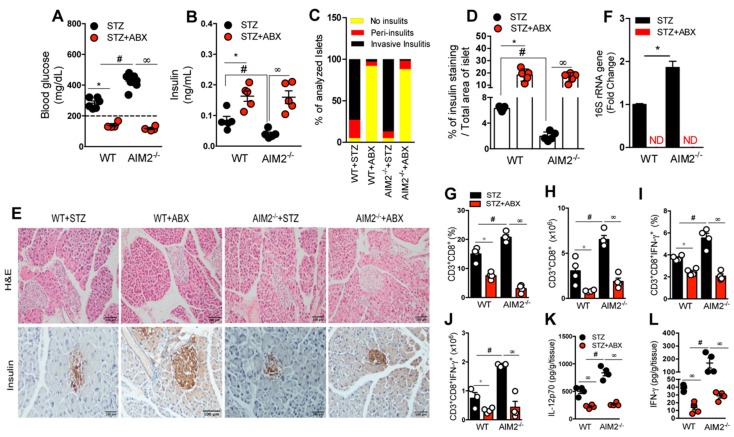
Figure 5.
AIM2 receptor restrains gut microbiota translocation and controls the generation of a proinflammatory response in PLNs during T1D. The WT and AIM2−/− mice were treated with an antibiotic cocktail (ABX) for 21 days before the STZ injections, and the clinical and immunological parameters were determined. (A) Blood glucose and (B) insulin levels in the serum of the WT and AIM2−/− mice at 15 days after the vehicle and STZ injections. (C) Score of the inflammatory infiltrates in the islets of the WT and AIM2−/− mice at 15 days after the vehicle and STZ injections or after the ABX and STZ injections. (D) Quantification of insulin in the pancreatic tissue of the WT and AIM2−/− mice at 15 days after the STZ injections. (E) Histopathology and insulin staining, assessed by immunohistochemistry, in the pancreatic tissue of the WT and AIM2−/− mice at 15 days after the vehicle and STZ injections or after the ABX and STZ injections. (F) The 16S rRNA gene expression in the PLNs of the WT and AIM2−/− mice at 15 days after the STZ injections. (G–J) The percentage and absolute numbers of CD3+CD8+ and CD3+CD8+IFN-γ+ cells in the PLNs of the WT and AIM2−/− mice at 15 days after the STZ injections. (K,L) The protein levels of IL-12 p70 and IFN-γ cytokines, assessed by ELISA, in the pancreatic tissue of the WT and AIM2−/− mice at 15 days after the STZ injections. The values are expressed as the mean ± SD. The results are considered statistically significant when p < 0.05 (*; #, ∞). N = 3–6 animals per group. Significant differences between the groups were determined by one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s multiple-comparison test.