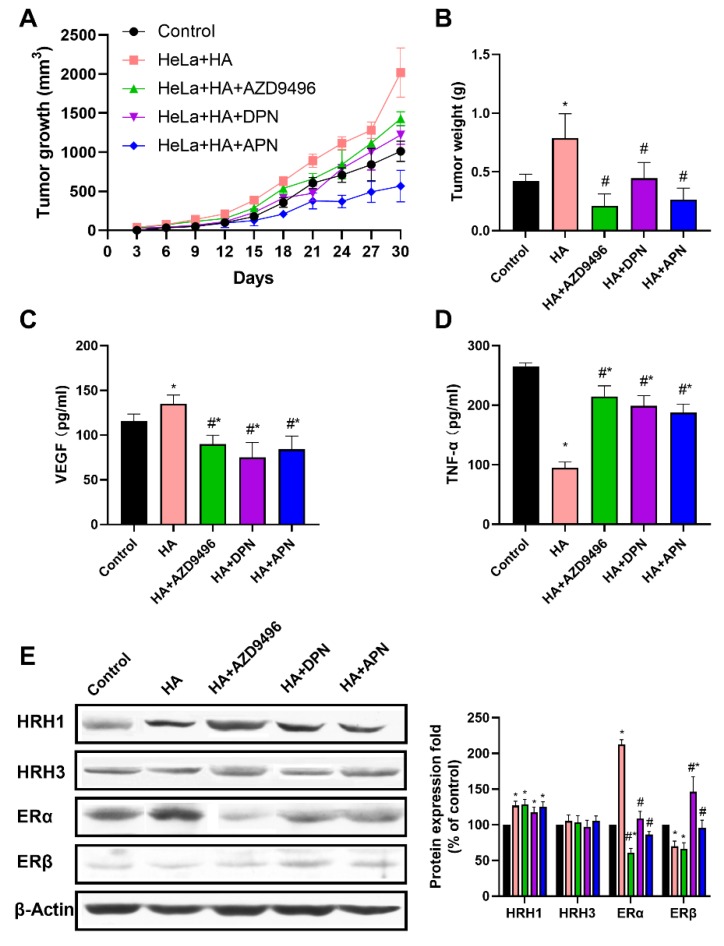
Figure 5.
Apigenin inhibited cervical tumor growth in vivo by attenuating the abnormal ER signaling caused by histamine. HeLa cells were injected subcutaneously into the lower right side of female BALB/c nude mice. After 6 days, mice were divided into five groups; control, HeLa + HA (1 mg/kg), HA + AZD9496 (1 mg/kg + 2 mg/kg), HA + DPN (1 mg/kg + 2 mg/kg) and HA + APN (1 mg/kg + 100 mg/kg). Animals were intraperitoneally injected with these reagents every 3 days. Effects of apigenin on cervical tumor growth was determined by the tumor volume and tumor weight. (A) Average tumor volume was measured every 3 days. (B) Tumor weights were measured at the end of treatment. (C) ELISA analysis for serum VEGF levels. (D) ELISA analysis for serum TNF-α levels. (E) Western blot analysis on the expression level of ERα, ERβ, HRH1 and HRH3 from respective tumor tissues. The antibodies used in this experiment were ERα (ab32063), ERβ (ab288), HRH1 (ABP51517) and HRH3 (ABP53626). The results are expressed as a percentage of control, which is set at 100%. The serum used in (C,D) was obtained from the orbital sinus of mice. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments. * p < 0.05 versus the control group, # p < 0.05 versus the HA group.