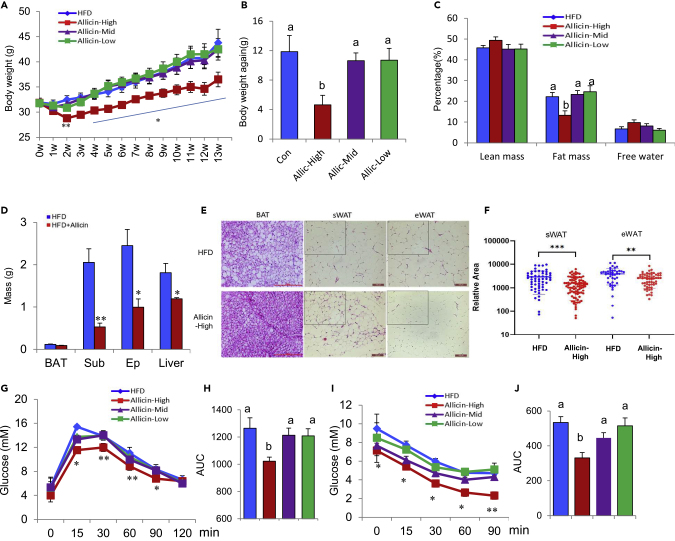
Figure 1.
Allicin Reduces Adiposity and Improves Glucose Homeostasis in DIO Mice
Vehicle (control) or different doses of allicin were administrated each day for a total of 13 weeks.
(A) Body weight evaluation of control HFD mice or mice treated with different doses of allicin. (n = 9).
(B) Body weight again of different groups of mice (n = 9).
(C) Body fat percentage test using nuclear magnetic resonance.
(D) Organ weight of control and allicin-treated HFD mice (n = 6).
(E) H&E staining of BAT, sWAT, and eWAT sections from DIO control and allicin-treated DIO mice. Scale bars, 100 μm.
(F) Quantification of the area of adipocytes in the selection of H&E sections in (E).
(G and H) (G) Glucose tolerance test of control and allicin-treated DIO mice (intraperitoneally with glucose as 1.0 g/kg after 16-h fast) (n = 8). (H) The average area under the curve (n = 8).
(I and J) (I) Insulin tolerance test was performed on control and allicin-treated DIO mice (injection insulin with 2.0 U/kg after 6 h of fasting (n = 8). (J) The average area under the curve (n = 8).
Values represent means ± SEM. Error bars represent SEM; significant differences compared with vehicle controls are indicated by ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01(assessed by Student's t test). Different letters indicate signicance among groups (P<0.05).