Abstract
Background
Since the placenta also has a sex, fetal sex–specific differences in the occurrence of placenta-mediated complications could exist.
Objective
To determine the association of fetal sex with multiple maternal pregnancy complications.
Search strategy
Six electronic databases Ovid MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane Central, Web-of-Science, PubMed, and Google Scholar were systematically searched to identify eligible studies. Reference lists of the included studies and contact with experts were also used for identification of studies.
Selection criteria
Observational studies that assessed fetal sex and the presence of maternal pregnancy complications within singleton pregnancies.
Data collection and analyses
Data were extracted by 2 independent reviewers using a predesigned data collection form.
Main results
From 6522 original references, 74 studies were selected, including over 12,5 million women. Male fetal sex was associated with term pre-eclampsia (pooled OR 1.07 [95%CI 1.06 to 1.09]) and gestational diabetes (pooled OR 1.04 [1.02 to 1.07]). All other pregnancy complications (i.e., gestational hypertension, total pre-eclampsia, eclampsia, placental abruption, and post-partum hemorrhage) tended to be associated with male fetal sex, except for preterm pre-eclampsia, which was more associated with female fetal sex. Overall quality of the included studies was good. Between-study heterogeneity was high due to differences in study population and outcome definition.
Conclusion
This meta-analysis suggests that the occurrence of pregnancy complications differ according to fetal sex with a higher cardiovascular and metabolic load for the mother in the presence of a male fetus.
Funding
None.
Keywords: Fetal sex, Pregnancy complications
Introduction
In pregnancy, the placenta constitutes the active interface between the maternal and fetal blood circulation. It regulates important physiological changes during pregnancy and accounts for fetal development and nutrient supply. Maternal physiological changes include cardiovascular changes in vascular tone, cardiac output, and plasma volume, providing a better placental perfusion [1, 2]. Impaired placentation leading to abnormal placental perfusion and hence placental dysfunction is believed to be the foundation of several pregnancy complications such as pre-eclampsia [3, 4]. The central role of the placenta in maternal health suggests an intensive interplay between the mother and the placenta, which might be sex dependent. During pregnancy, clear fetal sex-specific differences are noticeable in the occurrence of different pregnancy complications such as pre-eclampsia and gestational diabetes and even in maternal vascular adaptation to pregnancy [5]. Despite growing speculations that placentation and maternal adaptation to pregnancy are influenced by fetal sex, in most studies that assess these possible pathophysiological mechanisms, fetal sex is not being taken into account [6–9].
Several systematic reviews and meta-analyses have been performed to investigate the association between fetal sex and single pregnancy complications such as pre-eclampsia or gestational diabetes. It is plausible that if fetal sex is associated with one maternal pregnancy complication it might be associated with other pregnancy complications as well. However, some of the performed systematic reviews had restrictions concerning publication date and source population and did not check the references for additional inclusions. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies evaluating the association of fetal sex with multiple maternal pregnancy complications. To explore the worldwide impact of fetal sex on these maternal pregnancy complications, population attributable factors (PAF) were calculated.
Materials and methods
Data sources and search strategy
This review was conducted using a predefined protocol and in accordance with PRISMA and MOOSE guidelines (Additional file 3 and Additional file 4) [10, 11]. Six electronic databases (Ovid MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane Central, Web-of-Science, PubMed, and Google Scholar) were searched until April 5, 2019, without language or publication date restriction. The computer-based searches combined terms related to (1) the exposure such as (gender, sex, fetus, embryo, and baby); (2) maternal pregnancy complications (e.g., gestational hypertension, pre-eclampsia (total, preterm, term, and postterm), eclampsia, gestational diabetes, placental abruption, post-partum hemorrhage, and miscarriage); and (3) relevant population (humans, singleton pregnancy) (Additional file 1). Two independent reviewers screened the titles and abstracts of all studies initially identified, according to the selection criteria. Any disagreement was resolved through consensus or consultation with a third independent reviewer. Full texts were retrieved from studies that satisfied all selection criteria. From each selected manuscript we also searched their individual reference list for other possible includable studies. For this, we used a restriction of 20% most recently published studies.
Study selection and eligibility criteria
Observational studies were eligible if they assessed fetal sex as primary exposure in singleton pregnancies and collected end points for maternal pregnancy complications, including gestational hypertension, pre-eclampsia, eclampsia, gestational diabetes, placental abruption, post-partum hemorrhage, and miscarriage. Study populations in the eligible studies included women recruited from health care settings or general populations. Studies on newborns with an abnormal karyogram, congenital conditions involving sex steroids and/or sex characteristics were excluded.
Data extraction
Two authors independently extracted data and consensus was reached in case of any inconsistency with involvement of a third author. A predesigned electronic data extraction form was used to collect relevant information. The data collection form included questions on qualitative aspects of the study (such as date of publication, design, geographical origin and setting, funding source, selection criteria, patient samplings, and location of research group), participant characteristics (such as number included in the analysis, age, ethnicity, comorbidities) and information on the reported outcome (type of outcome, outcome assessment method, statistical analysis, adjustment variables). In instances of multiple publications, the most up-to-date and comprehensive information was extracted.
Assessing study quality
Two reviewers independently rated the quality of studies using the Newcastle–Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale (Additional file 2). This quality score system is applicable for case-control and cohort studies. The system allocates points for information on participants, comparability, and outcome with a maximum of eight points.
Statistical Analysis
We evaluated the differences between pregnancies with a male and female fetus on maternal pregnancy complications (including gestational hypertension, pre-eclampsia (total, preterm, term, and postterm), eclampsia, gestational diabetes, placental abruption, post-partum hemorrhage, and miscarriage). To enable a consistent approach to the meta-analysis and enhance interpretation of the findings, effect estimates were converted where appropriate. The inverse variance weighted method was used to combine summary measures using random-effects models to minimize effects of between-study heterogeneity [12]. The summary estimates presented were calculated using random-effects models (D+L) and fixed effects (I+V). We also conducted sensitivity analyses using fixed-effects models. Heterogeneity was assessed using the Cochrane X2 statistic and the I2 statistic and was distinguished as low (I2 ≤ 25%), moderate (I2 > 25% and < 75%), or high (I2 ≥ 75%) [13].
Sensitivity analyses were performed by restricting the analysis to studies with very strict in- or exclusion criteria resulting in a specific participant population (e.g., only inclusion of nulligravid, or women who were admitted with hyperemesis gravidarum patients or had gestational diabetes/placental abruption/SGA, etc.). Stratified analyses were performed on geographical location (Western vs non-Western), number of participants (< 10.000 vs ≥ 10.000), study design (case-control vs retrospective cohorts vs prospective cohort), and on quality score (< 7 vs ≥ 7), which were pre-specified as characteristics of assessment of heterogeneity and, in addition to stratification, were evaluated using random-effects meta-regression. Population attributable fractions (PAF) were calculated as PAF = (p (RR − 1))/(p (RR – 1) + 1) [14]. The PAF is an epidemiological measure widely used to assess the public health impact of exposures in a population. It describes the proportional reduction in population disease or mortality that would occur if the exposure to a risk factor was reduced to an alternative ideal exposure scenario (i.e., female fetal sex). A narrative synthesis and construction of descriptive summary tables were performed for these studies that could not be quantitatively pooled.
All tests were 2-tailed; p ≤ 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Stata release 13 (StataCorp) was used for all analyses.
Results
Study identification and selection
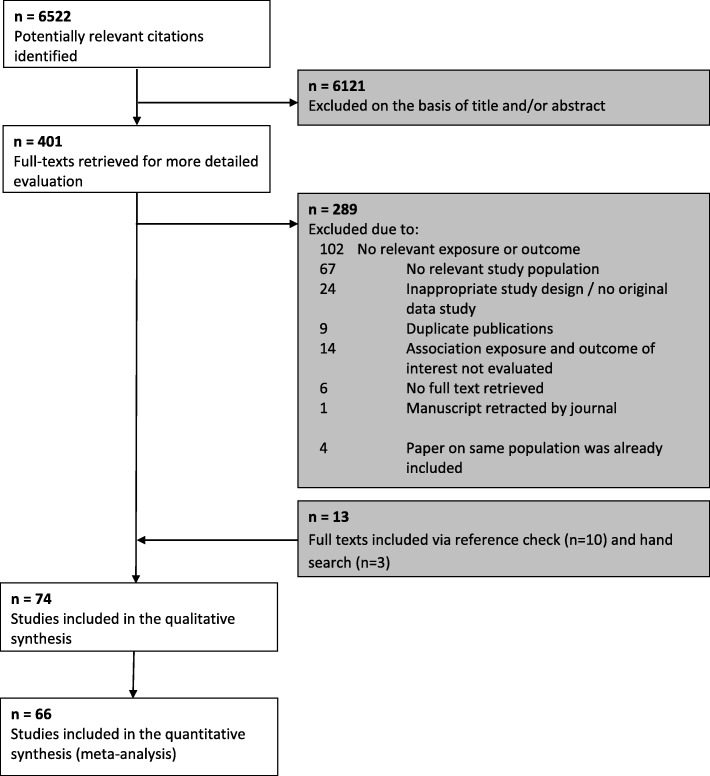
We identified 6522 relevant citations. After screening titles and abstracts, 401 articles were selected for detailed evaluation of their full texts. Of those, 74 articles met our inclusion criteria and were included in the review (Table 1, Fig. 1).
Table 1.
