Abstract
This study tests the hypothesis that activation of MAPK by physiologically relevant concentrations of IL-33 contributes to enhanced cytokine expression by IL-12 stimulated human NK cells. While IL-33 canonically triggers type 2 cytokine responses, this cytokine can also synergize with type 1 cytokines like IL-12 to provoke IFN-γ. We show that picogram concentrations of IL-12 and IL-33 are sufficient to promote robust secretion of IFN-γ by human NK cells that greatly exceeds resposes to either cytokine alone. Nanogram doses of IL-33, potentially consistent with levels in tissue microenvironments, synergize with IL-12 to induce secretion of additional cytokines, including TNF and GM-CSF. IL-33-induced activation of the p38 MAPK pathway in human NK cells is crucial for enhanced release of IFN-γ and TNF in response to IL-12. Mechanistically, IL-33-induced p38 MAPK signaling enhances stability of IFNG transcripts and triggers A disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain 17 (ADAM17) mediated cleavage of TNF from the cell surface. These data support our hypothesis and suggest that altered sensitivity of NK cells to IL-12 in the presence of IL-33 may have important consequences in diseases associated with mixed cytokine milieus, like asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Keywords: GM-CSF, IL-12, innate lymphoid cell, NK, synergy, TNF
1 |. INTRODUCTION
NK cells play a key role in the clearance of virus-infected cells and the pathogenesis of many diseases.1–3 The type 1 cytokine IL-12 provokes a canonical IFN-γ response by NK cells.4 Other type 1 cytokines, including IL-15, IL-18, and IL-1β enhance IL-12-induced IFN-γ release by NK cells.5–10 This type 1 cytokine synergy can also promote enhanced release of TNF-α and GM-CSF. Thus, type 1 cytokine rich environments associated with immune insults such as infection or injury can stimulate cytokine responses from NK cells that further promote type 1 responses. For example, in the experimental model of Leishmania infantum, the combination of IL-12 and IL-18 is critical for NK-cell IFN-γ expression.11
A central dogma of cytokine biology holds that type 1 cytokines (e.g., IL-12) suppress type 2 cytokine responses, while type 2 cytokines (e.g., IL-4) correspondingly suppress type 1 responses.12,13 Thus, type 2 cytokines should putatively suppress NK-cell production of IFN-γ. Yet the prototypical type 2 cytokine IL-4, alone or in combination with IL-12, triggered high levels of IFN-γ expression by mouse NK cells.14,15 Another type 2 cytokine, IL-33, can enhance IL-12-induced production of IFN-γ by both NK and NKT cells.16–18 Thus, NK cells in type 2 cytokine rich environments may exhibit hypersensitive IFN-γ responses following IL-12-inducing infections or insults.
In the present study, we confirm that primary human NK cells treated with a combination of IL-33 and IL-12 ex vivo produce high levels of IFN-γ,16 and we extend this observation to near physiological picogram concentrations of these cytokines. Mechanistically, we implicate the p38 MAPK pathway in IL-33-mediated enhancement of IL-12-induced responses of human NK cells and uncover a role for ADAM17 in enhanced release of TNF under these stimulatory conditions. These data provide mechanistic insights into how IL-33-rich inflammatory milieus may directly enhance proinflammatory activities of NK cells.
2 |. MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 |. Human cells
De-identified blood samples were obtained from healthy donors, as defined by Hoxworth Blood Center guidelines (https://hoxworth.org/donors/eligibility.html), with the approval of Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center Institutional Review Board. PBMCs were isolated on a ficoll-histopaque (GE, Marlborough, MA) gradient, and NK cells were enriched by negative selection using the NK-cell isolation kit immune magnetic beads per manufacturer’s protocol (Miltentyi Biotec, San Diego, CA). Enriched cells were >90% CD56+ CD3neg NK cells as determined by flow cytometry.
2.2 |. In vitro culture of NK cells
Enriched NK cells were cultured in SCGM media (Cellgenix®, Freiburg, Germany) supplemented with IL-2 (400 U/ml, Peprotech, Rocky Hill, NJ), 10% human serum (Sigma, St. Louis, MO), 10% heat-inactivated FBS, 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 U/ml streptomycin, 1% nonessential amino acids, 1% sodium pyruvate, 2 mM l-glutamine, and 10 mM HEPES. In experiments, NK cells were either used directly after blood isolation or after 7–30 days of ex vivo culture. Each scenario produced similar results.
2.3 |. Antibodies
The following conjugated Abs were used in the described studies: Brilliant violet (BV) 421-CD56 (5.1H11), BV711-CD16 (3G8), Alex-aFluor (AF) 647-NKp46 (9E2), PE-NKp44 (P44-8) were purchased from Biolegend (San Diego, CA); Brilliant Ultra violet (BUV) 395-CD3 (SK7), V500-CD3 (SP34-2), BUV737-CD69 (FN50), and BUV395-CD62L (SK11) were purchased from Becton and Dickinson (San Diego, CA); eFluor710-NKG2D (1D11) from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA); and mouse anti-human ST2 (AF523 or unconjugated) and anti-human IL-18R (70625) from R&D (Minneapolis, MN). Abs were used at doses titrated in our lab.
2.4 |. Cytokine stimulation
Enriched NK cells (unless mentioned otherwise, 5 × 104 per well in triplicate per condition) were cultured overnight in the presence of 60 U/ml of IL-2. Various concentrations of IL-12, IL-18, or IL-33 or (Peprotech®, Rocky Hill, NJ) were added to cultures for 6–16 h. Cell-free supernatant was collected and analyzed by ELISA for levels of human IFN-γ, TNF, and GM-CSF (Invitrogen, Waltham, MA). For inhibition of MAPK activity, 125 nM (measured IC50) of the selective p38 MAPK inhibitor Pamapimod (R-1503, Selleckchem, Houston, TX) was added 150 min prior to cytokine stimulation. The inhibition of MK2 (p38/mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 2) was performed with 5 μM MK2 IV (CAYMAN chemical, Ann Arbor, MI). The inhibition of ADAM-17 (a disintegrin and metalloprotease-17) was performed by adding 8 μM TAPI-1 (Merck Millipore, Burlington, MA). TAPI-1 and MK2 IV were added 60 min before cytokine stimulation. At the tested concentrations, none of the tested inhibitor affected cell viability (data not shown).
