expression during IVM and IVF decreases the BCL2/BAX ratio, whereas addition of PGE2 reverses this effect [28]. The BAX/BCL2 protein ratio has been found to be correlated with the developmental competence of bovine oocytes and embryos [66]. Other work found that mRNA expression of proapoptotic BAX and CASP3 in bovine early stage embryos was associated with the DNA fragmentation detected in blastocysts, implying that expression of these genes may serve as a marker of embryo viability [63]. Thus, our study provided evidence that PGE2 during IVM is involved in the regulation of apoptotic activity, decreasing the extent of apoptosis in the COCs and altering the expression of apoptosis related genes. Moreover, results of this study, together with the previous data from Nuttinck et al. [28], suggest that periconceptional PGE2 supports antiapoptotic events during bovine early embryo development following IVM.
Conclusions
This study provides evidence, from both functional and gene expression studies, that PGE2 autocrine/paracrine pathway is involved in the control of processes that occur during oocyte maturation in the cow. The exposure of COCs to PGE2 during IVM stimulated the expression patterns of genes associated with oocyte competence and enhanced the number of better-quality blastocysts. To the best of our knowledge, we are also the first to demonstrate that PGE2 has an influence on glucose metabolism. Furthermore, PGE2 appeared to improve the resistance of oocytes to oxidative attack and decreased the occurrence of apoptosis in the COCs, which may be reflected in oocyte viability. We suggest that PGE2 could represent an important player in the mechanisms that can facilitate successful oocyte maturation and oocyte survival in cattle.
Acknowledgments
The authors are indebted to Krzysztof Witek, Ph.D. for the help to capture the bovine oocytes.
Abbreviations
- ANOVA
Analysis of variance
- AREG
Amphiregulin
- BAX
BCL2 associated X, apoptosis regulator
- BCL2
BCL2 apoptosis regulator
- BME
Basal medium Eagle amino acids solution
- BSA
Bovine serum albumin
- CASP3
Caspase 3
- CASP8
Caspase 8
- CAT
Catalase
- COCs
Cumulus-oocyte complexes
- CTSB
Cathepsin B
- CTSK
Cathepsin K
- CTSS
Cathepsin S
- CTSZ
Cathepsin Z
- DAPI
4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole
- DCHFDA
2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate
- DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid
- EREG
Epiregulin
- EtOH
Ethanol
- FAS
Fas cell surface death receptor
- FASLG
Fas ligand
- FBS
Foetal bovine serum
- FITC
Fluorescein isothiocyanate
- GAPDH
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- GFPT1
Glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate transaminase 1
- GFPT2
Glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate transaminase 2
- GLUT1
Glucose transporter 1
- GLUT4
Glucose transporter 4
- GPX4
Glutathione peroxidase 4
- GSH
Glutathione
- HAS2
Hyaluronan synthase 2
- hCG
Human chorionic gonadotropin
- IETS
International Embryo Transfer Society
- IVC
In vitro culture
- IVF
In vitro fertilization
- IVM
In vitro maturation
- JC-1
Tetraethylbenzimidazolylcarbocyanine iodide dye
- LDHA
Lactate dehydrogenase A
- LH
Luteinizing hormone
- MEM
Minimum essential medium non-essential amino acids solution
- NAD
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
- PBS
Phosphate-buffered saline
- PFKP
Phosphofructokinase
- PGE2
Prostaglandin E2
- PMSG
Pregnant mare’s serum gonadotropin
- PTGER1
Prostaglandin E2 receptor 1
- PTGER2
Prostaglandin E2 receptor 2
- PTGER3
Prostaglandin E2 receptor 3
- PTGER4
Prostaglandin E2 receptor 4
- PTGES
Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase 1
- PTGES2
Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase 2
- PTGES3
Cytosolic prostaglandin E synthase
- PTGS2
Prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase 2
- PVA
Polyvinyl alcohol
- real-time PCR
real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction
- ROS
Reactive oxygen species
- RT
Reverse transcription
- RT
Room temperature
- TNFAIP6
TNF alpha induced protein 6
- TNFR1
Tumor necrosis factor receptor 1
- TNFR2
Tumor necrosis factor receptor 2
- TNFα
Tumor necrosis factor alpha
- TUNEL
Terminal-uridine nick-end labeling
Authors’ contributions
DB and IWP designed the research. IKZ, KS, JSCh, JJ, KL and IWP performed research and generated data. DB and IWP analyzed the data and DB wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Polish National Science Centre: 2015/17/B/NZ9/011688.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All experimental procedures were approved by the Local Animal Care and Use Committee in Olsztyn, Poland (Agreement No. 76/2014/DTN).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Karim SM, Hillier K. Prostaglandins in the control of animal and human reproduction. Br Med Bull. 1979;35:173–180. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Sales KJ, Jabbour HN. Cyclooxygenase enzymes and prostaglandins in pathology of the endometrium. Reproduction. 