Associations between fetal sex and maternal pregnancy outcomes
| First author | Statistical analyses | Subgroups | Tendency towards which sex (M/F/=) | Crude effect estimate (95% CI) | p value | Covariate adjustment | Adjusted effect estimate (95% CI) | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gestational hypertension | ||||||||
| Andersen et al. 2016 [15] | Logistic regression | F | 0..69 (0..38–1..25) | 0.22 | ||||
| Baibergenova et al. 2006 [16] | Logistic regression | F | 1.06 (0.55–2.50) | 0.87 | ||||
| Campbell et al. 1983 [17] | Logistic regression | M | 1.18 (1.09–1.27) | < 0.0001 | ||||
| Chien et al. 2011 [18] | Logistic regression | M | 0.97 (0.96–0.98) | < 0.0001 | ||||
| Engel et al. 2008 [19] | Chi-square | Total | M | 1.04 (0.94–1.14) | 0.46 | |||
| Mild | M | 1.04 (0.94–1.16) | 0.44 | |||||
| Moderate | F | 0.99 (0.80–1.24) | 0.95 | |||||
| Severe | F | 0.94 (0.62–1.42) | 0.76 | |||||
| Favilli et al. 2013 [20] | Logistic regression | F | 1.69 (0.63–4.57) | 0.43 | Maternal age > 40 years, weight gain, BMI, gestational diabetes | 0.98 (0.43–2.25) | 0.97 | |
| Hou et al. 2014 [21] | Logistic regression | F | 0.97 (0.91–1.02) | 0.25 | ||||
| Juberg et al. 1976 [22] | Chi-square | M | 0.03 | |||||
| Li et al. 2016 [23] | Logistic regression | F | 0.97 (0.78–1.21) | 0.79 | ||||
| Makhseed et al. 1998 [24] | Logistic regression | Total | M | 1.01 (0.86–1.20) | 0.87 | |||
| Primiparous | F | 0.87 (0.65–1.17) | 0.36 | |||||
| Multiparous | M | 1.09 (0.89–1.33) | 0.42 | |||||
| Persson et al. 2014 [25] | Logistic regression | Healthy population | M | 1.03 (1.01–1.06) | 0.003 | |||
| Gestational diabetes | M | 1.08 (0.93–1.26) | 0.31 | |||||
| Diabetes mellitus type I | F | 0.93 (0.79–1.09) | 0.35 | |||||
| Diabetes mellitus type II | F | 0.83 (0.44–1.57) | 0.56 | |||||
| Ricart et al. 2009 [76] | Logistic regression | M | 1.22 (0.91–1.63) | 0.19 | ||||
| Sheiner et al. 2004 [26] | Logistic regression | = | 1.00 (0.95–1.05) | 0.96 | ||||
| Shiozaki et al. 2011 [27] | Logistic regression | F | 0.88 (0.83–0.92) | < 0.0001 | ||||
| Sykes et al. 2014 [77] | Logistic regression | M | 1.33 (0.67–2.63) | 0.42 | ||||
| Tundidor et al. 2012 [28] | Relative risk | F | 0.81 (0.55–1.20) | NR | ||||
| Valvi et al. 2017 [109] | Logistic regression | M | 1.03 (0.58–1.85) | 0.91 | ||||
| Verburg et al. 2016 [29] | Relative risk | Total | M | 1.05 (1.03–1.07) | NR | |||
| 25–29 weeks | F | 0.69 (0.58–0.81) | NR | |||||
| 30–33 weeks | F | 0.87 (0.79–0.97) | NR | |||||
| 34–36 weeks | F | 0.93 (0.87–0.98) | NR | |||||
| 37–39 weeks | M | 1.06 (1.04–1.09) | NR | |||||
| 40–42 weeks | M | 1.07 (1.04–1.11) | NR | |||||
| Zheng et al. 2016 [30] | Logistic regression | F | 0.54 (0.26–1.14) | 0.11 | ||||
| Pre-eclampsia | ||||||||
| Aibar et al. 2012 [31] | Logistic regression | F | 0.99 (0.65–1.49) | 0.94 | ||||
| Aliyu et al. 2012 [32] | Logistic regression | F | 0.90 (0.79–1.03) | 0.12 | ||||
| Andersen et al. 2016 [15] | Logistic regression | Total | F | 0.95 (0.69–1.31) | 0.76 | |||
| Preterm | F | 1.04 (0.42–2.56) | 0.94 | |||||
| Term | M | 1.22 (0.85–1.74) | 0.29 | |||||
| Basso et al. 2001 [33] | Logistic regression | M | 0.94 (0.92–0.97) | < 0.05 | ||||
| Brettel et al. 2008 [34] | Logistic regression | F | 1.17 (1.01–1.35) | 0.03 | ||||
| Campbell et al. 1983 [17] | Logistic regression | F | 1.08 (0.94–1.24) | 0.3 | ||||
| Choong et al. 1995 [35] | Logistic regression | F | 1.45 (1.22–1.71) | < 0.0001 | ||||
| Chu et al. 2014 [36] | Logistic regression | M | 0.60 (0.19–1.83) | 0.39 | ||||
| Hadar et al. 2017 [37] | Logistic regression | F | 0.99 (0.68–1.43) | 0.95 | ||||
| Hou et al. 2014 [21] | Logistic regression | F | 0.95 (0.88–1.02) | 0.13 | ||||
| Juberg et al. 1976 [22] | Chi-square | M | 0.06 | |||||
| Khalil et al. 2013 [38] | Logistic regression | Total | M | 1.04 (0.91–1.19) | 0.57 | |||
| Preterm | F | 1.53 (1.07–2.20) | 0.02 | |||||
| Term | M | 1.08 (0.93–1.25) | 0.31 | |||||
| Postterm | M | 3.46 (1.40–8.53) | 0.007 | |||||
| Lao et al. 2011 [39] | Logistic regression | F | 0.92 (0.81–1.06) | 0.26 | ||||
| Lao et al. 2017 [40] | Logistic regression | M | 1.56 (1.41–1.73) | <0.0001 | ||||
| Li et al. 2016 [23] | Logistic regression | F | 0.66 (0.45–0.98) | 0.04 | ||||
| Lisonkova et al. 2013 [41] | Cox regression | < 34 weeks | M | 1.10 (1.07–1.14) | NR | NR | 1.10 (1.06–1.14) | NR |
| > 34 weeks | M | 1.10 (1.07–1.14) | NR | NR | 1.10 (1.06–1.14) | NR | ||
| Liu et al. 2016 [42] | Logistic regression | Total | 0.96 (0.88–1.04) | 0.31 | ||||
| Preterm | 1.15 (1.00–1.32) | 0.046 | ||||||
| Makhseed et al. 1998 [24] | Logistic regression | Total | F | 0.92 (0.68–1.24) | 0.57 | |||
| Nulliparous | F | 0.74 (0.49–1.10) | 0.13 | |||||
| Multiparous | M | 1.20 (0.76–1.90) | 0.43 | |||||
| Masoumi et al. 2017 [43] | Logistic regression | Total | M | 1.09 (0.90–1.31) | 0.40 | |||
| Severe | M | 1.43 (0.81–2.51) | 0.21 | |||||
| Morsing et al. 2018 [44] | Logistic regression | F | 0.80 (0.59–1.09) | 0.16 | ||||
| Myers et al. 2015 [45] | Logistic regression | = | 0.94 (0.65–1.36) | 0.74 | ||||
| Peled et al. 2013 [46] | Logistic regression | M | 1.79 (0.42–7.56) | 0.43 | ||||
| Persson et al. 2014 [25] | Logistic regression | Healthy population | M | 1.03 (1.01–1.06) | 0.003 | |||
| Gestational diabetes | M | 1.08 (0.93–1.26) | 0.31 | |||||
| Diabetes mellitus type I | F | 0.93 (0.79–1.09) | 0.35 | |||||
| Diabetes mellitus type II | F | 0.83 (0.44–1.57) | 0.56 | |||||
| Quiñones et al. 2005 [47] | Logistic regression | M | 1.15 (0.77–1.70) | 0.5 | ||||
| Reynolds et al. 2012 [48] | Logistic regression | Total | F | 0.85 (0.71–1.02) | 0.08 | |||
| Preterm | F | 1.25 (0.79–1.97) | 0.34 | |||||
| Term | F | 0.86 (0.71–1.04) | 0.13 | |||||
| Roy et al. 2015 [49] | Logistic regression | Total | M | 1.28 (0.72–2.29) | 0.4 | |||
| Preterm | M | 0.77 (0.33–1.81) | 0.55 | |||||
| Term | M | 1.28 (0.66–2.46) | 0.46 | |||||
| Sharifzadeh et al. 2012 [50] | F | 0.88 (0.33–2.35) | 0.8 | |||||
| Sheiner et al. 2004 [26] | Logistic regression | = | 1.00 (0.95–1.05) | 0.96 | ||||
| Shiozaki et al. 2011 [27] | Chi-square | Pre-eclampsia | F | 0.84 (0.79–0.89) | < 0.001 | |||
| Pre-eclampsia with fetal death | M | 1.21 (0.70–1.48) | 0.95 | |||||
| Severe pre-eclampsia | F | 1.21 (1.10–1.33) | 0.001 | |||||
| Severe pre-eclampsia with fetal death | F | 1.14 (0.67–1.93) | 0.63 | |||||
| Sykes et al. 2014 [77] | Logistic regression | M | 1.27 (0.64–2.51) | 0.49 | ||||
| Taylor et al. 2018 [51] | Logistic regression | F | 0.94 (0.67–1.30) | 0.70 | ||||
| Taylor et al. 2018 [51] | Logistic regression | PE overall | F | 0.89 (0.64–1.24) | 0.69 | |||
| Term (> 37 weeks) | F | 0.92 (0.65–1.30) | 0.63 | |||||
| Preterm (<37 weeks) | F | 0.72 (0.37–1.39) | 0.32 | |||||
| Very preterm (<34 weeks) | F | 0.38 (0.13–1.07) | 0.07 | |||||
| Toivanen et al. 1970 [52] | Logistic regression | M | 1.20 (1.06–1.37) | 0.005 | ||||
| Trudel et al. 2015 [53] | Logistic regression | M | 1.01 (0.95–1.07) | 0.82 | ||||
| Vatten et al. 2004 [54] | Logistic regression | Total | M | 1.05 (1.03–1.07) | < 0.0001 | |||
| Preterm (< 37 weeks) | F | 1.17 (1.11–1.22) | < 0.0001 | |||||
| Term (37–42 weeks) | M | 1.06 (1.04–1.08 | < 0.0001 | |||||
| Postterm (> 42 weeks) | M | 1.07 (0.96–1.18) | 0.23 | |||||
| 25–29 weeks | F | 1.55 (1.31–1.83) | < 0.0001 | |||||
| 30–33 weeks | F | 1.33 (1.21–1.46) | < 0.0001 | |||||
| 34–36 wls | F | 1.07 (1.01–1.14) | 0.03 | |||||
| 37–39 weeks | F | 0.98 (0.85–1.01) | 0.18 | |||||
| 40–42 weeks | M | 1.10 (1.07–1.13) | < 0.0001 | |||||
| Verburg et al. 2016 [29] | Relative risk | Total | M | 1.05 (1.03–1.07) | NR | |||
| 25–29 weeks | F | 0.69 (0.58–0.81) | NR | |||||
| 30–33 weeks | F | 0.87 (0.79–0.97) | NR | |||||
| 34–36 weeks | F | 0.93 (0.87–0.98) | NR | |||||
| 37–39 weeks | M | 1.06 (1.04–1.09) | NR | |||||
| 40–42 weeks | M | 1.07 (1.04–1.11) | NR | |||||
| Wandabwa et al. 2010 [79] | Logistic regression | F | 0.65 (0.45–0.95) | 0.03 | ||||
| Weinberg et al. 2017 [55] | Logistic regression | Total | M | 1.01 (0.98–1.04) | 0.71 | |||
| Term (> 37 weeks) | M | 1.05 (1.01–1.08) | 0.01 | |||||
| Preterm (<37 weeks) | F | 0.89 (0.84–0.94) | 0.0001 | |||||
| Zheng et al. 2016 [30] | Logistic regression | Total | F | 0.49 (0.27–0.89) | 0.02 | |||
| Mild | F | 0.65 (0.30–1.43) | 0.29 | |||||
