To the Editor,
A pneumonia of unknown pathogen that emerged in China had its first case announced in early December 2019 within Wuhan City, the capital of Hubei Province and one of the busiest and populated Chinese cities. 1 The causative agent was identified as a novel coronavirus and named SARS‐CoV‐2. Patients infected by the SARS‐CoV‐2 showed symptoms of fever and dyspnoea, lymphopenia, and ground‐glass lung changes in radiology. 2 , 3 Severe cases developed life‐threatening complications, such as respiratory failure, shock, and multiple organs dysfunction. 4 We report on an identified unique severe case involving co‐infection of SARS‐CoV‐2 and HIV.
On 28 January 2020, a 61‐years‐old male from Hankou district of Wuhan reported recurrent fever and dry cough for 2 days went to a local fever clinic, which was setup for screening the SARS‐CoV‐2‐infected and suspected subjects. The patient was a heavy smoker of between 20 to 30 cigarettes a day. He had also been diagnosed with type II diabetes 2 year ago and received alogliptin co‐administered with metformin. The body temperature was 37.5°C. The clinic physician ordered blood routine test and chest computed tomography (CT), and was confirmed to have a mild lymphopenia with a lymphocyte count of 1.1 × 109/L. The chest CT indicated the SARS‐CoV‐2 pneumonia with findings of multiple ground‐glass opacities (GGO) in bilateral lungs (Figure 1A). He was kept in isolation at home and separated from his family members. Due to the shortage of the test kits, real‐time reverse‐transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT‐PCR) assay for detection of coronavirus RNA was performed on his throat swabs on 3 February, which confirmed a positive result. From 1 to 4 February, apart from fever and cough, the patient developed shortness of breath. The follow‐up Chest CT displayed progressive GGO and consolidation in lungs (Figure 1B). On 4 February, he was referred, quarantined and treated in Wuhan Tongji Sino‐French New Town Hospital, a designated medical institution for the novel coronavirus infection.
Figure 1.
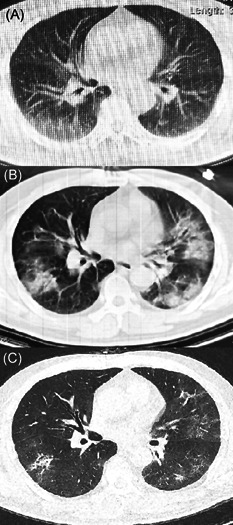
Representative chest CT images of the patient. CT, computed tomography
On admission, physical examination revealed a body temperature of 39°C, respiratory rate of 30 breaths per minute and oxygen saturation of 80%, which reached 91% while the patient was given mask flow oxygen at a rate of 5 liters per minute. On supplemental oxygen, arterial blood gas analysis revealed: pH 7.41, PCO2 37.4 mm Hg, PO2 63.9 mm Hg, and 23.4 mmol/L. Lymphopenia also got worse, with a lymphocyte count of 0.56 × 109/L and a low CD4+ T‐lymphocyte percentage at 4.75%. An antigen/antibody combination test on blood gave HIV‐positive result. Oral therapy with an anti‐HIV drug, lopinavir/ritonavir 400/100 mg per dose twice daily for 12 days, as was advised by Chinese health authority for the treatment of SARS‐CoV‐2 infection, was started on admission. 5 The patient also received moxifloxacin 400 mg once daily for 7 days, γ‐globulin 400 mg/kg once daily for 3 days, and methilprednisolone 0.8 mg/kg once daily for 3 days through intravenous route. On 9 February, the patient showed a marked clinical and radiological improvement (Figure 1C). His oxygen saturation measured by pulse maintained above 95% on supplemental oxygen via nasal cannula at 2 liters per minute. Two additional throat swabs were obtained on 15 February and both were tested negative for SARS‐CoV‐2 RT‐PCR assay. The patient was in stable condition and discharged on 17 February. He was asked to keep isolated at home for two more weeks.
We described a patient with HIV recovered from a coronavirus‐related pneumonia. Among the patients infected by SARS‐CoV‐2, immunocompromised patients, such as HIV infection need to be regarded as vulnerable group.
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTION
FZ and MZ drafted the manuscript. MZ, YC, and SYX cared for the patient and collected the data.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81700032). The Authors thank the patient for participation in this study.
REFERENCES
- 1. Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, et al. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(8):727‐733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;395(10223):497‐506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Pan Y, Guan H, Zhou S, et al. Initial CT findings and temporal changes in patients with the novel coronavirus pneumonia (2019‐nCoV): a study of 63 patients in Wuhan, China. Eur Radiol. 2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Wang D, Hu B, Hu C, et al. Clinical Characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus‐infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA. 2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Jin YH, Cai L, Cheng ZS, et al. A rapid advice guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019‐nCoV) infected pneumonia (standard version). Mil Med Res. 2020;7(1):4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


