We sequenced four severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) genomes from Malaysia during the second wave of infection and found unique mutations which suggest local evolution. Circulating Malaysian strains represent introductions from different countries, particularly during the first wave of infection. Genome sequencing is important for understanding local epidemiology.
ABSTRACT
We sequenced four severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) genomes from Malaysia during the second wave of infection and found unique mutations which suggest local evolution. Circulating Malaysian strains represent introductions from different countries, particularly during the first wave of infection. Genome sequencing is important for understanding local epidemiology.
ANNOUNCEMENT
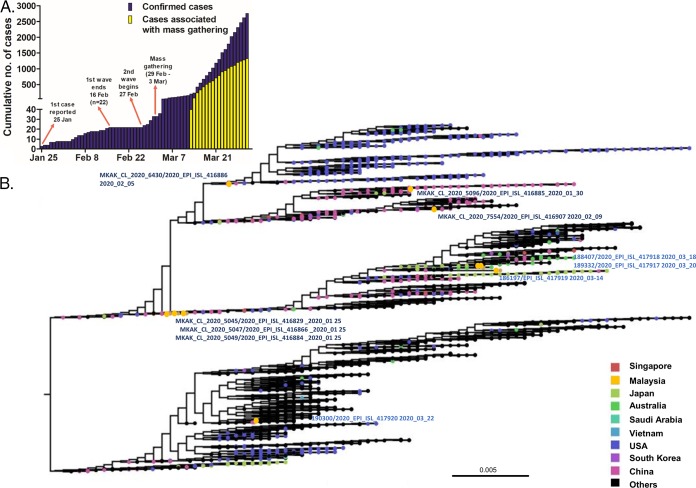
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) belongs to the family Coronaviridae and the genus Betacoronavirus and has caused a pandemic of coronavirus disease (COVID-19). As of 31 March 2020, Malaysia had 2,766 confirmed cases with 43 deaths (1). To obtain a preliminary understanding of SARS-CoV-2 molecular epidemiology in Malaysia, we performed complete genome sequencing of SARS-CoV-2 strains collected directly from nasopharyngeal swabs from four patients (186197, 188407, 189332, and 190300) in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, between 14 and 22 March 2020 (Fig. 1A).
FIG 1.
(A) Cumulative cases in Malaysia until 31 March 2020. There have been two waves of infection, separated by 11 days during which no cases were reported. Cases of the first wave were associated mainly with travel from China and Singapore. About 48% of the cases in the second wave were associated with a religious mass gathering. (B) Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree built with FastTree and based on the complete genomes of 2,364 sequences available at GISAID on 29 March 2020. The 10 Malaysian genomes are named and comprise six genomes from the first wave (dark blue) and the four genomes sequenced in this study (second wave, blue). The date of sample collection is recorded at the end of each strain name. The tree was midpoint rooted.
Viral RNA was extracted from the samples using a QIAamp viral RNA minikit (Qiagen, Germany) and amplified according to the ARTIC nCoV-2019 protocol (2). Briefly, cDNA was synthesized using a SuperScript IV first-strand synthesis system (Invitrogen, USA) with random hexamers. The ARTIC v1 primers were divided into two pools of 49 primer sets for PCR using Q5 high-fidelity DNA polymerase (NEB, USA). Overlapping amplicons of 400 bp were combined and purified using sample purification beads (SPB) (Illumina, USA), quantified with a Qubit 3.0 fluorometer, and used for library preparation. Nextera DNA Flex libraries were sequenced using iSeq 100 reagent (Illumina) on the iSeq 100 system (Illumina) with output of 2 × 100-bp paired-end reads and 4 million expected paired reads. Sequencing of one strain (186197) was also performed using a Nanopore MinION and ligation sequencing kit (SQK-LSK109) according to the Oxford Nanopore Technologies (ONT) standard protocol (ONT, UK). Briefly, purified amplicons were sequenced in an R9.4 flow cell and run for 30 min.