2.5 |. mRNA stability assay
Primary human NK cells were cultured at 1 × 105 cell per well. Cells were treated with media (0.1% DMSO) and IL-12 (2.5 ng/ml) with or without IL-33 (10 ng/ml). Actinomycin D (5 μg/ml, Sigma) was added to cell cultures 4 h after cytokine treatment, and RNA was isolated before addition of actinomycin D and 2 h after addition of actinomycin D. RNA was extracted from NK cells with RNeasy kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to manufacturer’s instructions. The detection of IFNG, TNF, IL5, and IL13 mRNA expression was performed by using TaqMan® probes (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA) according to manufacturer’s instructions.
2.6 |. Statistical analysis
We performed statistical analyses using GraphPad Prism 8.01. We used 2-way ANOVA to identify the contribution to multiple variables to an experimental measurement. We used 1-way ANOVA to perform multiple comparisons between experimental conditions. The specific statistical analysis test used is indicated in each figure legend.
3 |. RESULTS
3.1 |. IL-33 enhances IL-12-induced cytokine expression in primary human NK cells
IL-33 can bolster IFN-γ protein expression by IL-12 stimulated human NK cells,16 but whether this enhancement occurs at level of transcription is unknown. To test this, we isolated NK cells from the blood of healthy de-identified adults prior to incubation of these cells in media containing IL-12, IL-33, or a combination of these cytokines for 6 h. A concentration of 1 ng/ml of IL-12 induced a 10-fold increase of IFNG expression compared to unstimulated cells, while 0.5 ng/ml of IL-12 was insufficient to induce this response (Fig. 1A). The addition of IL-33 to NK cells cultured with either dose of IL-12 resulted in a >100-fold increase (interaction: P < 0.0001, 2-way ANOVA) in IFNG mRNA expression levels (Fig. 1A). In a similar fashion, TNF transcript expression was increased ~2.5-fold (interaction: P = 0.0061, 2-way ANOVA) by the combination of IL-12 and IL-33 in comparison to IL-12 alone (Fig. 1B). In other types of innate lymphocytes, IL-33 can stimulate IL-5 and IL-13 expression.19 In contrast, IL-33 alone or in combination with IL-12 had no measurable effect on expression of IL5 or IL13 expression by human NK cells (Fig. 1C).
FIGURE 1. Increased IFNG and TNF expression in IL-12/IL-33 stimulated NK cells.
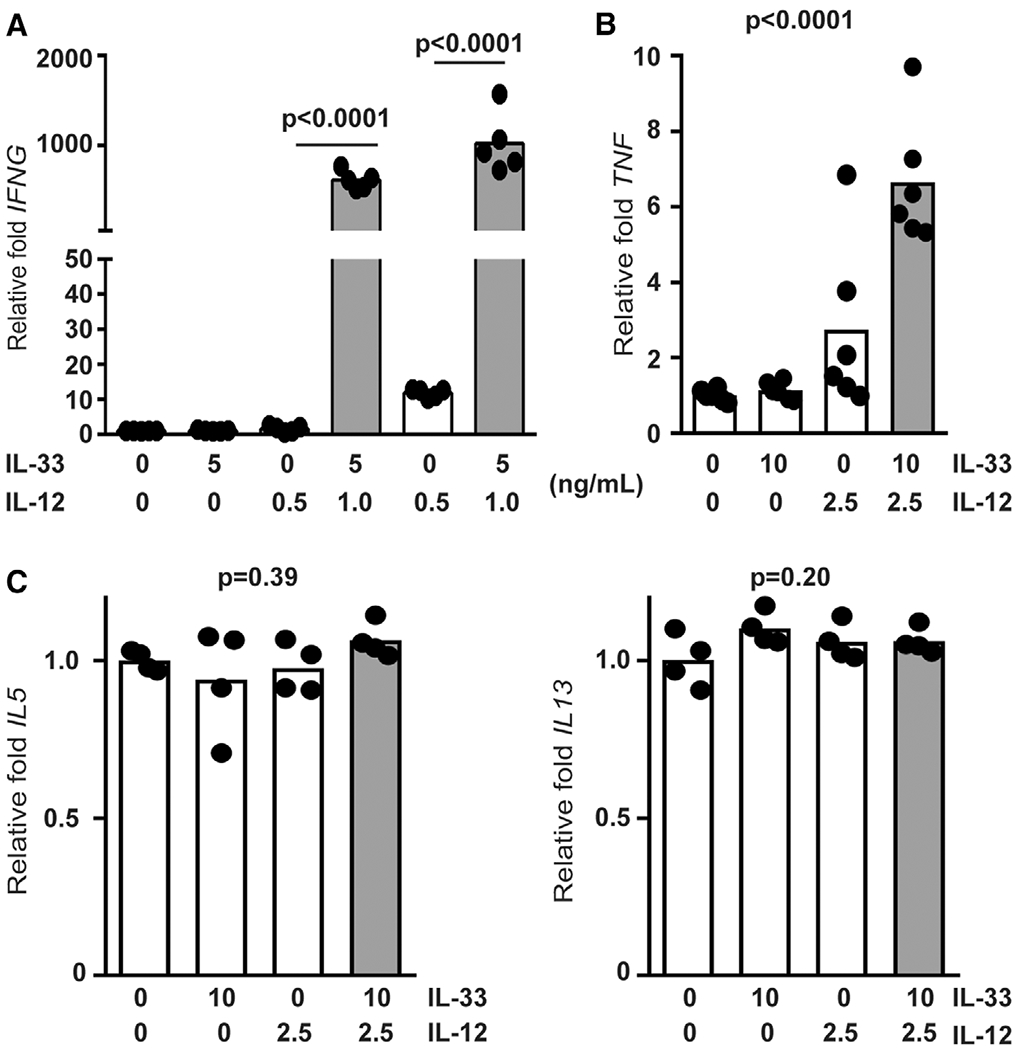
Enriched primary human NK cells (4 to 6 different donors) were stimulated with combinations of IL-12 and IL-33 (doses listed in ng/mL) for 6 hours prior to qRT-PCR determination of (A) IFNG, (B) TNF, (C) IL5, and IL13. Shaded bars reflect administration of more than one cytokine. Significant differences in group means determined by 1-way ANOVA (p values shown), while synergistic cytokine interactions assessed by 2-way ANOVA are reported in Section 3. Each dot represents the mean of 3 biological replicates from an independent subject
Next, we sought to examine whether near-physiological concentration of IL-33 could provoke enhanced IFN-γ expression in IL-12 stimulated NK cells. Isolated NK cells secreted IFN-γ in response to doses of IL-12 as low as 250 pg/ml (Fig. 2A). In contrast, production of IFN-γ by these cells was barely detectable after stimulation with IL-33 alone, even atdoses as high as ≥1ng/ml (Fig. 2A). However, 100 pg/ml ormore of IL-33 enhanced (1.7–2.9-fold) IL-12-elicited IFN-γ protein expression (Fig. 2A), with synergistic interactions between IL-12 and IL-33 contributing significantly (P < 0.0001, 2-way ANOVA) to the overall variation