Abstract
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‐CoV‐2) causes the recent COVID‐19 public health crisis. Bat is the widely believed original host of SARS‐CoV‐2. However, its intermediate host before transmitting to humans is not clear. Some studies proposed pangolin, snake, or turtle as the intermediate hosts. Angiotensin‐converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is the receptor for SARS‐CoV‐2, which determines the potential host range for SARS‐CoV‐2. On the basis of structural information of the complex of human ACE2 and SARS‐CoV‐2 receptor‐binding domain (RBD), we analyzed the affinity to S protein of the 20 key residues in ACE2 from mammal, bird, turtle, and snake. Several ACE2 proteins from Primates, Bovidae, Cricetidae, and Cetacea maintained the majority of key residues in ACE2 for associating with SARS‐CoV‐2 RBD. The simulated structures indicated that ACE2 proteins from Bovidae and Cricetidae were able to associate with SARS‐CoV‐2 RBD. We found that nearly half of the key residues in turtle, snake, and bird were changed. The simulated structures showed several key contacts with SARS‐CoV‐2 RBD in turtle and snake ACE2 were abolished. This study demonstrated that neither snake nor turtle was the intermediate hosts for SARS‐CoV‐2, which further reinforced the concept that the reptiles are resistant against infection of coronavirus. This study suggested that Bovidae and Cricetidae should be included in the screening of intermediate hosts for SARS‐CoV‐2.
Keywords: ACE2, Bovidae, Cricetidae, intermediate host, SARS‐CoV‐2
Research Highlights
Affinities to SARS‐CoV‐2 S protein of the 20 key residues in ACE2 from mammal, bird, turtle and snake were analyzed.
ACE2 proteins from Primates, Bovidae, Cricetidae and Cetacea were predicted to associate with SARS‐CoV‐2 RBD.
Neither snake nor turtle was the intermediate hosts for SARS‐CoV‐2
1. INTRODUCTION
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19), which was first reported in Wuhan, Hubei province, China, has caused over 80 422 human infections and more than 2984 deaths (as of 4 March 2020) in China. 1 , 2 The confirmed cases outside China are increasing, which raised major global concern. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‐CoV‐2) was identified to be the pathogen of COVID‐19. SARS‐CoV‐2 has joined SARS‐CoV and Middle East respiratory syndrome‐related coronavirus (MERS‐CoV) as another coronavirus that causes severe respiratory disease and human death. 3 , 4
The specificity of the interaction between virus and receptor determines its host range for the virus. Spike protein (S) of SARS‐CoV‐2 has attracted great attention because of its role in receptor binding. Angiotensin‐converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) binds to the receptor‐binding domain (RBD) of SARS‐CoV‐2 S protein and functions as a receptor for SARS‐CoV‐2. 5 , 6 The origin of SARS‐CoV‐2 is considered as bat. 6 However, the intermediate host is unknown. Some studies suggest that pangolin is involved in the evolution of SARS‐CoV‐2. 7 , 8 Others suggested that snake and turtles are potential intermediate hosts for SARS‐CoV‐2. 9 , 10 In this study, we compared the key amino acids (AAs) in ACE2 from different species for the binding ability to RBD. On the basis of potential interaction between S protein and ACE2, it was speculated that SARS‐CoV‐2 preserved the ability to infect Bovidae and Cricetidae but not snake or turtle.
2. METHODS
2.1. Sequence analysis of ACE2