The iSeq raw FastQ files were analyzed using Geneious Prime 2020 (Biomatters, New Zealand). The average number of raw paired reads obtained from iSeq was 1.8 million (Table 1). Paired reads were trimmed for quality using default parameters and mapped to reference strain Wuhan-Hu-1 (GenBank accession number MN908947) with the Geneious mapper. About 94% of the reads were mapped, except for strain 186197 (25.2%). The average depth of coverage for iSeq was 5,000×, except for strain 186197, which had only 1,000× coverage (Table 1). Therefore, the consensus sequence for strain 186197 was mapped from a combination of iSeq (359,453 paired reads) and MinION (23,390 reads) sequencing with Geneious mapper using default parameters. The four genome sizes ranged from 29,486 to 29,898 bp with GC contents of 36.6 to 37.9% (Table 1). Multiple sequence alignment was performed with MAFFT with default parameters (3). Phylogenetic analysis was conducted with FastTree 2.1.11 (4) implemented in Geneious with default parameters using whole genomes available at GISAID (www.gisaid.org), including six other previously deposited Malaysian strains (EPI_ISL_416829, EPI_ISL_416866, EPI_ISL_416884, EPI_ISL_416885, EPI_ISL_416886, and EPI_ISL_416907).
TABLE 1.
Comparison of nucleotide and amino acid differences among Malaysian strains
| Malaysian strain | NGSa (iSeq) |
Mutation in gene at indicated positionb |
||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of raw reads | No. of mapped reads | Maximum coverage (×) | Avg coverage (×) | Genome size (bp) | GC content (%) | ORF1a |
ORF1b |
S | M | ORF8 | N | 3 UTRc |
||||||||||
| Nucleotide position (in the genome) | 2737 | 6310 | 6312 | 8782 | 11083 | 13730 | 13975 | 19524 | 23929 | 27147 | 28144 | 28311 | 29862 | 29868 | 29869 | 29871 | ||||||
| Codon position (in the protein) | 824 | 2015 | 2016 | 2839 | 3606 | 88 | 2019 | 789 | 209 | 84 | 13 | |||||||||||
| Reference SARS-CoV-2 (MN908947) | 29,903 | 38.0 | T (T) | C (S) | C (T) | C (S) | G (L) | C (A) | G (G) | C (L) | C (Y) | G (D) | T (L) | C (P) | G | T | G | C | ||||
| hCoV-19/Malaysia/MKAK-CL-2020-5045/2020|EPI_ISL_416829 | T (T) | C (S) | C (T) | C (S) | G (L) | C (A) | G (G) | C (S) | C (Y) | C (H) | T (L) | C (P) | G | T | G | C | ||||||
| hCoV-19/Malaysia/MKAK-CL-2020-5049/2020|EPI_ISL_416884 | T (T) | C (S) | C (T) | C (S) | G (L) | C (A) | G (G) | C (S) | C (Y) | C (H) | T (L) | C (P) | G | T | G | C | ||||||
| hCoV-19/Malaysia/MKAK-CL-2020-5047/2020|EPI_ISL_416866 | T (T) | C (S) | C (T) | C (S) | G (L) | C (A) | G (G) | C (S) | C (Y) | C (H) | T (L) | C (P) | G | T | G | C | ||||||
| hCoV-19/Malaysia/MKAK-CL-2020-6430/2020|EPI_ISL_416886 | T (T) | C (S) | C (T) | T (S) | G (L) | C (A) | G (G) | C (S) | C (Y) | G (D) | C (S) | T (L) | G | T | G | C | ||||||
| hCoV-19/Malaysia/MKAK-CL-2020-5096/2020|EPI_ISL_416885 | T (T) | C (S) | C (T) | T (S) | G (L) | C (A) | G (G) | C (S) | C (Y) | G (D) | C (S) | T (L) | G | T | G | C | ||||||
| hCoV-19/Malaysia/MKAK-CL-2020-7554/2020|EPI_ISL_416907 | T (T) | C (S) | C (T) | C (S) | G (L) | C (A) | G (G) | C (S) | C (Y) | G (D) | T (L) | T (L) | G | T | G | C | ||||||
| hCoV-19/Malaysia/186197/2020/EPI_ISL_417919 | 1,467,222 | 369,427 | 73,335 | 1,087 | 29,486 | 36.6 | A (T) | C (S) | C (T) | C (S) | G (L) | C (A) | G (G) | C (S) | C (Y) | G (D) | T (L) | T (L) | G | A | A | A |
| hCoV-19/Malaysia/188407/2020|EPI_ISL_417918 | 2,057,020 | 1,952,563 | 20,231 | 5,696 | 29,898 | 37.9 | T (T) | A (R) | A (K) | C (S) | T (F) | T (V) | G (G) | T (S) | T (Y) | G (D) | T (L) | T (L) | G | A | A | A |
| hCoV-19/Malaysia/190300/2020|EPI_ISL_417920 | 1,796,760 | 1,647,233 | 30,677 | 4,986 | 29,865 | 37.6 | T (T) | C (S) | A (K) | C (S) | T (F) | T (V) | G (G) | T (S) | T (Y) | G (D) | T (L) | T (L) | A | A | A | A |
| hCoV-19/Malaysia/189332/2020|EPI_ISL_417917 | 1,895,160 | 1,821,267 | 17,208 | 5,289 | 29,868 | 37.9 | A (T) | A(R) | A (K) | C (S) | T (F) | T (V) | A (S) | T (S) | T (Y) | G (D) | T (L) | T (L) | A | A | A | A |
NGS, next-generation sequencing.