| Severe | F | 2.60 (1.18–5.73) | 0.02 | |||||
| Eclampsia | ||||||||
| Aibar et al. 2012 [31] | Logistic regression | M | 1.54 (0.50–4.72) | 0.45 | ||||
| Aliyu et al. 2012 [32] | Logistic regression | F | 0.92 (0.42–2.01) | 0.83 | ||||
| Campbell et al. 1983 [17] | Logistic regression | F | 0.89 (0.35–2.32) | 0.82 | ||||
| Chien et al. 2011 [18] | Logistic regression | = | 1.00 (0.97–1.04) | 0.89 | ||||
| Hou et al. 2014 [21] | Chi-square | M | 0.13 | |||||
| Llopez-Lera et al. 1990 [82] | Chi-square | M | < 0.05 | |||||
| Persson et al. 2014 [25] | Logistic regression | Healthy population | M | 1.03 (1.01–1.06) | 0.003 | |||
| Gestational diabetes | M | 1.08 (0.93–1.26) | 0.31 | |||||
| Diabetes mellitus type I | F | 0.93 (0.79–1.09) | 0.35 | |||||
| Diabetes mellitus type II | F | 0.83 (0.44–1.57) | 0.56 | |||||
| Wandabwa et al. 2010 [79] | Logistic regression | F | 0.65 (0.45–0.95) | 0.03 | ||||
| Gestational diabetes | ||||||||
| Aibar et al. 2012 [31] | Logistic regression | M | 1.21 (1.06–1.37) | 0.0034 | ||||
| Breschi et al. 1993 [56] | Logistic regression | F | 0.96 (0.36–2.52) | 0.93 | ||||
| Cosson et al. 2016 [57] | Logistic regression | = | 1.00 (0.93–1.08) | 0.96 | ||||
| Ehrlich et al. 2012 [58] | Logistic regression | M | 1.02 (0.99–1.05) | NR | Maternal ethnicity | 1.02 (0.99–1.05) | NR | |
| Maternal ethnicity. education and age | 1.02 (0.99–1.05) | NR | ||||||
| Engel et al. 2008 [19] | Logistic regression | M | 1.07 (0.85–1.36) | 0.54 | ||||
| Favili et al. 2013 [20] | Logistic regression | M | 2.36 (0.58–9.61) | 0.37 | Maternal age > 40 years, BMI, weight gain, gestational hypertension | 0.95 (0.37–2.46) | 0.92 | |
| Heckbert et al. 1988 [59] | Logistic regression | F | 0.97 (0.77–1.21) | 0.79 | ||||
| Hou et al. 2014 [21] | Logistic regression | M | 1.01 (0.96–1.07) | 0.61 | ||||
| Janssen et al. 1996 [60] | Logistic regression | M | 1.02 (0.96–1.08) | 0.5 | ||||
| Kale et al. 2005 [61] | Logistic regression | M | 1.64 (1.12–2.40) | 0.01 | ||||
| Khalil et al. 2013 [38] | Logistic regression | M | 1.41 (1.15–1.72) | < 0.001 | ||||
| Lao et al. 2011 [39] | Logistic regression | M | 1.05 (0.99–1.12 | 0.12 | ||||
| Lao et al. 2017 [40] | Logistic regression | M | 1.06 (1.01–1.11) | 0.08 | ||||
| Lawlor et al. 2009 [84] | Logistic regression | M | 1.61 (0.92–2.81) | 0.09 | ||||
| Liu et al. 2016 [42] | Logistic regression | M | 1.08 (1.00–1.16) | 0.048 | ||||
| Macaulay et al. 2018 [86] | Logistic regression | M | 1.16 (0.73–1.84) | 0.53 | ||||
| Oken et al. 2016 [62] | Logistic regression | M | 1.39 (0.81–2.36) | 0.23 | ||||
| Okereke et al. 2002 [63] | Logistic regression | M | 1.39 (0.81–2.36) | 0.23 | ||||
| Peled et al. 2013 [46] | Logistic regression | M | 3.24 (0.65–16.22) | 0.15 | ||||
| Retnakaran et al. 2015 [64] | Logistic regression | M | 1.03 (1.00–1.05) | 0.047 | ||||
| Retnakaran et al. 2015 [64] | Logistic regression | M | 1.24 (0.92–1.67) | 0.16 | ||||
| Ricart et al. 2009 [76] | Logistic regression | M | 1.05 (0.91–1.22) | 0.17 | ||||
| Sheiner et al. 2004 [26] | Logistic regression | M | 1.07 (1.01–1.12) | 0.01 | ||||
| Spellacy et al. 1985 [65] | Chi-square | M | NS | |||||
| Strutz et al. 2018 [66] | Logistic regression | M | 1.80 (0.40–8.18) | 0.45 | ||||
| Trudel et al. 2015 [53] | Logistic regression | F | 0.96 (0.90–1.04) | 0.32 | ||||
| Verburg et al. 2016 [29] | RR | M | 1.04 (1.01–1.07) | NR | ||||
| Xiao et al. 2014 [67] | Logistic regression | M | 1.29 (0.58–2.89) | 0.53 | ||||
| Placental abruption | ||||||||
| Aliyu et al. 2012 [32] | Logistic regression | F | 0.98 (0.87–1.12) | 0.8 | ||||
| Brettel et al. 2008 [34] | Logistic regression | M | 1.29 (0.97–1.71) | 0.08 | ||||
| Engel et al. 2008 [19] | Logistic regression | F | 0.53 (0.28–0.99) | 0.049 | ||||
| Hou et al. 2014 [21] | Logistic regression | F | 0.98 (0.83–1.15) | 0.76 | ||||
| Jakobovits et al. 1988 [68] | Chi-square | Total | M | NS | ||||
| 17–20 years | M | < 0.001 | ||||||
| 21–25 years | M | < 0.01 | ||||||
| 26–30 years | F | NS | ||||||
| 31–35 years | M | < 0.05 | ||||||
| 36–40 years | M | < 0.05 | ||||||
| 41–42 years | = | NS | ||||||
| Lopez-Llera et al. 1990 [82] | Logistic regression | M | 0.94 (0.54–1.66) | 0.84 | ||||
| Peled et al. 2013 [46] | Logistic regression | M | 2.90 (0.76–11.03) | 0.12 | ||||
| Raissanen et al. 2013 [110] | Logistic regression | Total | M | 1.19 (1.12–1.26) | < 0.0001 | |||
| Nulliparous | M | 1.23 (1.12–1.36) | < 0.0001 | NR | 1.36 (1.23–1.51) | |||
| Multiparous | M | 1.16 (1.08–1.26) | 0.001 | NR | 1.38 (1.27–1.50) | |||
| Schildberger et al. 2016 [69] | Logistic regression | F | 0.84 (0.81–0.87) | < 0.0001 | ||||
| Sheiner et al. 2002 [70] | Logistic regression | F | 0.98 (0.78–1.24) | 0.88 | ||||
| Sheiner et al. 2004 [26] | Logistic regression | M | 1.15 (0.89–1.49) | 0.28 | ||||
| Tikkanen et al. 2013 [90] | Logistic regression | M | 1.18 (1.11–1.25) | < 0.0001 | ||||
| Wandabwa et al. 2005 [91] | Logistic regression | M | 2.20 (1.20–4.90) | < 0.01 | Distance to hospital. age, type of house, hypertension, previous caesarean section, previous stillbirth | 1.90 (1.00–3.80) | NR | |
| Weissmann–Brenner et al. 2015 [71] | Logistic regression | Total | M | 1.20 (0.77–1.87) | 0.42 | |||
| Age < 40 years | M | 1.14 (0.73–1.79) | 0.56 | |||||
| Age > 40 years | M | 5.08 (0.24–106.0) | 0.29 | |||||
| Post-partum hemorrhage | ||||||||
| Favili et al. 2013 [20] | Logistic regression | Total | M | 1.12 (0.34–3.72) | 0.85 | |||
| Age ≥ 40 years | M | 2.10 (0.40–11.01) | 0.38 | |||||
| Age < 40 years | F | 0.35 (0.04–3.37) | 0.36 | |||||
| Weissmann–Brenner et al. 2015 [71] | Logistic regression | Total | M | 1.20 (0.88–1.65) | 0.25 | |||
| Age ≥ 40 years | M | 1.16 (0.84–1.61) | 0.35 | |||||
| Age < 40 years | M | 4.07 (0.45–36.5) | 0.21 | |||||
| Liu et al. 2016 [42] | Logistic regression | F | 0.91 (0.83–0.99) | 0.0046 | ||||
| Miscarriage | ||||||||
| Byrne et al. 1987 [72] | Risk ratio | Total | M | < 0.05 | ||||
| Morphological normal | M | < 0.05 | ||||||
| Morphological abnormal | F | > 0.05 | ||||||
| Cheng et al. 2014 [73] | Risk ratio | F | < 0.001 | |||||
| Del Fabro et al. 2011 [74] | Risk ratio | Total | F | < 0.05 | ||||
| 4–10 weeks | F | < 0.001 | ||||||
| 11–15 weeks | F | 0.07 | ||||||
| 16–20 weeks | F | 0.06 | ||||||
Fig. 1.
Search strategy for the studies included in the current systematic review (search until April 5, 2019). PRISMA flow diagram of selection process of eligible studies
Characteristics of included studies
The 74 included studies reported results for 12.658.554 unique women (Table 1). Forty-seven were retrospective cohort studies, 10 prospective cohort studies and the remaining 17 studies were case-control studies. The majority of studies were performed in Western countries (22 in Northern America, 25 in Europe, three in Australia, and one study in both Europe and Australia). Of the remaining studies, 11 were performed in Asia, nine in the Middle East, and three in Africa. More than one outcome was measured in 23 studies, and for these, the measure of association for each outcome was included in the analysis. One study was written in Spanish, all other studies were in English [75].
Association of fetal sex with maternal pregnancy outcomes
Fetal sex and gestational hypertension
Of the included studies, 19 investigated gestational hypertension with a total of 5.752.185 participants (Tables 1 and 2) [15–30, 76, 77]. Of these studies, five found an association with male fetal sex dominance, one with female fetal sex dominance, and 13 found no association. Four studies stratified their results. One study stratified for severity of gestational hypertension (mild, moderate, and severe) [19]. None of the subgroups were associated with fetal sex. Another study stratified for parity in which no association was found for both primiparous and multiparous women. Persson et al. stratified for comorbidity (gestational diabetes, diabetes mellitus type 1 or 2) [25]. They observed male fetal sex dominance for gestational hypertension in the non-diabetic group. No such association was found for women with diabetes. The last study stratified for gestational age and found that gestational hypertension was associated with male fetal sex only in term and postterm pregnancies [29].