A total of 93 ACE2 protein sequences were selected from 85 mammals, 4 birds, 3 turtles, and 1 snake. These ACEs with their corresponding species are listed as follows: hACE2: Homo sapiens (BAB40370.1), RhiACE2: Rhinopithecus roxellana (XP_010364367.2), MacmACE2: Macaca mulatta (NP_001129168.1), MuseACE2: Mustela erminea (XP_032187679.1), CamdACE2: Camelus dromedarius (XP_031301717.1), PlACE2: Procyon lotor (XP_031301717.1), PcACE2: Paguma larvata (AAX63775.1), RmACE2: Rhinolophus macrotis (ADN93471.1), RfACE2: Rhinolophus ferrumequinum (BAH02663.1), RsACE2: Rhinolophus sinicus (ADN93472.1), RlACE2: Rousettus leschenaultii (BAF50705.1), SsACE2: Sus scrofa (NP_001116542.1), MpfACE2: Mustela putorius furo (BAE53380.1), RatACE2: Rattus norvegicus (Q5EGZ1), MmACE2: Mus musculus (Q3URC9), ClfACE2: Canis lupus familiaris (J9P7Y2), FcACE2: Felis catus (A0A384DV19), MjACE2: Manis javanica (XP_017505752.1), RpACE2: Rhinolophus pearsonii (ABU54053.1), PvACE2: Pteropus vampyrus (XP_011361275.1), PoaACE2: Pongo abelii (NP_001124604.1), EcACE2: Equus caballus (F6V9L3), BtACE2: Bos taurus (Q58DD0), PtACE2: Pan troglodytes (A0A2J8KU96), OraACE2: Ornithorhynchus anatinus (F7FDA2), OvaACE2: Ovis aries (W5PSB6), PanACE2: Papio Anubis (A0A096N4X9), LaACE2: Loxodonta africana (G3T6Q2), SsdACE2: Sus scrofa domesticus (A0A220QT48), EeACE2: Erinaceus europaeus (A0A1S3APE5), OcACE2: Oryctolagus cuniculus (G1TEF4), NpACE2: Nyctereutes procyonoides (B4XEP4), VvACE2: Vulpes vulpes (A0A3Q7RAT9), PhcACE2: Phodopus campbelli (C7ECU7), MaACE2: Mesocricetus auratus (C7ECV1), CjACE2: Callithrix jacchus (F7CNJ6), SusACE2: Suricata suricatta (XP_029786256.1), HgACE2: Heterocephalus glaber (A0A0N8EUX7), DoACE2: Dipodomys ordii (A0A1S3GHT7), ItACE2: Ictidomys tridecemlineatus (XP_005316051.3), CpACE2: Cavia porcellus (XP_023417808.1), CgACE2: Cricetulus griseus (A0A061HZ66), ChACE2: Capra hircus(A0A452EVJ5); BibtACE2: Bos indicus x Bos taurus (A0A4W2H3A1), BmACE2: Bos mutus (L8I4I4), NlACE2: Nomascus leucogenys (G1RE79); CsACE2: Chlorocebus sabaeus (A0A0D9RQZ0); MfACE2: Macaca fascicularis (A0A2K5X283); PpACE2: Pan paniscus (A0A2R9BKD8); CaACE2: Cercocebus atys (A0A2K5KSD8); MnACE2: Macaca nemestrina (A0A2K6D1N8); MalACE2: Mandrillus leucophaeus (A0A2K5ZV99); TsACE2: Tarsius syrichta (A0A1U7TY97); PrcACE2: Propithecus coquereli (A0A2K6GHW5); UmACE2: Ursus maritimus (A0A452TT30); OgACE2: Otolemur garnettii (H0WMI5); SbbACE2: Saimiri boliviensis boliviensis (A0A2K6SBD4); CciACE2: Cebus capucinus imitator (A0A2K5PYM0); GggACE2: Gorilla gorillagorilla (G3QWX4); AnACE2: Aotus nancymaae (A0A2K5DQI6); ChaACE2: Chlorocebus aethiops (Q1LZX8); AmACE2: Ailuropoda melanoleuca (G1MC42); VuACE2: Vombatus ursinus (A0A4X2M679); UaACE2: Ursus americanus (A0A452R1Z9); UahACE2: Ursusarctos horribilis (A0A3Q7TE16); PmACE2: Physeter macrocephalus (A0A2Y9S5T9); LvACE2: Lipotes vexillifer (A0A340Y3Y6); BasACE2: Balaenoptera acutorostrata scammoni (A0A452CBT6); DlACE2: Delphinapterus leucas (A0A2Y9M9H3); TtACE2: Tursiops truncatus (A0A2U4AJL3); NaaACE2: Neophocaena asiaeorientalis asiaeorientalis (A0A341BCI8); CuACE2: Callorhinus ursinus (A0A3Q7N3M7); NsACE2: Neomonachus schauinslandi (A0A2Y9GEI9); TmlACE2: Trichechus manatuslatirostris (A0A2Y9E393); ElkACE2: Enhydra lutriskenyoni (A0A2Y9KLV0); ClACE2: Chinchilla lanigera (C7ECU0); MdACE2: Monodelphis domestica (F6WXR7); LpACE2: Lynx pardinus (A0A485NF12); PaACE2: Pipistrellus abramus (C7ECT9); MbACE2: Myotis brandtii (S7N573); DrACE2: Desmodus rotundus (K9INV8); RhpACE2: Rhinolophus pusillus (E2DHI9); RaACE2: Rhinolophus alcyone (A0A0N7IQX6); RlACE2(2): Rhinolophus landeri (A0A0P0IB69); MylACE2: Myotis lucifugus (G1PXH7), GgACE2: Gallus gallus (F1NHR4), ApACE2: Anas platyrhynchos (R0LHX5), MgACE2: Meleagris gallopavo (G1NPB8), CaaACE2: Cathartes aura (A0A091MDI4), OhACE2: Ophiophagus hannah (V8NIH2), CpbACE2: Chrysemys picta bellii (XP_023964517.1), CmACE2: Chelonia mydas (XP_007070561.1); and PsACE2: Pelodiscus sinensis (XP_006122891.1). On the basis of known 20 key sites in human ACE2 interacting with SARS‐CoV‐2 RBD, 11 we analyzed whether these sites were conserved on other ACE2 proteins. Phylogenetic and molecular evolutionary analysis of ACE2 protein was conducted using molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version X (MEGA‐X). 12 Phylogenetic tree was generated with Jones‐Taylor‐Thornton evolutionary model using a maximum‐likelihood method.