in IFN-γ expression. High concentrations of IL-33 (10 ng/ml) additionally provoked expression of TNF and GM-CSF when administered in combination with IL-12 (Fig. 2B). The bulk of variation in the expression of TNF (P = 0.011, 2-way ANOVA) and GM-CSF (P = 0.0008, 2-way ANOVA) were attributable to synergistic interactions between IL-33 and IL-12 (Fig. 2B). Ab blockade of the IL-33 receptor, ST2, abrogated the enhancing effect of IL-33 on IL-12-induced IFN-γ expression, consistent with previous studies,16 but had no measurable effect on IFN-γ induced by IL-12 alone (Fig. 3A). Since IL-33 is part of the IL-1 superfamily that includes IL-18,20 and IL-18 is a potent costimulator of IFN-γ expression by NK cells,9 we sought to examine if the IL-18 receptor (IL-18R) plays any role in the synergy observed with IL-12 and IL-33. In contrast to ST2 blockade, IL-18R blockade had no effect on the ability of IL-33 to enhance IFN-γ release (Fig. 3B), but did prevent synergy of IL-18 with IL-12 (Fig. 3C).
FIGURE 2. IL-33 enhances IL-12-induced cytokine expression in primary human NK cells.

Enriched primary human NK cells were stimulated with combinations of IL-12 and IL-33 (doses listed in ng/ml) for 16 hours prior to ELISA determination of (A) IFN-γ, (B) TNF, or GM-CSF expression in cell-free supernatant. Results from 1 representative iteration of (A) 10 or (B) 5 similar experiments using cells from different subjects is shown (each dot is biological replicate and columns represent mean). Shaded bars reflect administration of more than one cytokine. Results of ordinary 1-way ANOVA (B) assessment of group means with multiple comparisons (A) is shown. 2-Way ANOVA was used to assess synergistic cytokine interactions (reported in Section 3)
FIGURE 3. Role of ST2 in IL-33-mediated enhancement of IL-12 responsiveness of NK cells.

Enriched primary human NK cells were pretreated with (A) 1 μg anti-ST2 or (B and C) 0.1 μg anti-IL-18R Ab or isotype control Ab 1 h prior to stimulation with combinations of IL-12 and (A and B) IL-33 or (C) IL-18 (doses listed in ng/ml) for 16 h prior to ELISA determination of IFN-γ (columns represent mean). Shaded bars reflect administration of >1 cytokine. Multiple comparisons of ordinary 1-way ANOVA were used to compare groups with P < 0.1 shown. Each dot represents the mean of 3 biological replicates of an independent subject (n = 4–7)
3.2 |. IL-33 enhances IFN-γ and TNF release via activation of p38 MAPK
In Mϕs, IL-33 stimulates activation of p38 MAPK.21,22 To determine if IL-33 activates p38 MAPK in human NK cells, we measured phosphorylation of p38 MAPK and downstream targets of this kinase by flow cytometry. Primary human NK cells were cultured and stimulated with IL-12, IL-33, or both cytokines. Phosphorylation of p38 MAPK(Thr180, Tyr182) and activating transcription factor 2 (ATF2, Thr71) were measured by flow cytometry. IL-33 stimulation, irrespective of the presence of IL-12, stimulated p38 MAPK phosphorylation within 5 min of cytokine exposure (Fig. 4A). Levels of phospho-p38 MAPK remained elevated for at least 30 min poststimulation with IL-33. Likewise, IL-33 stimulation induced the phosphorylation of ATF2, albeit with slower kinetics (Fig. 4B). In contrast, IL-12 but not IL-33 induced phosphorylation (Tyr693) of STAT4 (Fig. 5). The extent of IL-33-induced phospho-p38 MAPK (Fig. 4A) and phospho-ATF2 (Fig. 4B), as well as IL-12-induced phospho-STAT4 (Fig. 5), was not measurably altered over this time scale by co-administration of the other cytokine.
FIGURE 4. IL-33 activates p38 MAPK in human NK cells.
