Abstract
This study was about a 70-year-old man with progressive dysphagia. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy showed a 1.2-cm circumferential ulcerative mass at the level of 23 cm from the upper incisors in the upper esophagus. The mass was first diagnosed as a poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma. McKeown esophagogastrectomy was performed with intention to treat the lesion. The pathological examination showed an esophageal neuroendocrine carcinoma that was mixed with squamous cell carcinoma component. In this report, we present a unique case of the extremely rare esophageal neoplasm, an esophageal neuroendocrine carcinoma with squamous cell carcinoma component.
Keywords: esophagus, esophageal neoplasm, neuroendocrine
Introduction
A neuroendocrine tumor of the esophagus is a very rare neoplasm, representing only 3.3% of all esophageal malignant neoplasm1 and 70% of esophageal neuroendocrine tumors present as neuroendocrine carcinomas (NECs).2 Squamous cell carcinoma is the most common histologic type of esophageal malignant neoplasm in Asia. However, combined tumor with components of both neuroendocrine and squamous cell cancer is extremely rare and only 3 other cases have been reported in the literature till now (Table 1).3-5 We now report a case of an esophageal NEC that was mixed with squamous cell carcinoma component.
Table 1.
Clinical Characteristics of the Esophageal Neuroendocrine Mixed With Squamous Cell Carcinoma Component.
| Year | Author | Age (Years) | Sex | Location | Chief Complaint | Histology | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | Uğraş et al3 | NR | NR | NR | NR | Squamous and small cell carcinoma | Chemotherapy |
| 2015 | Yazici et al4 | 65 | Female | Lower | Dysphagia | Squamous and neuroendocrine carcinoma | Neoadjuvant chemotherapy and esophagectomy |
| 2018 | Fujihara et al5 | 77 | Male | Middle | NR | Squamous and neuroendocrine carcinoma | Endoscopic mucosal resection and submucosal dissection |
| Current patient | Kang et al | 70 | Male | Upper | Dysphagia | Squamous and neuroendocrine carcinoma | Esophagectomy |
Abbreviation: NR, not reported.
Case Report
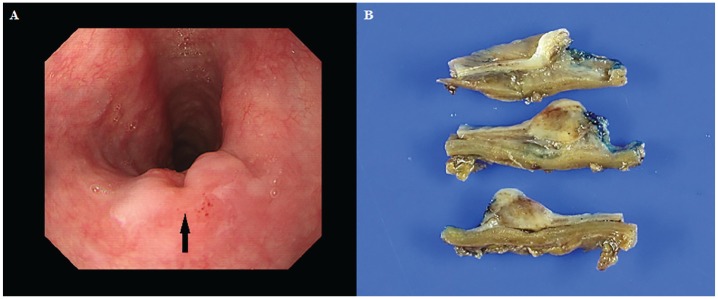
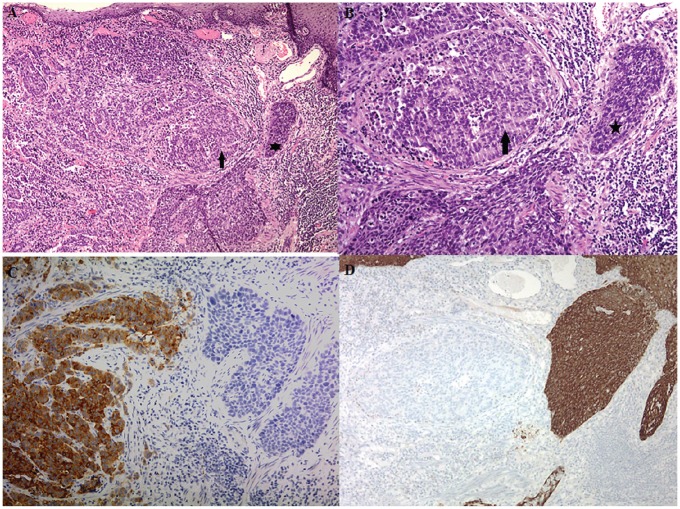
A 70-year-old man presented to our clinic with complaints of progressive dysphagia that had lasted for about 2 months. He was a 40-pack-year ex-smoker. A chest computed tomography scan revealed no visible space occupying lesion in esophagus. A 1.2-cm circumferential ulcerative mass was observed at the level of 23 cm from the upper incisors in the upper esophagus during an esophagogastroduodenoscopy. An endoscopic biopsy from the mass showed the presence of contiguous areas with squamous cell carcinoma. A hypoechoic disruption of the superficial, deep mucosal layer, and submucosa was noted in endoscopic ultrasound. The lesion further invaded into, but not through, the muscularis propria layer. Regional lymphadenopathy was not found. The patient underwent a McKeown esophagogastrectomy. A 1.0-cm ulcerofungating mass extending to the submucosa was identified in the upper esophagus. The cut surface of the mass was grayish white (Figure 1). Hematoxylin and eosin–stained sections showed neuroendocrine cell carcinoma arranged with mixed squamous cell carcinoma. Immunostaining for cytokeratin 5/6 markers confirmed the diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma. Immunostaining for synaptophysin was positive, confirming the diagnosis of neuroendocrine differentiation (Figure 2). The patient had an uneventful clinical course and discharged without complication.