Table 2.
Pooled odds ratios of the occurrence of maternal pregnancy complications by study characteristics
| Subgroup | No. of studies | Participants | OR (95% CI) | p value for heterogeneity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gestational hypertension | ||||
| Geographical location | ||||
| Western | 11 | 5.511.340 | 1.02 (0.98;1.06) | 0.3 |
| Non-Western | 5 | 125.016 | 0.99 (0.95;1.02) | |
| No of participants | ||||
| < 10.000 | 8 | 30.853 | 1.01 (0.98;1.05) | 0.47 |
| ≥ 10.000 | 8 | 5.605.503 | 0.96 (0.85;1.10) | |
| Study design | ||||
| Case-control | 1 | 294 | 0.54 (0.26;1.14) | 0.19 |
| Retrospective cohort | 11 | 5.508.737 | 1.02 (0.98;1.05) | |
| Prospective cohort | 4 | 127.325 | 0.98 (0.89;1.08) | |
| Quality score | ||||
| < 7 | 11 | 5.489.916 | 1.03 (1.01;1.05) | < 0.001 |
| ≥ 7 | 5 | 146.440 | 0.92 (0.81;1.05) | |
| Pre-eclampsia (total) | ||||
| Geographical location | ||||
| Western | 15 | 3.472.444 | 1.03 (1.00;1.05) | < 0.001 |
| Non-Western | 14 | 541.647 | 0.90 (0.83;0.97) | |
| No. of participants | ||||
| < 10.000 | 13 | 39.373 | 0.92 (0.78;1.08) | 0.84 |
| ≥ 10.000 | 16 | 3.974.718 | 0.97 (0.94;1.01) | |
| Study design | ||||
| Case-control | 7 | 2.174 | 0.86 (0.64;1.16) | 0.12 |
| Retrospective cohort | 18 | 3.884.545 | 0.98 (0.95;1.02) | |
| Prospective cohort | 4 | 127.372 | 0.90 (0.81;1.00) | |
| Quality score | ||||
| < 7 | 22 | 1.538.622 | 0.97 (0.93;1.02) | 0.71 |
| ≥ 7 | 7 | 2.475.469 | 0.95 (0.88;1.02) | |
| Eclampsia | ||||
| Geographical location | ||||
| Western | 5 | 4.820.821 | 1.02 (1.00;1.04) | 0.05 |
| Non-Western | 2 | 110.156 | 0.82 (0.57;1.18) | |
| No of participants | ||||
| < 10.000 | 1 | 434 | 0.65 (0.45;0.94) | 0.02 |
| ≥ 10.000 | 6 | 4.930.534 | 1.01 (0.99;1.04) | |
| Study design | ||||
| Case-control | 1 | 434 | 0.65 (0.45;0.95) | 0.01 |
| Retrospective cohort | 5 | 4.820.821 | 0.95 (0.88;1.02) | |
| Prospective cohort | 1 | 109.722 | 1.02 (1.00;1.04) | |
| Quality score | ||||
| < 7 | 6 | 4.920.963 | 1.00 (0.95;1.04) | 0.84 |
| ≥ 7 | 1 | 10.014 | 0.92 (0.42;2.01) | |
| Gestational diabetes | ||||
| Geographical location | ||||
| Western | 16 | 1.632.560 | 1.03 (1.01;1.05) | 0.17 |
| Non-Western | 8 | 379.756 | 1.09 (1.02;1.15) | |
| No of participants | ||||
| < 10.000 | 10 | 15.111 | 1.16 (1.02;1.33) | 0.14 |
| ≥ 10.000 | 14 | 1.997.205 | 1.04 (1.02;1.06) | |
| Study design | ||||
| Case-control | 5 | 1.062 | 1.15 (0.94;1.40) | 0.66 |
| Retrospective cohort | 12 | 2.009.749 | 1.04 (1.02;1.06) | |
| Prospective cohort | 7 | 1.505 | 1.16 (1.01;1.33) | |
| Quality score | ||||
| < 7 | 18 | 1.091.263 | 1.05 (1.02;1.09) | 0.75 |
| ≥ 7 | 6 | 921.053 | 1.04 (1.01;1.07) | |
| Placental abruption | ||||
| Geographical location | ||||
| Western | 7 | 2.876.604 | 1.03 (0.86;1.23) | 0.45 |
| Non-Western | 6 | 227.068 | 1.10 (0.93;1.31) | |
| No of participants | ||||
| < 10.000 | 4 | 7.801 | 1.31 (0.85;2.02) | 0.4 |
| ≥ 10.000 | 9 | 3.095.871 | 1.04 (0.90;1.22) | |
| Study design | ||||
| Case-control | 2 | 1.090 | 2.34 (1.25;4.35) | 0.08 |
| Retrospective cohort | 10 | 2.992.860 | 1.05 (0.90;1.22) | |
| Prospective cohort | 1 | 109.722 | 0.98 (0.83;1.15) | |
| Quality score | ||||
| < 7 | 6 | 224.641 | 1.21 (0.96;1.51) | 0.2 |
| ≥ 7 | 7 | 2.879.031 | 1.01 (0.85;1.19) | |
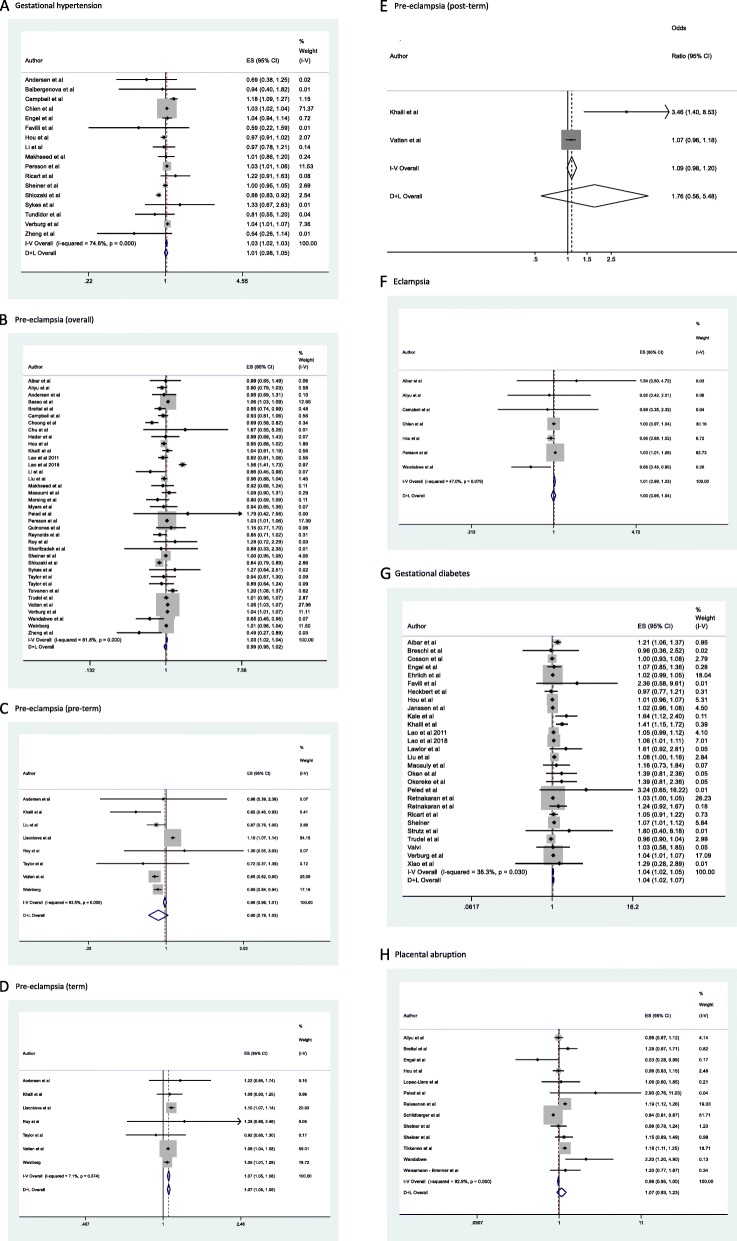
In our pooled meta-analyses which compared the occurrence of gestational hypertension in women carrying a male fetus compared with women carrying a female fetus, the OR was 1.01 (0.98–1.05) (Fig. 2a). The PAF for total gestational hypertension was 1.31% (95% CI [-0.22;2.84], p = 0.09). Assuming a worldwide prevalence of 7%, this resembles almost 200.000 cases worldwide of gestational hypertension associated to some degree with the presence of a male fetus [78].
Fig. 2.
Meta-analyses on the association between fetal sex and maternal pregnancy complications. The boxes are proportional to the weight of each study in the analysis, and the lines represent their 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Size of data markers are proportional to the inverse of the variance of the effect estimate. The open diamond represent the pooled odds ratio, and its width represents its 95% CI. The summary estimates presented were calculated using random-effects models (D + L) and fixed effects (I + V). Assessment of heterogeneity: gestational hypertension (I2 = 74,8%, p < 0.001) (a); total pre-eclampsia (I2 = 81,8%, p < 0.001) (b); preterm pre-eclampsia (I2 = 93,5%, p < 0.001) (c); term pre-eclampsia (I2 = 7,1%, p = 0.37) (d); postterm pre-eclampsia (I2 = 84.4%, p = 0.011) (e); eclampsia (I2 = 47.0%, p = 0.08) (f); gestational diabetes, (I2 = 36,3%, p = 0.03) (g); placental abruption (I2 = 92.9%, p < 0.001) (h)
Fetal sex and pre-eclampsia
Of the included studies, 39 investigated pre-eclampsia with a total of 4.766.334 participants (Tables 1 and 2) [15, 17, 21–27, 29–55, 77, 79, 80]. Eight studies found an association with male fetal sex, six with female fetal sex and the remaining 25 studies did not find a significant association. However, the association between fetal sex and pre-eclampsia was dependent of gestational age. Ten studies stratified their results for gestational age. Two studies stratified their results not only in term vs preterm but additionally investigated several gestational age periods showing a strong association between female pregnancies and very early pre-eclampsia [29, 54]. This association attenuated with gestational age. At term and postterm, the association is reversed and male fetal sex is associated with pre-eclampsia. Three studies stratified into severity of pre-eclampsia [27, 30, 43]. Two of these studies show that a more severe pre-eclampsia is associated with a female fetus while one study shows that severe pre-eclampsia is associated with a male fetus.