2.2. Structure simulation of ACE2‐RBD complex
On the basis of the structure of hACE2 with SARS‐CoV‐2 S RBD (PDB: 6LZG), the structure of SARS‐CoV‐2 S and ACE2 from Bos taurus, Cricetulus griseus, Pelodiscus sinensis, and Ophiophagus hannah were simulated by SWISS‐MODEL online server 13 and analyzed by Chimera software version 1.14. 14
3. RESULTS
3.1. Sequence alignment of ACE2
According to the recently resolved structure of the complex of human ACE2 and SARS‐CoV‐2 RBD, there are 20 key AAs in hACE2 for interacting with RBM. 11 We analyzed those AAs of ACE2 protein from a list of mammals, birds, turtles, and snake, as shown in Table 1. Next, a phylogenetic tree for mammalian ACE2 proteins was constructed by MEGA‐X software. There were 16 primates ACE2, 5 Bovidae ACE2, 2 Cricetidae ACE2, and 3 Cetacea ACE2 (Table 1 and Figure 1A), possessing at least 90% (18/20) critical AAs. Pangolin ACE2 preserved only 70% (14/20) AAs. Nearly half of the key residues in turtles (CpbACE2, CmACE2, and PsACE2) and snake (OhACE2) were changed (Table 1). ACE2 from Aves, including Gallus gallus, Anas platyrhynchos, Meleagris gallopavo, and Cathartes aura, only matched 10 to 11 AAs (Table 1).
Table 1.
Analysis of the key AAs in ACE2 for SARS‐CoV‐2 RBD binding
| ACE2 | AA position | Matched AA | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 | 27 | 28 | 30 | 31 | 34 | 35 | 37 | 38 | 41 | 42 | 45 | 82 | 83 | 330 | 353 | 354 | 355 | 357 | 393 | ||
| hACE2 | Q | T | F | D | K | H | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | M | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 20 |
| RhiACE2 | Q | T | F | D | K | H | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | M | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 20 |
| MacmACE2 | Q | T | F | D | K | H | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | M | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 20 |
| PoaACE2 | Q | T | F | D | K | H | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | M | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 20 |
| PtACE2 | Q | T | F | D | K | H | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | M | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 20 |
| PanACE2 | Q | T | F | D | K | H | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | M | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 20 |
| NlACE2 | Q | T | F | D | K | H | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | M | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 20 |
| CsACE2 | Q | T | F | D | K | H | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | M | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 20 |
| MfACE2 | Q | T | F | D | K | H | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | M | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 20 |
| PpACE2 | Q | T | F | D | K | H | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | M | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 20 |
| CaACE2 | Q | T | F | D | K | H | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | M | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 20 |
| MnACE2 | Q | T | F | D | K | H | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | M | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 20 |
| MalACE2 | Q | T | F | D | K | H | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | M | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 20 |
| GggACE2 | Q | T | F | D | K | H | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | M | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 20 |
| ChaACE2 | Q | T | F | D | K | H | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | M | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 20 |
| PrcACE2 | Q | T | F | D | K | H | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | T | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 19 |
| BtACE2 | Q | T | F | E | K | H | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | T | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 18 |
| OvaACE2 | Q | T | F | E | K | H | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | T | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 18 |
| MaACE2 | Q | T | F | D | K | Q | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | N | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 18 |
| CgACE2 | Q | T | F | D | K | Q | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | N | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 18 |
| ChACE2 | Q | T | F | E | K | H | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | T | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 18 |
| BibtACE2 | Q | T | F | E | K | H | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | T | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 18 |