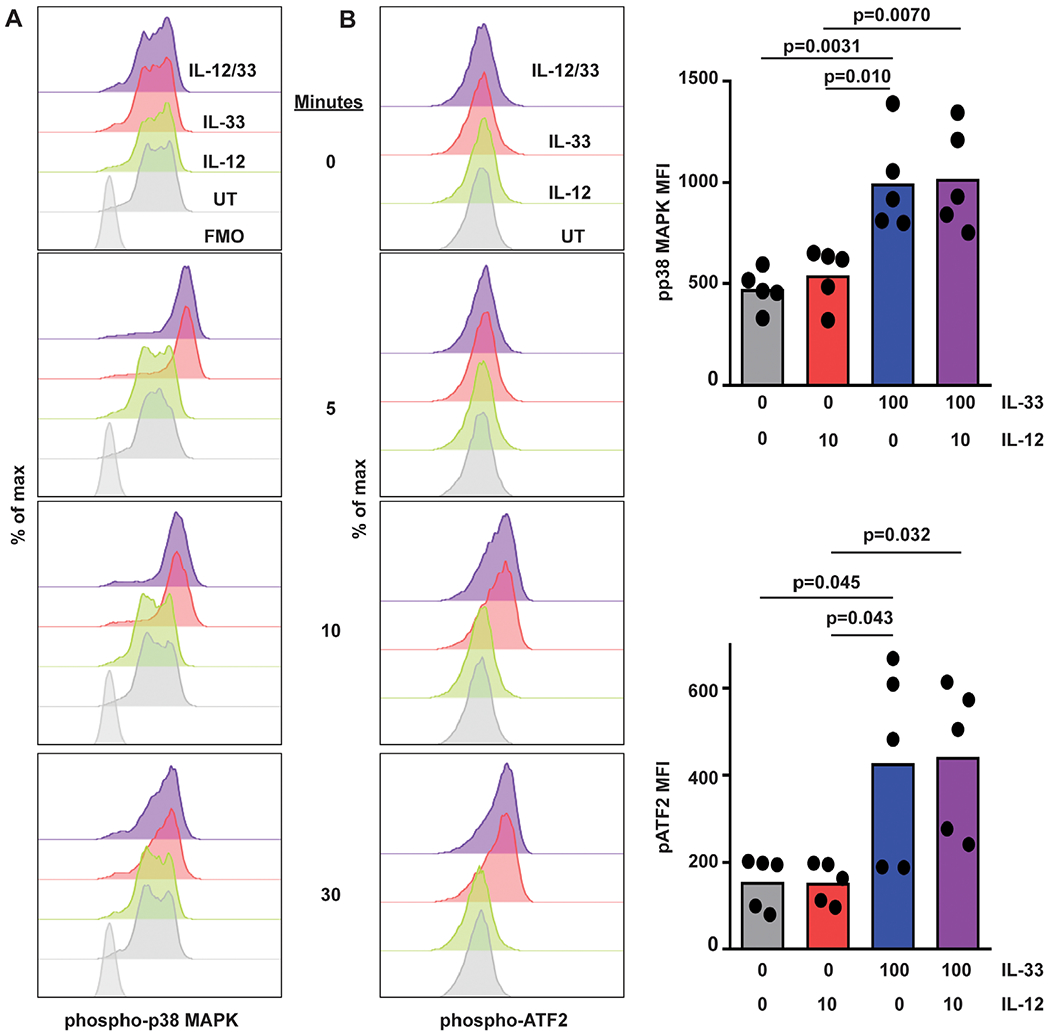
Human NK cells were left untreated (UT) or incubated with IL-12 or IL-33 (doses in ng/ml indicated on right) for 5–30 min prior to phosphoflow measurement of intracellular (A) phospho-p38 MAPK, (B) phospho-ATF2 levels. Representative histogram plots are shown (1 of 5 similar experiments with cells from different subjects), along with graphs of median of fluorescence intensity (MFI, each dot represents results obtained from an independent donor). Multiple comparisons of ordinary 1-way ANOVA were used to compare columns with P < 0.1 shown
FIGURE 5. IL-33 does not interfere IL-12 STAT4 phosphorylation.
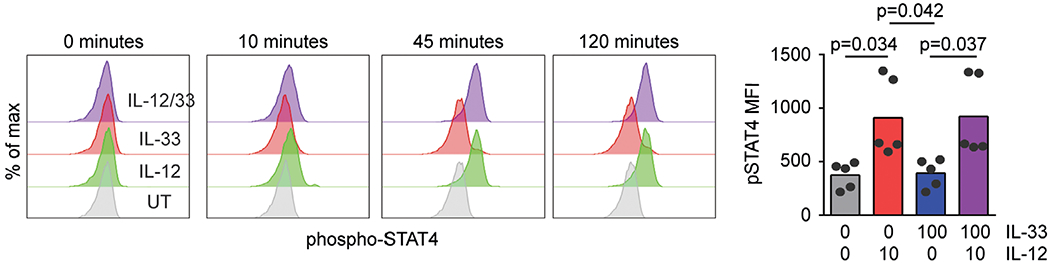
Human NK cells were left untreated (UT) or incubated with IL-12 or IL-33 for 10–120 min prior to phosphoflow measurement of phosphorylated STAT4 levels. Representative histogram plots are shown (1 of 5 similar experiments using cells from different donors), along with graphs of median fluorescence intensity (MFI, each dot represents results obtained from an independent donor). Multiple comparisons of ordinary 1-way ANOVA were used to compare columns with P < 0.1 shown
To determine the role of p38 MAPK in IL-33 enhancement of IL-12-induced cytokines, a specific p38 MAPK inhibitor, R-1503,21 was employed. NK cells were pretreated with R-1503 (0–500 nM) for 150 min prior to stimulation with IL-33 (10 ng/ml) and IL-12 (1 ng/ml) for 16 h. None of the concentrations of inhibitors used in this study measurably affected cell viability (data not shown). A dose of 125 nM R-1503 restored expression of IFN-γ in response to IL-12 plus IL-33 to levels seen with IL-12 alone (Fig. 6A). This concentration of R-1503 did not measurably impact IL-12-induced IFN-γ expression in the absence of IL-33 (Fig. 6B), but did diminish the enhancing effect of IL-33 on IL-12-induced TNF expression (Fig. 6C).