In our pooled meta-analyses which compared the occurrence of overall pre-eclampsia (i.e., preterm, term, and postterm) in women carrying a male fetus compared with women carrying a female fetus, the OR was 0.99 (0.95–1.02) (Fig. 2b). For preterm, term, and postterm pre-eclampsia the pooled ORs were 0.90 (0.78–1.03), 1.07 (1.06–1.09) and 1.76 (0.56–5.48) respectively for a male fetus compared to a female fetus (Fig. 2 c, d, and e respectively). The PAF for total pre-eclampsia was 1.23% (95% CI [− 0.64;3.11], p = 0.20). Assuming a worldwide prevalence of 5%, this resembles approximately 130.000 cases of pre-eclampsia worldwide associated to some degree with the presence of a female fetus [81].
Fetal sex and eclampsia
Of the included studies, eight investigated eclampsia with a total of 4.931.754 participants (Tables 1 and 2) [17, 18, 21, 25, 31, 32, 79, 82]. Two studies found an association with male fetal sex, one study with female fetal sex, the remaining studies did not find a significant association.
In our pooled meta-analyses which compared the occurrence of eclampsia in women carrying a male fetus compared with women carrying a female fetus, the OR was 1.00 (0.95–1.04) (Fig. 2e). The PAF for eclampsia was 0.71% (95% CI [− 3.60;5.02], p = 0.75). Assuming a worldwide prevalence of 0.01%, this resembles almost 2000 cases of eclampsia worldwide associated to some degree with the presence of a male fetus [83].
Fetal sex and gestational diabetes
Of the included studies, 28 investigated gestational diabetes, with a total of 2.126.446 participants (Tables 1 and 2) [19–21, 26, 29, 31, 38–40, 42, 46, 53, 56–67, 76, 84–86]. Of the included studies seven studies found an association between fetal sex and gestational diabetes all showing a higher rate of gestational diabetes within women carrying a male fetus.
In our pooled meta-analyses which compared the occurrence of gestational diabetes in women carrying a male fetus compared with women carrying a female fetus, the OR was 1.04 (1.02–1.07) (Fig. 2g). The PAF for gestational diabetes was 1.75% (95% CI [1.05;2.46], p < 0.001). Assuming a worldwide prevalence of 6%, this resembles almost 225,000 cases of gestational diabetes worldwide associated to some degree with the presence of a male fetus [87].
Fetal sex and placental abruption
Of the included studies, 14 investigated placental abruption, with a total of 3.130.530 participants (Tables 1 and 2) [19, 21, 26, 34, 46, 68–71, 82, 88–91]. All studies that found a significant association showed a higher rate of placental abruption within women carrying a male fetus. Two studies stratified their results according to maternal age [68, 71]. Despite stratification, in the majority of age groups, placental abruption was associated with the presence of a male fetus. One study stratified their analyses for parity (nulliparous vs multiparous). In both groups, placental abruption was associated with the presence of a male fetus.
In our pooled meta-analyses which compared the occurrence of placental abruption in women carrying a male fetus vs women carrying a female fetus, the OR was 1.07 (0.93–1.23) (Fig. 2h). The PAF for placental abruption was 1.18% (95% CI [1.05;2.46], p < 0.001). Assuming a worldwide prevalence of 1%, this resembles almost 38.000 cases of placental abruption worldwide associated so some degree with the presence of a male fetus [92].
Fetal sex and post-partum hemorrhage
Of the included studies, three investigated post-partum hemorrhage, with a total of 103.123 participants (Tables 1 and 2) [20, 42, 71]. One study found an association with the presence of a female fetus. This study however excluded preterm births. The other two studies did not find an association.
Fetal sex and miscarriage
Of the included studies, three investigated miscarriage, with a total of 1.217 participants (Tables 1 and 2) [72–74]. One study found an association between miscarriages and female sex. One other study stratified for morphological normal and abnormal embryos showing an association with male sex within the morphological normal embryos. The third study stratified their analyses for gestational age. In the total group and in the group 4–10 weeks, an association was found for female sex.
Study quality, heterogeneity, and sensitivity analyses
Study quality according to the Newcastle-Ottawa scale was good. Over 90% of all included studies had a quality score of ≥ 6 out of 8 and 15% percent of studies had the maximum score of 8.
In a separate sensitivity analysis, all studies with specific in- or exclusion criteria were excluded for the meta-analyses. All results remained the same except for preterm pre-eclampsia, OR 0.85 (0.81–0.89). Furthermore, all analyses were stratified according to geographical location, number of participants, study design and quality score (Table 3). Stratified analysis for gestational hypertension by the level of quality score showed that only in the low-quality studies (i.e., quality score < 7) an association with male fetal sex was found (p < 0.001). For eclampsia, stratification by the number of participants showed no association with fetal sex in the larger studies (i.e., ≥ 10.000 participants) and an association with female fetal sex in one smaller study (p = 0.02). When stratifying by study design an association between female fetal sex and eclampsia was found in the one included case-control study. On the contrary, in the one included prospective cohort study an association with male fetal sex was found. In the five included retrospective cohort no association with fetal sex could be found (p = 0.01).
Table 3.
Pooled odds ratios of the occurrence of maternal pregnancy complications by study characteristics
| Subgroup | No. studies | Participants | OR (95% CI) | p value for heterogeneity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gestational hypertension | ||||
| Geographical location | ||||
| Western | 12 | 5.511.490 | 1.02 (0.98;1.06) | 0.29 |
| Non-Western | 5 | 125.016 | 0.99 (0.95;1.02) | |
| No of participants | ||||
| < 10.000 | 9 | 31.003 | 0,98 (0.86;1.10) | 0.56 |
| ≥ 10.000 | 8 | 5.605.503 | 1,01 (0.98;1.05) | |
| Study design | ||||
| Case-control | 2 | 444 | 0.86 (0.35;2,07) | 0.57 |
| Retrospective cohort | 11 | 5.508.737 | 1.02 (0.98;1.05) | |
| Prospective cohort | 4 | 127.325 | 0.98 (0.89;1.08) | |
| Quality score | ||||
| < 7 | 11 | 5.489.916 | 1.03 (1.01;1.05) | < 0.001 |
| ≥ 7 | 6 | 146.590 | 0.94 (0.82;1.06) | |
| Pre-eclampsia (total) | ||||
| Geographical location | ||||
| Western | 22 | 3.970.495 | 1.02 (1.00;1.05) | 0,23 |
| Non-Western | 15 | 636.671 | 0.93 (0.83;1,04) | |
| No of participants | ||||
| < 10.000 | 18 | 42.194 | 0.92 (0.82;1.04) | 0.27 |
| ≥ 10.000 | 19 | 4.548.703 | 1,00 (0.96;1.03) | |
| Study design | ||||
| Case-control | 9 | 18.593 | 0.94 (0.75;1.02) | 0.50 |
| Retrospective cohort | 24 | 4.461.201 | 1,00 (0.96;1.04) | |
| Prospective cohort | 4 | 127.372 | 0.90 (0.81;1.00) | |
| Quality score | ||||
| < 7 | 22 | 1.539.869 | 0.97 (0.93;1.02) | 0.71 |
| ≥ 7 | 7 | 3.067.297 | 0.95 (0.88;1.02) | |
| Eclampsia | ||||
| Geographical location | ||||
| Western | 5 | 4.820.821 | 1.02 (1.00;1.04) | 0.05 |
| Non-Western | 2 | 110.156 | 0.82 (0.57;1.18) | |
| No of participants | ||||
| < 10.000 | 1 | 434 | 0.65 (0.45;0.94) | 0.02 |
| ≥ 10.000 | 6 | 4.930.534 | 1.01 (0.99;1.04) | |
| Study design | ||||
| Case-control | 1 | 434 | 0.65 (0.45;0.95) | 0.01 |
| Retrospective cohort | 5 | 4.820.821 | 0.95 (0.88;1.02) | |
| Prospective cohort | 1 | 109.722 | 1.02 (1.00;1.04) | |
| Quality score | ||||
| < 7 | 6 | 4.920.963 | 1.00 (0.95;1.04) | 0.84 |
| ≥ 7 | 1 | 10.014 | 0.92 (0.42;2.01) | |
| Gestational diabetes | ||||
| Geographical location | ||||
| Western | 18 | 1.728.325 | 1.03 (1.01;1.05) | 0.13 |
| Non-Western | 10 | 380.388 | 1.07 (1.03;1.12) | |
| No of participants | ||||
| < 10.000 | 13 | 16.484 | 1.12 (1.02;1.24) | 0.13 |
| ≥ 10.000 | 15 | 2.092.229 | 1.04 (1.02;1.06) | |
| Study design | ||||
| Case-control | 6 | 1.092 | 1.15 (0.95;1.39) | 0.66 |
| Retrospective cohort | 14 | 2.105.377 | 1.04 (1.02;1.06) | |
| Prospective cohort | 8 | 2.246 | 1.16 (1.02;1.31) | |
| Quality score | ||||
| < 7 | 21 | 1.092.636 | 1.05 (1.02;1.09) | 0.75 |
| ≥ 7 | 7 | 1.016.077 | 1.04 (1.02;1.06) | |
| Placental abruption | ||||
| Geographical location | ||||
| Western | 7 | 2.876.604 | 1.03 (0.86;1.23) | 0.45 |
| Non-Western | 6 | 227.068 | 1.10 (0.93;1.31) | |
| No of participants | ||||
| < 10.000 | 4 | 7.801 | 1.31 (0.85;2.02) | 0.4 |
| ≥ 10.000 | 9 | 3.095.871 | 1.04 (0.90;1.22) | |
| Study design | ||||
| Case-control | 2 | 1.090 | 2.34 (1.25;4.35) | 0.08 |
| Retrospective cohort | 10 | 2.992.860 | 1.05 (0.90;1.22) | |
| Prospective cohort | 1 | 109.722 | 0.98 (0.83;1.15) | |
| Quality score | ||||
| < 7 | 6 | 224.641 | 1.21 (0.96;1.51) | 0.2 |
| ≥ 7 | 7 | 2.879.031 | 1.01 (0.85;1.19) | |
Four of eight analyses showed high between-study heterogeneity, with an I2 estimate exceeding 75% (p < 0.05 for the Cochrane X2 statistic) (Fig. 2). This level of heterogeneity could be explained by differences between studies attributable to heterogeneous study populations, methods, and outcome definition.
Discussion
This is the first systematic review and meta-analyses investigating the association between fetal sex and multiple major pregnancy outcomes showing that sexual dimorphisms in maternal pregnancy complications exist.