| BmACE2 | Q | T | F | E | K | H | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | T | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 18 |
| PmACE2 | Q | T | F | Q | K | H | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | T | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 18 |
| DlACE2 | Q | T | F | Q | K | H | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | T | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 18 |
| NaaACE2 | Q | T | F | Q | K | H | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | T | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 18 |
| PhcACE2 | Q | T | F | D | K | Q | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | N | Y | N | K | E | D | R | R | 17 |
| HgACE2 | Q | T | F | D | K | Q | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | A | Y | N | K | D | D | R | R | 17 |
| ItACE2 | L | T | F | D | K | Q | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | A | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 17 |
| BasACE2 | Q | T | F | Q | K | H | E | E | D | Y | R | L | T | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 17 |
| CamdACE2 | L | T | F | E | E | H | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | T | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 16 |
| RlACE2 | L | T | F | E | K | T | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | T | Y | K | K | G | D | R | R | 16 |
| SsACE2 | L | T | F | E | K | L | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | T | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 16 |
| FcACE2 | L | T | F | E | K | H | E | E | E | Y | Q | L | T | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 16 |
| SsdACE2 | L | T | F | E | K | L | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | T | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 16 |
| OcACE2 | L | T | F | E | K | Q | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | T | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 16 |
| CjACE2 | Q | T | F | D | K | H | E | E | D | H | E | L | T | Y | N | K | Q | D | R | R | 16 |
| DoACE2 | L | T | F | D | N | Q | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | I | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 16 |
| UmACE2 | L | T | F | E | K | Y | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | T | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 16 |
| SbbACE2 | Q | T | F | D | K | H | E | E | D | H | E | L | T | Y | N | K | Q | D | R | R | 16 |
| CciACE2 | Q | T | F | D | K | H | E | E | D | H | E | L | T | Y | N | K | Q | D | R | R | 16 |
| AnACE2 | Q | T | F | D | K | H | E | E | D | H | E | L | T | Y | N | K | Q | D | R | R | 16 |
| AmACE2 | L | T | F | E | K | Y | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | T | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 16 |
| UaACE2 | L | T | F | E | K | Y | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | T | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 16 |
| UahACE2 | L | T | F | E | K | Y | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | T | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 16 |
| LvACE2 | R | T | F | Q | K | H | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | T | F | N | K | G | D | R | R | 16 |
| TtACE2 | R | T | F | Q | K | R | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | T | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 16 |
| LpACE2 | L | T | F | E | K | H | E | E | E | Y | Q | L | T | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 16 |
| MpfACE2 | L | T | F | E | K | Y | E | E | E | Y | Q | L | T | Y | N | K | R | D | R | R | 15 |
| ClfACE2 | L | T | F | E | K | Y | E | E | E | Y | Q | L | T | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 15 |
| RpACE2 | R | T | F | D | K | H | E | E | D | H | E | L | D | Y | N | K | D | D | R | R | 15 |
| LaACE2 | L | T | F | D | T | Q | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | D | F | N | K | G | D | R | R | 15 |
| VvACE2 | L | T | F | E | K | Y | E | E | E | Y | Q | L | T | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 15 |
| CpACE2 | Q | T | F | D | E | L | K | E | D | Y | Q | L | A | Y | N | K | N | D | R | R | 15 |
| TsACE2 | Q | T | F | D | K | Q | E | E | D | H | Q | L | S | Y | N | N | S | D | R | R | 15 |
| TmlACE2 | L | T | F | D | T | Q | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | N | F | N | K | G | D | R | R | 15 |
| ClACE2 | Q | T | F | D | N | E | K | E | D | Y | Q | L | A | Y | N | K | D | D | R | R | 15 |
| MuseACE2 | L | T | F | E | K | Y | E | E | E | Y | Q | L | T | Y | N | K | R | D | R | R | 14 |
| PlACE2 | L | T | F | E | N | N | E | E | E | Y | Q | L | T | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 14 |
| MjACE2 | E | T | F | E | K | S | E | E | E | Y | Q | L | N | Y | N | K | H | D | R | R | 14 |