2003;126:559–567. doi: 10.1530/rep.0.1260559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kudo I, Murakami M. Prostaglandin E synthase, a terminal enzyme for prostaglandin E2 biosynthesis. J Biochem Mol Biol. 2005;38:633–638. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2005.38.6.633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Asselin E, Lacroix D, Fortier MA. IFN-tau increases PGE2 production and COX-2 gene expression in the bovine endometrium in vitro. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1997;132:117–126. doi: 10.1016/S0303-7207(97)00128-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Arosh JA, Parent J, Chapdelaine P, Sirois J, Fortier MA. Expression of cyclooxygenases 1 and 2 and prostaglandin E synthase in bovine endometrial tissue during the estrous cycle. Biol Reprod. 2002;67:161–169. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod67.1.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Murakami M, Nakashima K, Kamei D, Masuda S, Ishikawa Y, Ishii T, et al. Cellular prostaglandin E2 production by membrane-bound prostaglandin E synthase-2 via both cyclooxygenases-1 and -2. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:37937–37947. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M305108200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tanioka T, Nakatani Y, Semmyo N, Murakami M, Kudo I. Molecular identification of cytosolic prostaglandin E2 synthase that is functionally coupled with cyclooxygenase-1 in immediate prostaglandin E2 biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:32775–32782. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M003504200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Negishi M, Sugimoto Y, Ichikawa A. Molecular mechanisms of diverse actions of prostanoid receptors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995;1259:109–119. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(95)00146-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sugimoto Y, Narumiya S. Prostaglandin E receptors. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:11613–11617. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R600038200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Park JY, Pillinger MH, Abramson SB. Prostaglandin E2 synthesis and secretion: the role of PGE2 synthases. Clin Immunol. 2006;119:229–240. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2006.01.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Takahashi T, Morrow JD, Wang H, Dey SK. Cyclooxygenase-2-derived prostaglandin E(2) directs oocyte maturation by differentially influencing multiple signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:37117–37129. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M608202200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.McKenzie LJ, Pangas SA, Carson SA, Kovanci E, Cisneros P, Buster JE, et al. Human cumulus granulosa cell gene expression: a predictor of fertilization and embryo selection in women undergoing IVF. Hum Reprod. 2004;19:2869–2874. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deh535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Nuttinck F, Reinaud P, Tricoire H, Vigneron C, Peynot N, Mialot JP, et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 is expressed by cumulus cells during oocyte maturation in cattle. Mol Reprod Dev. 2002;61:93–101. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Nuttinck F, Marquant-Le Guienne B, Clément L, Reinaud P, Charpigny G, Grimard B. Expression of genes involved in prostaglandin E2 and progesterone production in bovine cumulus-oocyte complexes during in vitro maturation and fertilization. Reproduction. 2008;135:593–603. doi: 10.1530/REP-07-0453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ben-Ami I, Freimann S, Armon L, Dantes A, Strassburger D, Friedler S, et al. PGE2 up-regulates EGF-like growth factor biosynthesis in human granulosa cells: new insights into the coordination between PGE2 and LH in ovulation. Mol Hum Reprod. 2006;12:593–599. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gal068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Duffy DM, Stouffer RL. Follicular administration of a cyclooxygenase inhibitor can prevent oocyte release without alteration of normal luteal function in rhesus monkeys. Hum Reprod. 2002;17:2825–2831. doi: 10.1093/humrep/17.11.2825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hizaki H, Segi E, Sugimoto Y, Hirose M, Saji T, Ushikubi F, et al. Abortive expansion of the cumulus and impaired fertility in mice lacking the prostaglandin E receptor subtype EP2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96:10501–10506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.18.10501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Liu Z, Fan H-Y, Wang Y, Richards JS. Targeted disruption of Mapk14 (p38MAPKalpha) in granulosa cells and cumulus cells causes cell-specific changes in gene expression profiles that rescue COC expansion and maintain fertility. Mol Endocrinol. 2010;24:1794–1804. doi: 10.1210/me.2010-0086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sayre BL, Lewis GS. Arachidonic acid metabolism during early development of ovine embryos: a possible relationship to shedding of the zona pellucida. Prostaglandins. 