FIGURE 6. p38 MAPK inhibition abrogates IL-33-enhancement of IL-12-induced activity.

(A) IFN-γ production (pooled results of 4 independent subjects) by human NK cells following 150 min pretreatment with vehicle (0.1% DMSO) or various concentrations of R-1503 (0–500 nM) and subsequent stimulation with IL-12 and IL-33 (doses listed in ng/ml). Shaded bars reflect administration of >1 cytokine. (B and C) Effect of pretreatment with 125 nM R-1503 on levels of IFN-γ and TNF in cell-free supernatant collected 6 h after cytokine stimulation. Each dot represents the mean of 3 biological replicates of an independent subject (n = 5). Multiple comparisons of ordinary 1-way ANOVA were used to compare groups with P < 0.1 shown
IL-18 can enhance IL-12-provoked IFN-γ. production by promoting IFNG transcript stability, which is mediated by p38 MAPK signaling.23 To determine whether IL-33 exerts a similar effect on IFNG transcript stability, human NK cells were incubated with IL-12 alone or in combination with IL-33 for 6 h in conjunction with pretreatment with R-1503 or vehicle control. Four hours after cytokine administration, cultures were treated with actinomycin D (5 μg/ml) to halt de novo transcription, thereby permitting measurement of decay of existing IFNG transcripts. As shown in Fig. 7, IFNG levels dropped in all experimental groups after addition of actinomcyn D. Treatment of NK cells with IL-33 and IL-12 (Fig. 7, red lines and bar) resulted in a significantly greater half-life of IFNG transcripts (116 ± 3 min for IL-33/IL-12 vs. 75 ± 3 minutes for IL-12, P < 0.0001) compared to NK cells stimulated with IL-12 alone (Fig. 7, gray lines and bar). The addition of R-1503 accelerated the decay of INFG transcripts (Fig. 7 top plot, blue and black lines), and largely abrogated the enhancing effects of IL-33 (Fig. 7, bottom plot, blue bar) relative to IL-12 alone (Fig. 7, bottom plot, open bar) in terms of half-life of IFNG transcripts (62 ± 2 min for IL-33/IL-12 vs. 52 ± 2 min for IL-12, P = 0.045). Thus, IL-33 acts to enhance IFNG transcript stability via p38 MAPK.
FIGURE 7. p38 MAPK inhibition disrupts IL-33-mediated IFNG mRNA stability.

NK cells were pretreated with R-1503 or DMSO 0.1% and then stimulated with IL-12 (2.5 ng/ml, gray lines) or with IL-12/33 (2.5 and 10 ng/ml respectively, red lines) for 4 h. After 4 h, actinomycin D (ActD 5 μg/ml, red and gray lines) or actinomycin D with R-1503 (125 nM, blue and black lines) were added. IFNG expression was measured by qRT-PCR(left) and IFNG mRNA half-life was calculated (right) via linear regression. Each line or dot represents 1 of 2 biological replicates for 1 of 3 different subjects. Multiple comparisons of ordinary 1-way ANOVA were used to compare cell treatments
3.3 |. MAPK-MAPK contributes to IL-33 enhancement of IL-12-induced IFN-γ
Previous studies showed that MAPK-MAPK (MK2) is down-stream of p38 MAPK, and that MK2 mediates inflammatory responses.24,25 Addition of a specific MK2 inhibitor (MK2 IV) to NK-cell cultures diminished the enhancing effect of IL-33 on IL-12-stimulated IFN-γ production (Fig. 8). In contrast to R-1503, no dose of MK2 IV that we tested completely abrogated IL-33 enhancement of IFN-γ expression. Thus, MK2 contributes to the enhancing effect of IL-33 but does not fully account for the effects mediated by p38 MAPK.
FIGURE 8. MK2 inhibition interferes with IL-33 enhancement of IL-12 induced activity.

IFN-γ production by human NK cells following 150-min pretreatment with vehicle (0.1% DMSO) or various concentrations of MK2 IV (0–10 μM) and subsequent stimulation with IL-12 (2.5 ng/ml) and IL-33 (10 ng/ml) for 16 h, IFN-γ levels were measured in cell-free supernatant. Each dot represents the mean of 3 biological replicates of an independent subject (n = 4). Shaded bars reflect administration of >1 cytokine. Multiple comparisons of ordinary 1-way ANOVA were used to compare columns with P < 0.1 shown
3.4 |. IL-33 and IL-12 regulate TNF release via ADAM17
TNF is shed from the cell membrane via activity of ADAM-17.26 In addition to IL-33 induced increases in TNFmRNA expression (Fig. 1B), we hypothesize that IL-33 further enhances TNF secretion by NK cells (Fig. 2B) via elevated ADAM-17 cleavage of cell-surface TNF. Addition of the ADAM17 inhibitor (TAPI-1)27 to NK-cell cultures resulted in reduction of secreted TNF from 97.1 ± 10.4 to 45.8 ± 5.2 pg/ml (ELISA) in response to IL-33 and IL-12 stimulation (Fig. 9A). In contrast, R-1503 more completely ablated the enhancing effect of IL-33 on IL-12-induced TNF secretion. Thus, enhanced TNF secretion in response to IL-12 and IL-33 is at least partially dependent on ADAM-17, which may function downstream of p38 MAPK or be dependent on p38 MAPK induced changes in TNF mRNA expression.
FIGURE 9. IL-33 and IL-12 regulate TNF release via ADAM17.