| PvACE2 | L | T | F | E | K | T | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | A | Y | K | K | G | D | R | K | 14 |
| EcACE2 | L | T | F | E | K | S | E | E | E | H | Q | L | T | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 14 |
| NpACE2 | L | T | F | E | K | Y | E | E | E | Y | Q | L | T | Y | N | R | G | D | R | R | 14 |
| OgACE2 | Q | T | F | D | N | R | E | E | E | H | Q | L | T | Y | N | K | D | D | R | R | 14 |
| VuACE2 | R | E | F | E | T | K | E | E | E | Y | Q | L | T | F | N | K | G | D | R | R | 14 |
| NsACE2 | L | T | F | E | K | Y | E | E | E | Y | Q | L | T | Y | N | K | H | D | R | R | 14 |
| ElkACE2 | P | T | F | E | K | Y | E | E | E | Y | Q | L | T | Y | N | K | R | D | R | R | 14 |
| RhpACE2 | L | K | F | N | D | S | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | N | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 14 |
| RmACE2 | E | K | F | D | K | S | K | E | D | Y | E | L | N | Y | K | K | G | D | R | R | 13 |
| RsACE2 | E | I | F | D | K | T | K | E | D | H | Q | L | N | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 13 |
| RatACE2 | K | S | F | N | K | Q | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | N | F | N | H | G | D | R | R | 13 |
| MmACE2 | N | T | F | N | N | Q | E | E | D | Y | Q | L | S | F | N | H | G | D | R | R | 13 |
| CuACE2 | L | T | F | E | K | S | E | E | E | Y | Q | F | T | Y | N | K | H | D | R | R | 13 |
| RlACE2(2) | L | T | F | D | D | S | A | E | N | Y | Q | L | N | F | N | K | G | D | R | R | 13 |
| PcACE2 | L | T | F | E | T | Y | E | Q | E | Y | Q | V | T | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 12 |
| RfACE2 | L | K | F | D | D | S | E | E | N | H | Q | L | N | F | N | K | G | D | R | R | 12 |
| SusACE2 | L | T | F | E | Q | H | E | Q | E | Y | L | V | A | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 12 |
| MdACE2 | D | T | F | D | D | A | K | E | E | H | Q | L | T | Y | N | K | N | D | R | R | 12 |
| DrACE2 | E | T | F | E | N | T | E | E | E | Y | Q | L | T | Y | N | N | K | D | R | R | 12 |
| RaACE2 | L | I | F | D | N | S | E | E | N | H | Q | L | N | F | N | K | G | D | R | R | 12 |
| OraACE2 | E | Q | F | T | Q | K | Q | E | D | Y | Q | L | K | F | N | K | N | D | R | R | 11 |
| EeACE2 | E | K | F | D | D | R | Q | E | N | Y | E | L | N | Y | N | N | G | D | R | R | 11 |
| MbACE2 | K | I | F | E | N | S | K | E | D | H | E | L | T | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 11 |
| MylACE2 | K | I | F | E | N | S | A | E | D | H | E | L | T | Y | N | K | G | D | R | R | 11 |
| GgACE2 | E | T | F | A | E | V | R | E | D | Y | E | L | R | F | N | K | N | D | R | R | 11 |
| ApACE2 | Q | M | F | A | E | V | R | E | D | Y | E | L | N | F | N | K | N | D | R | R | 11 |
| MgACE2 | E | T | F | A | E | V | R | E | D | Y | E | L | R | F | N | K | N | D | R | R | 11 |
| CpbACE2 | E | N | F | S | Q | V | R | E | D | Y | A | L | K | Y | N | K | K | D | R | R | 11 |
| CmACE2 | E | N | F | S | Q | V | R | E | D | Y | A | L | K | Y | N | K | K | D | R | R | 11 |
| PsACE2 | E | N | F | S | E | V | Q | E | D | Y | A | L | K | Y | N | K | K | D | R | R | 11 |
| PaACE2 | E | R | F | V | K | H | E | E | N | H | E | L | G | F | D | K | N | D | R | R | 10 |
| CaaACE2 | Q | I | F | E | E | P | R | E | N | Y | E | L | S | F | N | K | N | D | R | R | 10 |
| OhACE2 | … | K | F | E | Q | A | R | T | D | Y | N | I | M | F | N | K | E | D | R | R | 9 |
Note: hACE2, Homo sapiens (BAB40370.1), RhiACE2, Rhinopithecus roxellana (XP_010364367.2), MacmACE2, Macaca mulatta (NP_001129168.1), MuseACE2, Mustela erminea (XP_032187679.1), CamdACE2, Camelus dromedarius (XP_031301717.1), PlACE2, Procyon lotor (XP_031301717.1), PcACE2, Paguma larvata (AAX63775.1), RmACE2, Rhinolophus macrotis (ADN93471.1), RfACE2, Rhinolophus ferrumequinum (BAH02663.1), RsACE2, Rhinolophus sinicus (ADN93472.1), RlACE2, Rousettus leschenaultii (BAF50705.1), SsACE2, Sus scrofa (NP_001116542.1), MpfACE2, Mustela putorius furo (BAE53380.1), RatACE2, Rattus norvegicus (Q5EGZ1), MmACE2, Mus musculus (Q3URC9), ClfACE2, Canis lupus familiaris (J9P7Y2), FcACE2, Felis catus (A0A384DV19), MjACE2, Manis javanica (XP_017505752.1), RpACE2, Rhinolophus pearsonii (ABU54053.1), PvACE2, Pteropus vampyrus (XP_011361275.1), PoaACE2, Pongo abelii (NP_001124604.1), EcACE2, Equus caballus (F6V9L3), BtACE2, Bos taurus (Q58DD0), PtACE2, Pan troglodytes (A0A2J8KU96), OraACE2, Ornithorhynchus anatinus (F7FDA2), OvaACE2, Ovis aries (W5PSB6), PanACE2, Papio Anubis (A0A096N4X9), LaACE2, Loxodonta africana (G3T6Q2), SsdACE2, Sus scrofa domesticus (A0A220QT48), EeACE2, Erinaceus europaeus (A0A1S3APE5), OcACE2, Oryctolagus cuniculus (G1TEF4), NpACE2, Nyctereutes procyonoides (B4XEP4), VvACE2, Vulpes vulpes (A0A3Q7RAT9), PhcACE2, Phodopus campbelli (C7ECU7), MaACE2, Mesocricetus auratus (C7ECV1), CjACE2, Callithrix jacchus (F7CNJ6), SusACE2, Suricata suricatta (XP_029786256.1), HgACE2, Heterocephalus glaber (A0A0N8EUX7), DoACE2, Dipodomys ordii (A0A1S3GHT7), ItACE2, Ictidomys tridecemlineatus (XP_005316051.3), CpACE2, Cavia porcellus (XP_023417808.1), CgACE2, Cricetulus griseus (A0A061HZ66), ChACE2, Capra hircus(A0A452EVJ5); BibtACE2, Bos indicus x Bos taurus (A0A4W2H3A1), BmACE2, Bos mutus (L8I4I4), NlACE2, Nomascus leucogenys (G1RE79); CsACE2, Chlorocebus sabaeus (A0A0D9RQZ0); MfACE2, Macaca fascicularis (A0A2K5X283); PpACE2, Pan paniscus (A0A2R9BKD8); CaACE2, Cercocebus atys (A0A2K5KSD8); MnACE2, Macaca nemestrina (A0A2K6D1N8); MalACE2, Mandrillus leucophaeus (A0A2K5ZV99); TsACE2, Tarsius syrichta (A0A1U7TY97); PrcACE2, Propithecus coquereli (A0A2K6GHW5); UmACE2, Ursus maritimus (A0A452TT30); OgACE2, Otolemur garnettii (H0WMI5); SbbACE2, Saimiri boliviensis boliviensis (A0A2K6SBD4); CciACE2, Cebus capucinus imitator (A0A2K5PYM0); GggACE2, Gorilla gorillagorilla (G3QWX4); AnACE2, Aotus nancymaae (A0A2K5DQI6); ChaACE2, Chlorocebus aethiops (Q1LZX8); AmACE2, Ailuropoda melanoleuca (G1MC42); VuACE2, Vombatus ursinus (A0A4X2M679); UaACE2, Ursus americanus (A0A452R1Z9); UahACE2, Ursusarctos horribilis (A0A3Q7TE16); PmACE2, Physeter macrocephalus (A0A2Y9S5T9); LvACE2, Lipotes vexillifer (A0A340Y3Y6); BasACE2, Balaenoptera acutorostrata scammoni (A0A452CBT6); DlACE2, Delphinapterus leucas (A0A2Y9M9H3); TtACE2, Tursiops truncatus (A0A2U4AJL3); NaaACE2, Neophocaena asiaeorientalis asiaeorientalis (A0A341BCI8); CuACE2, Callorhinus ursinus (A0A3Q7N3M7); NsACE2, Neomonachus schauinslandi (A0A2Y9GEI9); TmlACE2, Trichechus manatuslatirostris (A0A2Y9E393); ElkACE2, Enhydra lutriskenyoni (A0A2Y9KLV0); ClACE2, Chinchilla lanigera (C7ECU0); MdACE2, Monodelphis domestica (F6WXR7); LpACE2, Lynx pardinus (A0A485NF12); PaACE2, Pipistrellus abramus (C7ECT9); MbACE2, Myotis brandtii (S7N573); DrACE2, Desmodus rotundus (K9INV8); RhpACE2, Rhinolophus pusillus (E2DHI9); RaACE2, Rhinolophus alcyone (A0A0N7IQX6); RlACE2(2), Rhinolophus landeri (A0A0P0IB69); MylACE2, Myotis lucifugus (G1PXH7), GgACE2, Gallus gallus (F1NHR4), ApACE2, Anas platyrhynchos (R0LHX5), MgACE2, Meleagris gallopavo (G1NPB8), CaaACE2, Cathartes aura (A0A091MDI4), OhACE2, Ophiophagus hannah (V8NIH2), CpbACE2, Chrysemys picta bellii (XP_023964517.1), CmACE2, Chelonia mydas (XP_007070561.1); and PsACE2, Pelodiscus sinensis (XP_006122891.1).
Abbreviations: AA, amino acid; ACE2, angiotensin‐converting enzyme 2; RBD, receptor‐binding domain; SARS‐CoV‐2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
Figure 1.
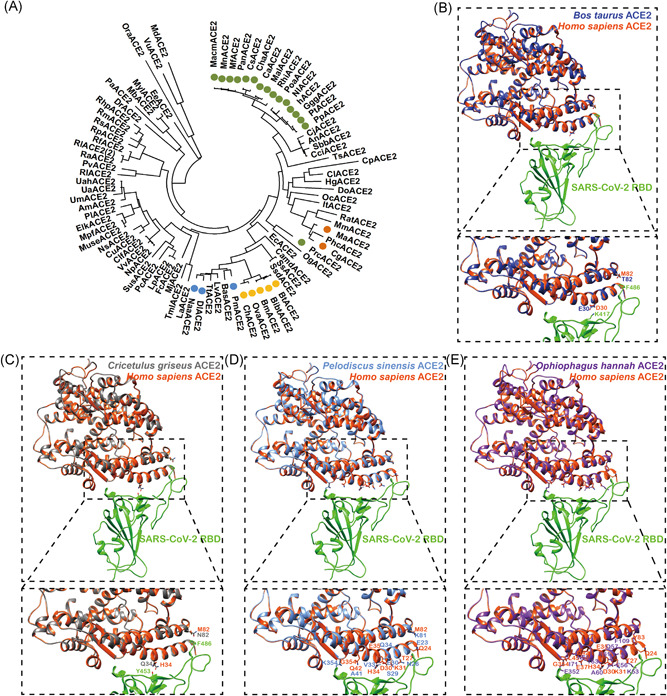
Structure simulation of SARS‐CoV‐2 RBD with ACE2 from different species. A, Phylogenetic tree of mammalian ACE2. ACE2 proteins from a total of 85 mammals were analyzed by MEGA‐X and the phylogenetic tree was constructed using a maximum‐likelihood method. The green, yellow, orange, and blue represent ACE2 from Primates, Bovidae, Cricetidae, and Cetacea, respectively. B, Structural simulation of the protein complex of Bos taurus ACE2 and SARS‐CoV‐2 RBD. Bos taurus ACE2, Homo sapiens ACE2, and SARS‐CoV‐2 RBD are in medium blue, orange red, and green, respectively. C, Structural simulation of the protein complex of Cricetulus griseus ACE2 and SARS‐CoV‐2 RBD. Cricetulus griseus ACE2, Homo sapiens ACE2, and SARS‐CoV‐2 RBD are in dim gray, orange red, and green, respectively. D, Structural simulation of the protein complex of Pelodiscus sinensis ACE2 and SARS‐CoV‐2 RBD. Pelodiscus sinensis ACE2, Homo sapiens ACE2, and SARS‐CoV‐2 RBD are in cornflower blue, orange red, and green, respectively. E, Structural simulation of the protein complex of Ophiophagus hannah ACE2 and SARS‐CoV‐2 RBD. Ophiophagus hannah ACE2, Homo sapiens ACE2, and SARS‐CoV‐2 RBD are in purple, orange red, and green, respectively. ACE2, angiotensin‐converting enzyme 2; MEGA‐X, Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version X; RBD, receptor‐binding domain; SARS‐CoV‐2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2
3.2. Structure simulation of the protein complex of SARS‐CoV‐2 RBD and Bovidae/Cricetidae/turtle/snake ACE2
Recently, the structure of SARS‐CoV‐2 RBD with human ACE2 has been resolved. To investigate whether Bovidae/Cricetidae ACE2 maintained the binding affinity with SARS‐CoV‐2 RBD, we simulated the potential structure of the protein complex. T82 and E30 in Bos taurus ACE2 kept the contact to F486 and K417 in SARS‐CoV‐2 S (Figure 1B). N82 and Q34 in Cricetulus griseus ACE2 maintained the contact to F486 and Y453 in SARS‐CoV‐2 S (Figure 1C). We concluded that Bovidae/Cricetidae ACE2 could associate with SARS‐CoV‐2 S (Figure 1B,C).