Within pre-eclampsia diverse results were found when stratifying for gestational age. Pregnancies with a female fetus were tended to be associated with preterm pre-eclampsia, while pregnancies with a male fetus were associated with developing term and postterm pre-eclampsia. This phenomenon is in line with results presented in a recent individual patient meta-analysis where women with a female fetus were more at risk for preterm pre-eclampsia and women with a male fetus for term pre-eclampsia [93]. In line with this, sexual dimorphic differences in vascular adaptation to pregnancy have been shown [9]. Women carrying a male fetus have a higher second-trimester uterine artery pulsatility index and more often present themselves with notching in the third trimester of pregnancy. This reflects an increased utero-placental resistance among male pregnancies which may originate from suboptimal implantation and placentation. A time diverse pattern was also seen in previous research on fetal sex-specific differences in blood pressure patterns during pregnancy [9]. Within complicated pregnancies (including pre-eclampsia) a different diastolic blood pressure was observed for women with a male fetus compared with women with a female fetus, with cross-over in the second trimester. Women carrying a female fetus started with a higher diastolic blood pressure compared with women carrying a male fetus. However, from 24 weeks of gestation onwards these women had a lower diastolic blood pressure. Although the exact underlying mechanisms of these changing patterns are still subject of investigation they might strengthen the hypothesis that pregnancies with a male embryo are more susceptible to suboptimal implantation or abnormal placental development which consequently leads to altered maternal adaptation to pregnancy. Recently Gonzalez et al. reported on the later first-trimester placental transcriptome [8]. They observed sexual dimorphic expression patterns of not only X- but also Y-linked genes in first-trimester placentas. Cell adhesion, ciliogenesis, and cell-cell communication genes also differed in their study. This suggests sex differences in how placenta cells interact with their environment [94–97]. Furthermore, they observed a significant downregulation of the ITGB8 gene (encodes integrin-β8). This gene promotes tumor angiogenesis and invasiveness in glioblastoma [97] functions necessary for normal first-trimester development when placental cells invade maternal tissue and access maternal blood. The results of Gonzalez et al. underscribe those of previous research by Cvitic et al. They found fetal sex differentially affected gene expression in a cell phenotype–dependent manner among cytotrophoblasts, syncytiotrophoblast, arterial and venous endothelial cells. The pathways that they observed in male placenta villi were identified to be signaling pathways for graft-versus-host disease as well as the immune and inflammatory systems that parallel the reported poorer outcome of male fetuses [98]. Orzack et al. studied the trajectory of the human sex ratio from conception to birth by analyzing data from 3 to 6 days old embryos, including abortions, chorionic villus sampling, amniocentesis, fetal deaths, and live births. They showed a sex ratio among abnormal embryos that was male biased, and a sex ratio among normal embryos that was female biased. This strengthened the study of Buckberry et al. who detected a higher female expression from genes involved in the maintenance of pregnancy and the maternal immune tolerance of the conceptus [6]. From this, we, and others, speculate that pregnancies with a male embryo are more susceptible to impaired placentation. This would imply that those pregnancies with a male embryo that are susceptible to develop pre-eclampsia due to impaired placentation may already have miscarried in the first trimester [98–100]. The male fetuses that survive the period of placentation will thereby represent a relatively healthy group of fetuses leading to a female-biased prevalence of pre-eclampsia [99]. Since especially late-onset pre-eclampsia is thought to originate from abnormal placentation a so-called sexual dimorphic cross-over can be observed for term and postterm pre-eclampsia [4, 6, 7, 72, 98, 100].
The implication that male embryos are more susceptible to placental development is in line with the results described in this systematic review since other placental related pregnancy complications are also mainly associated with the presence of a male fetus. Although beyond the scope of this review, this is in line with the association of the presence of a male fetus with preterm birth [101]. Many cases of spontaneous preterm birth appear to be caused by placental insufficiency, similar to pre-eclampsia. Other causes of preterm birth including placental abruption and chronic villitis also have specific placental pathology related to placental insufficiency and are also associated with male sex [102]. Furthermore, we hypothesize that carrying a male fetus demands a higher degree of metabolic and vascular maternal adaptation to pregnancy compared with carrying a female fetus. For example, women carrying a male fetus have poorer pancreatic beta-cell function in pregnancy [64]. This is in line with our finding that women carrying a male fetus are at higher risk for developing gestational diabetes. Previous research also showed that within women who experienced gestational diabetes, those women who carried a male fetus are at higher risk of developing diabetes type 2 after delivery compared with women who carried a female fetus [85].
Not only during pregnancy the consequences of carrying a male fetus for maternal health are evident. Also, long term adverse health outcomes have been measured. Helle et al. were the first to suggest a shorter maternal lifespan is associated with the number of sons born [103]. More recently research has shown that that women’s post-reproductive survival declines with the number of sons they gave birth to [104, 105]. The number of daughters born was not associated with women’s post-reproductive survival. Helle et al. validated their results by demonstrating that this effect was independent on the number of sons and daughters surviving to adulthood and by showing that the number of sons and daughters was not associated with post-reproductive survival in men [104]. These findings support the hypothesis that baring sons is more energetically costly than baring daughters.
Conclusions on fetal sex and miscarriage rates are difficult to draw from the included studies. One of our exclusion criteria was an abnormal karyogram, which is highly prevalent in miscarriages [106]. This could have introduced a selection bias if an abnormal karyogram occurs more often in male pregnancies and give rise to a female dominance in miscarriages with a normal karyogram while in the total group of miscarriages there is a male dominance. Furthermore, the pregnancy product after a miscarriage is only investigated in specific cases like recurrent miscarriages and is not part of daily practice. To investigate if a sexual dimorphism in miscarriages exists, future research should focus on the total rate of miscarriages, stratified for chromosomal abnormalities.
To our knowledge, this is the first comprehensive quantitative review that assessed the association between fetal sex and multiple major pregnancy outcomes. Our analyses included over 12 million women and assessed seven pregnancy outcomes. Some systematic reviews exist focusing on one pregnancy complication, for example on gestational diabetes and pre-eclampsia/eclampsia by Jaskolka et al. [107, 108]. Eleven of our 25 included studies on gestational diabetes and 22 of our 31 included studies on pre-eclampsia were not included in these systematic reviews. For pre-eclampsia, this resulted in one million more participants included. In the systematic review and meta-analyses on pre-eclampsia, the authors unfortunately do not take into account that the effect of fetal sex on the occurrence of pre-eclampsia is gestational age specific and therefore stratification into preterm, term and postterm pre-eclampsia was not performed.
However, strength and limitations in the current study merit careful consideration. First, all systematic reviews are prone to reporting bias, owing to the possibility that studies with more extreme results are more likely to be published. In this systematic review, multiple included articles did not primarily investigate the effect of fetal sex on pregnancy outcome. However, due to the fact that the information was given anyway in the manuscript, odds ratios could be calculated. Additionally, all meta-analyses are limited by the quality of the individual published studies. However, the majority of studies included in the current analyses were of high quality, with a low risk of bias. Furthermore, the majority of studies did not give a clear definition of the pregnancy outcome which was assessed. Also, definition changed internationally across time. The publication year of included studies varies between 1970 and 2019. In this time span, the definition of several pregnancy complications such as pre-eclampsia and gestational diabetes have changed multiple times. Moreover, there might not be international consensus to a definition which causes other definition in different continents or countries. This introduces heterogeneity into the analyses.
Most studies that were included did not adjust for any confounders. From an epidemiological point of view, when using fetal sex as an exposure we don’t have to deal with any confounding factors since there are no factors described influencing fetal sex.
Conclusions
Our findings support the emerging concept of a sexual dimorphism in the maternal-fetal-placental interplay. Most importantly all results are consistent with each other and validate the hypothesis that carrying a male fetus is accompanied with a higher cardiovascular and metabolic load for the mother resulting in maternal pregnancy complications and adverse health in later life. Although the increases in odds ratios in this meta-analysis are modest, they hold important implications for our understanding of maternal-fetal physiology. Moreover, approximately half of pregnant women worldwide are exposed to the presence of a male fetus. Hence, the absolute numbers of pregnancy complications worldwide occurring due to the presence of a male fetus are high. Experiencing one of the pregnancy complications described in this systematic review holds important implications for future life. Fetal sex should therefore be taken into account as a risk factor when assessing risk of pregnancy complications and adverse cardiovascular health in later life.
Supplementary information
Additional file 2. Newcastle-Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale.
Acknowledgements
We have no acknowledgements.
Authors’ contributions
ZB screened all titles and abstracts, read all full-text articles, and included all manuscript mentioned in this systematic review. ZB analyzed all results, interpreted all results, and wrote the article. LB, MT, MA, RG, JS, TV contributed to screening the title and abstract and reading full-text articles and gave input in writing the article. WB designed the search strategy. TM contributed to performing the meta-analyses. ES, OF, and SS contributed to all stages of the article. The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
OF received a grant from Nestle on child health. All other authors have nothing to disclose.
Availability of data and materials
The extracted data from included articles supporting the conclusions of this manuscript can be found in Table 1 and 2.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at 10.1186/s13293-020-00299-3.
References
- 1.Carlin A, Alfirevic Z. Physiological changes of pregnancy and monitoring. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2008;22:801–823. doi: 10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2008.06.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hunter S, Robson SC. Adaptation of the maternal heart in pregnancy. Br Heart J. 1992;68:540–543. doi: 10.1136/hrt.68.12.540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Baschat AA, Hecher K. Fetal growth restriction due to placental disease. Semin Perinatol. 2004;28:67–80. doi: 10.1053/j.semperi.2003.10.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Steegers EA, von Dadelszen P, Duvekot JJ, Pijnenborg R. Pre-eclampsia. Lancet. 2010;376:631–644. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60279-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Broere-Brown ZA, Schalekamp-Timmermans S, Hofman A, Jaddoe V, Steegers E. Fetal sex dependency of maternal vascular adaptation to pregnancy: a prospective population-based cohort study. Bjog. 2015. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 6.Buckberry S, Bianco-Miotto T, Bent SJ, Dekker GA, Roberts CT. Integrative transcriptome meta-analysis reveals widespread sex-biased gene expression at the human fetal-maternal interface. Mol Hum Reprod. 2014;20:810–819. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gau035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cvitic S, Longtine MS, Hackl H, Wagner K, Nelson MD, Desoye G, et al. The human placental sexome differs between trophoblast epithelium and villous vessel endothelium. PLoS One. 2013;8:e79233. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0079233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gonzalez TL, Sun T, Koeppel AF, Lee B, Wang ET, Farber CR, et al. Sex differences in the late first trimester human placenta transcriptome. Biol Sex Differ. 2018;9:4. doi: 10.1186/s13293-018-0165-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Broere-Brown ZA. Fetal sex dependency of maternal vascular adaptation to pregnancy: a prospective population-based cohort study. J Obstet. 2015. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 10.Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Group P Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6:e1000097. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, Olkin I, Williamson GD, Rennie D, et al. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis Of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA. 2000;283:2008–2012. doi: 10.1001/jama.283.15.2008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986;7:177–188. doi: 10.1016/0197-2456(86)90046-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327:557–560. doi: 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Rockhill B, Newman B, Weinberg C. Use and misuse of population attributable fractions. Am J Public Health. 1998;88:15–19. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.88.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Andersen LB, Jørgensen JS, Herse F, Andersen MS, Christesen HT, Dechend R. The association between angiogenic markers and fetal sex: Implications for preeclampsia research. J Reprod Immunol. 2016;117:24–29. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2016.05.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Baibergenova A, Thabane L, Akhtar-Danesh N, Levine M, Gafni A. Is fetal gender associated with emergency department visits for asthma during pregnancy? J Asthma. 2006;43:293–299. doi: 10.1080/02770900600622984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Campbell DM, MacGillivray I, Carr Hill R, Samphier M. Fetal sex and pre-eclampsia in primigravidae. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1983;90:26–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1983.tb06741.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chien EK, Jayakrishnan A, Dailey TL, Raker CA, Phipps MG. Racial and ethnic disparity in male preterm singleton birth. J Reprod Med Obstet Gynecol. 2011;56:58–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Engel PJ, Smith R, Brinsmead MW, Bowe SJ, Clifton VL. Male sex and pre-existing diabetes are independent risk factors for stillbirth. Aust New Zealand J Obstet Gynaecol. 2008;48:375–383. doi: 10.1111/j.1479-828X.2008.00863.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Favilli A, Pericoli S, Renzo GCD. The role of advanced maternal age and newborn sex in pregnancy outcome: does it really matter? J Evid. 2013.