1993;45:557–569. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(93)90019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Yamashita Y, Okamoto M, Kawashima I, Okazaki T, Nishimura R, Gunji Y, et al. Positive feedback loop between prostaglandin E2 and EGF-like factors is essential for sustainable activation of MAPK3/1 in cumulus cells during in vitro maturation of porcine cumulus oocyte Complexes1. Biol Reprod. 2011;85:1073–1082. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.110.090092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Stout TA, Allen WR. Role of prostaglandins in intrauterine migration of the equine conceptus. Reproduction. 2001;121:771–775. doi: 10.1530/rep.0.1210771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wijayagunawardane MP, Miyamoto A, Taquahashi Y, Gabler C, Acosta TJ, Nishimura M, et al. In vitro regulation of local secretion and contraction of the bovine oviduct: stimulation by luteinizing hormone, endothelin-1 and prostaglandins, and inhibition by oxytocin. J Endocrinol. 2001;168:117–130. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1680117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Parent J, Chapdelaine P, Sirois J, Fortier MA. Expression of microsomal prostaglandin E synthase in bovine endometrium: coexpression with cyclooxygenase type 2 and regulation by interferon-tau. Endocrinology. 2002;143:2936–2943. doi: 10.1210/endo.143.8.8969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Arosh JA, Banu SK, Kimmins S, Chapdelaine P, Maclaren LA, Fortier MA. Effect of interferon-tau on prostaglandin biosynthesis, transport, and signaling at the time of maternal recognition of pregnancy in cattle: evidence of polycrine actions of prostaglandin E2. Endocrinology. 2004;145:5280–5293. doi: 10.1210/en.2004-0587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Eppig JJ. Maintenance of meiotic arrest and the induction of oocyte maturation in mouse oocyte-granulosa cell complexes developed in vitro from preantral follicles. Biol Reprod. 1991;45:824–830. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod45.6.824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Nuttinck F, Gall L, Ruffini S, Laffont L, Clement L, Reinaud P, et al. PTGS2-related PGE2 affects oocyte MAPK phosphorylation and meiosis progression in cattle: late effects on early embryonic development. Biol Reprod. 2011;84:1248–1257. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.110.088211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Marei WF, Abayasekara DRE, Wathes DC, Fouladi-Nashta AA. Role of PTGS2-generated PGE2 during gonadotrophin-induced bovine oocyte maturation and cumulus cell expansion. Reprod BioMed Online. 2014;28:388–400. doi: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2013.11.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Nuttinck F, Jouneau A, Charpigny G, Hue I, Richard C, Adenot P, et al. Prosurvival effect of cumulus prostaglandin G/H synthase 2/prostaglandin2 signaling on bovine blastocyst: impact on in vivo posthatching development. Biol Reprod. 2017;96:531–541. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.116.145367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Stringfellow DA, Seidel SM, International Embryo Transfer Society . Manual of the international embryo transfer society : a procedural guide and general information for the use of embryo transfer technology, emphasizing sanitary procedures. 3. Savoy: The Society; 1998. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Andersen CL, Jensen JL, Ørntoft TF. Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Res. 2004;64:5245–5250. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Zhao S, Fernald RD. Comprehensive algorithm for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. J Comput Biol. 2005;12:1047–1064. doi: 10.1089/cmb.2005.12.1047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Gurevich M, Harel-Markowitz E, Marcus S, Shore LS, Shemesh M. Prostaglandin production by the oocyte cumulus complex around the time of fertilization and the effect of prostaglandin E on the development of the early bovine embryo. Reprod Fertil Dev. 1993;5:281–283. doi: 10.1071/RD9930281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Calder MD, Caveney AN, Westhusin ME, Watson AJ. Cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandin E(2)(PGE(2)) receptor messenger RNAs are affected by bovine oocyte maturation time and cumulus-oocyte complex quality, and PGE (2) induces moderate expansion of the bovine cumulus in vitro. Biol Reprod. 2001;65:135–140. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod65.1.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Bettegowda A, Patel OV, Lee K-B, Park K-E, Salem M, Yao J, et al. Identification of novel bovine cumulus cell molecular markers predictive of oocyte competence: functional and diagnostic implications. Biol Reprod. 2008;79:301–9. 10.1095/biolreprod.107.067223. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 35.Cetica P, Pintos L, Dalvit G, Beconi M. Activity of key enzymes involved in glucose and triglyceride catabolism during bovine oocyte maturation in vitro. Reproduction. 2002;124:675–681. doi: 10.1530/rep.0.1240675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Rose-Hellekant TA, Libersky-Williamson EA, Bavister BD. Energy substrates and amino acids provided during in vitro maturation of bovine oocytes alter acquisition of developmental competence. Zygote. 1998;6:285–294. doi: 10.1017/S0967199498000239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Steeves TE, Gardner DK. Metabolism of glucose, pyruvate, and glutamine during the maturation of oocytes derived from pre-pubertal and adult cows. Mol Reprod Dev. 1999;54:92–101. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2795(199909)54:1<92::AID-MRD14>3.0.CO;2-A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Bertolini M, Beam SW, Shim H, Bertolini LR, Moyer AL, Famula TR, et al. Growth, development, and gene expression by in vivo- and in vitro-produced day 7 and 16 bovine embryos. Mol Reprod Dev. 2002;63:318–328. doi: 10.1002/mrd.90015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Cetica P, Pintos L, Dalvit G, Beconi M. Effect of lactate dehydrogenase activity and isoenzyme localization in bovine oocytes and utilization of oxidative substrates on in vitro maturation. Theriogenology. 1999;51:541–550. doi: 10.1016/S0093-691X(99)00008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Sutton-McDowall ML, Gilchrist RB, Thompson JG. The pivotal role of glucose metabolism in determining oocyte developmental competence. Reproduction. 2010;139:685–695. doi: 10.1530/REP-09-0345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Sutton-McDowall ML, Gilchrist RB, Thompson JG. Cumulus expansion and glucose utilisation by bovine cumulus-oocyte complexes during in vitro maturation: the influence of glucosamine and follicle-stimulating hormone. Reproduction. 2004;128:313–319. doi: 10.1530/rep.1.00225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Salustri A, Yanagishita M, Hascall VC. Synthesis and accumulation of hyaluronic acid and proteoglycans in the mouse cumulus cell-oocyte complex during follicle-stimulating hormone-induced mucification. J Biol Chem. 1989;264:13840–13847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Marshall S, Bacote V, Traxinger RR. Discovery of a metabolic pathway mediating glucose-induced desensitization of the glucose transport system. Role of hexosamine biosynthesis in the induction of insulin resistance. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:4706–4712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Chen L, Wert SE, Hendrix EM, Russell PT, Cannon M, Larsen WJ. Hyaluronic acid synthesis and gap junction endocytosis are necessary for normal expansion of the cumulus mass. Mol Reprod Dev. 1990;26:236–247. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1080260307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Sutton ML, Gilchrist RB, Thompson JG. Effect of in-vivo and in-vitro environments on the metabolism of the cumulus-oocyte complex and its influence on oocyte developmental capacity. Hum Reprod Update. 2003;9:35–48. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmg009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Pandey AN, Chaube SK. A moderate increase of hydrogen peroxide level is beneficial for spontaneous resumption of meiosis from Diplotene arrest in rat oocytes cultured in vitro. Biores Open Access. 2014;3:183–191. doi: 10.1089/biores.2014.0013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Shkolnik K, Tadmor A, Ben-Dor S, Nevo N, Galiani D, Dekel N. Reactive oxygen species are indispensable in ovulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:1462–1467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1017213108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Tiwari M, Chaube SK. Moderate increase of reactive oxygen species triggers meiotic resumption in rat follicular oocytes. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2016;42:536–546. doi: 10.1111/jog.12938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Bedaiwy MA, Elnashar SA, Goldberg JM, Sharma R, Mascha EJ, Arrigain S, et al. Effect of follicular fluid oxidative stress parameters on intracytoplasmic sperm injection outcome. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2012;28:51–55. doi: 10.3109/09513590.2011.579652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Palini S, Benedetti S, Tagliamonte MC, De Stefani S, Primiterra M, Polli V, et al. Influence of ovarian stimulation for IVF/ICSI on the antioxidant defence system and relationship to outcome. Reprod BioMed Online. 2014;29:65–71. doi: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2014.03.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Tarín JJ, Vendrell FJ, Ten J, Blanes R, Van Blerkom J, Cano A. The oxidizing agent tertiary butyl hydroperoxide induces disturbances in spindle organization, c-meiosis, and aneuploidy in mouse oocytes. Mol Hum Reprod. 