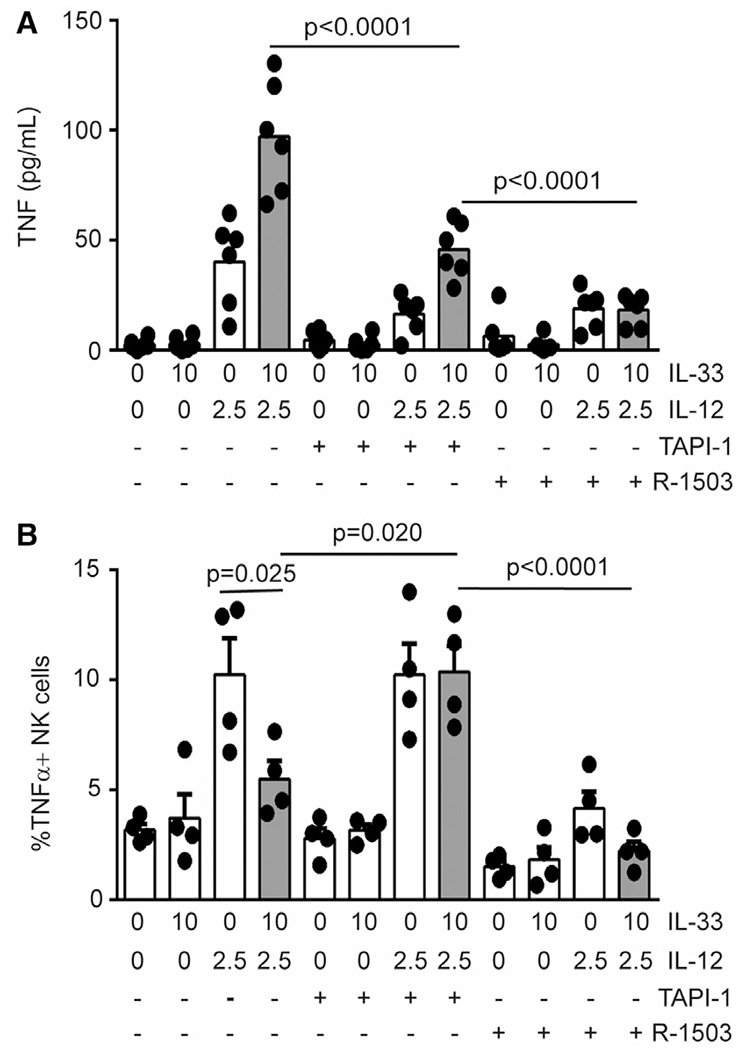
Enriched human NK cells were pretreated with 0.1% DMSO, R-1503 (0.25 μM) or TAPI-1 (8 μM) and then stimulated in the presence of cytokines (doses listed in ng/mL) for 16 h. (A) Secreted TNF expression was measured by ELISA where each dot represents the mean of 3 biological replicates of an independent subject (n = 6). (B) Cell-associated TNF was measured by flow cytometry where each dot represents the mean of 2 biological replicates of an independent subject (n = 4). Shaded bars reflect administration of >1 cytokine. Multiple comparisons of ordinary 1-way ANOVA were used to compare columns with P < 0.1 shown
While TNF secretion increased in response to the combination of IL-33 and IL-12, cell-associated TNF was reduced 1.9-fold to levels near those induced by IL-12 alone (Fig. 9B). These flow cytometry measurements were made in the absence of brefeldin-A or other secretion inhibitors, thus reflecting TNF naturally retained by the cells. Importantly, reduced TNF secretion by TAPI-I-treated, IL-12 and IL-33 stimulated cells (Fig. 9A) was associated with a 2.0-fold increase in cell-associated TNF to levels observed with IL-12 alone (Fig. 9B). Thus, IL-33-stimulated ADAM17 activity contributes to TNF secretion at the expense of cell-associated TNF, likely via cleavage of TNF from the cell surface.
4 |. DISCUSSION
We augment previous observations in mouse17,18 and human16 NK cells by showing that near-physiological (e.g., pM) concentrations28,29 of the type 2 cytokine IL-33 trigger hypersensitivity of primary human NK cells to the type I cytokine IL-12. In addition, superphysiological concentrations of IL-33 and IL-12 synergistically induced the release of TNF and GM-CSF, suggesting that high concentrations of these cytokines in a tissue microenvironment may have even stronger effects on NK-cell function. IL-33-mediated potentiation of IFN-γ and TNF secretion depended on p38 MAPK, and to a lesser extent, the downstream kinase MK2. Moreover, enhanced TNF secretion was partially attributable to ADAM17. These results highlight the possibility for exaggerated cytokine secretion by human NK cells in physiological setting that are characterized by dual exposure to type 1 (IL-12) and type 2 (IL-33) cytokines.
The type 1 cytokine, IL-18, enhances expression of IFNG by IL-12-stimulated human NK cells30 in part via p38 MAPK stabilization of IFNG transcripts.23 Our data suggest that a type 2 cytokine, IL-33, similarly enhances IL-12-induced IFN-γ expression by human NK cells. Moreover, IL-33 amplification of IFN-γ is dependent on p38 MAPK activity and associated with increased stability of IFNG mRNA. The p38 MAPK regulates inflammatory responses via phosphorylation of downstream mediators, including MK2.31,32 Yet, MK2 inhibitors had only a partial inhibitory effect in contrast to the abrogation of IL-12/IL-33 synergistic interactions following p38 MAPK inhibition. This finding implies that other p38 MAPK-stimulated mediators, including ATF2, may also be crucial for the enhancing effect of IL-33. In fact, IL-33 rapidly induced the phosphorylation of p38 MAPK and ATF2 in human NK cells. Of note, p38 MAPK-induced activation of ATF2 initiates activator protein 1 (AP-1) complex-mediated transcription of inflammatory cytokines, including IFN-γ.33–35 Coupled with the lack of apparent effects of IL-33 on IL-12-induced phosphorylation of STAT4, our results highlight the possibility that IL-33 enhances IFN-γ via enhanced AP-1-dependent promotion of transcription.
In addition to p38 MAPK-driven intracellular signaling leading to transcription factor activation, p38 MAPK can also directly phosphorylate membrane proteins like ADAM17.36 The activation of ADAM17 by p38 MAPK can promote shedding of TNF.21,37 Our data are consistent with these possibilities, revealing p38 MAPK-dependent enhancement of TNF expression coupled to ADAM17-dependent release of cell-associated TNF. Collectively, our data suggest that p38 MAPK govern several molecular pathways that regulates inflammatory cytokine release in human NK cells.