Figure 1.
Endoscopic image of esophageal tumor (A, arrow). Gross appearance of esophageal tumor: ulcerofungating mass in the upper esophagus shows grayish white–colored cut surface (B).
Figure 2.
Microscopic examination of the mass revealed neuroendocrine cell carcinoma (star) arranged with mixed squamous cell carcinoma (A, arrow; hematoxylin and eosin [H&E] staining, ×100), (B; H&E staining, ×200). Immunohistochemistry for synaptophysin (C) and cytokeratin 5/6 (D) were positive in tumor cells.
Discussion
Esophageal NECs were first reported by McKeown in 1952.6 NECs are very rare but aggressive tumors with a poor prognosis and low survival rate. There is no established treatment recommendation for its paucity. However, the coexistence of neuroendocrine and other component is rarer. Tumors with 2 different histological morphologies are classified as either composite or collision tumors. A collision of tumor consists of 2 independent neoplasms growing in close proximity, which is believed to result from coincidental neoplastic change.7 Two different tumors are clearly demarcated. In composite tumors, 1 neoplastic clone diverges in to 2 different cell lineages.8 Histologically, composite tumors emerge from a single pluripotent precursor stem cell. We consider our case to be a collision tumor. Our report serves as reminder that neuroendocrine carcinoma with focal squamous cell carcinoma component might be considered in the diagnosis of esophageal cancer although it is extremely rare.
Footnotes
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Funding: The author(s) received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Ethics Approval: Our institution does not require ethical approval for reporting individual cases or case series.
Informed Consent: Written informed consent was obtained from the patient(s) for their anonymized information to be published in this article.
References
- 1. Kanakasetty GB, Dasappa L, Lakshmaiah KC, et al. Clinicopathological profile of pure neuroendocrine neoplasms of the esophagus: a South Indian center experience. J Oncol. 2016;2016:2402417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Glickman JN, Odze RD. Epithelial neoplasms of the esophagus. In: Odze RD, Goldblum JR, eds. Odze and Goldblum Surgical Pathology of the GI Tract, Liver, Biliary Tract, and Pancreas. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2015:674-706. [Google Scholar]
- 3. Uğraş S, Akpolat N, Er M, Yalçýnkaya I, Karaayvaz M. Primary composite tumour with bipartite differentiation of the esophagus. Acta Chir Belg. 2000;100:39-43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Yazici O, Aksoy S, Özhamam EU, Zengin N. Squamous cell and neuroendocrine carcinoma of esophagus: collision versus composite tumor: a case report and review of literature. Indian J Cancer. 2015;52:603-604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Fujihara S, Kobayashi M, Nishi M, et al. Composite neuroendocrine carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma with regional lymph node metastasis: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2018;12:227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. McKeown F. Oat-cell carcinoma of the oesophagus. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1952;64:889-891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Fenoglio-Preiser CM. Carcinomas and other epithelial and neuroendocrine tumors of the large intestine. In: Fenoglio-Preiser CM, Lantz P, Listrom M, Noffsinger A, Rilke F, Stemmermann G, eds. Gastrointestinal Pathology. An Atlas and Text. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott-Raven; 1999:909-910. [Google Scholar]
- 8. Lyda MH, Fenoglio-Preiser CM. Adenoma-carcinoid tumors of the colon. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1998;122:262-265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]