To investigate the potential association between SARS‐CoV‐2 and ACE2 from turtle and snake, we simulated the potential structure of turtle/snake ACE2 with SARS‐CoV‐2 RBD. The AA correlated to hACE2 Q42 is changed to A (A41) in turtle (Figure 1D). We also noticed that the AA correlated to hACE2 H34 is changed to A (A60) in a snake (Figure 1E). When the contact AA was mutated to smaller AA (A), the contact force for protein‐protein interaction will be reduced. Moreover, the corresponding AA of K31 was changed to E (E30) in turtle and Q (Q57) in snake ACE2 (Figure 1D). K31 in hACE2 was critical for SARS‐CoV RBD binding and ACE2‐K31D mutant abolished its association with SARS‐CoV RBD. 15 Taken together, turtle and snake ACE2 are unlikely to bind to S protein of SARS‐CoV‐2.
4. DISCUSSION
SARS‐CoV, MERS‐CoV, and SARS‐CoV‐2 have caused severe human infectious diseases in the last 2 decades. These three human coronaviruses originated from bats, but the intermediate hosts were different. SARS‐CoV came from the Paguma larvata, 16 and the intermediate host for MERS‐CoV is Camelus dromedaries. 17 The new coronavirus SARS‐CoV‐2 has recently caused a serious pandemic in China and other countries. However, it is not clear which animals are involved in the evolution of SARS‐CoV‐2 and which animals may be infected by SARS‐CoV‐2. RBD region in S protein of pangolin coronavirus is similar to that of SARS‐CoV‐2, 7 , 8 indicating the involvement of pangolin in the recombination of SARS‐CoV‐2. By analyzing the codon usage of SARS‐CoV‐2, people suggested that snake might be a potential host for SARS‐CoV‐2. 9 Another study indicated that turtle is a potential intermediate host for SARS‐CoV‐2 based on the key AAs in ACE2 for interacting with SARS‐CoV RBD. 10 The late study raised the concerns of SARS‐CoV‐2 infection in the turtle aquaculture and pet turtle. Most of the coronaviruses hosts are mammals; with a few of exceptions are birds. Considering that all known hosts for coronaviruses are thermostatic animals, it is unlikely that reptiles will be infected with SARS‐CoV‐2.
There are 20 key AAs in ACE2 critical for binding S protein of SARS‐CoV‐2. 11 On the basis of these 20 AAs, we analyzed the corresponding AAs in ACE2 from a list of mammal, bird, turtle, and snake. We found that the ACE2 of turtles and snake lost the capability to associate with S protein (Table 1 and Figure 1D,E). These reptiles should be ruled out from the potential host list for SARS‐CoV‐2. Aves ACE2 was unlikely to associate with SARS‐CoV‐2 RBD because they lost the critical K corresponding to K31 in human ACE2 (Table 1). Pangolin ACE2 was predicted to recognize SARS‐CoV‐2 RBD less efficiently because it only preserved 14 of 20 critical AAs (Table 1). Interestingly, we found that ACE2 proteins from Primates, Bovidae, Cricetidae, and Cetacea were capable to recognize RBD of SARS‐CoV‐2 by maintaining the majority of key residues in ACE2 for associating with SARS‐CoV‐2 RBD. Swine ACE2 (CpACE2) with 15 of 20 matched critical AAs was shown to support SARS‐CoV‐2 entry. 6 Bovidae/Cricetidae ACE2 matched more AAs than swine ACE2, thus they should recognize SARS‐CoV‐2 RBD. It would strengthen our conclusion if we have biochemical evidence for the S‐ACE2 interaction analysis for Bovidae/Cricetidae ACE2. On the basis of human ACE2 and SARS‐CoV‐spike complex structure model (PDB ID: 2AJF), we and others recently predicted that hamster ACE2 could associate with SARS‐CoV‐2 and hamster might be a candidate small animal model for SARS‐CoV‐2 infection. 18 , 19 Indeed, golden Syrian hamster (Mesocricetus auratus) has been established as a model to study the pathogenesis and transmission of COVID‐19. 19 One of Cetacea, Neophocaena asiaeorientalis asiaeorientalis (Yangtze finless porpoise), lives in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River and its lakes, where Wuhan located nearby. 20 It will be interesting to investigate whether Yangtze finless porpoise could be infected with SARS‐CoV‐2 or related coronavirus.
