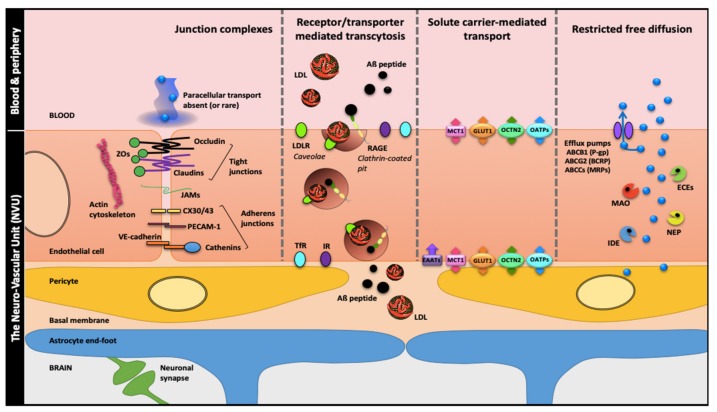
Figure 1.
The blood-brain barrier (BBB), a solid wall within the brain microvasculature. Brain microvessels endothelial cells (ECs) are the bricks supporting the BBB phenotype with two main components: (i) a physical barrier which restricts transcytosis and seals the paracellular spaces between ECs through apical tight junctions (claudins, tricellulin and occludin linked to actin cytoskeleton by zonula occludens proteins), median junctional adhesion molecules (JAMs) and medio-basolateral Ca2+-dependent adherens junctions; (ii) a metabolic barrier supported by enzymes and efflux pumps restricting nonspecific transport and favor receptor or transporter-specific routes. These features which cement the BBB ‘wall’ are induced, organized and maintained by cell–cell communications between the ECs and the close neighboring cells: brain pericytes, astrocytes (through their end-feet surrounding the brain microvessels) and neurons. These four cell types together with the basal membrane form the neurovascular unit (NVU). Abbreviations: ABCB1: ATP-Binding Cassette sub-family B member 1; ABCCs: ATP-Binding Cassette sub-family C members; ABCG2: ATP-Binding Cassette sub-family G member 2; Aβ: amyloid-β; BCRP: Breast Cancer Resistance Protein; CX30/43: Connexin 30/43; ECEs: Endothelin-Converting Enzymes; EEATs: Excitatory Amino acid Transporter 2; GLUT1: Glucose Transporter 1; IDE: Insulin Degrading Enzyme; IR: Insulin Receptor; LDL: Low-Density Lipoproteins; LDLR: Low-Density Lipoproteins Receptor; MAO: MonoAmine Oxidase; MCT1: Monocarboxylate Transporter 1, MRPs: Multidrug-Resistance Proteins; NEP: Neprilysin; OATPs: Organic Anion Transporting Polypeptides; OCTN2: Organic Cation/Carnitine Transporter 2; PECAM-1 (also CD31): Platelet Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule-1; P-gp: P-glycoprotein; RAGE: Receptor for Advanced Glycation End-products; TfR: Transferrin Receptor; ZOs: Zonula Occludens.