The ability of type 2 cytokines to mediate IFN-γ release is not limited to IL-33. Past studies demonstrated that IL-4 enhance IFN-γ production in IL-12 and IL-15 stimulated mouse NK cells.15,38 We also observed IL-4 or IL-13 enhancement of IL-12-induced IFN-^ production by human NK cells (D.O. and S.N.W. unpublished observations). Whereas IL-4 and IL-13 predominately signal via activation of STAT6, both cytokines appear capable of triggering the p38 MAPK pathway.39 In fact, synergy between IL-4 and IL-12 in mouse NK cells is partially dependent on p38 MAPK.15 Whether distinct type 2 cytokines enhance IL-12-induced IFN-γ production via similar or distinct mechanisms remains to be determined.
In pathologies such as asthma and COPD, IL-33 plays a central role in disease pathology, those pathologies were shown to be exacerbated by respiratory virus infection that mediates the release of type 1 cytokines such as IL-12.40–43 Thus, we speculate that NK cells derived from the blood or tissues of patients exhibiting elevated levels of IL-33 would be more sensitive to ex vivo IL-12 stimulation. As an example, cigarette smoke induces epithelial damage resulting in increased expression of IL-33,17,42 which provokes hypersensitive IFN-γ production by mouse NK cells in response to IL-12.44 Our initial data suggest that NK cells from smokers exhibit greater sensitivity to IL-12 in terms of IFN-γ expression than NK cells derived from healthy, non-smokers (D.O., M.B., and S.N.W unpublished observations). We speculate that elevated IL-33 levels in smokers or asthmatic patients provokes hypersensitivity to type 1 inflammatory cues triggered by virus infection. Thus, smokers exposed to virus infections likely produce high, potentially pathogenic expression of IFN-γ. Our findings provide new insights about potential functional hypersensitivity of NK cells in type 2 cytokine rich inflammatory milieus such as asthma and COPD as well as in smokers.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This project was supported in part by NIH P30 DK078392 (Gene Analysis Core) of the Digestive Diseases Research Core Center in Cincinnati and the NIH P30 AR070549 Center for Rheumatic Disease Research. This work was supported by NIH grants DK107502 (L.C.K.), AR073228 (S.N.W. and L.C.K.), HL1195338 (M.T.B.), HL141236 (M.T.B.), AI148080 (S.N.W.), and DA038017 (S.N.W.); the Veteran’s Administration (I01BX002347 to M.T.B); research initiation funds (S.N.W. and L.C.K.) and an Arnold W. Strauss Fellow Award (D.E.O.) from the Cincinnati Children’s Research Foundation; and a postdoctoral fellowship from the American Heart Association (D.E.O.). A.A and P.C.A were supported by MSTP NIH T32 GM063483, while A.A. is also supported by T32 AI118697.
Abbreviations:
- ADAM
A disintegr in and metalloprotease
- ATF2
Activation transcription factor
- COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder
- MK2
MAPKMAPK
- TAPI-1
TNF-alpha protease inhibitor I
Footnotes
DISCLOSURE
The authors declare no confilict of interest.
REFERENCES
- 1.Mace EM, Orange JS. Emerging insights into human health and NK cell biology from the study of NK cell deficiencies. Immunol Rev. 2019;287:202–225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chiossone L, Dumas PY, Vienne M, Vivier E. Natural killer cells and other innate lymphoid cells in cancer. Nat Rev Immunol. 2018;18: 671–688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Waggoner SN, Reighard SD, Gyurova IE, et al. Roles of natural killer cells in antiviral immunity. Curr Opin Virol. 2016;16:15–23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Trinchieri G Interleukin-12: a proinflammatory cytokine with immunoregulatory functions that bridge innate resistance and antigen-specific adaptive immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1995;13: 251–276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Peritt D, Robertson S, Gri G, Showe L, Aste-Amezaga M, Trinchieri G. Differentiation of human NK cells into NK1 and NK2 subsets. J Immunol. 1998;161:5821–5824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kaplanski G Interleukin-18: biological properties and role in disease pathogenesis. Immunol Rev. 2018;281:138–153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Rautela J, Huntington ND. IL-15 signaling in NK cell cancer immunotherapy. Curr Opin Immunol. 2017;44:1–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Fehniger TA, Shah MH, Turner MJ, et al. Differential cytokine and chemokine gene expression by human NK cells following activation with IL-18 or IL-15 in combination with IL-12: implications for the innate immune response. J Immunol. 1999;162:4511–4520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Okamura H, Tsutsi H, Komatsu T, et al. Cloning of a new cytokine that induces IFN-gamma production by T cells. Nature. 1995;378:88–91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hunter CA, Timans J, Pisacane P, et al. Comparison of the effects of interleukin-1 alpha, interleukin-1 beta and interferon-gamma-inducing factor on the production of interferon-gamma by natural killer. Eur J Immunol. 1997;27:2787–2792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Haeberlein S, Sebald H, Bogdan C, Schleicher U. IL-18, but not IL-15, contributes to the IL-12-dependent induction of NK-cell effect-tor functions by Leishmania infantum in vivo. Eur J Immunol. 2010;40: 1708–1717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gor DO, Rose NR, Greenspan NS. TH1-TH2: a procrustean paradigm. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:503–505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.O’Garra A Cytokines induce the development of functionally heterogeneous T helper cell subsets. Immunity. 1998;8:275–283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Morris SC, Orekhova T, Meadows MJ, Heidorn SM, Yang J, Finkelman FD. IL-4 induces in vivo production of IFN-gamma by NK and NKT cells. J Immunol. 2006;176:5299–5305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bream JH, Curiel RE, Yu CR, et al. IL-4synergistically enhances both IL-2-and IL-12-induced IFN-gamma expression in murine NK cells. Blood. 2003;102:207–214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Smithgall MD, Comeau MR, Yoon BR, Kaufman D, Armitage R, Smith DE. IL-33 amplifies both Th1- and Th2-type responses through its activity on human basophils, allergen-reactive Th2 cells, iNKT and NK cells. Int Immunol. 2008;20:1019–1030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kearley J, Silver JS, Sanden C, et al. Cigarette smoke silences innate lymphoid cell function and facilitates an exacerbated type I interleukin-33-dependent response to infection. Immunity. 