In conclusion, we found that Bovidae/Cricetidae ACE2 but not turtle/snake ACE2 could recognize SARS‐CoV‐2 RBD. More attention should be paid to Bovidae and Cricetidae in hunting the potential intermediate host for SARS‐CoV‐2.
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
LZ conceived the work. JL and XJ collected and analyzed the data. JL and YL contributed to graphics processing. LZ wrote the manuscript. All authors approved the final version for publication.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors would like to thank Dr Shan Gao for the discussion. This study is supported by grants from National Key Plan for Research and Development of China (2016YFD0500300), Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences Grant (2017‐52), the Innovation Project of Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences, and Academic Promotion Program of Shandong First Medical University (2019LJ001). Molecular graphics and analyses performed with UCSF Chimera, developed by the Resource for Biocomputing, Visualization, and Informatics at the University of California, San Francisco, with support from NIH P41‐GM103311.
Luan J, Jin X, Lu Y, Zhang L. SARS‐CoV‐2 spike protein favors ACE2 from Bovidae and Cricetidae . J Med Virol. 2020;92:1649–1656. 10.1002/jmv.25817
REFERENCES
- 1. Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, et al. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(8):727‐733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Wu F, Zhao S, Yu B, et al. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature. 2020;579(7798):265‐269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Zhong N, Zheng B, Li Y, et al. Epidemiology and cause of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) in Guangdong, People's Republic of China, in February, 2003. Lancet. 2003;362(9393):1353‐1358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Zaki AM, van Boheemen S, Bestebroer TM, Osterhaus AD, Fouchier RA. Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N Engl J Med. 2012;367(19):1814‐1820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Letko M, Marzi A, Munster V. Functional assessment of cell entry and receptor usage for SARS‐CoV‐2 and other lineage B betacoronaviruses. Nat Microbiol. 2020;5(4):562‐569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Zhou P, Yang XL, Wang XG, et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature. 2020;579(7798):270‐273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Wong MC, Cregeen SJJ, Ajami NJ, Petrosino JF. Evidence of recombination in coronaviruses implicating pangolin origins of nCoV‐2019. bioRxiv. 2020. 10.1101/2020.02.07.939207 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Lam TT‐Y, Shum MH‐H, Zhu H‐C, et al. Identification of 2019‐nCoV related coronaviruses in Malayan pangolins in southern China. bioRxiv. 2020. 10.1101/2020.02.13.945485 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Ji W, Wang W, Zhao X, Zai J, Li X. Cross‐species transmission of the newly identified coronavirus 2019‐nCoV. J Med Virol. 2020;92(4):433‐440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Liu Z, Xiao X, Wei X, et al. Composition and divergence of coronavirus spike proteins and host ACE2 receptors predict potential intermediate hosts of SARS‐CoV‐2. J Med Virol. 2020. 10.1002/jmv.25726 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Lan J, Ge J, Yu J, et al. Crystal structure of the 2019‐nCoV spike receptor‐binding domain bound with the ACE2 receptor. bioRxiv. 2020. 10.1101/2020.02.19.956235 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol. 2018;35(6):1547‐1549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Waterhouse A, Bertoni M, Bienert S, et al. SWISS‐MODEL: homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46(W1):W296‐W303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, et al. UCSF Chimera—a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem. 2004;25(13):1605‐1612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Li W, Zhang C, Sui J, et al. Receptor and viral determinants of SARS‐coronavirus adaptation to human ACE2. EMBO J. 2005;24(8):1634‐1643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Kan B, Wang M, Jing H, et al. Molecular evolution analysis and geographic investigation of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus‐like virus in palm civets at an animal market and on farms. J Virol. 2005;79(18):11892‐11900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Chan RWY, Hemida MG, Kayali G, et al. Tropism and replication of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus from dromedary camels in the human respiratory tract: an in‐vitro and ex‐vivo study. Lancet Respir Med. 2014;2(10):813‐822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Luan J, Lu Y, Jin X, Zhang L. Spike protein recognition of mammalian ACE2 predicts the host range and an optimized ACE2 for SARS‐CoV‐2 infection. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.03.047 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Chan JFW, Zhang AJ, Yuan S. Simulation of the clinical and pathological manifestations of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19) in golden Syrian hamster model: implications for disease pathogenesis and transmissibility. Clin Infect Dis. 2019. 10.1093/cid/ciaa325 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Zhou X, Guang X, Sun D, et al. Population genomics of finless porpoises reveal an incipient cetacean species adapted to freshwater. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