1996;2:895–901. doi: 10.1093/molehr/2.12.895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Choi WJ, Banerjee J, Falcone T, Bena J, Agarwal A, Sharma RK. Oxidative stress and tumor necrosis factor-α-induced alterations in metaphase II mouse oocyte spindle structure. Fertil Steril. 2007;88:1220–1231. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2007.02.067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Tamura H, Takasaki A, Miwa I, Taniguchi K, Maekawa R, Asada H, et al. Oxidative stress impairs oocyte quality and melatonin protects oocytes from free radical damage and improves fertilization rate. J Pineal Res. 2008;44:280–287. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2007.00524.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Leite RF, Annes K, Ispada J, De Lima CB, Dos Santos ÉC, Fontes PK, et al. Oxidative stress alters the profile of transcription factors related to early development on in vitro produced embryos. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017. 10.1155/2017/1502489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 55.Boggs SE, McCormick TS, Lapetina EG. Glutathione levels determine apoptosis in macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;247:229–233. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1998.8765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Meister A. Selective modification of glutathione metabolism. Science (80- ) 1983;220:472–477. doi: 10.1126/science.6836290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Furnus CC, De Matos DG, Moses DF. Cumulus expansion during in vitro maturation of bovine oocytes: relationship with intracellular glutathione level and its role on subsequent embryo development. Mol Reprod Dev. 1998;51:76–83. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2795(199809)51:1<76::AID-MRD9>3.0.CO;2-T. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.De Matos DG, Furnus CC, Moses DF, Martinez AG, Matkovic M. Stimulation of glutathione synthesis of in vitro matured bovine oocytes and its effect on embryo development and freezability. Mol Reprod Dev. 1996;45:451–457. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2795(199612)45:4<451::AID-MRD7>3.0.CO;2-Q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Kowaltowski AJ, Vercesi AE. Mitochondrial damage induced by conditions of oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med. 1999;26:463–471. doi: 10.1016/s0891-5849(98)00216-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Orrenius S, Gogvadze V, Zhivotovsky B. Mitochondrial oxidative stress: implications for cell death. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2007;47:143–183. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.47.120505.105122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Brison DR, Schultz RM. Apoptosis during mouse blastocyst formation: evidence for a role for survival factors including transforming growth factor α1. Biol Reprod. 1997;56:1088–1096. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod56.5.1088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Byrne AT, Southgate J, Brison DR, Leese HJ. Analysis of apoptosis in the preimplantation bovine embryo using TUNEL. J Reprod Fertil. 1999;117:97–105. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.1170097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Melka MG, Rings F, Hölker M, Tholen E, Havlicek V, Besenfelder U, et al. Expression of apoptosis regulatory genes and incidence of apoptosis in different morphological quality groups of in vitro-produced bovine pre-implantation embryos. Reprod Domest Anim. 2010;45:915–921. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0531.2009.01463.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Van Soom A, Ysebaert MT, De Kruif A. Relationship between timing of development, morula morphology, and cell allocation to inner cell mass and trophectoderm in in vitro-produced bovine embryos. Mol Reprod Dev. 1997;47:47–56. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2795(199705)47:1<47::AID-MRD7>3.0.CO;2-Q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Yuan YQ, Van Soom A, Leroy JLMR, Dewulf J, Van Zeveren A, de Kruif A, et al. Apoptosis in cumulus cells, but not in oocytes, may influence bovine embryonic developmental competence. Theriogenology. 2005;63:2147–2163. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2004.09.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Yang MY, Rajamahendran R. Expression of Bcl-2 and Bax proteins in relation to quality of bovine oocytes and embryos produced in vitro. Anim Reprod Sci. 2002;70:159–169. doi: 10.1016/S0378-4320(01)00186-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Danial NN, Korsmeyer SJ. Cell death: critical control points. Cell. 2004;116:205–19. 10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00046-7. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 68.Cory S, Adams JM. The BCL2 family: regulators of the cellular life-or-death switch. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:647–656. doi: 10.1038/nrc883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.