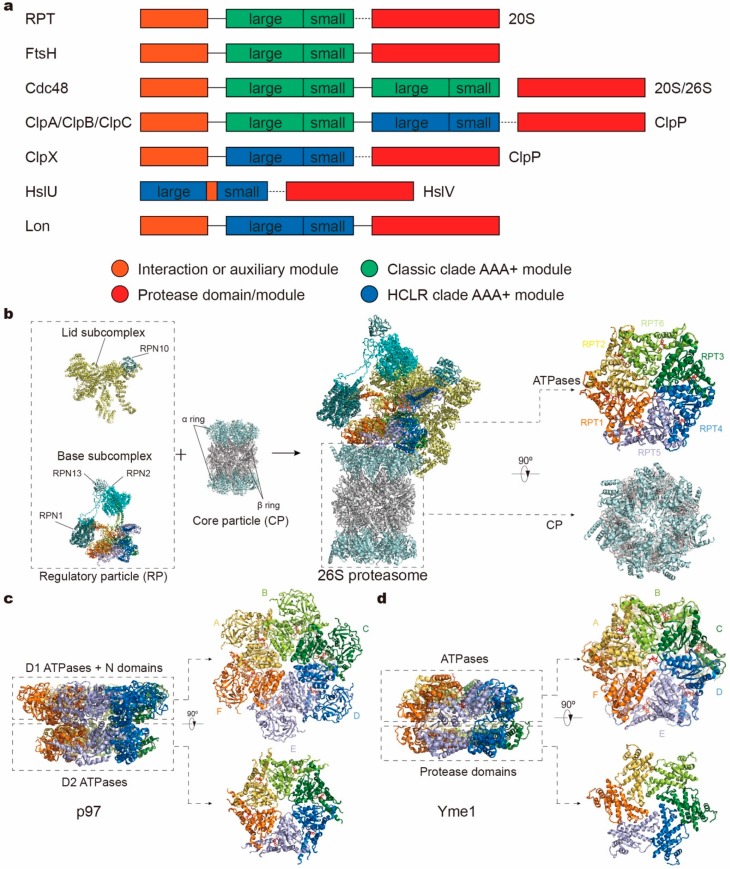
Figure 1.
Domain organizations and structures of protease complex machineries of adenosine triphosphatases (ATPases) associated with a variety of cellular activities (AAA+). (a) Domain organizations of AAA+ proteases in different families. The length of the bar is not linearly proportional to the real length of the corresponding sequence. Each protein contains one or two AAA+ modules, each consisting of a large and small subdomain, and additional family-specific domains, which are not specifically depicted here. Protease modules reside in separate protein subunits except for FtsH and Lon. Protein subunits connected by dotted line can assemble into one complex. (b–d) Atomic models of the yeast 26S proteasome (a; PDB ID: 6FVT), the ADP-bound human p97 (b; PDB ID: 5FTK) and the substrate-bound yeast Yme1 (c; PDB ID: 6AZ0) as the representative AAA+ proteases. Orthogonal views of their proteolytic complexes/domains and hexameric ATPase rings are shown here.