- 21.Hou L, Wang X, Li G, Zou L, Chen Y, Zhang W. Cross sectional study in China: fetal gender has adverse perinatal outcomes in mainland China. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2014;14:372. doi: 10.1186/s12884-014-0372-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Juberg RC, Gaar DG, Humphries JR. Sex ratio in the progeny of mothers with toxemia of pregnancy. J Reprod Med Obstet Gynecol. 1976;16:299–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Li X, Tan H, Huang X, Zhou S, Hu S, Wang X, et al. Similarities and differences between the risk factors for gestational hypertension and preeclampsia: A population based cohort study in south China. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2016;6:66–71. doi: 10.1016/j.preghy.2015.11.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Makhseed M, Musini VM, Ahmed MA. Association of fetal gender with pregnancy-induced hypertension and pre-eclampsia. Int J Gynecol Obstet. 1998;63:55–56. doi: 10.1016/S0020-7292(98)00078-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Persson M, Fadl H. Perinatal outcome in relation to fetal sex in offspring to mothers with pre-gestational and gestational diabetes-a population-based study. Diabet Med. 2014;31:1047–1054. doi: 10.1111/dme.12479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sheiner E, Levy A, Katz M, Hershkovitz R, Leron E, Mazor M. Gender does matter in perinatal medicine. Fetal Diagn Ther. 2004;19:366–369. doi: 10.1159/000077967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Shiozaki A, Matsuda Y, Satoh S, Saito S. Impact of fetal sex in pregnancy-induced hypertension and preeclampsia in Japan. J Reprod Immunol. 2011;89:133–139. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2010.12.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Tundidor D, García-Patterson A, María MA, Ubeda J, Ginovart G, Adelantado JM, et al. Perinatal maternal and neonatal outcomes in women with gestational diabetes mellitus according to fetal sex. Gender Med. 2012;9:411–417. doi: 10.1016/j.genm.2012.09.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Verburg PE, Tucker G, Scheil W, Erwich JJHM, Dekker GA, Roberts CT. Sexual dimorphism in adverse pregnancy outcomes - A retrospective Australian population study 1981-2011. PLoS One. 2016;11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 30.Zheng Q, Deng Y, Zhong S, Shi Y. Human chorionic gonadotropin, fetal sex and risk of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy: A nested case-control study. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2016;6:17–21. doi: 10.1016/j.preghy.2016.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Aibar L, Puertas A, Valverde M, Carrillo MP, Montoya F. Fetal sex and perinatal outcomes. J Perinat Med. 2012;40:271–276. doi: 10.1515/jpm-2011-0137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Aliyu MH, Salihu HM, Lynch O, Alio AP, Marty PJ. Placental abruption, offspring sex, and birth outcomes in a large cohort of mothers. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012;25:248–252. doi: 10.3109/14767058.2011.569615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Basso O, Olsen J. Sex ratio and twinning in women with hyperemesis or pre-eclampsia. Epidemiology. 2001;12:747–749. doi: 10.1097/00001648-200111000-00026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Brettell R, Yeh PS, Impey LWM. Examination of the association between male gender and preterm delivery. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2008;141:123–126. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2008.07.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Choong CF, Fung ESM, Tang L. Fetal sex ratio and pre-eclamptic pregnancies. Med Sci Res. 1995;23:35–36. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Chu T, Bunce K, Shaw P, Shridhar V, Althouse A, Hubel C, et al. Comprehensive analysis of preeclampsia-associated DNA methylation in the placenta. PLoS One. 2014;9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 37.Hadar E, Hiersch L, Ashwal E, Aviram A, Wiznitzer A, Gabbay-Benziv R. Risk of caesarean delivery after induction of labour stratified by foetal sex. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2017;37:731–735. doi: 10.1080/01443615.2017.1292224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Khalil MM, Alzahra E. Fetal gender and pregnancy outcomes in Libya: A retrospective study. Libyan J Med. 2013;8:1–4. doi: 10.3402/ljm.v8i0.20008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lao TT, Sahota DS, Suen SSH, Law LW. The impact of fetal gender on preterm birth in a southern Chinese population. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2011;24:1440–1443. doi: 10.3109/14767058.2011.589872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lao TT, Sahota DS, Law LW, Leung TY. Maternal rubella immunity status and pre-eclampsia. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2017;78. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 41.Lisonkova S, Joseph KS. Incidence of preeclampsia: Risk factors and outcomes associated with early-versus late-onset disease. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2013;209:544.e541-544.e512. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2013.08.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Liu Y, Li G, Zhang W. Effect of fetal gender on pregnancy outcomes in Northern China. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016:1–6. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 43.Masoumi Z, Familari M, Källén K, Ranstam J, Olofsson P, Hansson SR. Fetal hemoglobin in umbilical cord blood in preeclamptic and normotensive pregnancies: A cross-sectional comparative study. PLoS One. 2017;12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 44.Morsing E, Maršál K, Ley D. Reduced Prevalence of Severe Intraventricular Hemorrhage in Very Preterm Infants Delivered after Maternal Preeclampsia. Neonatology. 2018;114:205–211. doi: 10.1159/000489039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Myers JE, Thomas G, Tuytten R, Van Herrewege Y, Djiokep RO, Roberts CT, et al. Mid-trimester maternal ADAM12 levels differ according to fetal gender in pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia. Reprod Sci. 2015;22:235–241. doi: 10.1177/1933719114537713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Peled Y, Melamed N, Hiersch L, Hadar E, Wiznitzer A, Yogev Y. Pregnancy outcome in hyperemesis gravidarum - the role of fetal gender. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2013;26:1753–1757. doi: 10.3109/14767058.2013.798293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Quinones JN, Stamilio DM, Coassolo KM, Macones GA, Odibo AO. Is fetal gender associated with adverse perinatal outcome in intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR)? Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2005;193:1233–1237. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2005.05.053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Reynolds SA, Roberts JM, Bodnar LM, Haggerty CL, Youk AO, Catov JM. Newborns of preeclamptic women show evidence of sex-specific disparity in fetal growth. Gender Med. 2012;9:424–435. doi: 10.1016/j.genm.2012.10.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Roy S, Dhobale M, Dangat K, Mehendale S, Lalwani S, Joshi S. Differential oxidative stress levels in mothers with preeclampsia delivering male and female babies. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2015;28:1973–1980. doi: 10.3109/14767058.2014.974537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Sharifzadeh F, Kashanian M, Fatemi F. A comparison of serum androgens in pre-eclamptic and normotensive pregnant women during the third trimester of pregnancy. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2012;28:834–836. doi: 10.3109/09513590.2012.683061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Taylor BD, Haggerty CL, Ness RB, Hougaard DM, Skogstrand K, Roberts JM, et al. Fetal sexual dimorphism in systemic soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 among normotensive and preeclamptic women. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2018;80. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 52.Toivanen P, Hirvonen T. Sex ratio of newborns: preponderance of males in toxemia of pregnancy. Science. 1970;170:187–188. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3954.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Trudell AS, Cahill AG, Tuuli MG, MacOnes GA, Odibo AO. Stillbirth and the small fetus: Use of a sex-specific versus a non-sex-specific growth standard. J Perinatol. 2015;35:566–569. doi: 10.1038/jp.2015.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Vatten LJ, Skjærven R. Offspring sex and pregnancy outcome by length of gestation. Early Hum Dev. 2004;76:47–54. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2003.10.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Weinberg CR, Shi M, Basso O, DeRoo LA, Harmon Q, Wilcox AJ, et al. Season of conception, smoking, and preeclampsia in Norway. Environ Health Perspect. 2017;125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 56.Breschi MC, Seghieri G, Bartolomei G, Gironi A, Baldi S, Ferrannini E. Relation of birthweight to maternal plasma glucose and insulin concentrations during normal pregnancy. Diabetologia. 1993;36:1315–1321. doi: 10.1007/BF00400812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Cosson E, Diallo A, Docan M, Sandre-Banon D, Banu I, Cussac-Pillegand C, et al. Fetal gender is not associated with either gestational diabetes mellitus or placental weight: A cohort study. Diabetes Metab. 2016. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 58.Ehrlich SF, Eskenazi B, Hedderson MM, Ferrara A. Sex ratio variations among the offspring of women with diabetes in pregnancy. Diabet Med. 2012;29:e273–e278. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2012.03663.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Heckbert SR, Stephens CR, Daling JR. Diabetes in pregnancy: maternal and infant outcome. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 1988;2:314–326. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3016.1988.tb00225.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Janssen PA, Rothman I, Schwartz SM. Congenital malformations in newborns of women with established and gestational diabetes in Washington State, 1984-91. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 1996;10:52–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3016.1996.tb00026.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Kale SD, Kulkarni SR, Lubree HG, Meenakumari K, Deshpande VU, Rege SS, et al. Characteristics of gestational diabetic mothers and their babies in an Indian diabetes clinic. J Assoc Physicians India. 2005;53:857–863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Oken E, Morton-Eggleston E, Rifas-Shiman SL, Switkowski KM, Hivert MF, Fleisch AF, et al. Sex-Specific Associations of Maternal Gestational Glycemia with Hormones in Umbilical Cord Blood at Delivery. Am J Perinatol. 2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 63.Okereke NC, Uvena-Celebrezze J, Hutson-Presley L, Amini SB, Catalano PM. The effect of gender and gestational diabetes mellitus on cord leptin concentration. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2002;187:798–803. doi: 10.1067/mob.2002.125887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Retnakaran R, Kramer CK, Ye C, Kew S, Hanley AJ, Connelly PW, et al. Fetal sex and maternal risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: the impact of having a boy. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:844–851. doi: 10.2337/dc14-2551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Spellacy WN, Miller S, Winegar A, Peterson PQ. Macrosomia - maternal characteristics and infant complications. Obstet Gynecol. 1985;66:158–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Strutz J, Cvitic S, Hackl H, Kashofer K, Appel HM, Thüringer A, et al. Gestational diabetes alters microRNA signatures in human feto-placental endothelial cells depending on fetal sex. Clin Sci. 2018;132:2437–2449. doi: 10.1042/CS20180825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Xiao L, Zhao JP, Nuyt AM, Fraser WD, Luo ZC. Female fetus is associated with greater maternal insulin resistance in pregnancy. Diabet Med. 2014. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 68.Jakobovits AA, Zubek L. Abruptio placentae and fetal sex ratio. Acta Med Hung. 1988;45:191–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Schildberger B, Leitner H. Foetal Gender and Obstetric Outcome. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 2016;76:255–260. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-109198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Sheiner E, Shoham-Vardi I, Hadar A, Hallak M, Hackmon R, Mazor M. Incidence, obstetric risk factors and pregnancy outcome of preterm placental abruption: a retrospective analysis. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2002;11:34–39. doi: 10.1080/jmf.11.1.34.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Weissmann-Brenner A, Simchen MJ, Zilberberg E, Kalter A, Dulitzky M. Combined effect of fetal sex and advanced maternal age on pregnancy outcomes. Med Sci Monit. 2015;21:1124–1130. doi: 10.12659/MSM.893057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Byrne J, Warburton D. Male excess among anatomically normal fetuses in spontaneous abortions. Am J Med Genet. 1987;26:605–611. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320260315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Cheng HH, Ou CY, Tsai CC, Chang SD, Hsiao PY, Lan KC, et al. Chromosome distribution of early miscarriages with present or absent embryos: Female predominance. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2014;31:1059–1064. doi: 10.1007/s10815-014-0261-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.del Fabro A, Driul L, Anis O, Londero AP, Bertozzi S, Bortotto L, et al. Fetal gender ratio in recurrent miscarriages. Int J Women's Health. 2011;3:213–217. doi: 10.2147/IJWH.S20557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Yegüez-Marín F, Marisol García de Y, Gil D. Depression in pregnant women in the second trimester of gestation and its impact on blood pressure. Salus. 2013;17:15–24. [Google Scholar]
- 76.Ricart W, López J, Mozas J, Pericot A, Sancho MA, González N, et al. Maternal glucose tolerance status influences the risk of macrosomia in male but not in female fetuses. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2009;63:64–68. doi: 10.1136/jech.2008.074542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Sykes SD, Pringle KG, Zhou A, Dekker GA. Fetal sex and the circulating renin–angiotensin system during early gestation in women who later develop preeclampsia or gestational hypertension. J Hum. 2014. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 78.Yoder SR, Thornburg LL, Bisognano JD. Hypertension in pregnancy and women of childbearing age. Am J Med. 2009;122:890–895. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2009.03.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Wandabwa J, Doyle P, Kiondo P, Campbell O, Maconichie N, Welishe G. Risk factors for severe pre-eclampsia and eclampsia in Mulago Hospital, Kampala, Uganda. East Afr Med J. 2010;87:415–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Taylor BD, Ness RB, Klebanoff MA, Tang G, Roberts JM, Hougaard DM, et al. The impact of female fetal sex on preeclampsia and the maternal immune milieu. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2018;12:53–57. doi: 10.1016/j.preghy.2018.02.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Abalos E, Cuesta C, Grosso AL, Chou D, Say L. Global and regional estimates of preeclampsia and eclampsia: a systematic review. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2013;170:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2013.05.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Lopez-Llera M. Eclampsia and fetal sex. Int J Gynecol Obstet. 1990;33:211–213. doi: 10.1016/0020-7292(90)90003-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Liu S, Joseph KS, Liston RM, Bartholomew S, Walker M, Leon JA, et al. Incidence, risk factors, and associated complications of eclampsia. Obstet Gynecol. 2011;118:987–994. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0b013e31823311c1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Lawlor DA, Fraser A, Lindsay RS, Ness A, Dabelea D, Catalano P, et al. Association of existing diabetes, gestational diabetes and glycosuria in pregnancy with macrosomia and offspring body mass index, waist and fat mass in later childhood: findings from a prospective pregnancy cohort. Diabetologia. 2010;53:89–97. doi: 10.1007/s00125-009-1560-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Retnakaran R, Shah BR. Fetal Sex and the Natural History of Maternal Risk of Diabetes During and After Pregnancy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100:2574–2580. doi: 10.1210/jc.2015-1763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Macaulay S, Munthali RJ, Dunger DB, Norris SA. The effects of gestational diabetes mellitus on fetal growth and neonatal birth measures in an African cohort. Diabet Med. 2018;35:1425–1433. doi: 10.1111/dme.13668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Deputy NP, Kim SY, Conrey EJ, Bullard KM. Prevalence and Changes in Preexisting Diabetes and Gestational Diabetes Among Women Who Had a Live Birth - United States, 2012-2016. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67:1201–1207. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6743a2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Aliyu MH, Salihu HM, Lynch O, Alio AP, Marty PJ. Fetal sex and differential survival in preeclampsia and eclampsia. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2012;285:361–365. doi: 10.1007/s00404-011-1984-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Räisänen S, Gissler M, Nielsen HS, Kramer MR, Williams MA, Heinonen S. Social disparity affects the incidence of placental abruption among multiparous but not nulliparous women: A register-based analysis of 1,162,126 singleton births. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2013;171:246–251. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2013.09.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Tikkanen M, Luukkaala T, Gissler M, Ritvanen A, Ylikorkala O, Paavonen J, et al. Decreasing perinatal mortality in placental abruption. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2013;92:298–305. doi: 10.1111/aogs.12030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Wandabwa J, Doyle P, Paul K, Wandabwa MA, Aziga F. Risk factors for severe abruptio placenta in Mulago Hospital, Kampala, Uganda. Afr Health Sci. 2005;5:285–290. doi: 10.5555/afhs.2005.5.4.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Ananth CV, Keyes KM, Hamilton A, Gissler M, Wu C, Liu S, et al. An international contrast of rates of placental abruption: an age-period-cohort analysis. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0125246. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Global Pregnancy C, Schalekamp-Timmermans S, Arends LR, Alsaker E, Chappell L, Hansson S, et al. Fetal sex-specific differences in gestational age at delivery in pre-eclampsia: a meta-analysis. Int J Epidemiol. 2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 94.Adly N, Alhashem A, Ammari A, Alkuraya FS. Ciliary genes TBC1D32/C6orf170 and SCLT1 are mutated in patients with OFD type IX. Hum Mutat. 2014;35:36–40. doi: 10.1002/humu.22477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Berx G, van Roy F. Involvement of members of the cadherin superfamily in cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2009;1:a003129. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a003129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Lehto M, Mayranpaa MI, Pellinen T, Ihalmo P, Lehtonen S, Kovanen PT, et al. The R-Ras interaction partner ORP3 regulates cell adhesion. J Cell Sci. 2008;121:695–705. doi: 10.1242/jcs.016964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Tchaicha JH, Reyes SB, Shin J, Hossain MG, Lang FF, McCarty JH. Glioblastoma angiogenesis and tumor cell invasiveness are differentially regulated by beta8 integrin. Cancer Res. 2011;71:6371–6381. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-0991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Orzack SH, Stubblefield JW, Akmaev VR, Colls P, Munne S, Scholl T, et al. The human sex ratio from conception to birth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112:E2102–E2111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1416546112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Sandman CA, Glynn LM, Davis EP. Is there a viability-vulnerability tradeoff? Sex differences in fetal programming. J Psychosom Res. 2013;75:327–335. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2013.07.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Global Pregnancy C. Schalekamp-Timmermans S, Arends LR, Alsaker E, Chappell L, Hansson S, et al. Fetal sex-specific differences in gestational age at delivery in pre-eclampsia: a meta-analysis. Int J Epidemiol. 2017;46:632–642. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyw178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Murray SR, Juodakis J, Bacelis J, Sand A, Norman JE, Sengpiel V, et al. Geographical differences in preterm delivery rates in Sweden: A population-based cohort study. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2019;98:106–116. doi: 10.1111/aogs.13455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Morgan TK. Role of the Placenta in Preterm Birth: A Review. Am J Perinatol. 2016;33:258–266. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1570379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Helle S, Lummaa V, Jokela J. Sons reduced maternal longevity in preindustrial humans. Science. 2002;296:1085. doi: 10.1126/science.1070106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Helle S, Lummaa V. A trade-off between having many sons and shorter maternal post-reproductive survival in pre-industrial Finland. Biol Lett. 2013;9:20130034. doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2013.0034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Van de Putte B, Matthijs K, Vlietinck R. A social component in the negative effect of sons on maternal longevity in pre-industrial humans. J Biosoc Sci. 2004;36:289–297. doi: 10.1017/S0021932003006266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Sugiura-Ogasawara M, Ozaki Y, Katano K, Suzumori N, Kitaori T, Mizutani E. Abnormal embryonic karyotype is the most frequent cause of recurrent miscarriage. Hum Reprod. 2012;27:2297–2303. doi: 10.1093/humrep/des179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Jaskolka D, Retnakaran R, Zinman B, Kramer CK. Sex of the baby and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus in the mother: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetologia. 2015. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 108.Jaskolka D, Retnakaran R, Zinman B, Kramer CK. Fetal sex and maternal risk of pre-eclampsia/eclampsia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Bjog. 2017;124:553–560. doi: 10.1111/1471-0528.14163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Valvi D, Oulhote Y, Weihe P, Dalgård C, Bjerve KS, Steuerwald U, Grandjean P. Gestational diabetes and offspring birth size at elevated environmental pollutant exposures. Environ Int. 2017;107:205–215. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2017.07.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Räisänen S, Gissler M, Nielsen HS, Kramer MR, Williams MA, Heinonen S. Social disparity affects the incidence of placental abruption among multiparous but not nulliparous women: a register-based analysis of 1,162,126 singleton births. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2013;171:246–51. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2013.09.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 2. Newcastle-Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale.
Data Availability Statement
The extracted data from included articles supporting the conclusions of this manuscript can be found in Table 1 and 2.