2015; 42:566–579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bourgeois E, Van LP, Samson M, et al. The pro-Th2 cytokine IL-33 directly interacts with invariant NKT and NK cells to induce IFN-gamma production. Eur J Immunol. 2009;39:1046–1055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Riedel JH, Becker M, Kopp K, et al. IL-33-mediated expansion of type 1 innate lymphoid cells protects from progressive glomerulosclerosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;28:2068–2080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Cayrol C, Girard JP. Interleukin-33 (IL-33): a nuclear cytokine from the IL-1 family. Immunol Rev. 2018;281:154–168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Fehr S, Unger A, Schaeffeler E, et al. Impact of p38 MAP kinase inhibitors on LPS-Induced release of TNF-alpha in whole blood and primary cells from different species. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;36: 2237–2249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Endo Y, Hirahara K, Iinuma T, et al. The interleukin-33-p38 kinase axis confers memory T helper 2 cell pathogenicity in the airway. Immunity. 2015;42:294–308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Mavropoulos A, Sully G, Cope AP, Clark AR. Stabilization of IFN-gamma mRNAbyMAPKp38 in IL-12-and IL-18-stimulated human NK cells. Blood. 2005;105:282–288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wang C, Hockerman S, Jacobsen EJ, et al. Selective inhibition of the p38alpha MAPK-MK2 axis inhibits inflammatory cues including inflammasome priming signals. J Exp Med. 2018;215:1315–1325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Huang X, Shipps GW Jr, Cheng CC, et al. Discovery and hit-to-lead optimization of Non-ATP competitive MK2 (MAPKAPK2) inhibitors. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2011;2:632–637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Black RA, Rauch CT, Kozlosky CJ, et al. A metalloproteinase disintegrin that releases tumour-necrosis factor-alpha from cells. Nature. 1997;385:729–733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lambert DW, Yarski M, Warner FJ, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha convertase (ADAM17) mediates regulated ectodomain shedding of the severe-acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus (SARS-CoV) receptor, angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE2). J Biol Chem. 2005;280:30113–30119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Momen T, Ahanchian H, Reisi M, Shamsdin SA, Shahsanai A, Keivanfar M. Comparison of interleukin-33 serum levels in asthmatic patients with a control group and relation with the severity of the disease. Int J Prev Med. 2017;8:65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hamzaoui A, Berraies A, Kaabachi W, Haifa M, Ammar J, Kamel H. Induced sputum levels of IL-33 and soluble ST2 in young asthmatic children. J Asthma. 2013;50:803–809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lusty E, Poznanski SM, Kwofie K, et al. IL-18/IL-15/IL-12 synergy induces elevated and prolonged IFN-gamma production by ex vivo expanded NK cells which is not due to enhanced STAT4 activation. Mol Immunol. 2017;88:138–147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Gopfert C, Andreas N, Weber F, et al. The p38-MK2/3 module is critical for IL-33-induced signaling and cytokine production in dendritic cells. J Immunol. 2018;200:1198–1206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Clerk A, Harrison JG, Long CS, Sugden PH. Pro-inflammatory cytokines stimulate mitogen-activated protein kinase subfamilies, increase phosphorylation of c-Jun and ATF2 and upregulate c-Jun protein in neonatal rat ventricular myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1999;31: 2087–2099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Samten B, Townsend JC, Weis SE, et al. CREB, ATF, and AP-1 transcription factors regulate IFN-gamma secretion by human T cells in response to mycobacterial antigen. J Immunol. 2008;181:2056–2064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Weber A,Wasiliew P, Kracht M. Interleukin-1 (IL-1) pathway. Sci Signal. 2010;3:cm1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Zhang S, Kaplan MH. The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase is required for IL-12-induced IFN-gamma expression. J Immunol. 2000;165:1374–1380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Goulopoulou S, McCarthy CG, Webb RC. Toll-like receptors in the vascular system: sensing the dangers within. Pharmacol Rev. 2016;68: 142–167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Xu P, Derynck R. Direct activation of TACE-mediated ectodomain shedding by p38 MAP kinase regulates EGF receptor-dependent cell proliferation. Mol Cell. 2010;37:551–566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kiniwa T, Enomoto Y, Terazawa N, et al. NK cells activated by interleukin-4 in cooperation with interleukin-15 exhibit distinctive characteristics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016;113: 10139–10144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Dames P, Bergann T, Fromm A, et al. Interleukin-13 affects the epithelial sodium channel in the intestine by coordinated mod-ulation of STAT6 and p38 MAPK activity. J Physiol. 2015;593: 5269–5282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lambrecht BN, Hammad H, Fahy JV. The cytokines of asthma. Immunity. 2019;50:975–991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Bauer CMT, Morissette MC, Stampfli MR. The influence of cigarette smoking on viral infections: translating bench science to impact COPD pathogenesis and acute exacerbations of COPD clinically. Chest. 2013;143:196–206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Gabryelska A, Kuna P, Antczak A, Bialasiewicz P, Panek M. IL-33 mediated inflammation in chronic respiratory diseases-understanding the role of the member of IL-1 superfamily. Front Immunol. 2019; 10:692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Holgado A, Braun H, Van Nuffel E, et al. IL-33trap is a novel IL-33-neutralizing biologic that inhibits allergic airway inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019;144:204–215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Qiu C, Li Y, Li M, et al. Anti-interleukin-33 inhibits cigarette smoke-induced lung inflammation in mice. Immunology. 2013;138:76–82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