Amino acids are denoted in parentheses; the four genomes of the second wave (sequenced in the present study) are italicized. Unique mutations found only in Malaysian strains (as of 29 March 2020) are bold.
UTR, untranscribed region.
The four complete genome sequences reported here date from the main second wave of infections in Malaysia (Fig. 1A). Strain 188407 was linked to a religious mass gathering which has been associated with 48% of national cases and clusters with strains from Japan, Australia, and Saudi Arabia (Fig. 1B). Strain 189332 clusters with strain 188407, but the patient from whom it was isolated had no clear link to the gathering. This suggests that the strains associated with the gathering have established community transmission. The person with strain 186197 had travelled to Vietnam, while strain 190300, from a patient with no history of travelling or attending gatherings, was clustered with strains from Europe (Fig. 1B). Compared to reference strain Wuhan-Hu-1, Malaysian sequences have 16 nucleotide substitutions (Table 1). Four substitutions in the nonstructural region (ORF1a-T2737A, ORF1a-C6310A, ORF1b-G13975A, and ORF1b-C19524T) are unique to Malaysia, suggesting a degree of local evolution.
Our data showed that current circulating strains in Malaysia represent introductions from different countries and local evolution. More genomic data will clarify virus spread in Malaysia, particularly with respect to the role played by the mass gathering.
Data availability.
These sequences have been deposited in the GISAID EpiCoV newly emerging coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 platform under identifiers EPI_ISL_417917 to EPI_ISL_417920. The sequences were also deposited in the following NCBI databases: GenBank (accession numbers MT372480 to MT372483), BioProject (PRJNA616147), BioSample (SAMN14483189, SAMN14483190, SAMN14596408, and SAMN14596409), and SRA (SRR11514750, SRR11514749, SRR11542244, and SRR11542243 [Illumina raw reads] and SRR11547279 [Nanopore raw reads]).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We gratefully acknowledge the authors from the originating and submitting laboratories of GISAID sequence data on which this analysis is based. We are part of the University of Malaya COVID-19 Research Group, which includes the health care workers involved in the care of COVID-19 patients in the University of Malaya Medical Centre.
REFERENCES
- 1.Ministry of Health Malaysia. 2020. Press statement from the Director-General of Health, 1 April 2020: updates on the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) situation in Malaysia. https://kpkesihatan.com/2020/04/01/kenyataan-akhbar-kpk-1-april-2020-situasi-semasa-jangkitan-penyakit-coronavirus-2019-covid-19-di-malaysia/. Accessed 23 April 2020.
- 2.ARTIC Network. 2020. nCoV-2019 sequencing protocol. https://www.protocols.io/view/ncov-2019-sequencing-protocol-bbmuik6w. Accessed 23 April 2020.
- 3.Katoh K, Standley DM. 2013. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Mol Biol Evol 30:772–780. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Price MN, Dehal PS, Arkin AP. 2010. FastTree 2: approximately maximum-likelihood trees for large alignments. PLoS One 5:e9490. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
These sequences have been deposited in the GISAID EpiCoV newly emerging coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 platform under identifiers EPI_ISL_417917 to EPI_ISL_417920. The sequences were also deposited in the following NCBI databases: GenBank (accession numbers MT372480 to MT372483), BioProject (PRJNA616147), BioSample (SAMN14483189, SAMN14483190, SAMN14596408, and SAMN14596409), and SRA (SRR11514750, SRR11514749, SRR11542244, and SRR11542243 [Illumina raw reads] and SRR11547279 [Nanopore raw reads]).